Wk3 Neurology
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Ventral
anterior
Dorsal
posterior
Ramus
singular
Rami
plural
Ganglion
collection of nerve cell bodies
Peripheral NS made up of
somatic and autonomic
Somatic ns
peripheral nerves
Autonomic ns
sympathetic and parasympathetic
spinal nerves
PNS. Mixed- carry sensory info to CNS and motor info out of CNS. 31 pairs. C1 (highest, exits above cervical veterbrae), rest exit below veterbrae
CNS and PNS recovery
CNS has limited/no ability to recover, PNS has greater ability to recover
Spinal cord terminates at
~L2, called the conus medullaris
Most superficial layer of spinal cord
border between CNS and PNS, outside of that is PNS. Some peripheral nerves are inside canal and dural sac
Between vertebrae
fibral cartilage for shock absorption
Motor neuron cell body
inside CNS
Sensory neuron cell body
inside PNS, cell body dorsal root ganglion
Cell body made up of
grey matter
Myelin sheaths made up of
white matter
Schwann cells
regen myelin sheath, only in PNS
Somatic
provides sensory and motor information to all body at conscious level
Autonomic
controls function of body not under conscious control, autonomic reflexes, visceral function and pain
Sensory information
touch, pain, position sensation
Motor information
innervates skeletal muscles for voluntary and reflective movements
Efferent
convey neural impulses from CNS to effector organs (muscles and glands). Form anterior (ventral) nerve root of spinal nerve
Afferent
convey neural impulses to the CNS from the sensory receptors in various parts of body. Form posterior (dorsal) nerve root of spinal nerve
Nerves
bunched together vasicles
Epineurium
covers nerve
Perineurium
surrounds fasicle
Fascicle
made up of peripheral (myelinated) nerve fibres which are lined by endoneurium
Axon to muscle fibres
one axon covers many nerve fibres. Fine motor control, more nerves.
Neuromuscular junction
Motor nerve fibre attaches to muscle fibres
Fascia
covers nerve fibres
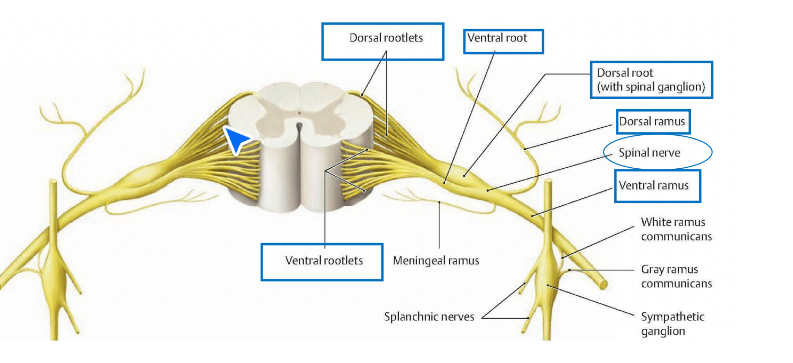
Ventral roots
anterior. Formed by rootlets. motor
Dorsal root
posterior. Formed by rootlets. Sensory. Moves towards brain
Splits of spinal nerve
dorsal ramus and ventral ramus
Ventral gray horn
ventral rootlets emmerge from, taking motor information to effectors. Gray matter.
Dorsal gray horn
sensory information lead into horn by dorsal rootlets by dorsal ganglion. Gray matar
Intervertebral foramen
bony part gap. Where spinal nerves exit
Dorsal ramus
mixed. Innovates skin on posterior aspect of body and deep instrinsic back muscles
Ventral ramus
innovates structures on anterior and lateral aspects of body and contributes to plexuses in every region but thoracic. mixed
Epidural fat
outside spinal cord
Spinal reflex eg
flexor (withdrawal) reflex
Internuncials/interneurons
connect neurons and act as medium of communication. May ascend or descend cord and stimulate motor fibres at diff levels depending on what innovates the muscle. Connects motor and sensory in spinal reflex.
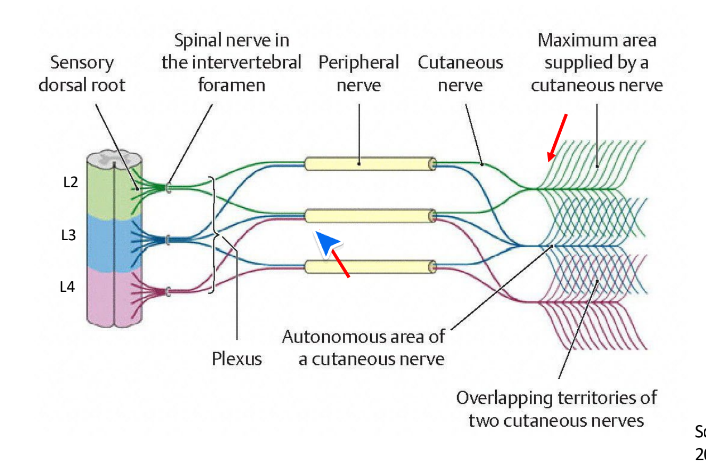
Neural plexus
an intertwining network of nerves derived from several spinal nerves that give rise to peripheral nerves that supply the structures of arm or leg
Plexus
formed by ventral rami. Cervical, brachial, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
Thoracic region supplied
not by plexus, supplied segmentally
Advantage of plexus
if one nerve is damaged (if theres compression), it can receive info from other nerves. Backup system.
Hypoaesthesia
numb
Paraesthesia
abnormal sensation, Pins and needles, tingling
Lumbosacral plexus
six main nerves. Femoral nerve, lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, obturator nerve
Lumbar plexus
superior nerves, lateral femoral cutaneous from L2 and L3, femoral nerve from L2, L3, L4, obturator nerve from L2, L3, L4, accessory obturator from L3 and L4
Femoral nerve innervates
hip flexors (iliacus, pectineus, sartorius) quadriceps/knee extensors (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, articularis genu)
What femoral nerve targets general
anterior hip and thigh
Obturator nerve innervates
hip adductors- adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus gracilis, obturator externus
Obturator nerve targets general
medial thigh
Femoral nerve branches into
saphenous nerve (medial leg)
Saphenous nerve
terminal cutaneous branch of femoral nerve
Obturator cutaneous supply
Obturator neuropathy
pregnancy- pressure within pelvis. Stretched during surgery- within pelvis. Entrapment due to adductor muscles. AFL and rugby- running with turning and twisting
Sacral plexus
sciatic nerve from L1, L5, S1, S2, S3, S4. superior gluteal L4 L5 S1 (dorsal). inferior gluteal L5, S1, S2 (dorsal). Posterior femoral cutaneous S1 S2 S3. pudendal nerve from S2, S3, S4
Sacral plexus
lies in pelvis. Formed from lumbosacral trunk (L4 and L5) and ventral rami of S1-S4
Sciatic nerve
innervates hamstrings (semitendinosis, semimembranosus, biceps femoris (long and short head), adductor magnus
Sciatic nerve targets generally
posterior thigh
Dermatomal map
gives singular levels of spinal cord. Pattern recognition. For one pinch. Stems from embryological development
Dermatome
a dermatome is a unilateral area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve