PMLS - History of Medical Technology Profession
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
ANNA FAGELSON (1961)
WHAT IS MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY?
“the branch of medicine concerned with the performance of laboratory determinations and analyses used in the diagnosis and treatment of disease an the maintenance of health.”
RUTH HEINEMANN (1963)
WHAT IS MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY?
“the application of the principles of the natural, physical and biological sciences to the performance of laboratory procedures which aid in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.”
WALTERS (1966)
WHAT IS MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY?
“as the health profession concerned with performing laboratory analyses in view of obtaining information necessary in the diagnosis and treatment of disease as well as in the maintenance of good health.”
RA 5527 (“THE PHILIPPINE MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY ACT OF 1969)
WHAT IS MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY?
Defined Medical Technology as an auxiliary branch of laboratory medicine which deals with the examination of tissues, secretion and excretion of the human body and body fluids by various electronic, chemical, microscopic and other medical laboratory procedures or techniques either manual or automated which will aid in the diagnosis study and treatment of disease and in the promotion of health in general.
June 21, 1969
RA 5527 when?
Vivian Herrick
EMERGENCE OF THE PROFESSION
said that Medical Technology can be traced back in 1550 B.C.
Ebers Papyrus
Intestinal parasitic infection caused by intestinal parasites (Taenia spp. and Ascaris lumbricoides)
Anna Fagelson
EMERGENCE OF THE PROFESSION
Prefers to date Medical Technology from the 14th century when a prominent Italian physician at the University of Bologna employed one Alessandra Giliani to perform certain tasks which would now be considered those of the medical technologist.
It is of interest that Giliani died from a laboratory acquired infection.
Alessandra Giliani
A prominent Italian physician at the University of Bologna employed ______________ to perform certain tasks which would now be considered those of the medical technologist.
Died from a laboratory acquired infection.
yellow bile
black bile
blood
phlegm
4 humours
Hippocrates
“Father of Medicine”
Utilization of drugs, surgery, bloodletting
Hippocrates made this triad for treatment
Galen
Instigated a rudimentary and qualitative assessment of disorder
Urine
One of the body fluids that underwent examination
Rufus Ephesus
50 AD: he made the first description of hematuria as the presence of blood in the urine
“water casting” or uroscopy
Medieval period (1098-1438): ___________________ was widely practiced
Isaac Judaeus
900 AD: __________ described the concepts of urine formation, urinary sediments, and urine characteristics in relation to diseases
“Kitab al Baul” or Book of Urine
where did Isaac Judaeus described the concepts of urine formation, urinary sediments, and urine characteristics in relation to diseases
Jerusalem Code 1090
failure to examine the urine exposed a physician to public beating
Isaac Judaeus
founder of nephrology
Athanasius Kircher
(1602-1680) he was a German Jesuit scholar who studied microorganisms in blood during the plague epidemic in Italy in the 1600s
His work was a key step in the development of blood cultures and the understanding of contagion.
Used an early microscope to examine the blood of plague victims
Observed tiny worms in the blood, which he called "animalcules"
Concluded that the plague was caused by microorganisms that were too small to see without a microscope
Recommended isolation, quarantine, and face masks to prevent the spread of the plague
animalcules
Athanasius Kircher observed tiny worms in the blood, which he called
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
“Father of Microbiology”
New, improved compound microscope
Bacteria (classified according to shape), blood cells, muscle fibers, spermatozoa, protozoa
Hans and Zacharias Janssen
First Microscope was invented by
Marcello Malphigi
Served as a physician to Pope Innocent XII
“Father of Modern Anatomic Pathology”
Embryology of the chick
Histology and physiology of the glands and viscera
Rudolf Virchow
“Father of Microscopic Pathology”
First scientist/physician of the time who emphasized the study of the manifestation of diseases and infections
18th century
When were mechanical techniques, along with cadaver dissection, utilized to achieve a more objective and precise diagnosis.
