General Info, Sympathetic & Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is the autonomic Nervous System? What is it mainly used for?
Nervous system OUTSIDE of the Brain and Spinal Cord. Mainly used for unconscious actions and reflexes.
What type of muscle does the ANS innervate?
Smooth Muscle
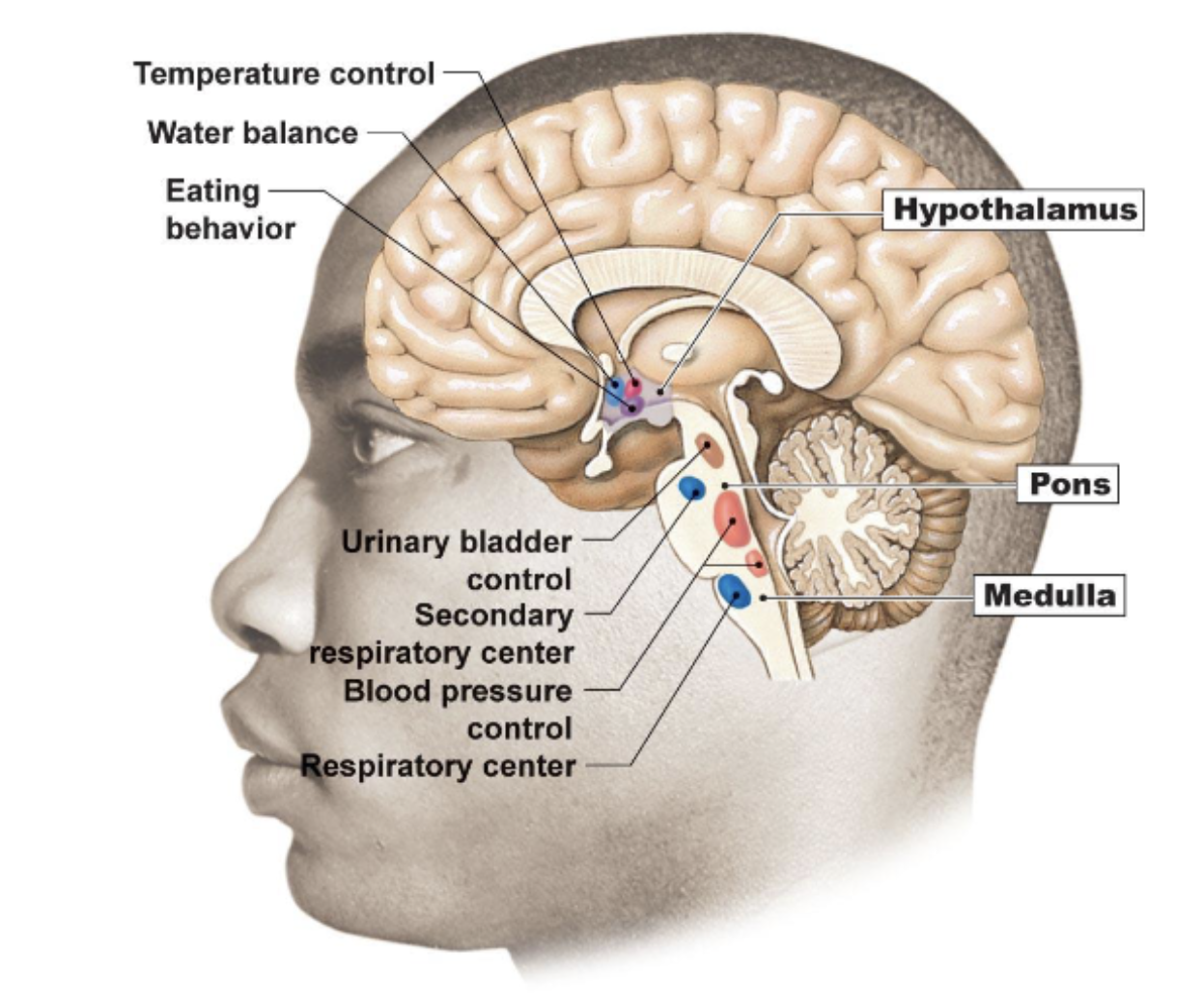
What are the CNS control points for the ANS, and what do they do?
Hypothalamus —> Hunger, Temp, water
Pons → Respirations (breathing rate), cardiovascular
Medulla Oblongata → Respiratory, Cardiovascular
Where do cell bodies in the ANS originate?
