Intro to Brain and Behavior #4
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
paralytic dementia
sudden onset of delusions, grandiosity, poor judgment, impulsivity
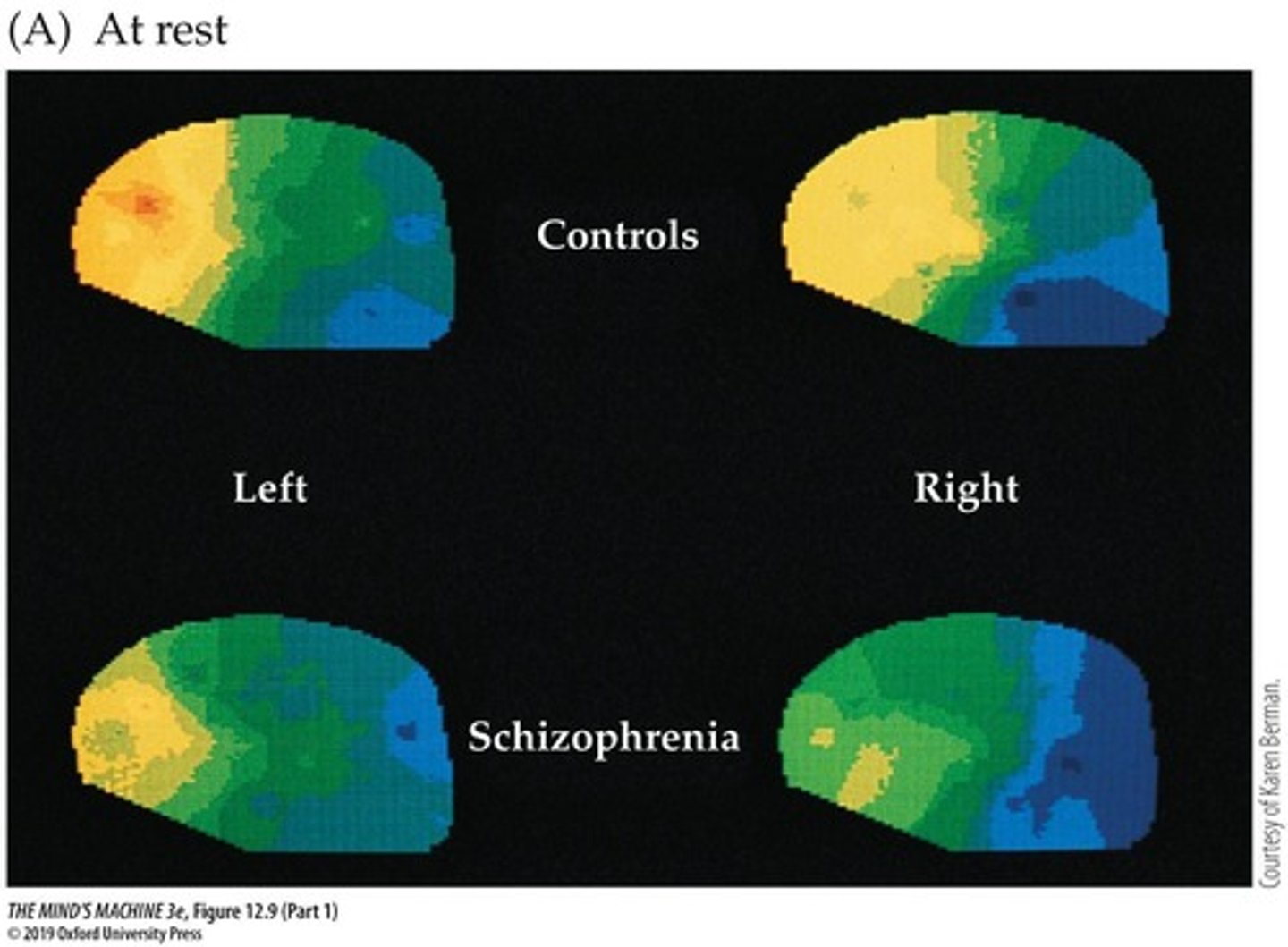
schizophrenia
a group of severe disorders characterized by disorganized and delusional thinking, disturbed perceptions, and inappropriate emotions and actions

hypofrontality hypothesis
the idea that schizophrenia may reflect underactivation of the frontal lobes
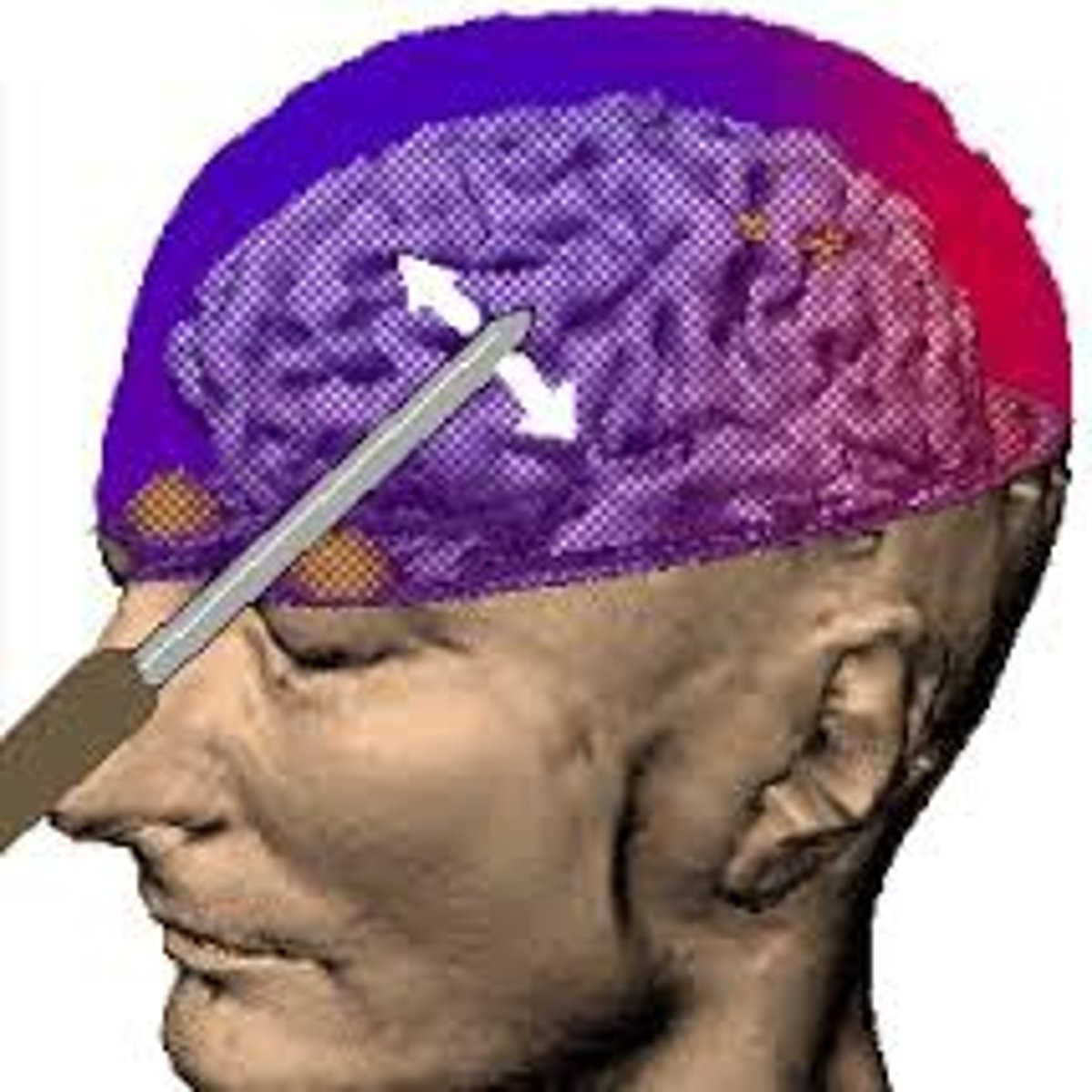
lobotomy
a psychosurgical procedure once used to calm uncontrollably emotional or violent patients. The procedure cut the nerves connecting the frontal lobes to the emotion-controlling centers of the inner brain
chloropromazine
low potency typical antipsychotic
antipsychotic
a drug that opposes psychoses
