Bone Lesions
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
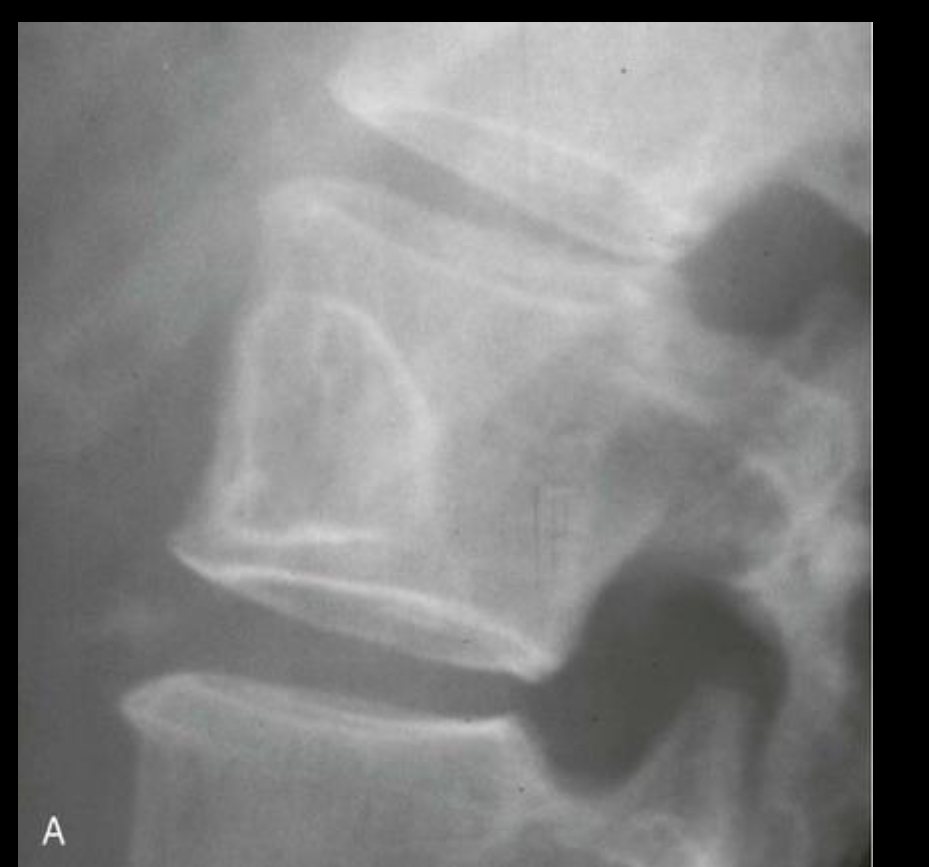
A: Well-defined benign defect characteristically exhibiting a thick surrounding margin and short zone of transition between the defect and the normal bone
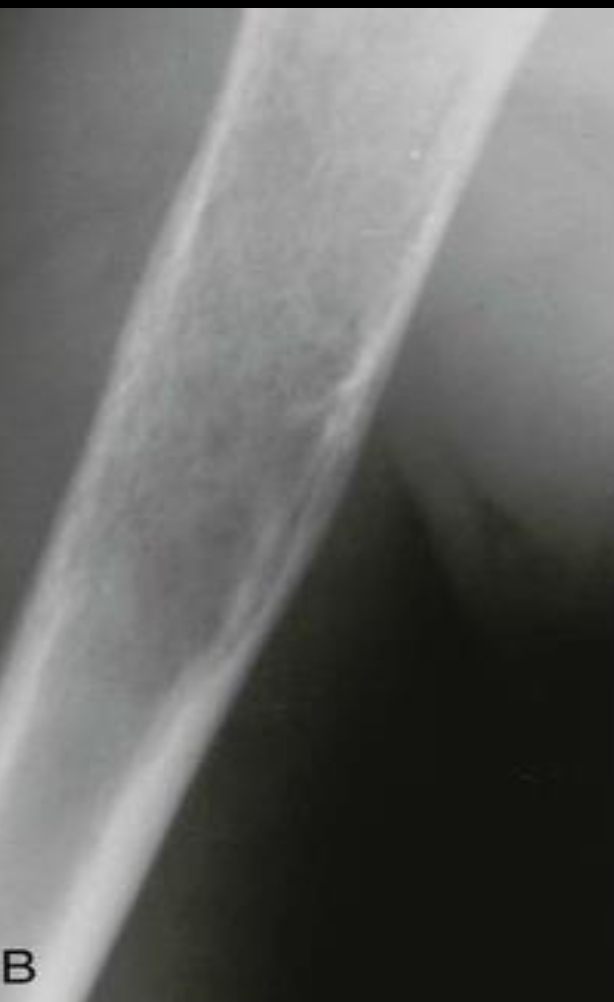
B: Osteosarcoma with a wide zone between the centre of the lesion and the normal bone
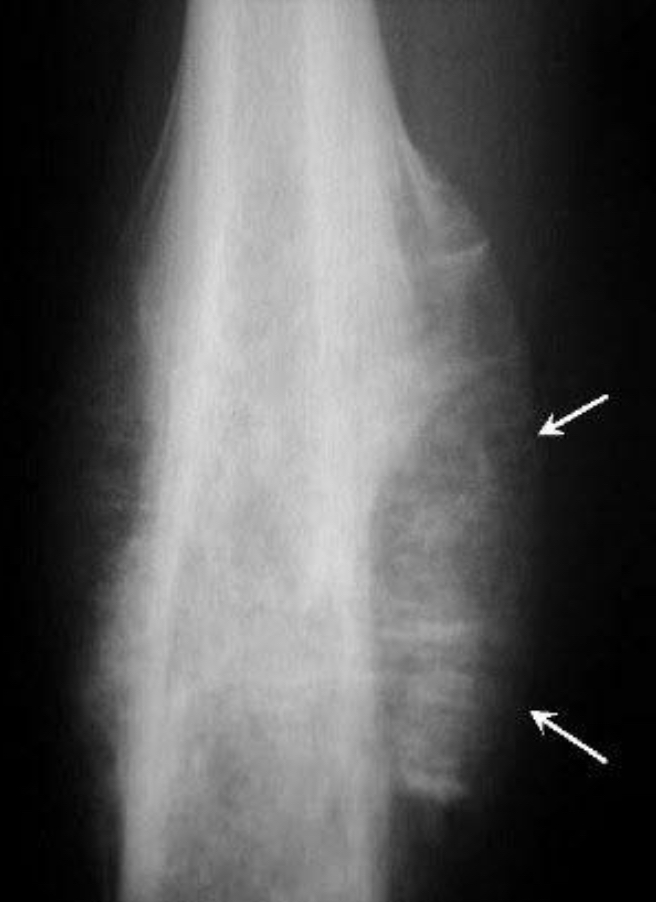
Codmans triangle and sunburst spiculated reaction
a distinctive triangular form of periosteal reaction seen when an aggressive bone lesion grows faster than new periosteum can be ossified. Only the periosteum at the very margin of the lesion has time to ossify creating a triangular lip of new bone
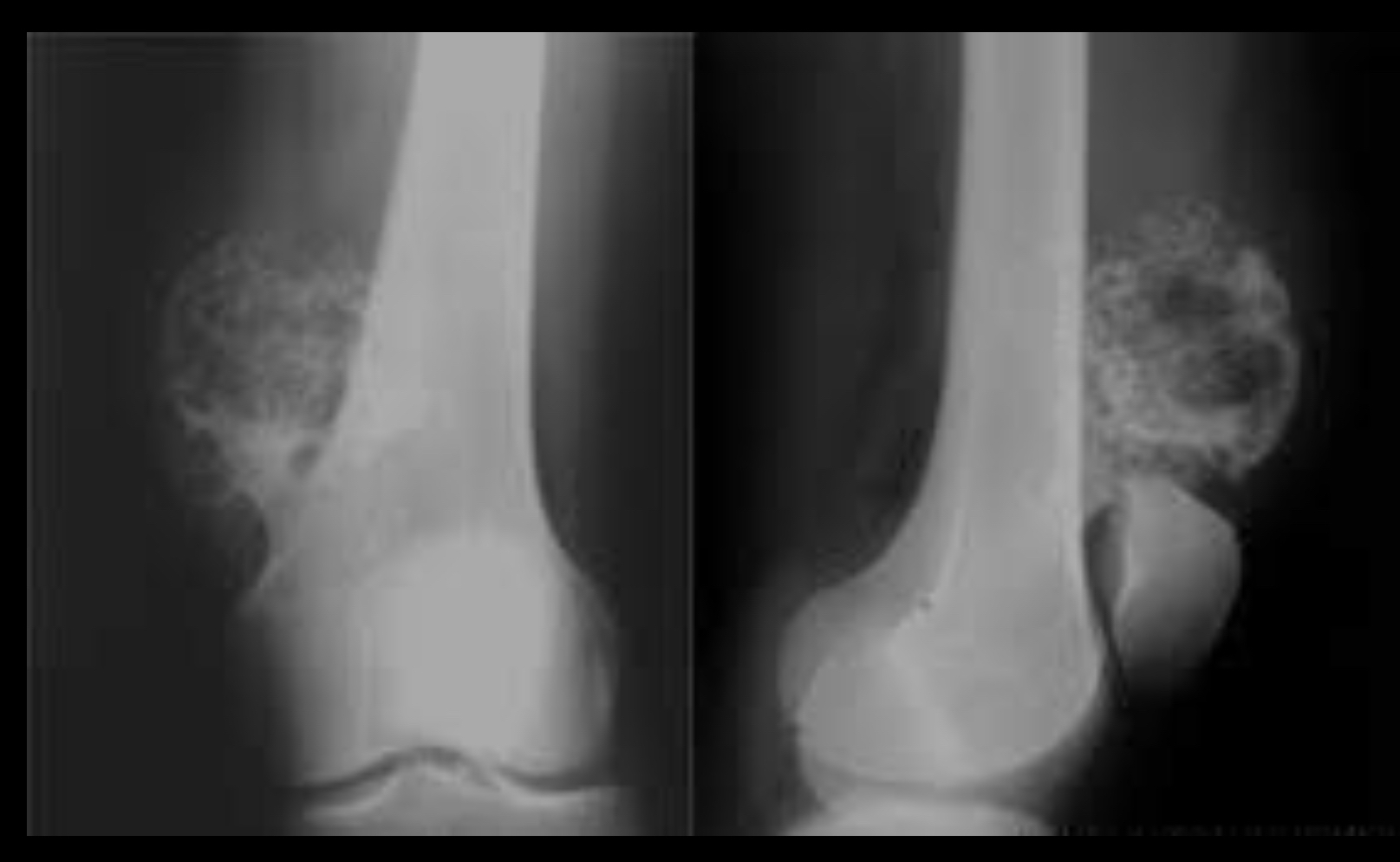