WITHIN the CNS (either brain or Spinal Cord)
They synapse with cell bodies outside the CNS, innervating targert
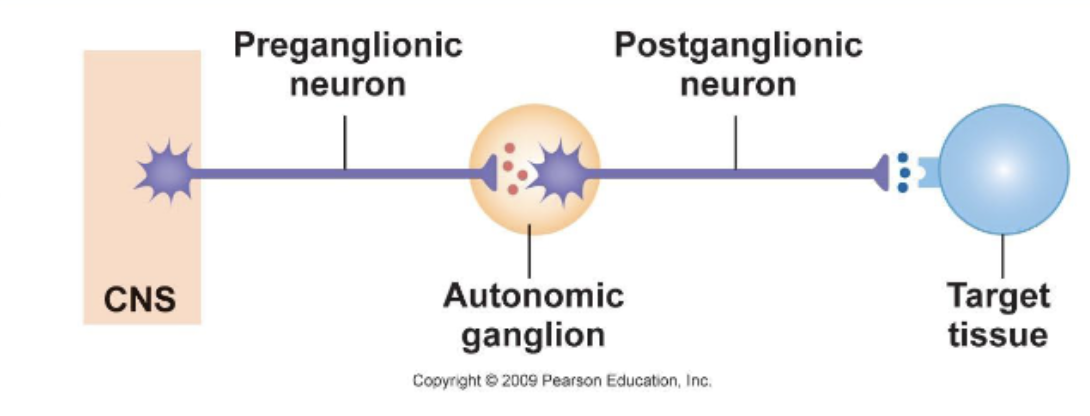
Sequence of Innervation for ANS?
CNS → Pregangliotic Neuron → Autonomic Ganglion → Postgangliotic Neuron → Target Tissue
Function of the Sympathetic Nervous System, and when is it dominant?
Fight/Flight, Dominant during Stress
Homeostatic
Function of Parasympathetic Nervous System, and when is it dominant?
Rest/Digest, Dominant during Rest
Homeostatic
Where does the Pathway start in the Sympathetic Nervous System? What are the characteristics of the nerves?
Pathway starts in the Spinal cord
LONG nerve Projections to target that travel SHORT distances
need to be short for quick reactions during stress
Where does the Pathway start in the Parasympathetic Nervous System? WHat are the characteristics of the nerves>
Pathway starts in the Brain
SHORT nerve projections to target that travel LONG distances
What signaling molecules does the Sympathetic Nervous system use?
Epinepherine and Acetylcholine
What signaling molecules does the parasympathetic nervous system use?
Acetylcholine
What type of control does the ANS utilize?
Antagonistic Control (increase in sympathetic, decrease in parasympathetic, vise versa)
What is Somatic Motor division?
Voluntary movement
What is the path taken in the Somatic Motor Division? What types of receptors?
Single neuron in the CNS → long myelinated axon → Skeletal muscle
More sympathetic because of the long myelinated axon
Has multiple different acetylcholine receptors (Nicotinic, Muscarinic)
What is Acetylcholine?
Excitatory neurotransimtter used in sympathetic, parasympathetic and somatic systems.
What is cholinergic signaling
Idea that a different receptor elicits a different response (regardless of signaling molecule)
How do the different receptors act (antagonist and agonist)?
Act agnoistically (causing a physiological response when binding with a receptor).
Act antagonistically (inhibiting a physiological response when binding with a receptor)
What are Nicotinic Receptors? How is it used?
Ligand Ion-Gated Channels.
Excitatory (usually) receptors
Composed of 5 subunits
Used agonistically and anatgonistically, used differently in somatic, parasympathetic, sympathetic systems.
What are muscarinic receptors?
GPCR gated (g-protein coupled receptors)
Involved in neuromodulation
Muscarine = Poisonous mushroom
USES NICOTINIC RECEPTORS FOR PREGANGLION → POSTGANGLION
What are Adrengernic receptors?
Used by Epi
Has many functions and targets, but stimulates all of them
ONLY in the sympathetic (since only Epi used)
USES NICOTINIC RECEPTORS FOR PREGANGLION → POSTGANGLION
What are the different “second” postsynaptic ganglia in the sympathetic pathway? Where are they, What do they target?
Chain Ganglia → Next to spinal cord
Targets head, heart, lung tissues and glands
Collateral Ganglia → Abdominal cavity
Targets GI tract, pancreas, liver, colon
Adrenal medulla → Modified Chain Ganglia
What is unique about the Adrenal medulla?
When stimulated, the ENTIRE thing is stimulated, producing Epi and NorEpi
Causes the whole entire scale of fight/flight
What are ANS reflexes, and how do they work? What are two types of reflexes?
Rapid, focused pathways to detect and fix changes in body homeostasis
Barcoceptor Reflex
Pupil Dialation
What is the barcoceptor reflex?
detects sudden changes in the effects of gravity (lightheadedness when you stand up
quickly)Uses Adrengernic Receptors (so ONLY in Sympathetic)
What is the Pupil Dialation Reflex?
Pupil dialating based on light present, protecting it from birght light and allowing vision in dim light
Bright Light —> Pupil constricts via Parasympathetic
Dim Light —> Pupil dilates via Sympathetic