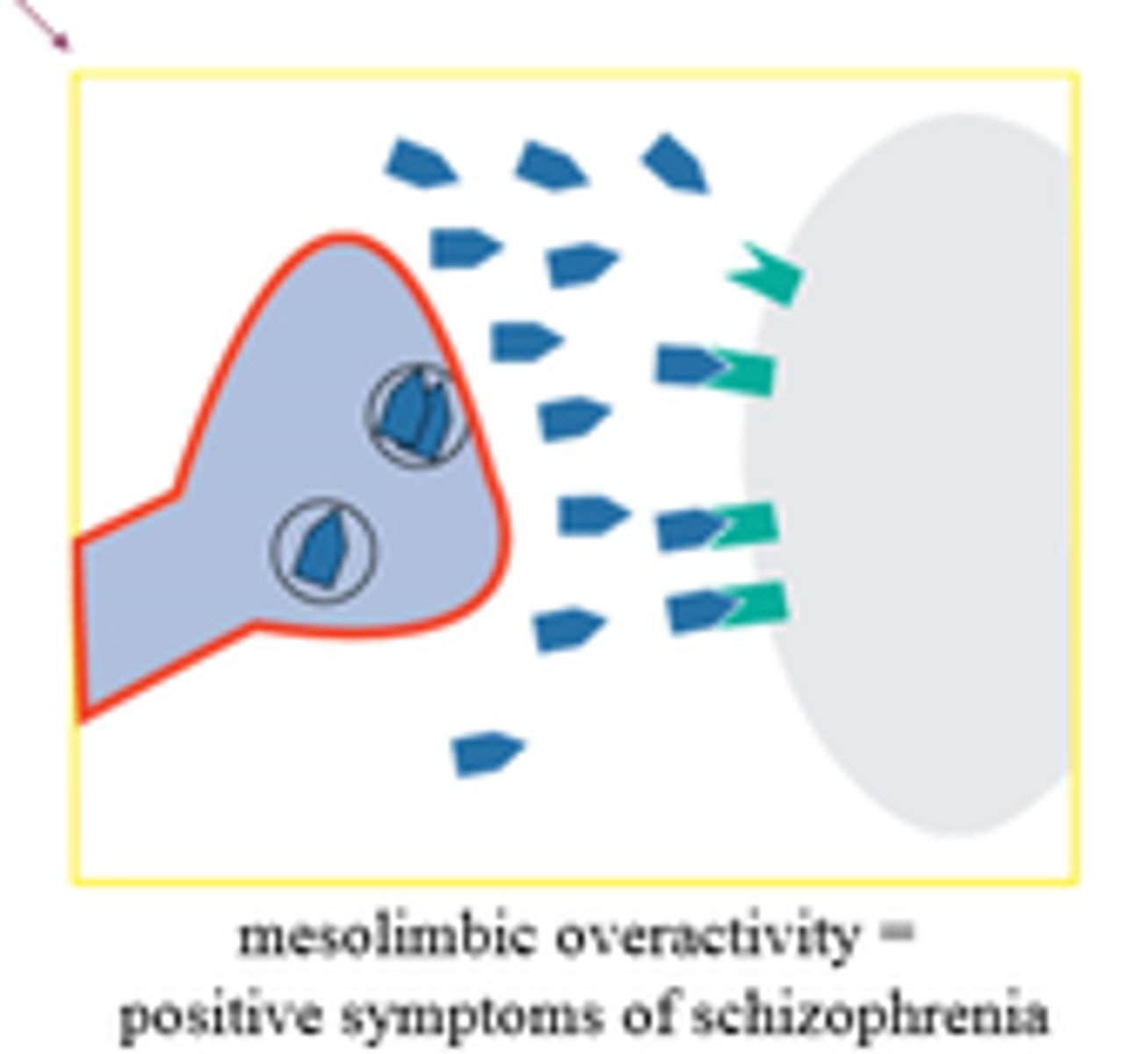
dopamine hypothesis
the idea that schizophrenia involves an excess of dopamine activity
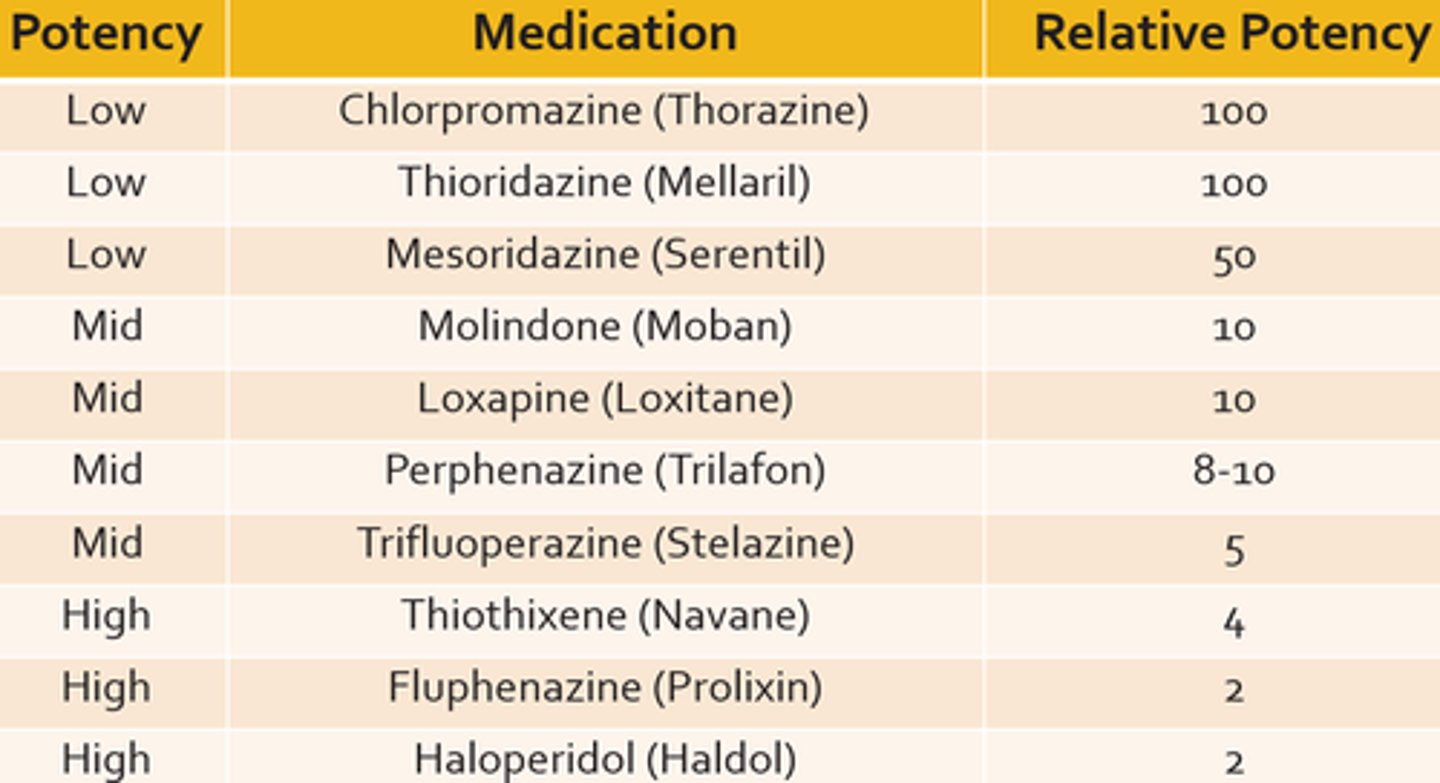
first-generation antipsychotics
a group of medications originally developed to combat psychotic symptoms by reducing dopamine levels in the brain; also called conventional or typical antipsychotics
second-generation antipsychotics
drugs that alleviate schizophrenia without producing movement problems
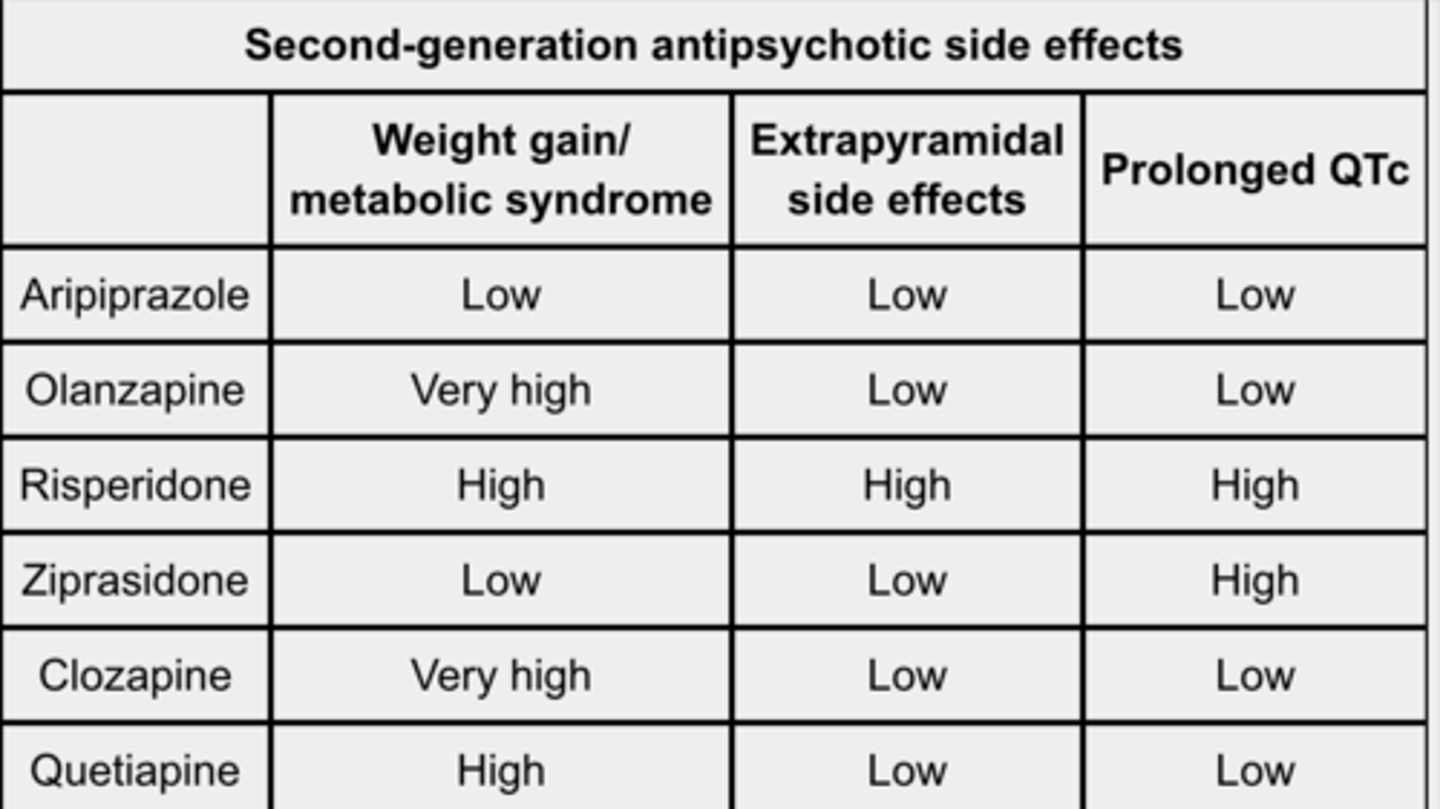
clozapine
atypical antipsychotic

mood disorder
an illness that involves mood extremes that interfere with everyday living

depression
a prolonged feeling of helplessness, hopelessness, and sadness

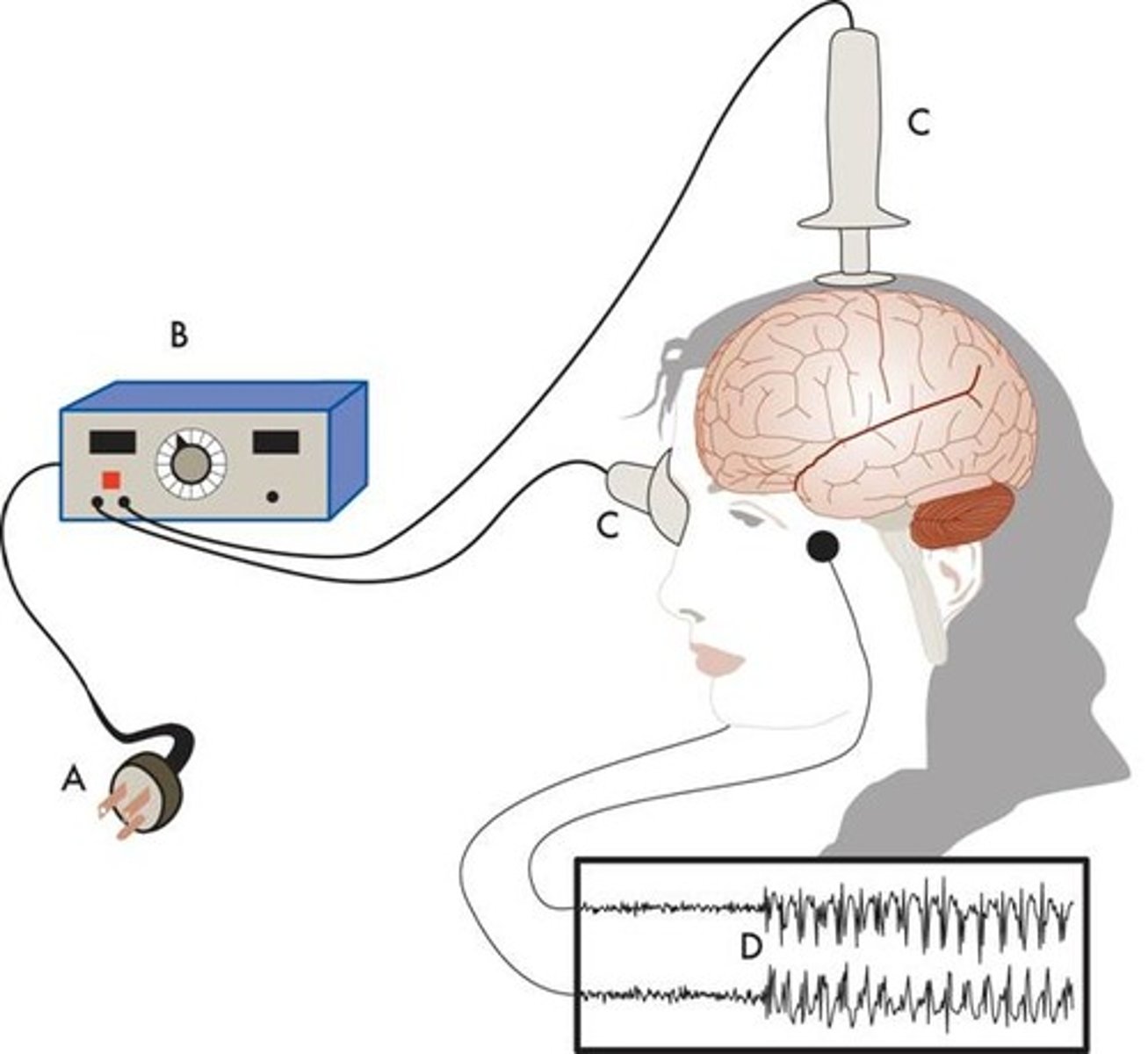
electroconvulsive shock therapy
electric shock therapy used to treat severe cases of depression
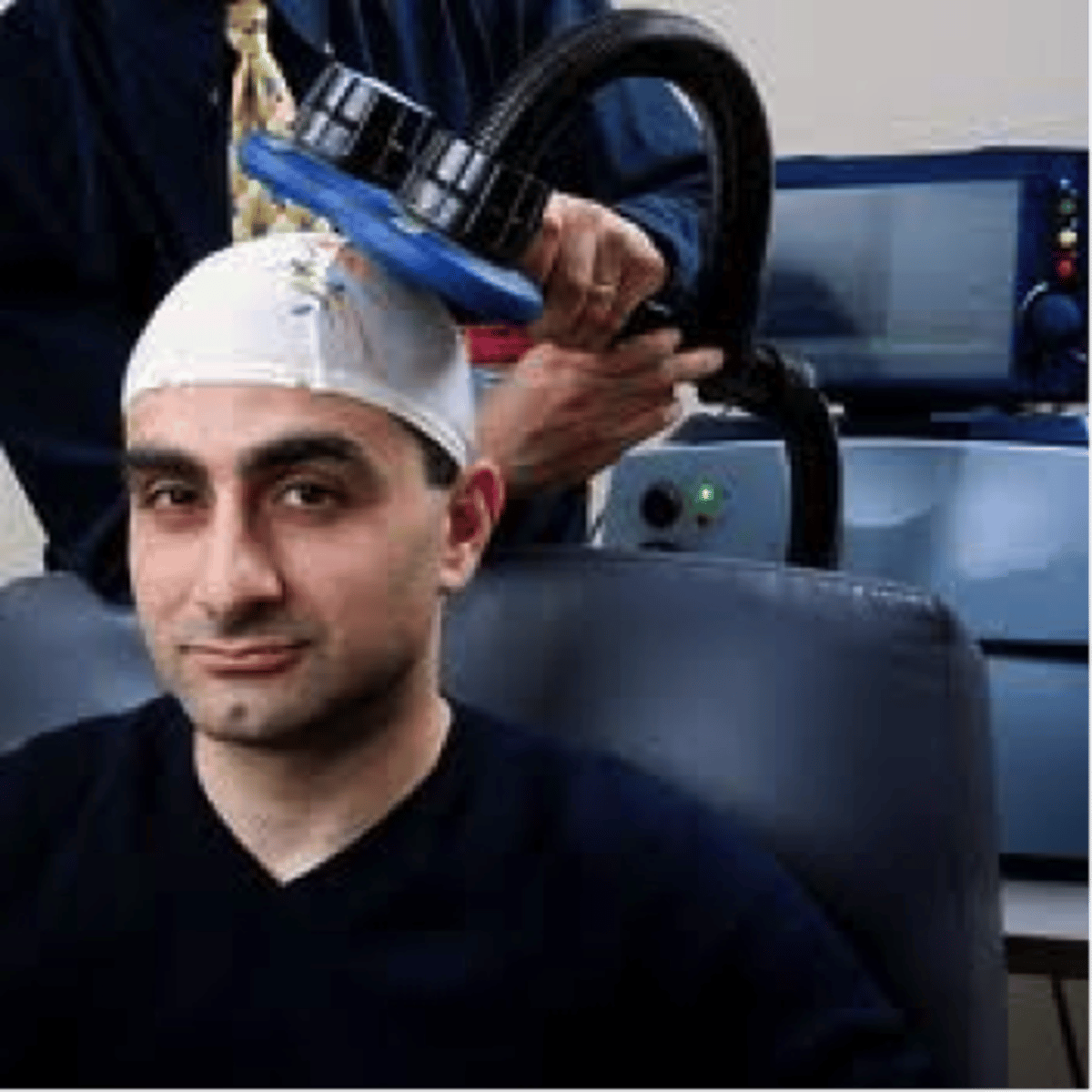
repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
the application of repeated pulses of magnetic energy to the brain; used to stimulate or suppress brain activity
antidepressants
a class of psychotropic medications used for the treatment of depression
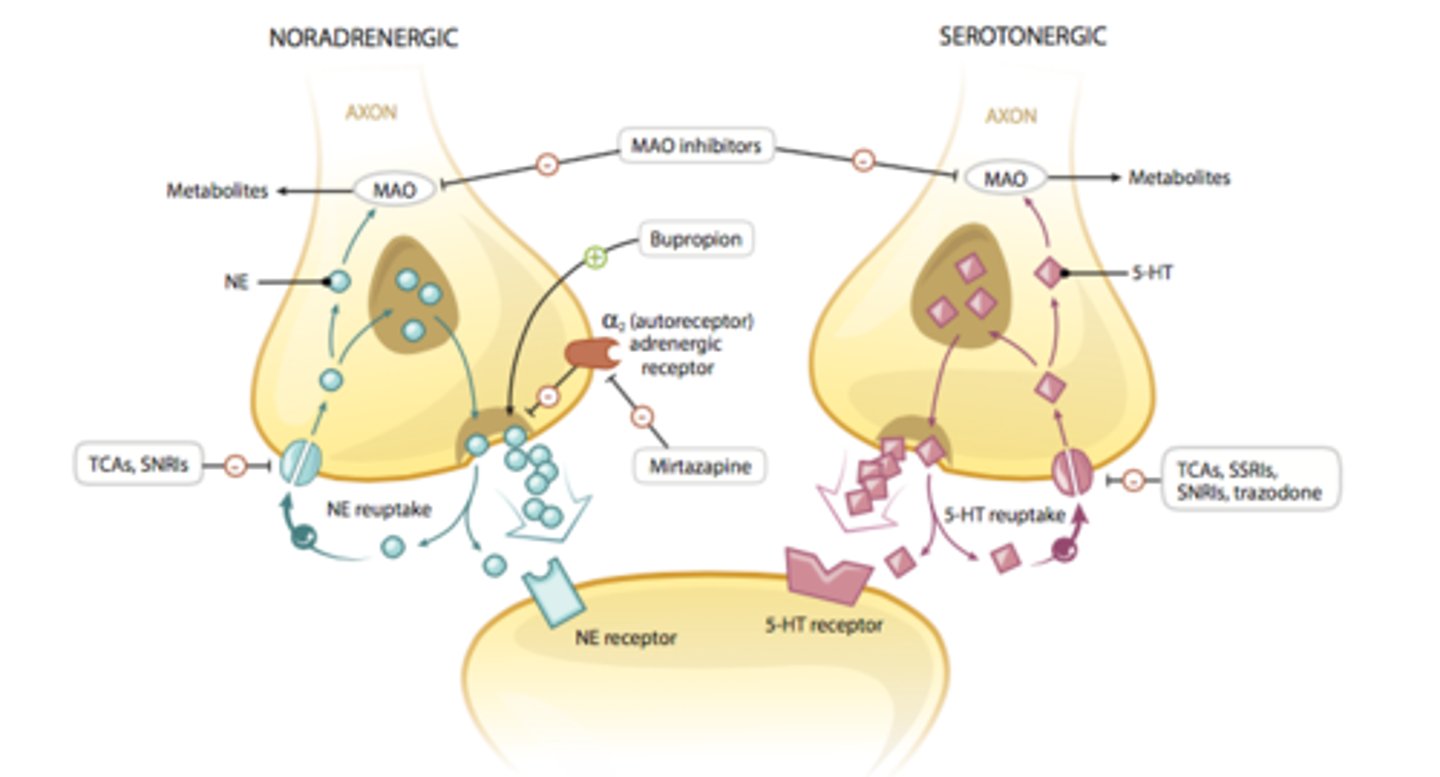
monoamine oxidase
a class of enzymes that destroy the monoamines: dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin
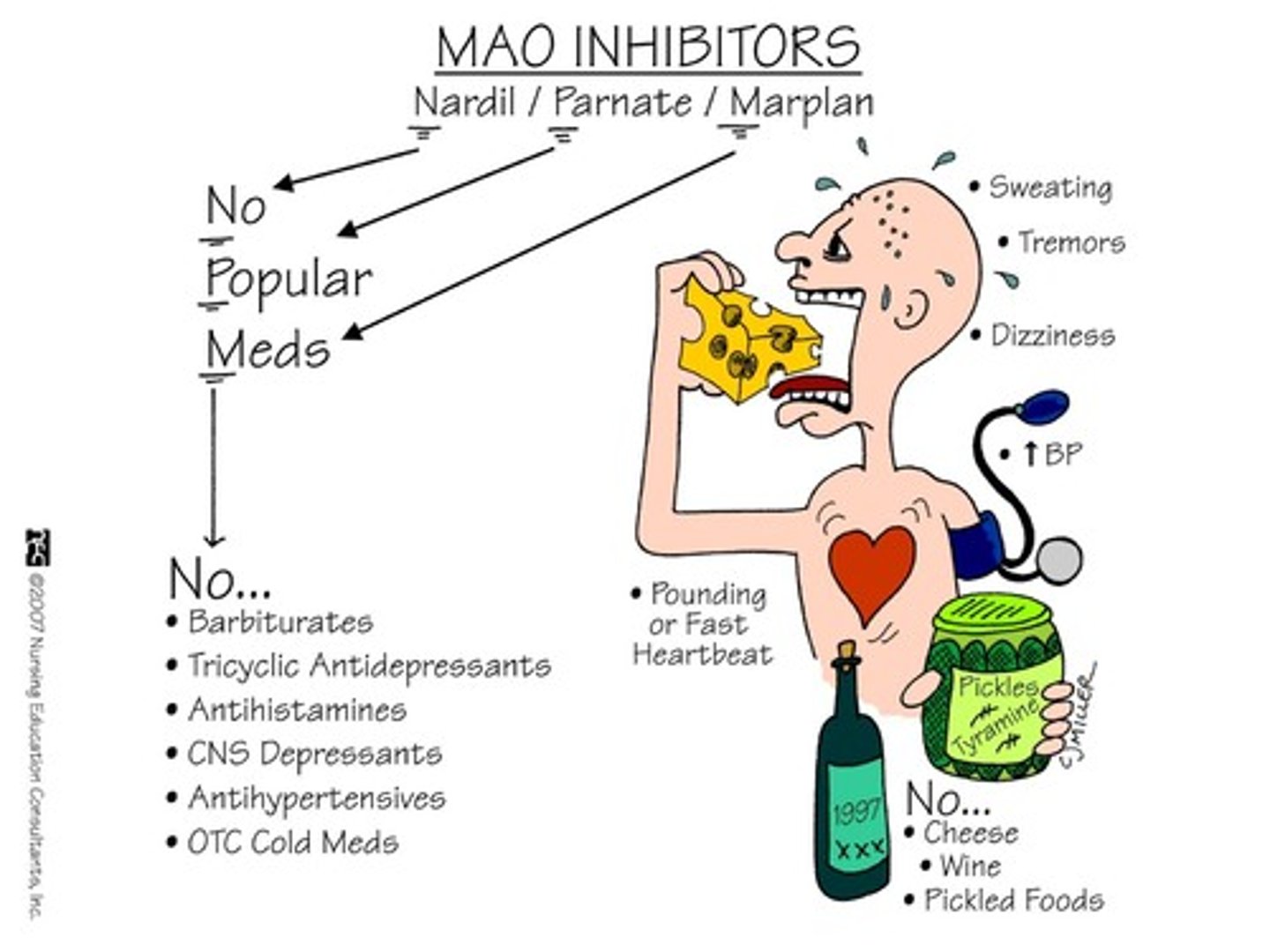
selective serotonin uptake inhibitors
a type of antidepressant which prevents the uptake of serotonin by pre-synaptic neurons so it leads to a relief of symptoms
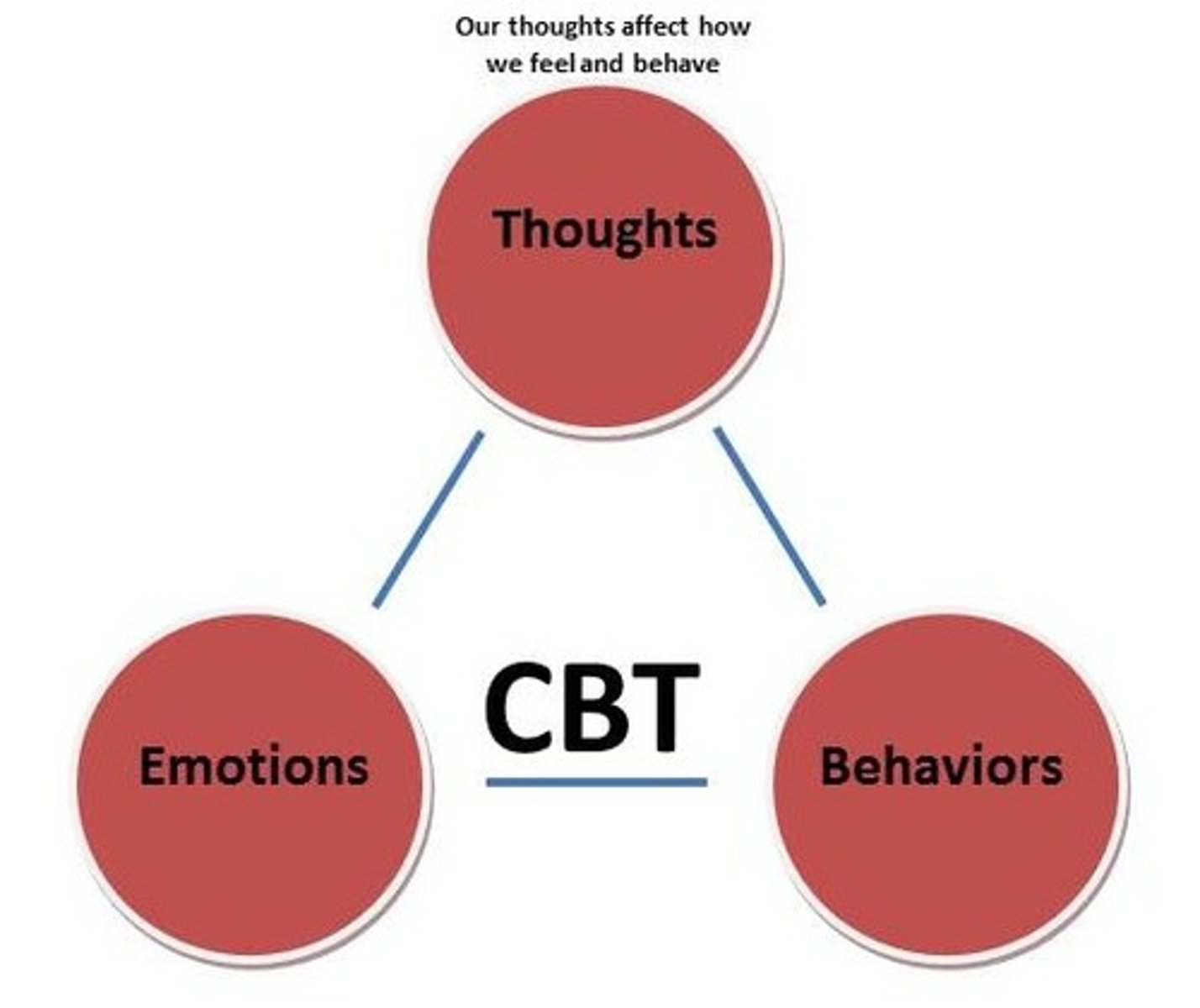
cognitive behavioral therapy