19th Century
Physicians began using machines for diagnosis or therapeutics
julius harrison
Sphygmomanometer was discovered by
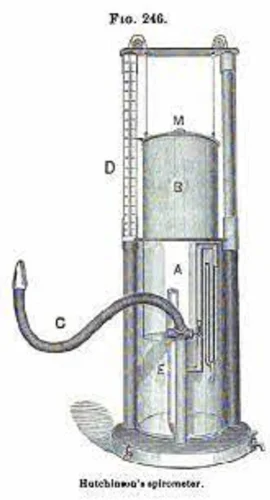
John Hutchinson
Spirometer was discovered by
Sphygmomanometer

Spirometer
University of Michigan Hospital
First clinical laboratory setup
1969
during this year, 80% medical professionals in the hospital are not physicians
University of Pennsylvania’s William Pepper Laboratory of Clinical Medicine (1895)
laboratory by William Pepper Jr.
Dr. William Welch
The first physician recruited to be a professor at the John Hopkins University in Baltimore (1886)
Appointed as the head of the Department of Pathology
Became the first dean of the John Hopkins University School of Medicine
Bellevue Medical College (New York University Medical School)
Dr. William Welch opened a teaching laboratory in America at
Dr. William Osler
1880: Introduced and used the microscope and a blood counting machine in the hospital based laboratory
1898: established ward laboratories at the John Hopkins Hospital
James Campbell Todd
1908: Wrote a book entitled “Clinical Diagnosis: A Manual of Laboratory methods”
John Bernard Henry
Edited the book, “Clinical Diagnosis: A Manual of Laboratory methods” and was then named “Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods”
Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods
“Clinical Diagnosis: A Manual of Laboratory methods” by James Campbell Todd was furthered edited by John Bernard Henry to become _______________________________________________ (the Bible of MedTechs)
John Kolmer
1918: Published “The Demand for and Training of Laboratory Technicians”
Description of the first formal training course in Medical Technology
1915
In what year did the state legislature of Pennsylvania enacted a law requiring all hospitals and institutions to have a fully-equipped laboratory fit for routine testing and to employ a full time laboratory technician
1920
In this year, administrative units of clinical laboratories in hospitals were directed by a chief physician
Clinical pathology, bacteriology, microbiology, serology, and radiology
4-5 divisions
Chief Pathologist
Supervisors of Medtechs, the head of the laboratory
American Society for Clinical Pathology
1922: Founded with the objective of encouraging the cooperation between physicians and clinical pathologists as well as maintaining the status of clinical pathologists
code of ethics
American Society for Clinical Pathology established the ___________ for technicians and technologists
University of Minnesota
1923: First to offer a degree program on Medical Technology
American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science
formerly the American Society for Medical Technologists
Originally formed as a subgroup of ASCP
Helped in the recognition of nonphysician clinical laboratory scientists as autonomous professionals
1950s
In this year, medical technologists in the US sought professional recognition from the government through licensure exams
HOSPITAL REAL
first hospital of the Philippines
1565: Moved from Cebu to Manila
Cater to military patients
San Lazaro Hospital
1578: Built by the Franciscans for the poor and lepers
Ketong
Filipino for Leprosy
San Juan de Dios Hospital
1596: Founded for the poor Spaniards
Hospital de San Jose
1641: Founded in Cavite
University of Santo Tomas
Founded in 1611
1871: Established the first faculties of pharmacy and medicine
Boletin de Medicina de Manila (1886)
Revisita Farmaceutica de Filipinas (1893)
Cronicas de Ciencias Medicas (1895)
JOURNALS OF SCIENCE AND MEDICINE
Central board of vaccination
1806: Production and distribution of vaccine lymph
122 regular vaccinators (vacunadores)
Laboratorio Municipal de Manila
1887: Established to perform laboratory examinations of food, water, and clinical samples
General Antonio Luna
was employed as a chemical expert and pioneered water testing, forensics, and environmental studies
studied in the Institution of Paris
Lt. Col. Henry Lipincott
Chief surgeon of the Division of the Pacific and 8th Army Corps
1898: Converted the Spanish Military Hospital into the First Reserve Hospital
Diagnostic laboratory not fully maximized --> following contraction of typhoid by the director
Richard P. Strong
Successor to the First Reserve Hospital
Utilized to perform autopsies, examination of blood, feces, and urine, and other laboratory services
Bureau of Government Laboratories
1901: Established by the US Government through the Philippine Commission
Science library, chemical section, serum laboratory
Philippine Commission Act No. 156