Osteochondroma
Cortex of the osteochondroma blends with that of normal bone
Usually starts in epiphyseal plate and extends laterally
Either flat, sessile lesion or a stalk like process
Tumour runs parallel to long bone and points away from nearest joint
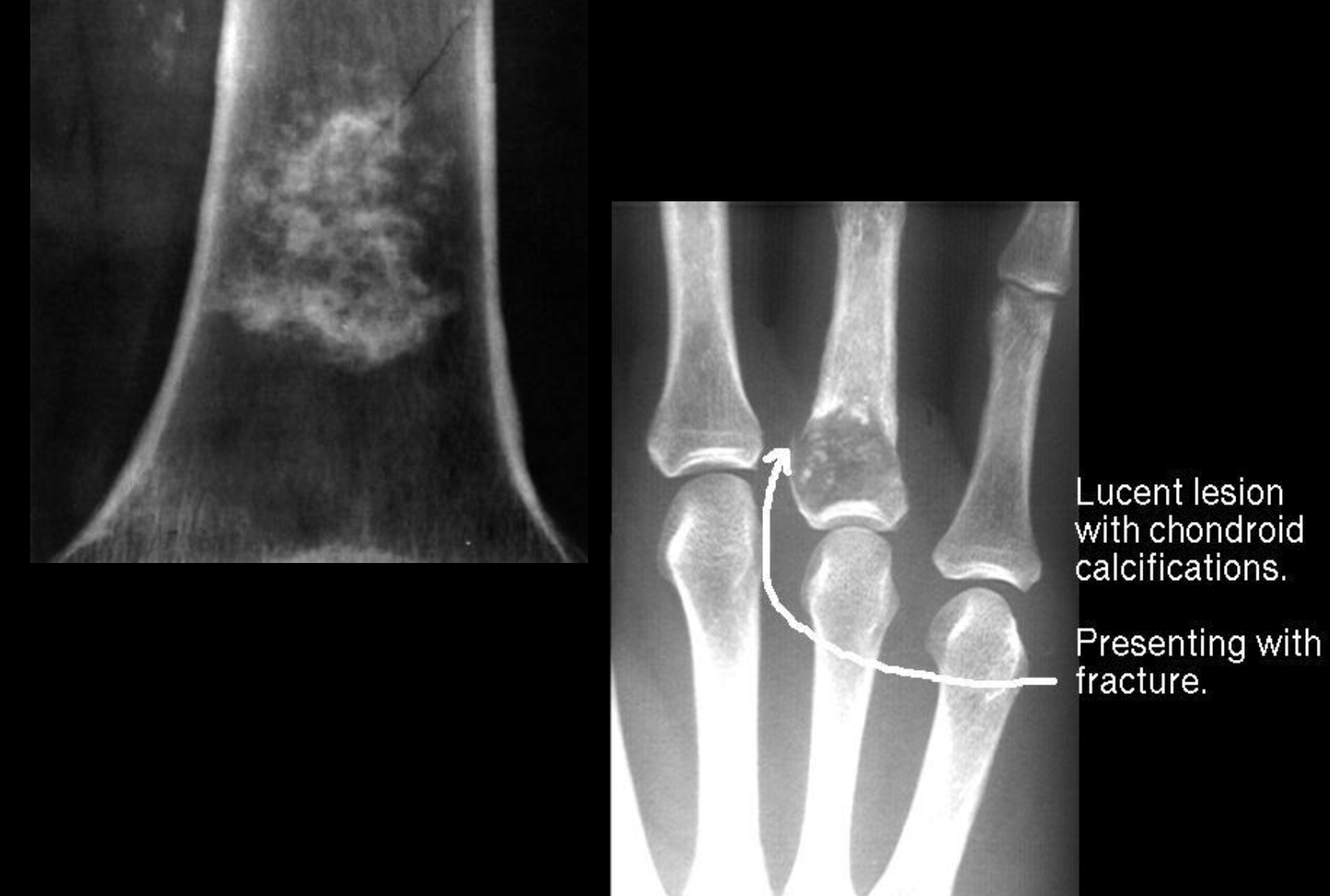
Endochondroma
Begin as slow growing cartilaginous tumours arising in the medullary canal