a popular integrative therapy that combines cognitive therapy (changing self-defeating thinking) with behavior therapy (changing behavior)
bipolar disorder
mood disorder in one experiences both manic and depressed episodes

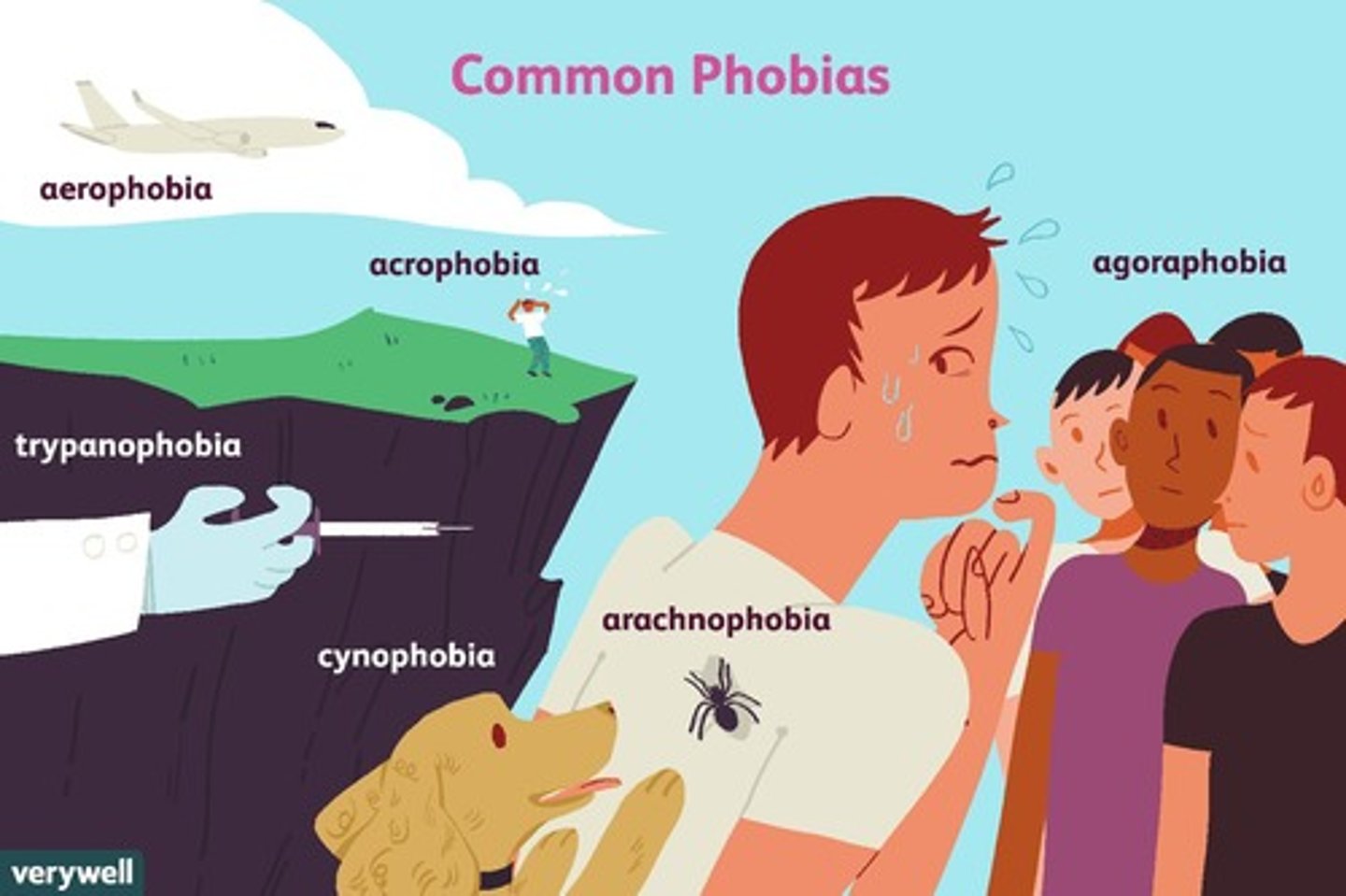
anxiety disorder
a condition in which real or imagined fears are difficult to control

phobic disorders
disorders characterized by marked, persistent, and excessive fear and avoidance of specific objects, activities, or situations
panic disorders
recurrent attacks of overwhelming anxiety that usually occur suddenly or unexpectedly
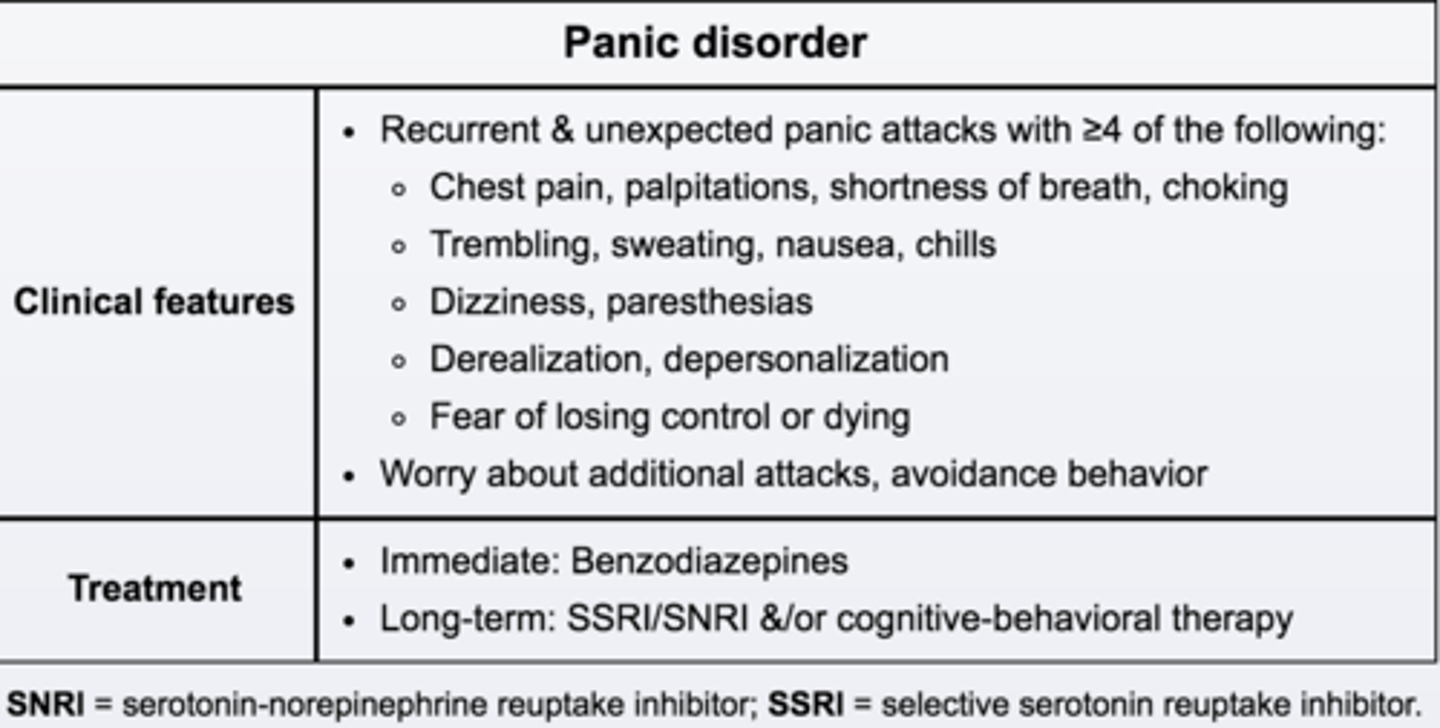
anxiolytic drugs
medication administered to temporarily relieve anxiety and reduce tension
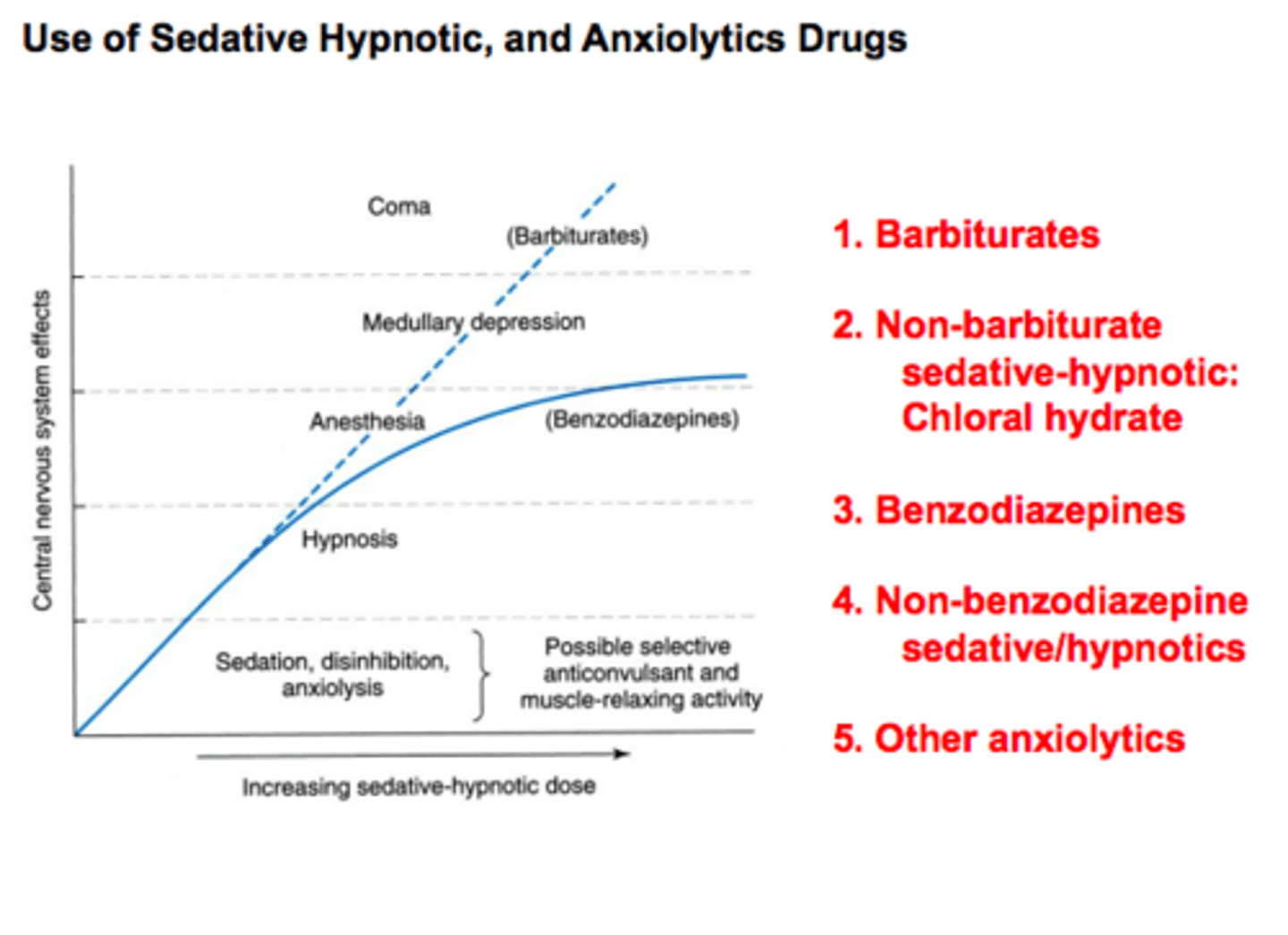
generalized anxiety disorder
