Biology Paper 1-CGP->B1
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
What are cells?
They're the basic building blocks of all living organisms
Organisms can be either prokaryotes or eukaryotes(cells), but what are they?
Prokaryotic cells are cells without a nucleus while Eukaryotic cells are cells with a nucleus
->Eukaryotic cells are complex e.g animal and plant cells
->Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler e.g bacteria
What are Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes are organisms made up of eukaryotic cells while prokaryotes are a prokaryotic cell(single-cell organism)
What is a Subcellular structure?
Different parts of a cell e.g animal cells
What does animal cells consist of?
Nucleus, Cell membrane, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Cytoplasm
What's the Nucleus?
A nucleus contains genetic material that controls the activities of the cell
What's the Cell Membrane?
It holds the cell together and controls what goes in and out of the cell
What's the Mitochondria?
These are where most of the reactions for aerobic respiration takes place. Respiration transfers energy that the cell needs to work
What's the Ribosomes?
They're where proteins are made in the cell
What's the Cytoplasm?
A gel-like substance where most of the chemical reactions happen. It contains enzymes that control these chemical reactions
what do plant cells already from from an animal cell?
Nucleus, cell membrane, mitochondria, ribosomes and a cytoplasm
Other than all the bits an animal cell has, what else does a plant cell consist of?
Cell wall, Permanent Vacuole and Chloroplasts
In an animal cell, What is a Cell wall?
It's made if cellulose and it supports the cell and strengthens it
In an animal cell, What is the Permanent Vacuole?
It contains cell sap, a weak solution of sugars and salts
In an animal cell, What is the Chloroplasts?
Where Photosynthesis occurs, which makes food for the plant. They contain a green substance called Chlorophyll, which absorbs the light needed for photosynthesis
Since a Bacteria Cell doesn't have a nucleus, what does it have instead?
A single-circular strand of DNA that floats freely in the cytoplasm. They may also contain one or more small rings of DNA called Plasmids
Other than a nucleus, what does a Bacteria Cell not contain?
Chloroplasts or mitochondria
Since Bacteria are prokaryotes, what does it consist of?
Cell wall, Cell membrane, Cytoplasm
What can Microscopes allow for use?
To see things we can't see with the naked eye
What do light microscopes use and what can they do?
Light Microscopes use light and lenses to form an image of a specimen and magnify it(make it look bigger)
->They also let us see individual cells and large subcellular structures e.g nuclei