Destroys normal bone by erupting as a mixture of calcified and uncalcified hyaline cartilage
Often multiple
As it grows it expands bone locally, causing thinning and scalloping of the cortex
Speckled ring-like calcifications within a lucent matrix
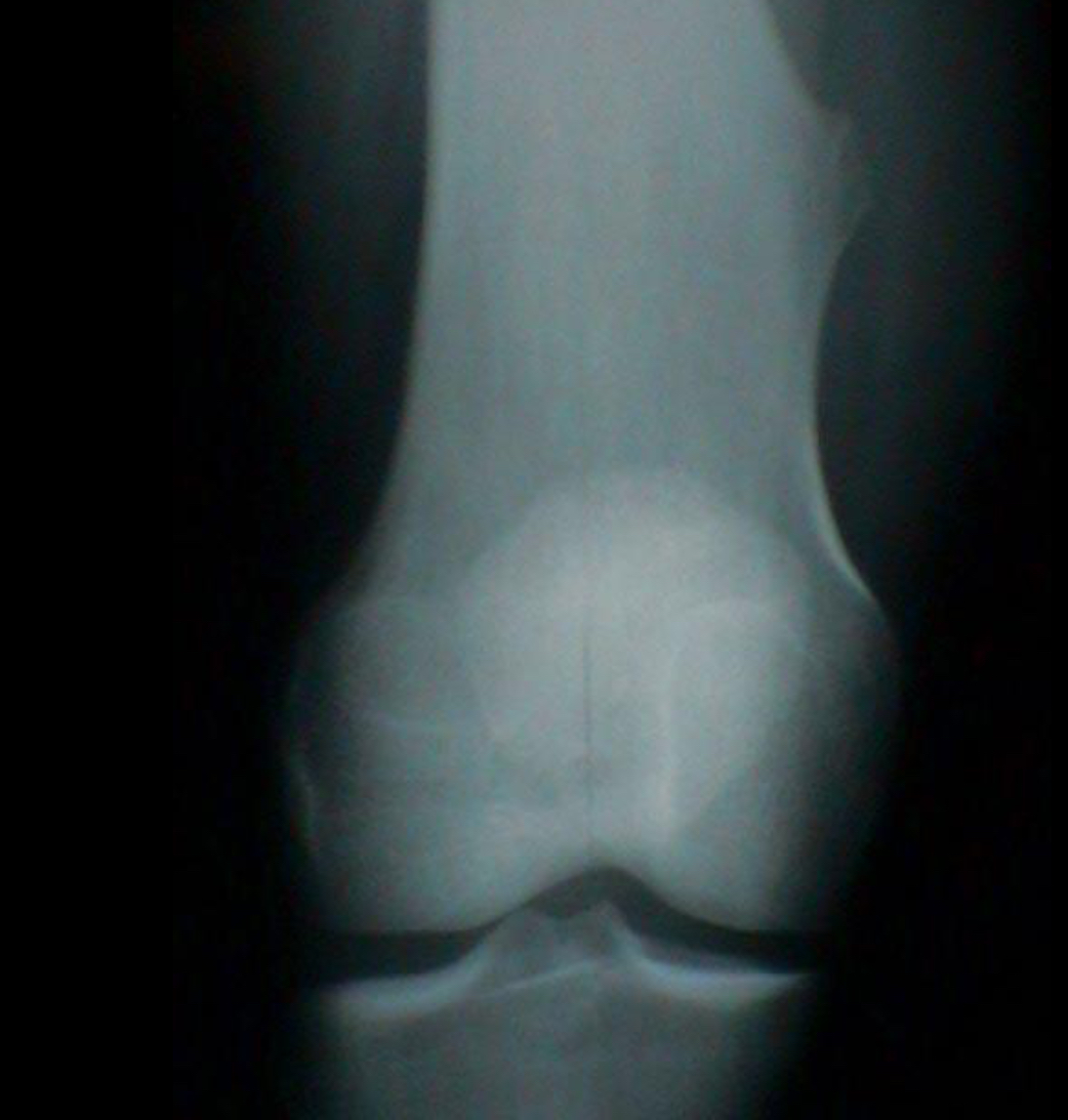
Osteochondroma
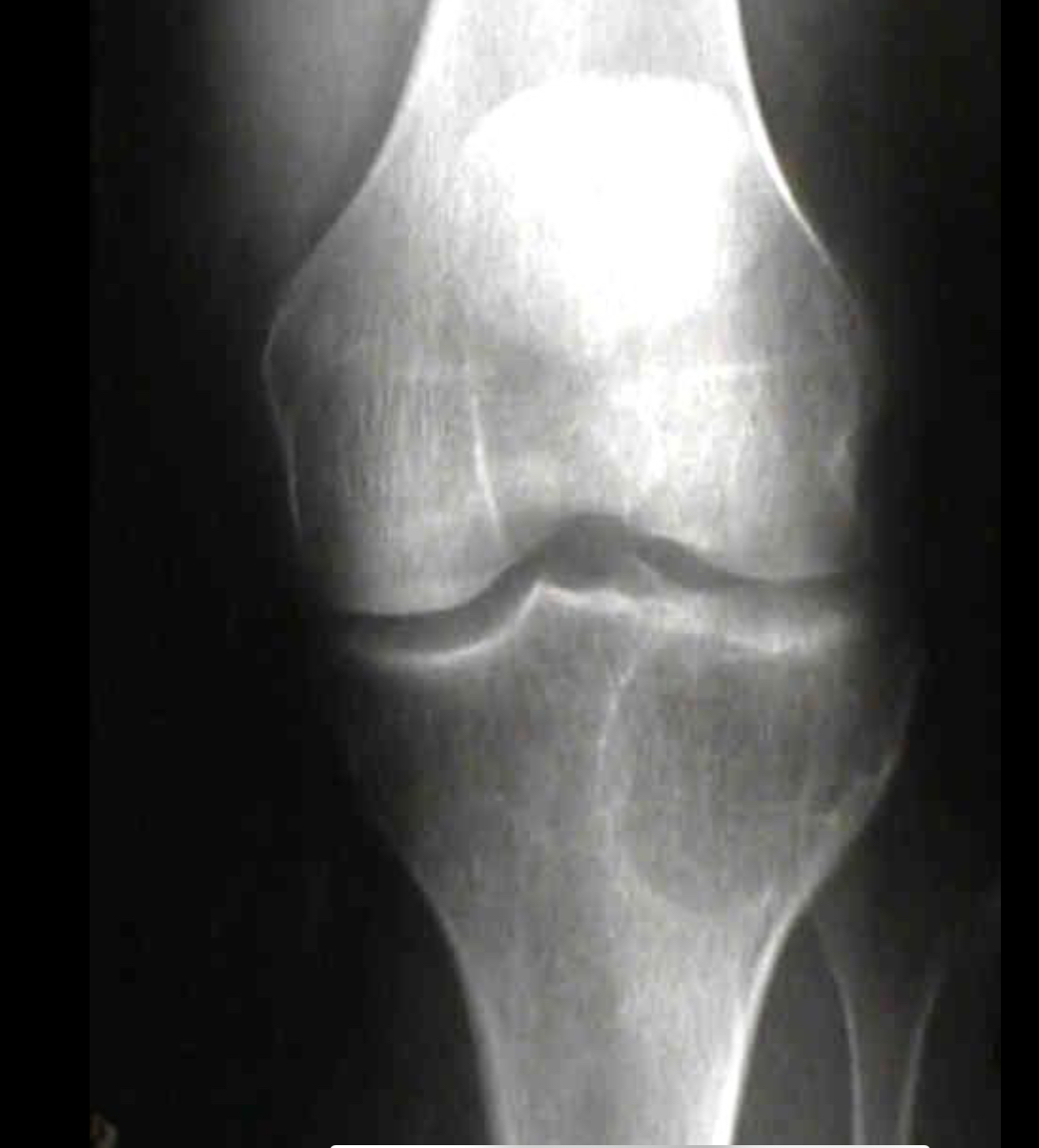
Giant cell tumour