an anxiety disorder in which a person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic nervous system arousal
benzodiazepines
drugs that lower anxiety and reduce stress
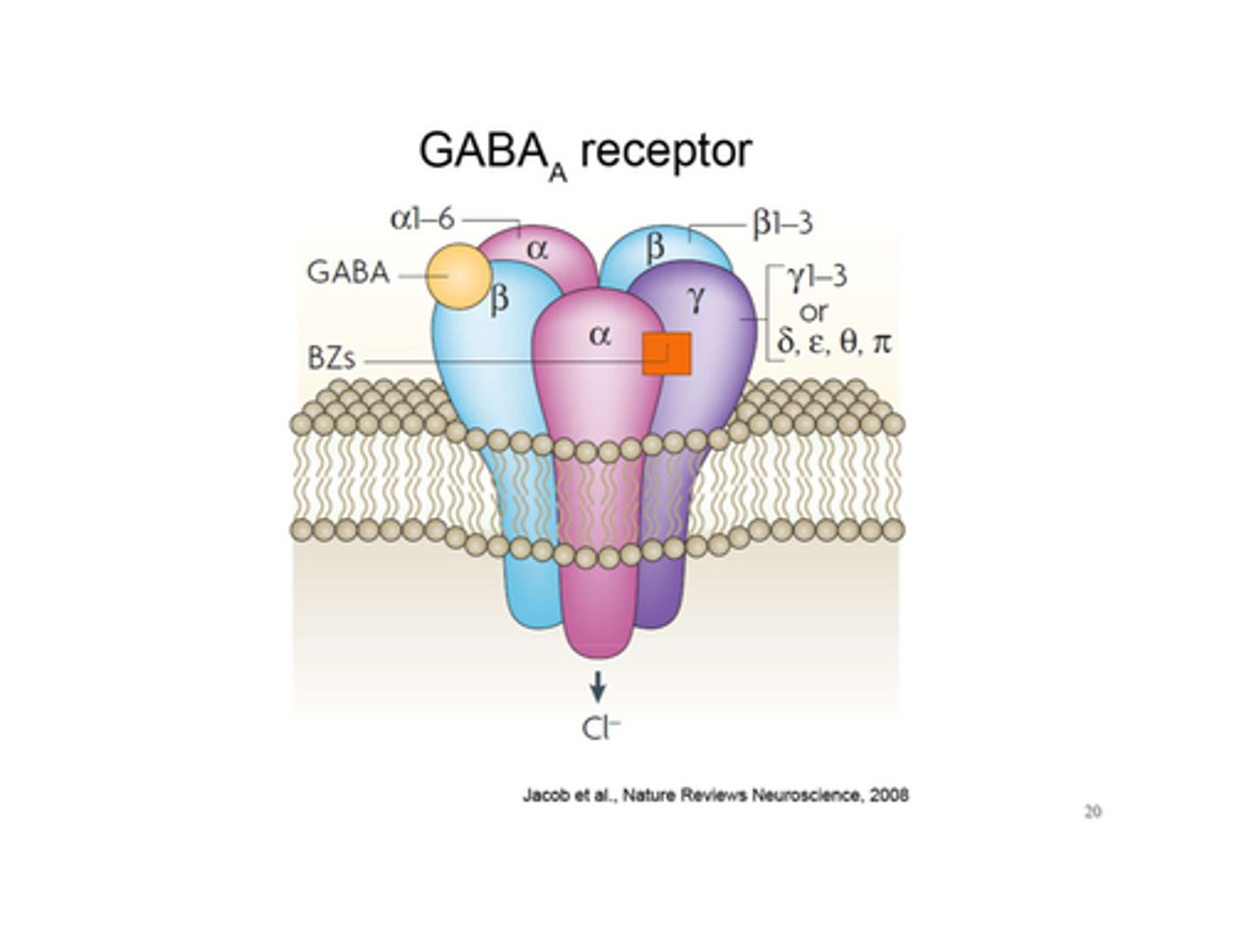
post-traumatic stress disorder
an anxiety disorder characterized by haunting memories, nightmares, social withdrawal, jumpy anxiety, and/or insomnia that lingers for four weeks or more after a traumatic experience

obsessive-compulsive disorder
an anxiety disorder characterized by repetitive obsessions and compulsions

Tourette's syndrome
A neurological disorder beginning in childhood that involves stereotypical, repetitive motor movements (tics). These are often accompanied by multiple vocal outbursts such grunting or inappropriate words such as swearing. It is about three times more prevalent in boys than in girls.