Philippine commission act that established the bureau of government laboratories
Bureau of Science
1905: this was established for medical officers who sought a career in laboratory research
⚬ The Bureau worked with the Army Board --> Study of the Tropical Diseases
⚬ Together with PGH and UP >> active center for scientific research and instruction in the country
Study of the Tropical Diseases
Bureau of Science worked with the Army Board for the
PGH
UP
Bureau of Science together with ___ and __ became the active center for scientific research and instruction in the country
Paul Freer
Bureau of Government Laboratories’ 1st Director
bombing of Manila by Japan
Bureau of Science got destroyed during the
BUREAU OF HEALTH
From the civilian Board of Health established by the Americans
1915: Reorganized into the Philippine Health Service
1933: Reverted into the Bureau of Health
UP College of Public Health
Aims to provide proper training to the Philippine Health Services Medical Officers
Certificate in Public Health Program
June 1927: UP College of Public Health opened its
December 8, 1941
when did Japan attack the whole of Manila
Laboratory unit of the US Army provided medical services with the available laboratory supplies, supplementary laboratory examinations, epidemiological and sanitary investigations:
⚬ Routine water analysis
⚬ Examination of food supplies
⚬ Distribution of special reagents and solutions
⚬ Culture media
⚬ Investigation of epidemics and epizootics
⚬ Special serological, bacteriological, pathological and chemical examiantions, post-mortem examinations, preservation of pathological specimens
1944
when did they deploy separately as small detachments or mobile laboratory sections to military bases in different islands
Medical Units Deployed
⚬ Leyte
■ 19th Medical General Laboratory
■ 3rd Medical Laboratory
■ 363rd Medical Composite Detachment
■ 27th Medical Laboratory (Tacloban)
⚬ Luzon
■ 26th Medical Laboratory (Lingayen Gulf)
26th Medical Laboratory (Lingayen Gulf)
the only laboratory for 6 months following the US invasion on January 9, 1945
3D Medical Laboratory
first laboratory unit to be assigned in the South West Pacific Area (SWPA)
Manila Public Health Laboratory
First clinical laboratory in the Philippines
6th Infantry Division of the US Army
Manila Public Health Laboratory was established during the WWII by the ____________________________ at Quiricada St., Sta. Cruz, Manila
June 1945
when was the Manila Public Health Laboratory endorsed to the National Department of Health
Dr. Alfredo Pio de Roda
Dr. Mariano Icasiano
the Manila Public Health Laboratory was non- operational until reopened by ___________________ with the help of _________________
October 1945
when was the the Manila Public Health Laboratory reopened
Dr. Alfredo Pio de Roda and Dr. Prudencia Sta. Ana
conducted a training program for aspiring laboratory workers
Dr. Sta. Ana
tasked to prepare a 6-month formal syllabus with certificate upon completion
Dr. Tirso Briones
he joined later on in creating a training program for aspiring laboratory workers
1954
the training program for aspiring laboratory workers ended in
4-year course in BSMT
in 1954, what was approved by the Bureau of Private Education
Manila Sanitarium and Hospital (MSH)
opened the first School of Medical Technology in the Philippines
Mrs. Willa Hilgert Hedrick
made the syllabus and course for medtechs
wife of Dr. Elvin Hedrick
Medical Internship and Residency training program - Loma Linda University (California)
Antonette Mckelvey
helped Willa Hilgert Hedrick with the making of the syllabus and course
Philippine Union College (PUC)
absorbed MSH’s School of Medical Technology in 1954
Dr. Jesse Umali
the first graduate of the Medical Technology Program
later graduated as a Doctor of Medicine at FEU and a successful OB-gynecologist in the US
Manila Adventist Medical Center
Manila Sanitarium and Hospital became
Adventist University of the Philippines
Philippine Union College became
University of Sto. Tomas
offered the Medical Technology course as an elective for pharmacy students (1957)
1961
this is when Medical Technology was recognized as an official program in UST
Dr. Horacio Ylagan
Dr. Serafin J. Juliano
Bachelor of Science in Medical Technology
FEU (1961): _______________ and ________________ (granted authority by Dr. Lauro H. Panganiban and Dr. Jesus B. Nolasco)
1963
what year were there first graduates of medtech in FEU
President Carmen de Luna
Purificacion Sunico-Suaco
Bachelor of Science in Medical Technology
CEU: ______________________ delegated ___________________ to work on the offering of Medical Technology course