Only occur in patients with closed epiphyses
Lesion must be epiphyseal and at the articular surface
Lesion is eccentrically located in the bone as opposed to centrally located
The lesion must have a sharp defined zone of transition that is not sclerotic
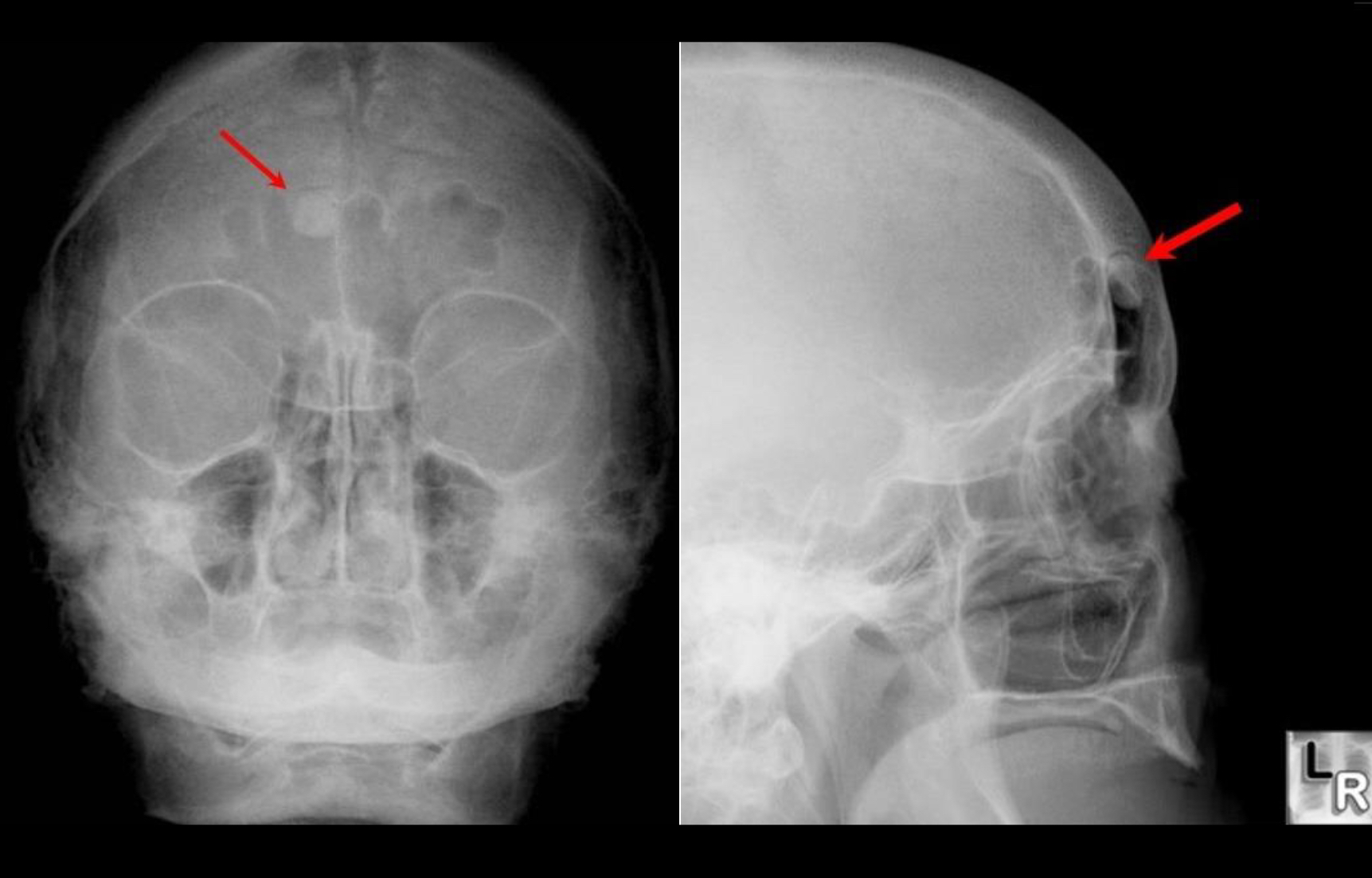
Osteoma
New piece of bone usually growing on another piece of bone