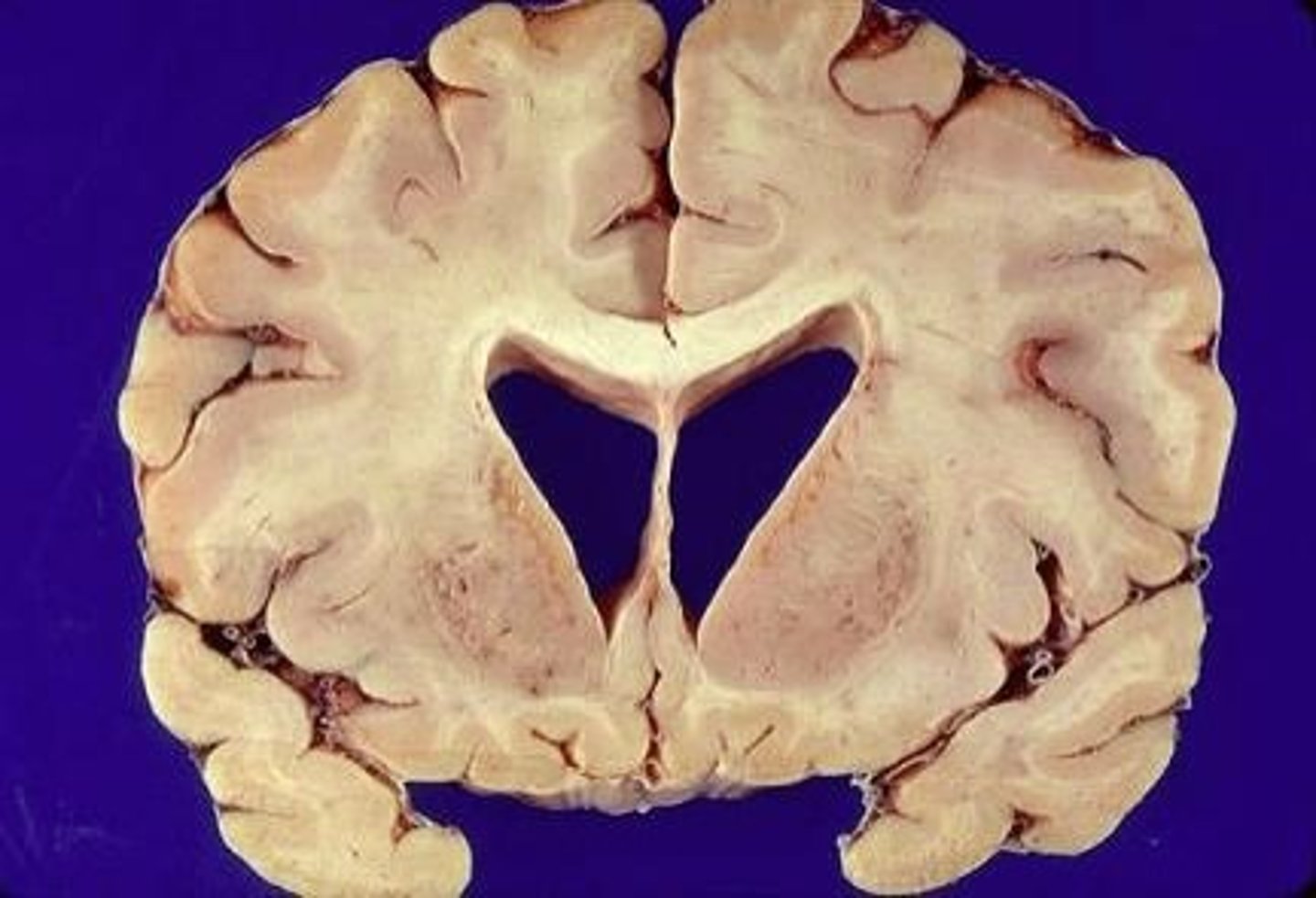
dementia
a slowly progressive decline in mental abilities, including memory, thinking, and judgment, that is often accompanied by personality changes
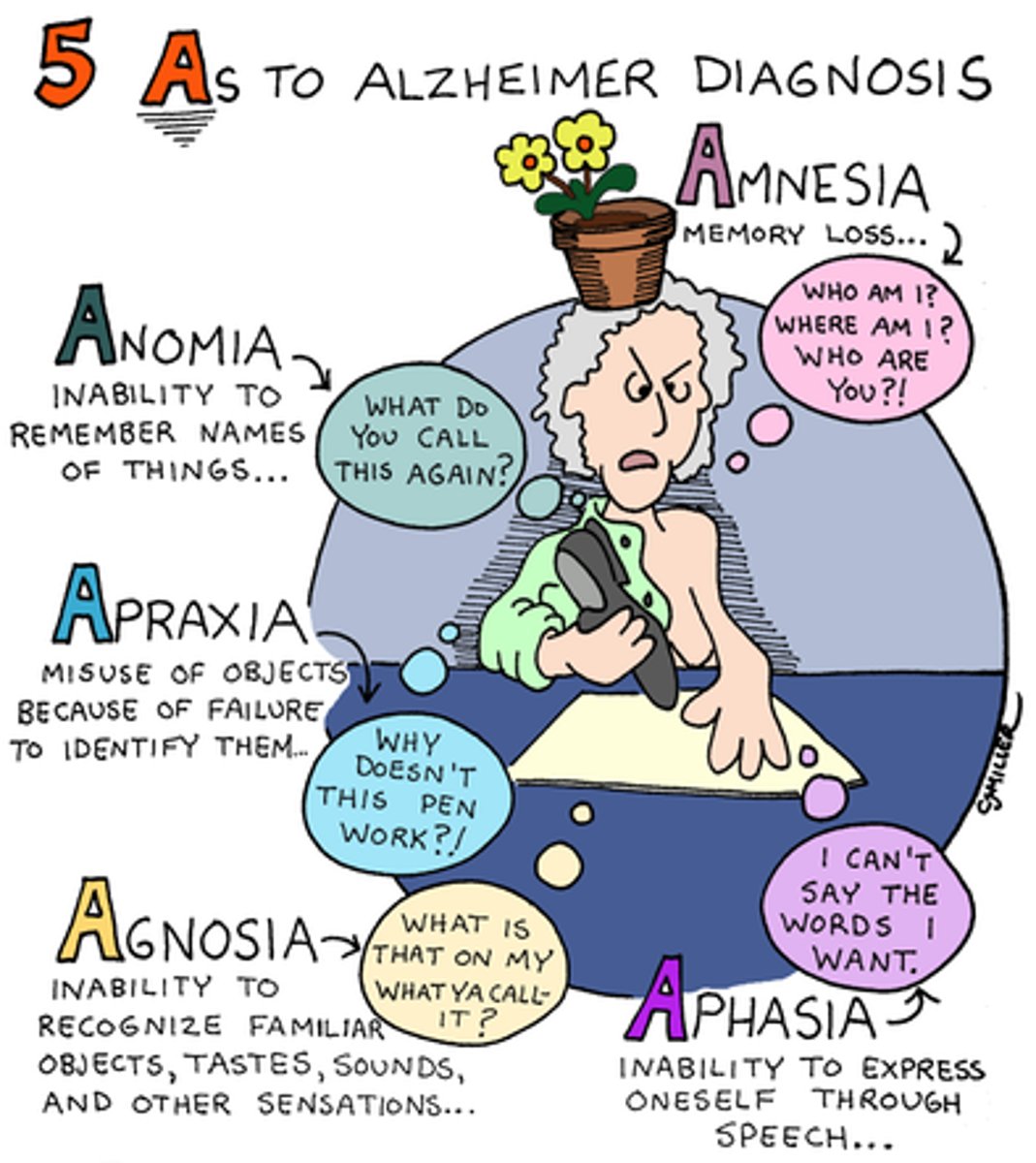
Alzheimer's disease
a progressive and irreversible brain disorder characterized by gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and, finally, physical functioning