What do electron microscopes use and what can they do?
Electron microscopes use electrons to form an image. They have a much higher magnification than light microscopes and higher resolution
What is a Resolution?
How well a microscope can distinguish between two very close points. A higher resolution gives a sharper image
How are electron microscopes better than light microscopes?
They allow us to see much smaller things in more detail e.g the internal structure of mitochondria and chloroplasts and they even let us see finer things like ribosomes and plasmids
What is the magnification formula?
Magnification = image size / real size
(Image size and real size should have the same units and if they don't you will need to convert them first)
How can we work out the image size of the real size of an object?
By using the formula triangle by covering up the thing you're trying to find. The parts you can still see are the formula you need to use
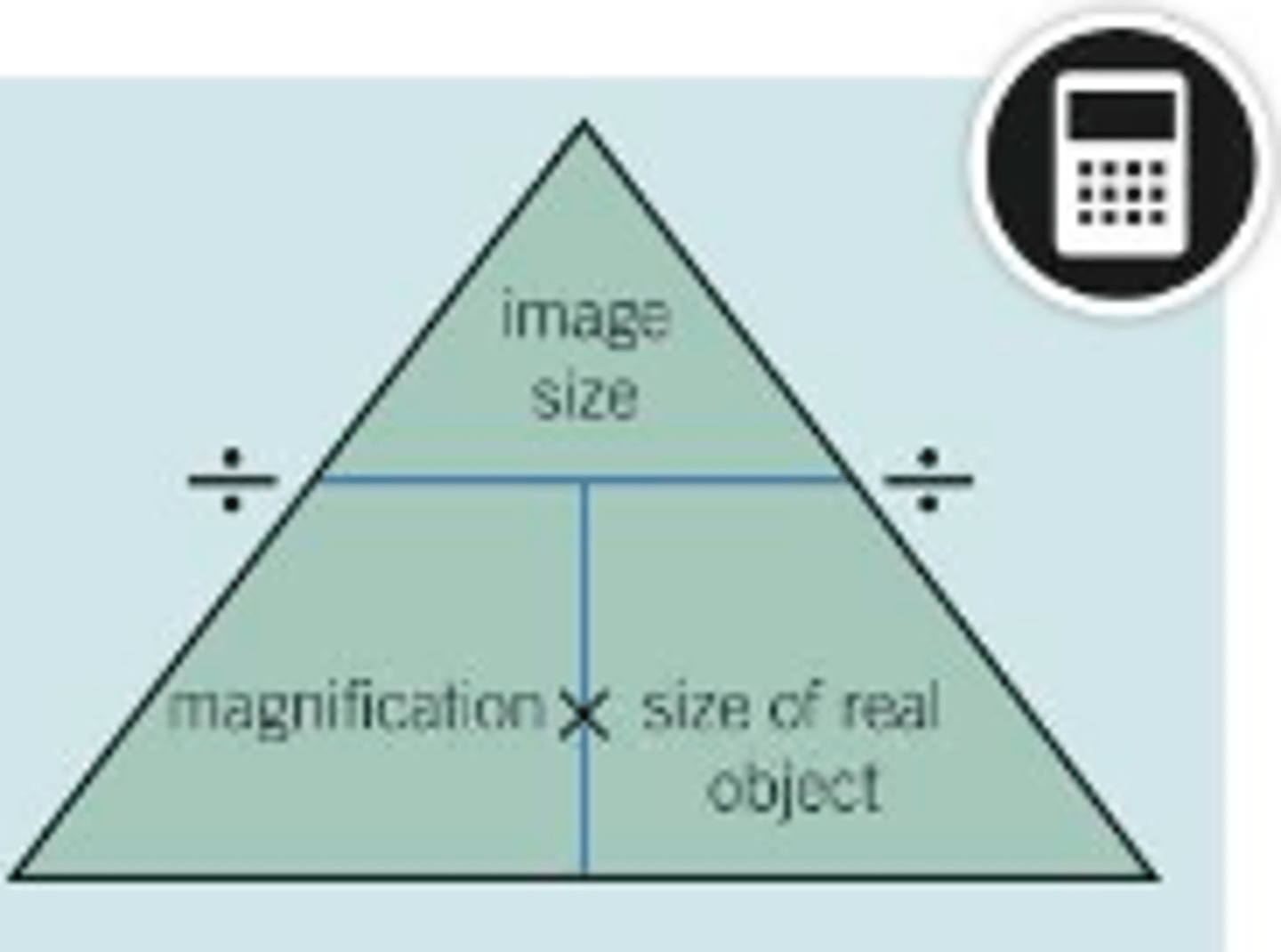
What are the units for magnification?
It doesn't have units
What are the units for image size and actual size?
They're both millimetres(mm)
Since we know the units for image and actual size are (mm) then how do we convert them from different units?
cm-> x10
m-> x1000
nm-> ÷ 1000
μm-> ÷ 1,000,000
What was the aim for the microscopy practical?
To view onion cells
What are the independent, control and dependent variables?
Independent variable- What you change
Control variable- What you keep the same to ensure it's a fair test
Dependent variable- what you measure
What's the equipment needed for the microscopy practical?
A slide, cover slip, water drop mixed with iodine, specimen stained with iodine
What is a slide that's used for practical's?
A slide is a strip of clear glass or plastic onto which the specimen is mounted.
What's the cover slip used in practical's?
A Square of thin, transparent plastic or glass
What is the first step in preparing a microscope slide?
Add a drop of water to the middle of a clean slide.
2nd step: What should you do after adding water to the slide?
Cut up an onion and separate it into layers, then use tweezers to peel off some epidermal tissue from the bottom of one of the layers.
3rd step=How do you place the epidermal tissue onto the slide?
Using tweezers, place the epidermal tissue into the water on the slide.
4th step=What is the purpose of adding iodine solution to the slide?
Iodine solution is a stain used to highlight the objects in a cell by adding color to them.
Last step=How do you properly place a cover slip on the slide?
Stand the cover slip upright on the slide next to the water droplet, then carefully tilt and lower it to cover the specimen, avoiding air bubbles.