Usually seen in skull, sinuses and mandible
Incidental finding
Well circumscribed, extremely dense round lesions that are rarely larger then 2cm in diameter
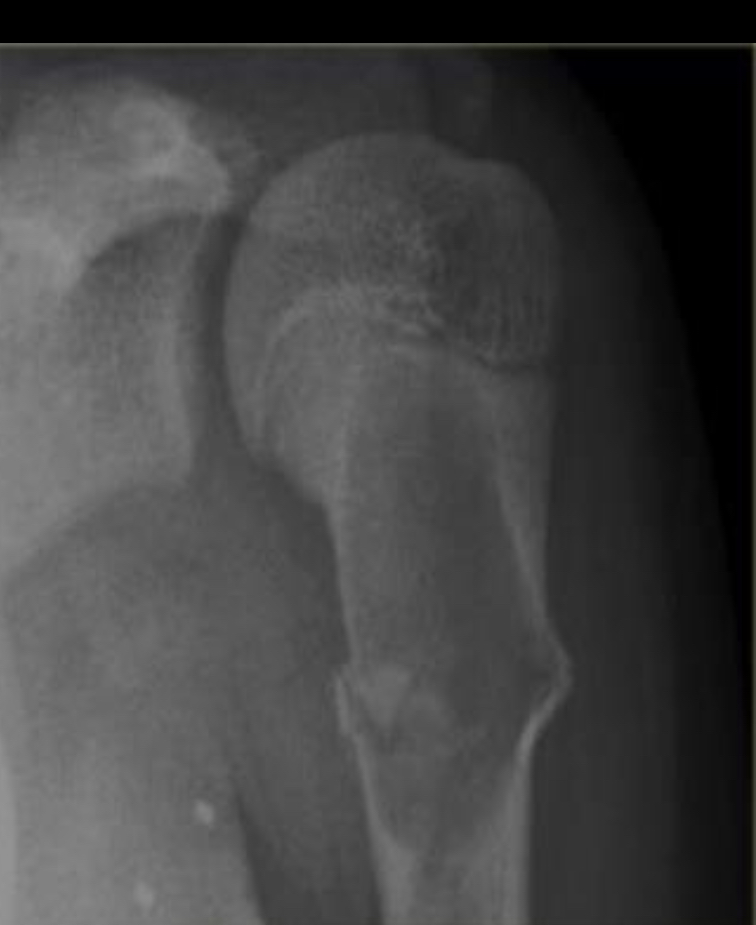
Simple bone cyst
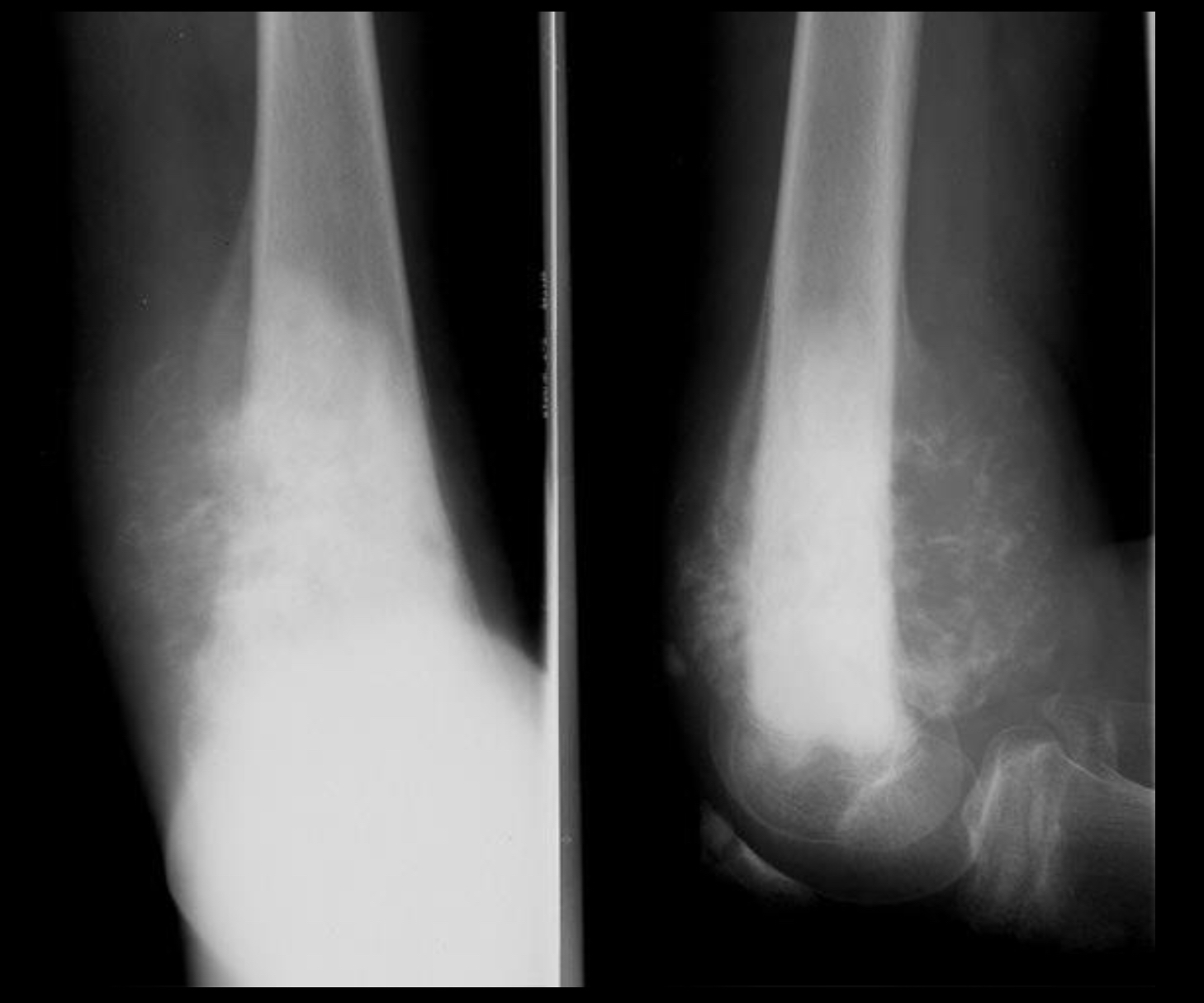
Osteosarcoma
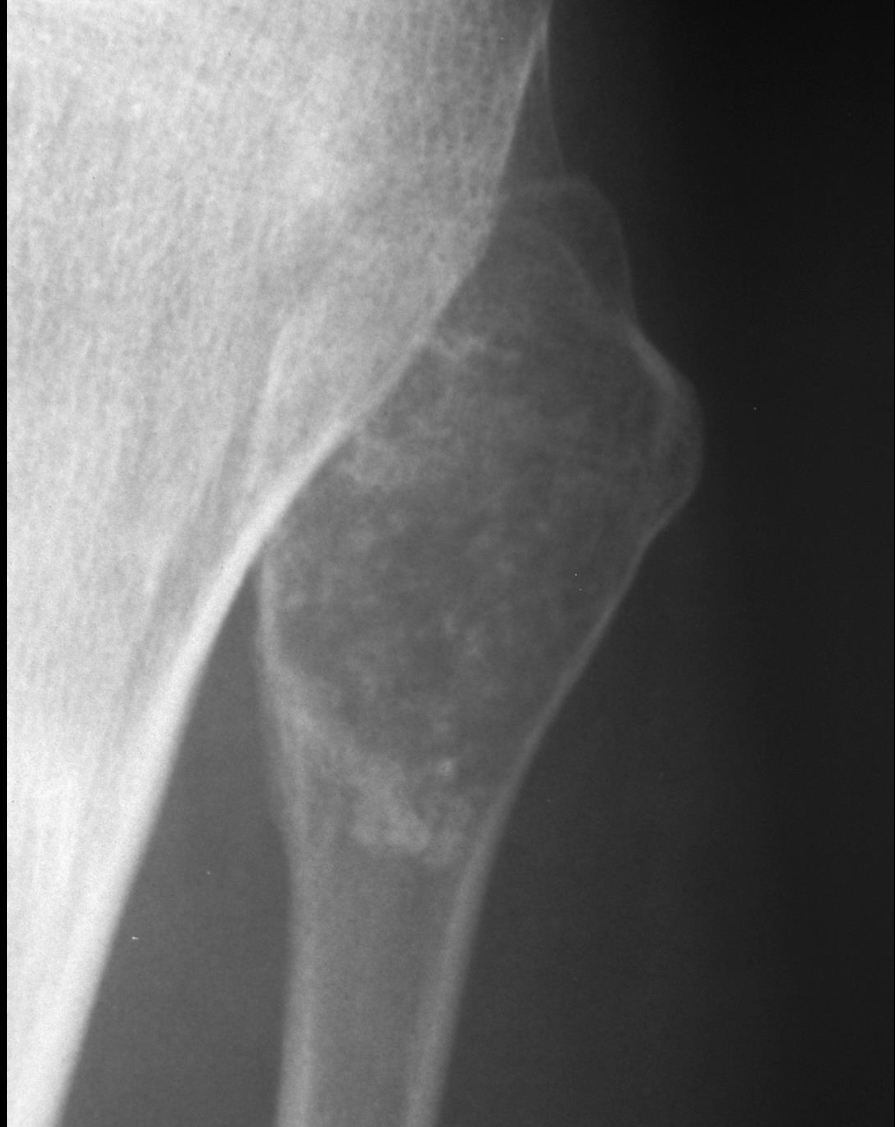
Chondrosarcoma
Commonly occur in long bones, but can originate in a rib, scapula or vertebra
In addition to bone destruction features associated with malignant tumours, punctate (tiny spots) or
amorphous/malformed calcification within its cartilaginous matrix - snowflake calcification
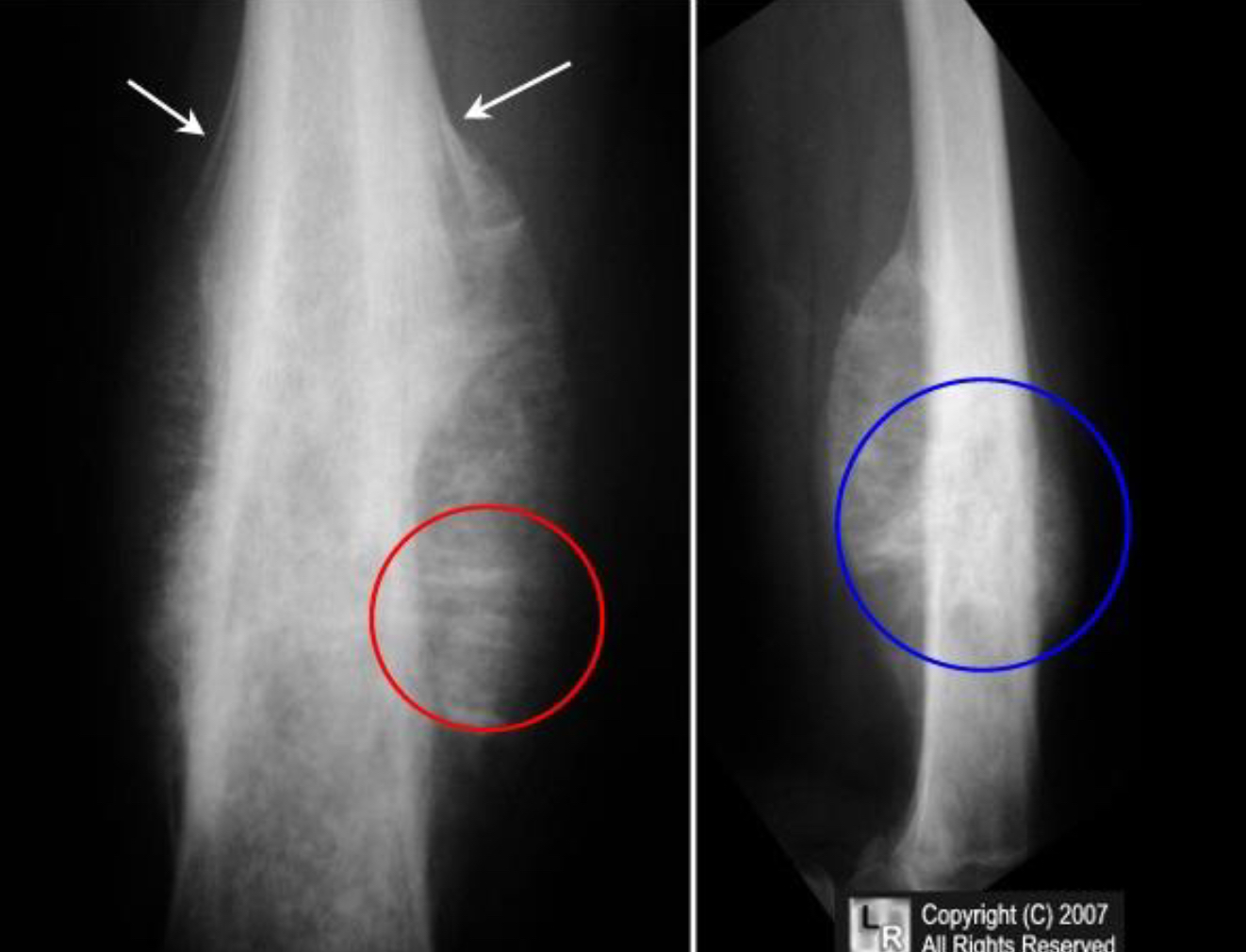
Ewings sarcoma
AP and Lat Femur demonstrate mottled, osteolytic lesion (blue circle) with poorly marginated edges in the diaphysis of the bone.