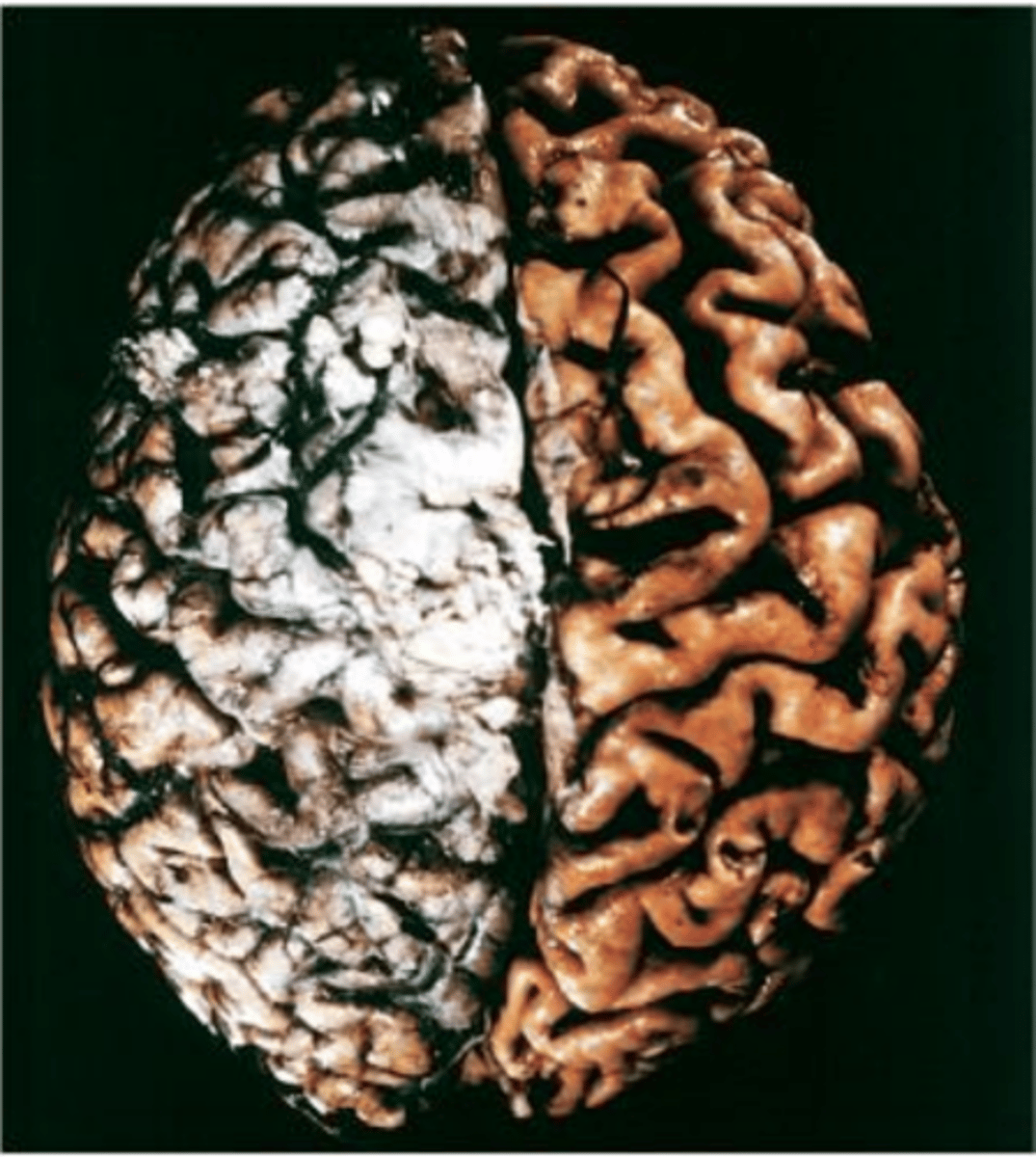
cortical atrophy
death of cells in the cerebral cortex
amyloid plaques
fragments of the protein beta-amyloid that accumulate into insoluble plaques that inhibit communication between neurons
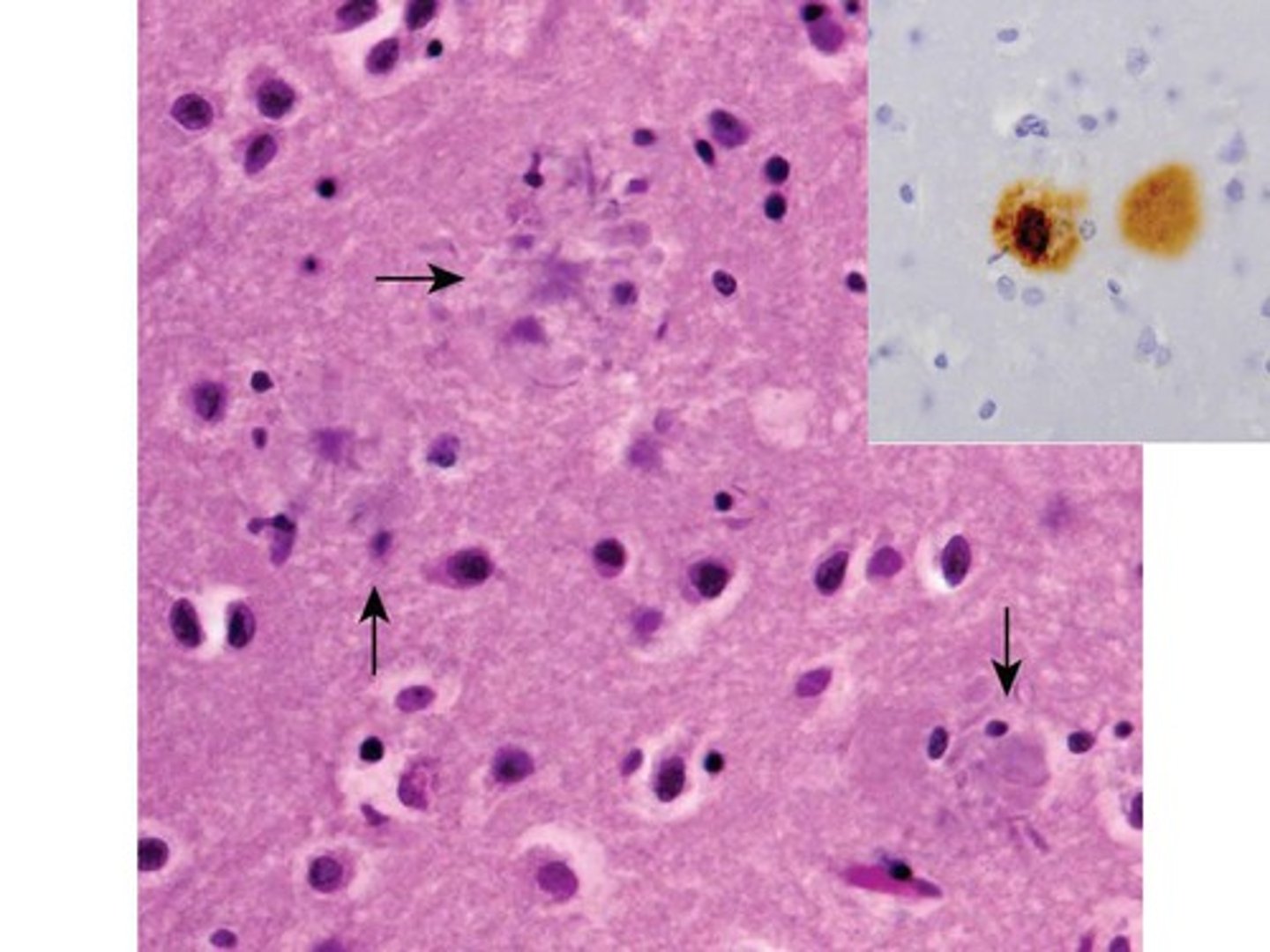
beta-amyloid
a protein that accumulates in amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease
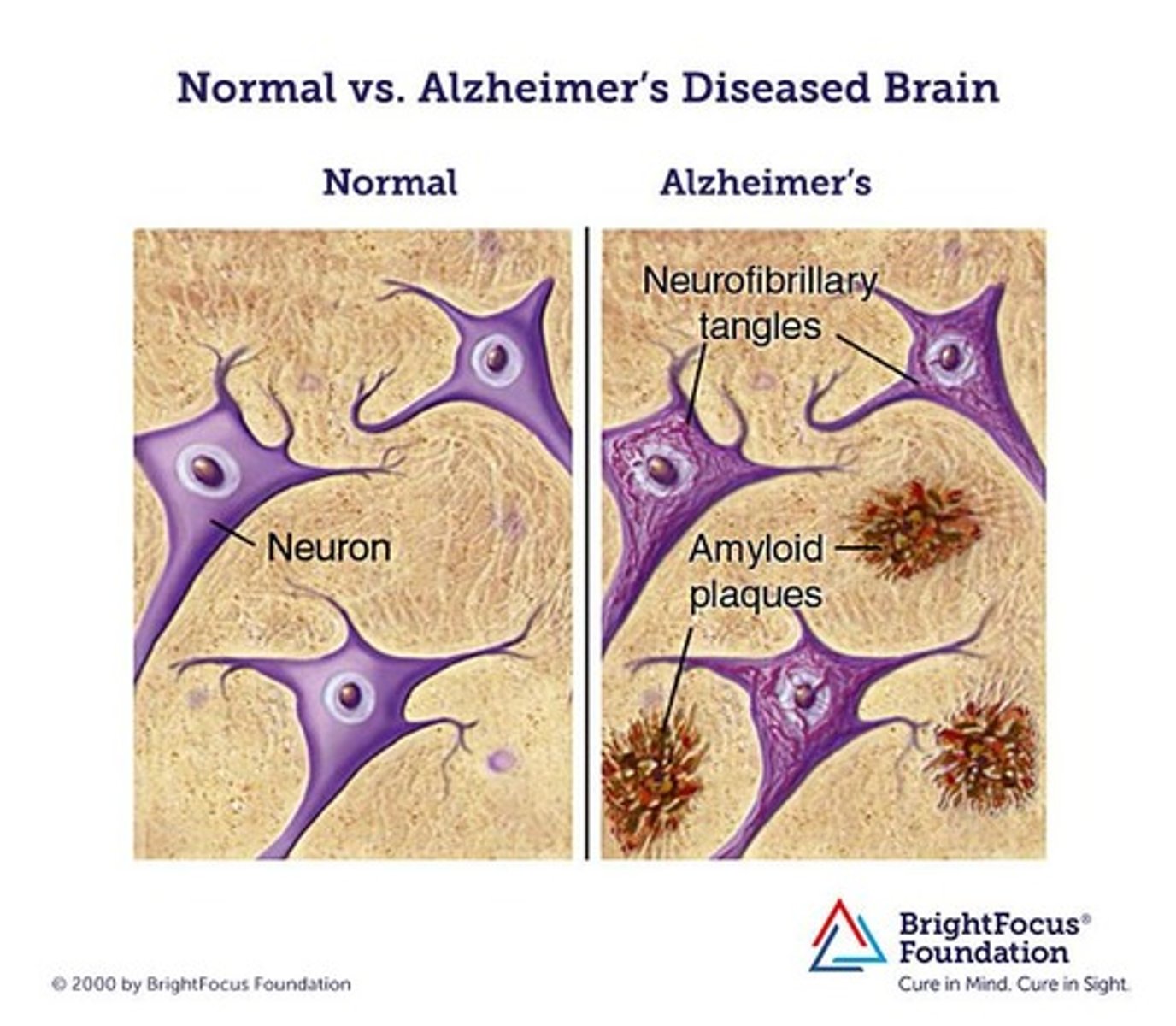