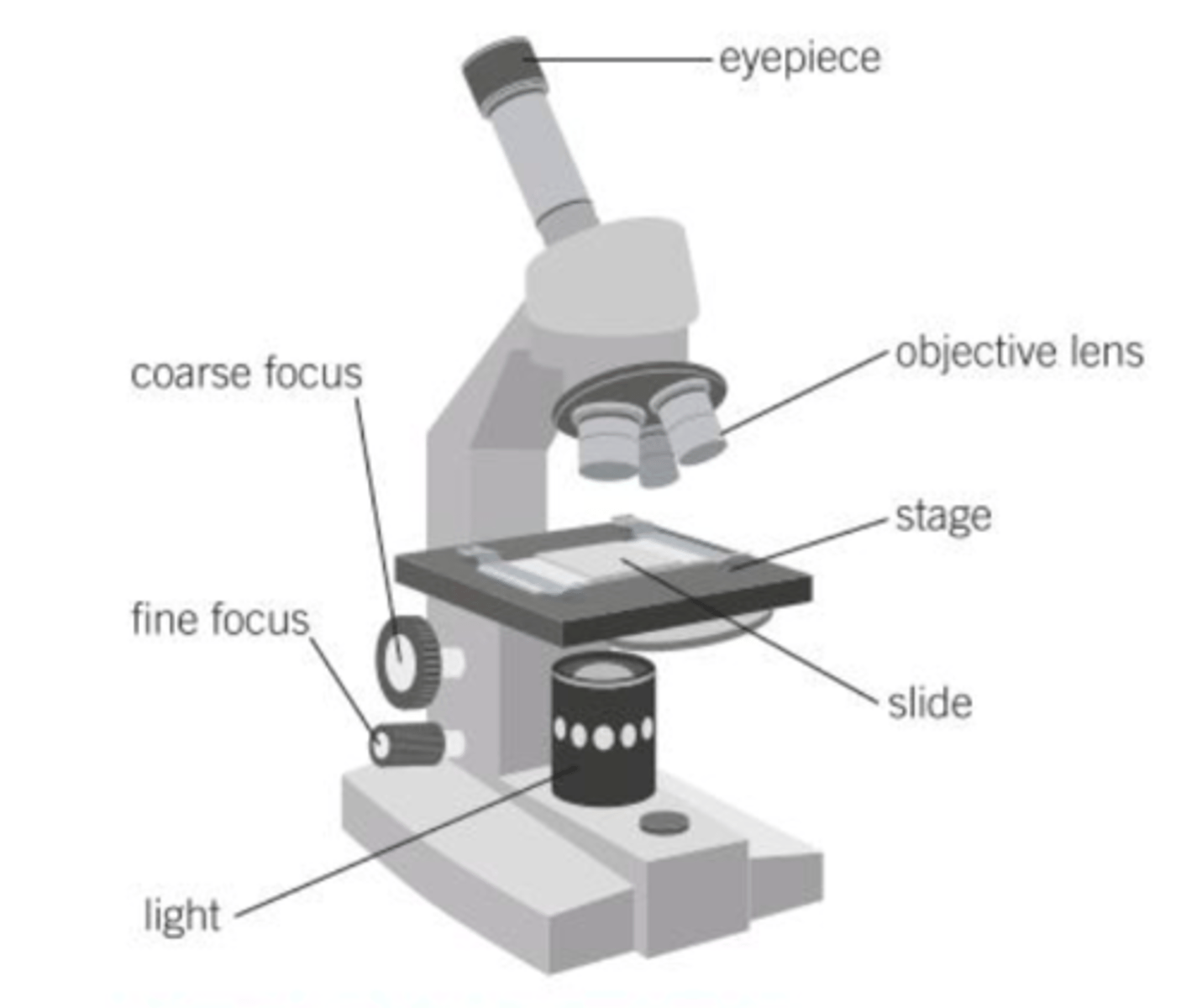
What are the parts of a microscope?
Eyepiece, coarse adjustment knob, fine adjustment knob, high and low power objective lenses, stage, light
How do I draw the onion cell observation?