There is sunburst periosteal reaction (red circle) and lamellated periosteal reaction (white arrows).
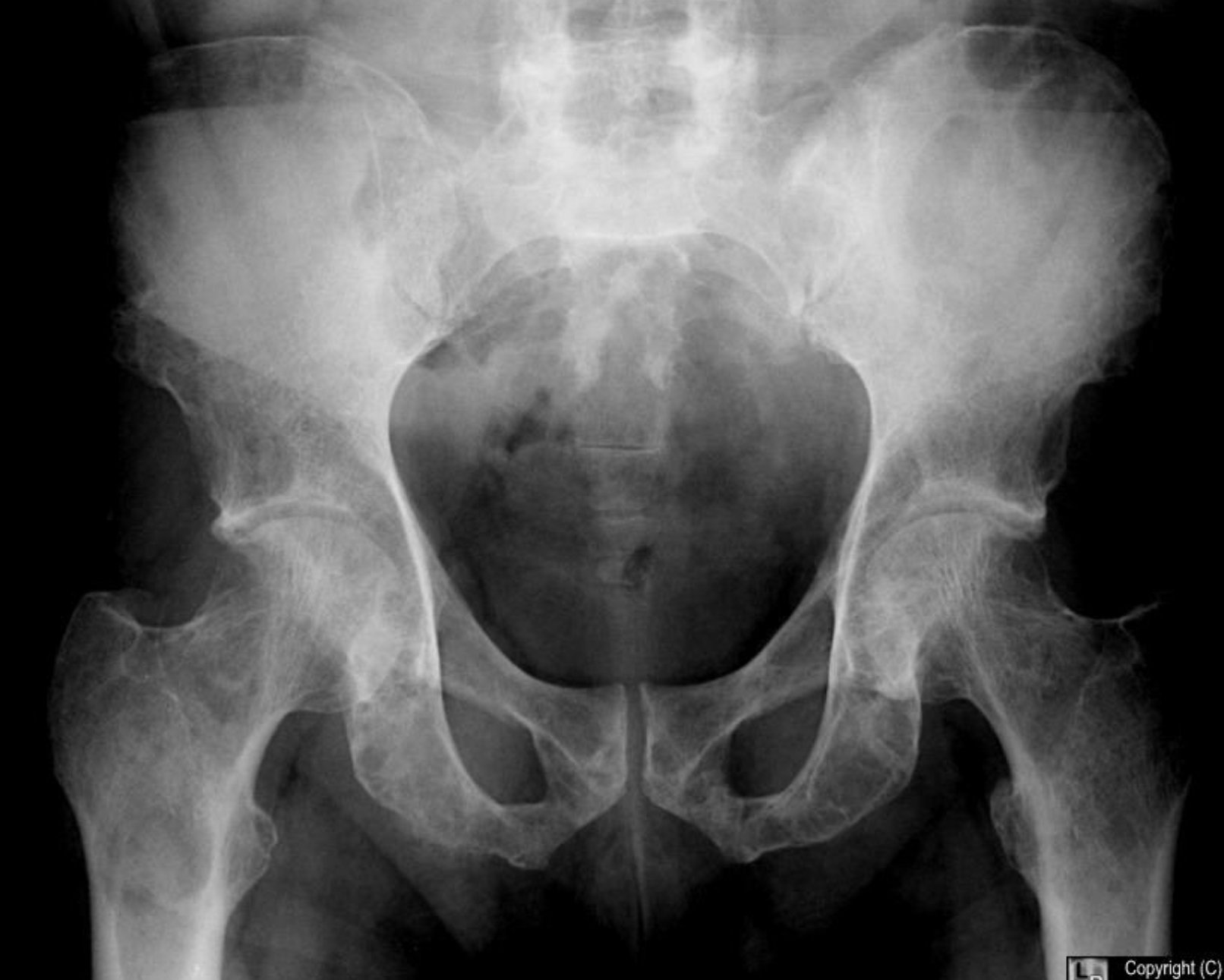
Multiple myeloma