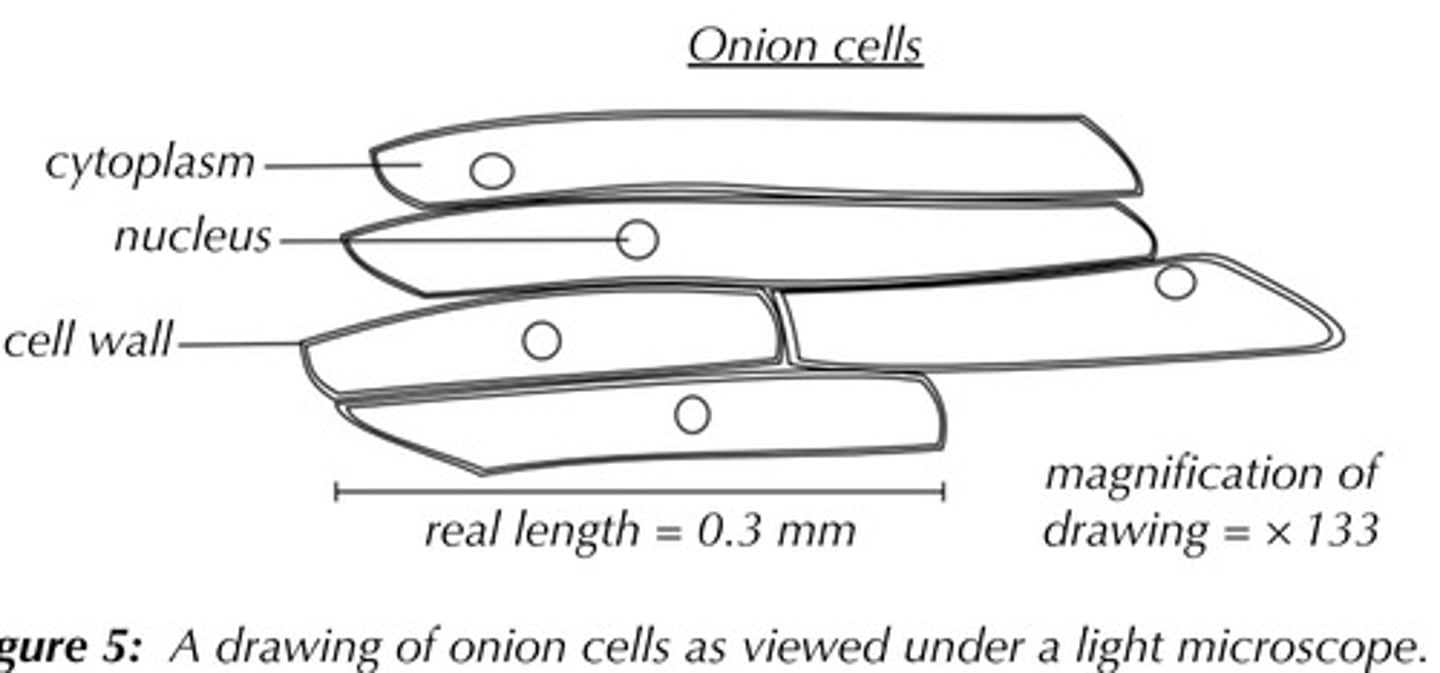
What's the Scale bar formula?
Scale bar length(μm)=drawn length of cell(μm) x 500 / actual length of cell(μm)
Do Plant and animal cells all look like the typical ones?
No because there are lots of different types of eukaryotic cells which all have particular shapes and subcellular structures that help them do specific jobs
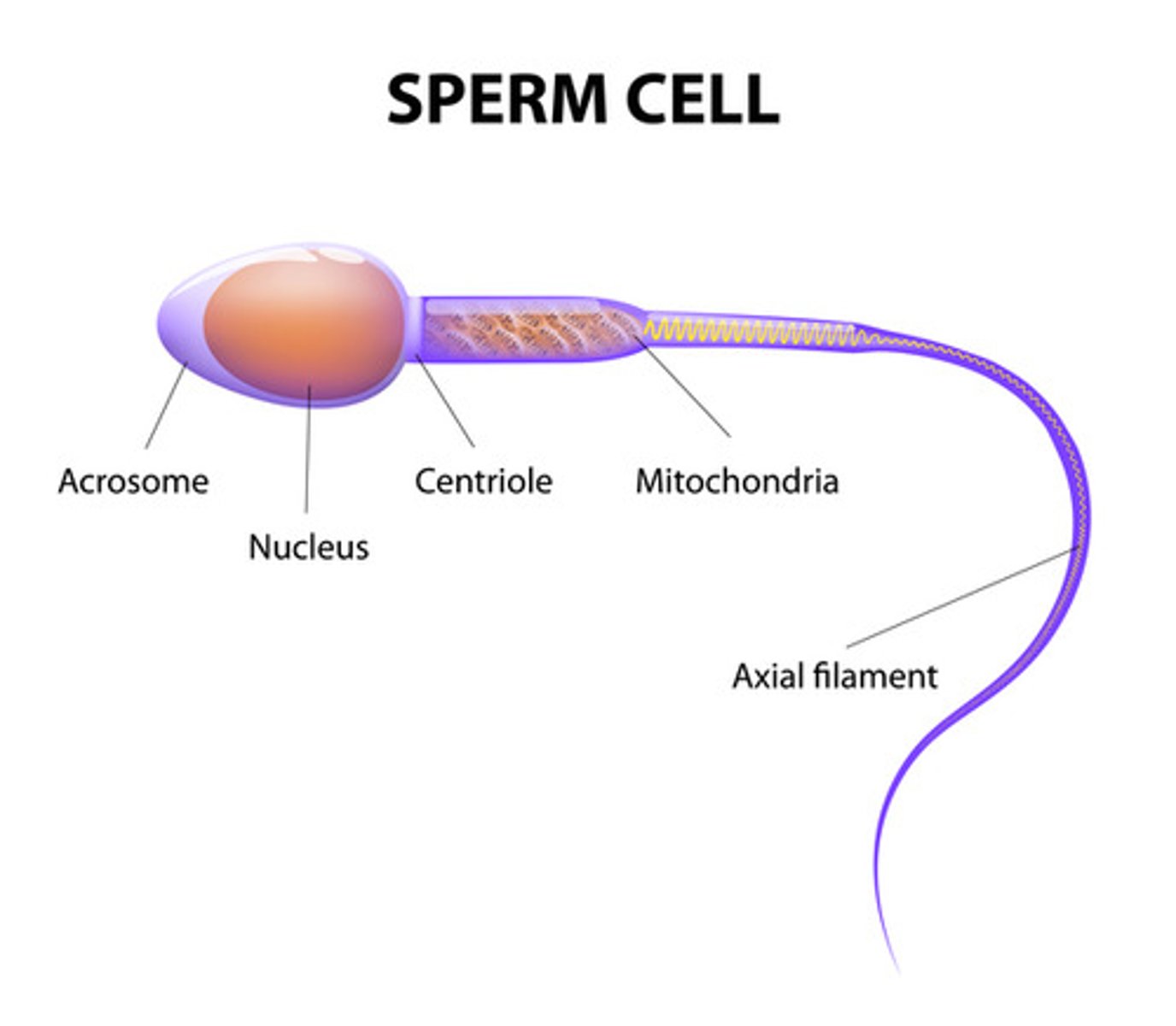
Sperm Cell function
To get the male DNA to the female DNA
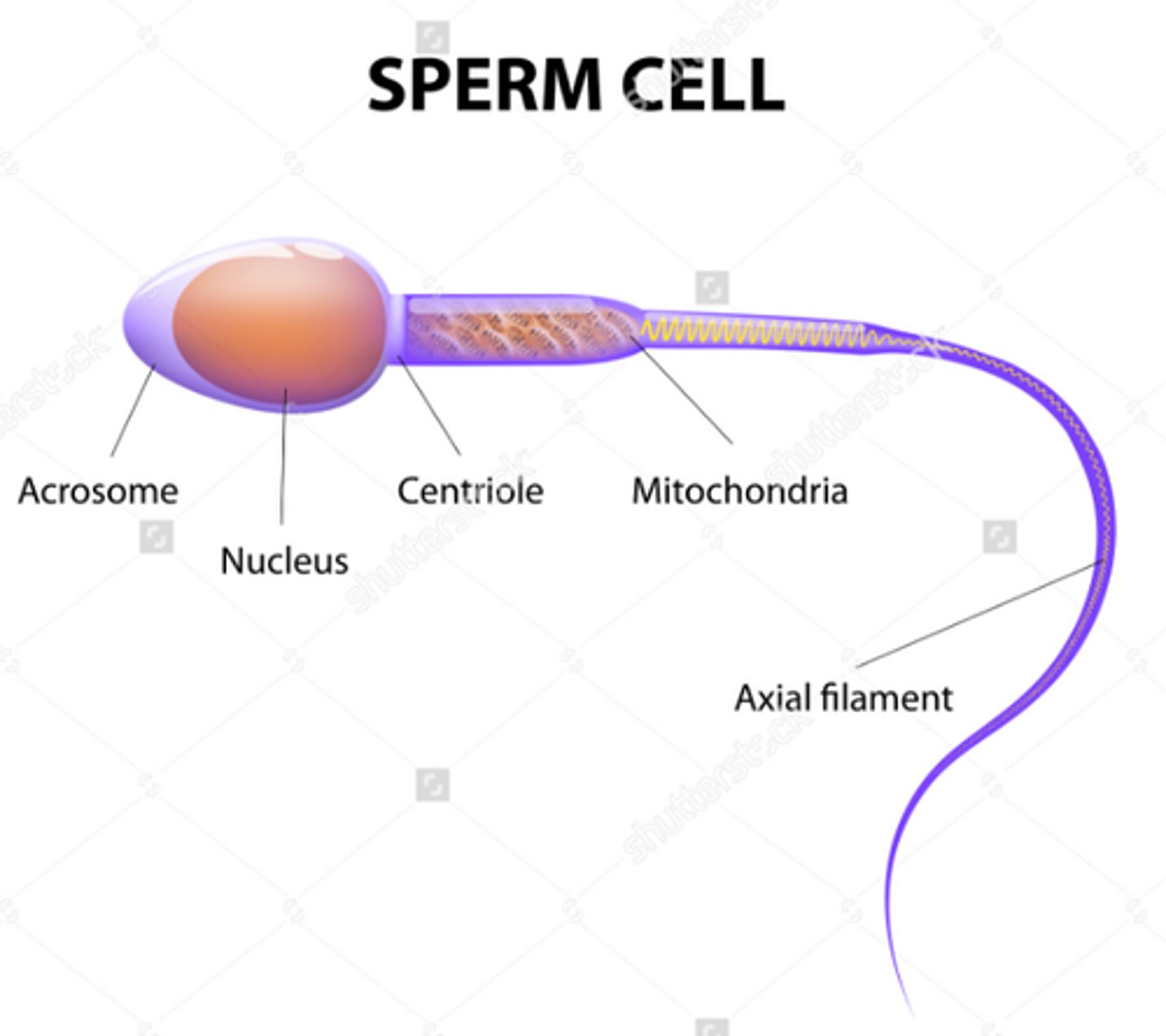
What are the Adaptions of the Sperm cell?
- A long tail and streamlined head to help it swim to the egg
- Lots of mitochondria to provide the energy needed
- Enzymes in it's head to digest through the egg cell membrane
Nerve Cell function
To carry electrical signals from one part of the body to another
What are the Adaptions of the Nerve cell?
- Long to cover more distance
- have branched connections at their ends to connect to other nerve cells and form a network throughout the body
Muscle Cell function
To contract quickly
What are the Adaptions of the Muscle cell?
- long so that they have space to contract
- contain lots of mitochondria to generate energy for contraction
Root hair cell function
To absorb water and mineral ions from the soil
What are the Adaptions of the Root hair cell?
They have long "projections" which give the plant a big surface area for absorption
Phloem and Xylem Cells function
Form phloem and xylem tubes which transport substances such as food and water around plants
What are the Adaptions of the phloem and Xylem Cells?
- The cells are long and joined end to end
- Xylem cells are hollow in the centre and phloem cells have very few subcellular structures, so that stuff can flow through them
What is Differentiation?
Where a cell changes to become specialised for carrying out its function
What's the first step when preparing a slide for viewing?
Clip the slide onto the stage.
Which objective lens should you select initially?
The lowest-powered objective lens (lowest magnification).
After selecting the objective lens, how do you position the stage?
Use the coarse adjustment knob to move the stage up to just below the objective lens.
Once you're looking through the eyepiece, which knob should you use to get the image roughly in focus
The coarse adjustment knob to move the stage down until the image is roughly in focus.
What knob do you use to get a clear image once it's roughly in focus?
The fine adjustment knob.
What should you do if you need to view the slide with greater magnification?
Swap to a higher-powered objective lens and then refocus.
What's the first step to estimate cell size using a microscope and ruler?
Place a clear ruler on top of the microscope slide and clip both onto the stage.
Which objective lens magnification should you select for this procedure?
The objective lens that gives an overall magnification of x100.
After selecting the objective lens, what's the next step to view the cells?
Adjust the focus to get a clear image of the cells.
How do you measure the number of cells for the calculation?
Move the ruler so that the cells are lined up along 1mm, then count the number of cells along this 1mm sample.
How do you calculate the length of a single cell in micrometers?
Since 1mm = 1000μm you divide 1000μm by the number of cells in the 1mm sample.
What is the final step after calculating the length of a single cell?
Calculate how long your scale bar should be using the appropriate formula.
When does most differentiation occur in an organism?
As an organism develops.
In most animal cells, when is the ability to differentiate typically lost?
At an early stage, after they become specialized.
Do plant cells lose their ability to differentiate?
No, lots of plant cells don't ever lose this ability.
What is the primary purpose of differentiated cells in mature animals?
Mainly for repairing and replacing cells (e.g., skin or blood cells).
What are undifferentiated cells called?
Stem cells.
What are undifferentiated cells called, and what can they do?
Undifferentiated cells are called stem cells. They can divide to produce lots more undifferentiated cells and differentiate into different types of cells.
What determines the type of cell a stem cell becomes?
The instructions the stem cell is given.
Where do embryonic stem cells come from and what is their potential?
They come from early human embryos and can turn into any kind of cell.
What can stem cells be used for in medicine and research?
To replace faulty cells or tissues (like insulin-producing cells for diabetes or nerve cells for spinal injuries).
Why are adult stem cells more limited?
They can only turn into certain cell types, like blood cells.
How are adult stem cells used in medicine?
Stem cells from bone marrow can be grown in labs and used in medicine or research.
What are clones in the context of stem cells?
Genetically identical cells produced from embryos.
How is medicine already using adult stem cells?
To cure some diseases using bone marrow from a healthy person.
How can embryonic stem cells be useful in treating diseases?
They can be used to replace faulty cells in sick people.
How can therapeutic cloning help in medicine?
The embryo is made with the same genetic information as the patient so the body won't reject it.
What is the main ethical issue with embryonic stem cells?
The embryo used is destroyed, raising ethical concerns.
What are the risks involved with stem cell use?
Stem cells grown in a lab may become contaminated with a virus, which could be passed to the patient.
What are some arguments against embryonic stem cell research?
Human embryos shouldn't be used for experiments, Scientists should focus on finding other sources, People could be helped without using embryos.
What are some arguments for embryonic stem cell research?
Curing suffering patients is more important than embryo rights, Embryos used are often unwanted and would otherwise be destroyed.
Where are plant stem cells found?
In meristems (parts of the plant where growth occurs).
What can meristem cells differentiate into?
Any type of plant cell throughout the plant's entire life.
What can plant stem cells be used for?
Producing clones of whole plants quickly and cheaply, Growing rare species to prevent extinction, Growing crops with desired features like disease resistance.
What is the fundamental purpose of cells in terms of survival and growth?
To survive and grow, cells have got to be able to divide.
What does DNA contain that dictates the information for an organism's development?
Our DNA is our genetic material.
What are the main components of a human body cell, and where is the genetic material found?
Most cells in your body have a nucleus, The nucleus contains your genetic material in the form of chromosomes, Chromosomes are coiled up lengths of DNA molecules.
What is the general purpose of genes?
Each chromosome carries a large number of genes.
How do different genes contribute to an organism's development?
Different genes control the development of different characteristics, e.g., hair color.
How do body cells typically reproduce and how many chromosomes do they have compared to the original cell?
Body cells normally have two copies of each chromosome; one from the organism's 'mother' and one from its 'father', humans have two copies of chromosome 1, two copies of chromosome 2, etc.
What is Mitosis?
the process by which body cells in multicellular organisms divide to produce new cells
What is the name given to the stage of the cell cycle when the cell divides?
Mitosis
What happens to multicellular organisms when their cells are damaged?
Multicellular organisms use mitosis to grow or replace cells that have been damaged.
What is the outcome of the cell cycle in terms of new cells?
The end of the cell cycle results in two new cells identical to the original cell, with the same number of chromosomes.
What are the two main stages of the cell cycle?
Growth & DNA Replication, and Mitosis.
In a cell that isn't dividing, what form is DNA in, and what is it spread out in?
In a cell that isn't dividing, the DNA is all spread out in long strings.
Before a cell divides, what happens to its DNA and subcellular structures?
Before it divides, the cell has to grow and increase the amount of subcellular structures such as mitochondria and ribosomes.