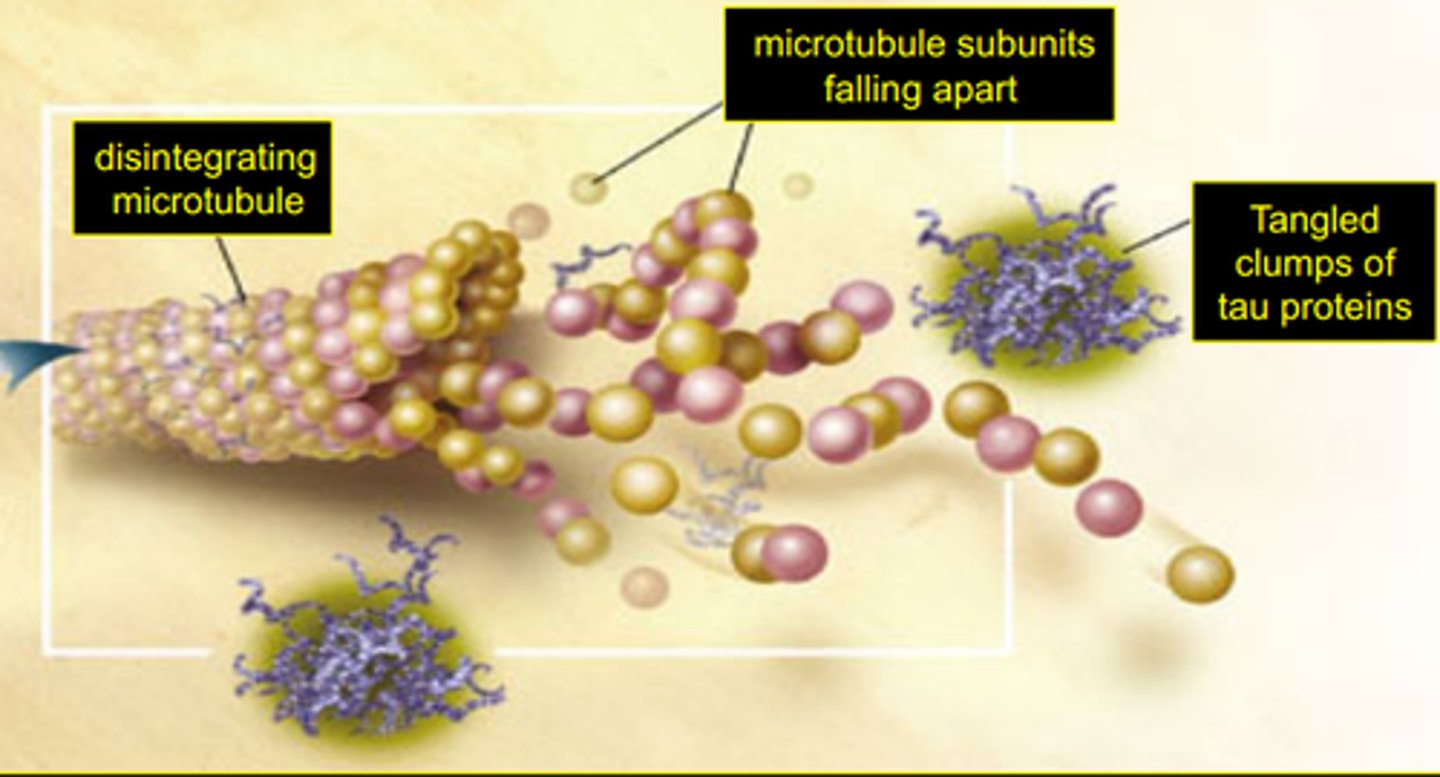
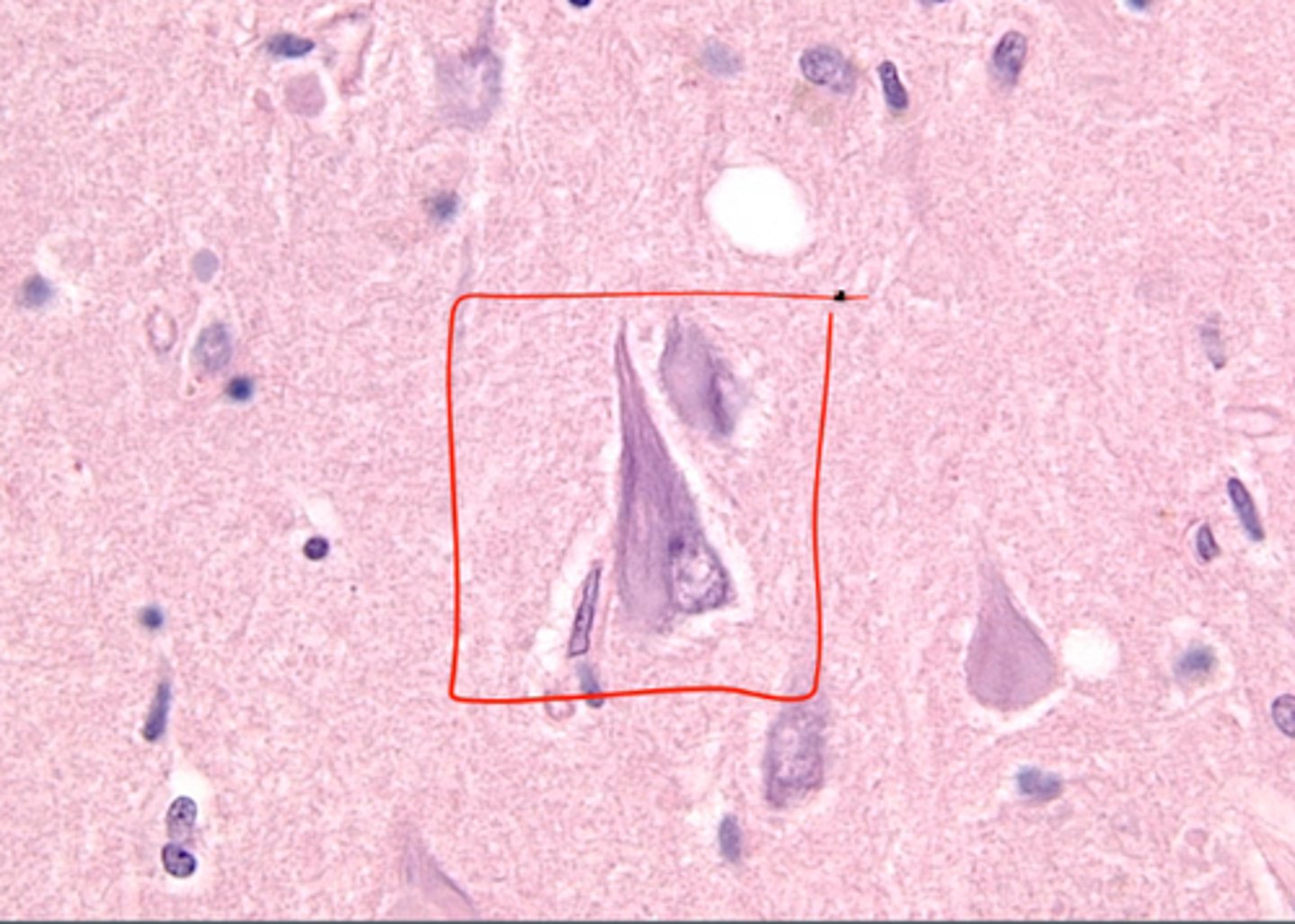
neurofibrillary tangles
spiral-shaped masses formed when fibers that compose the axon become twisted together
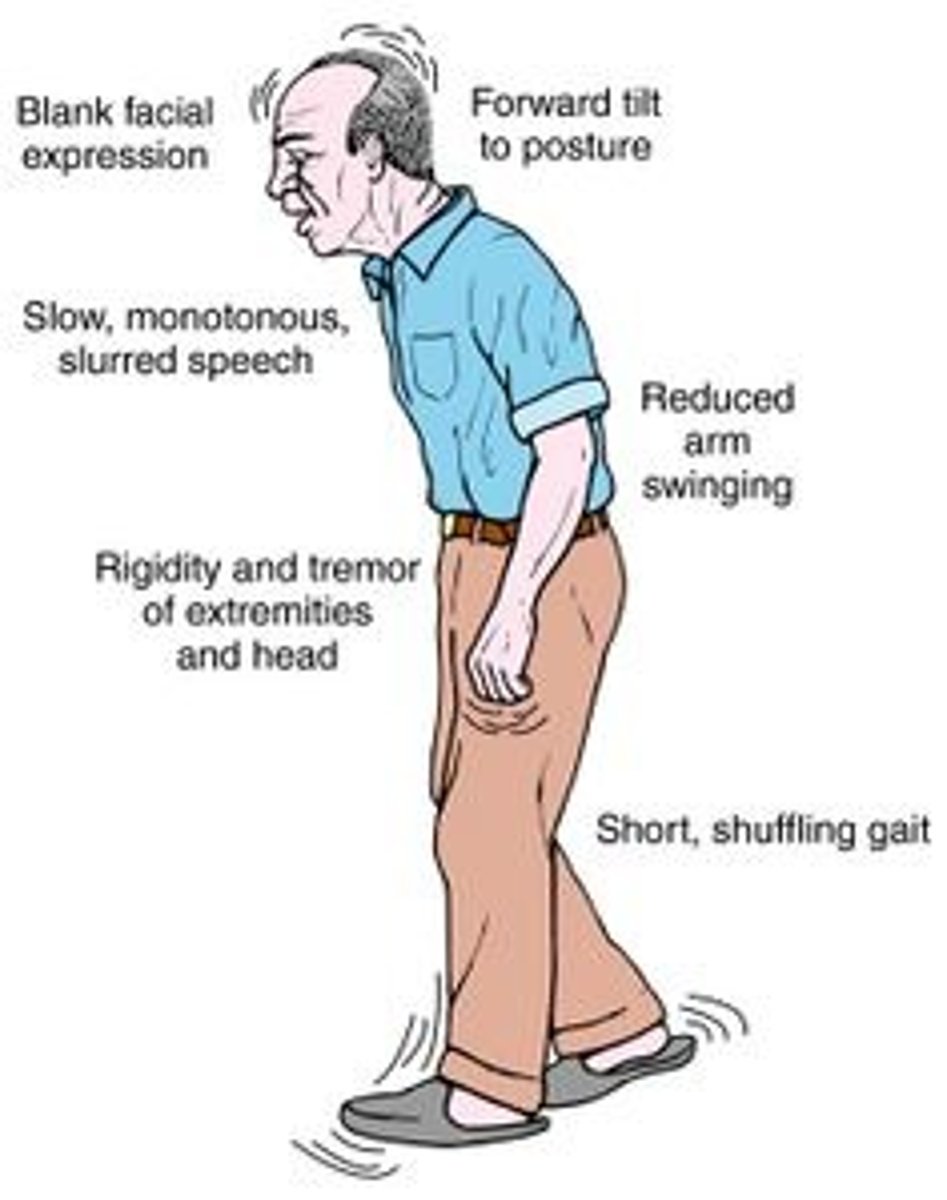
Parkinson's disease
a progressive disease that destroys brain cells and is identified by muscular tremors, slowing of movement, and partial facial paralysis
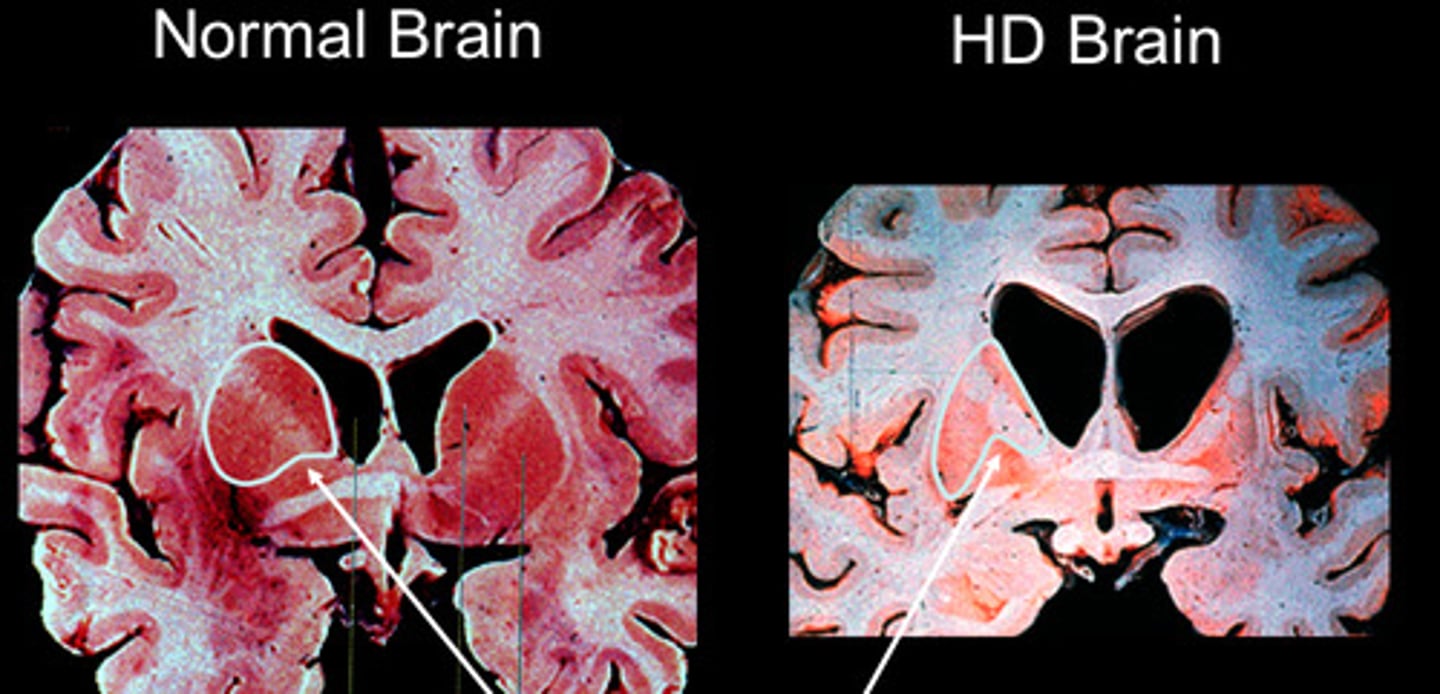
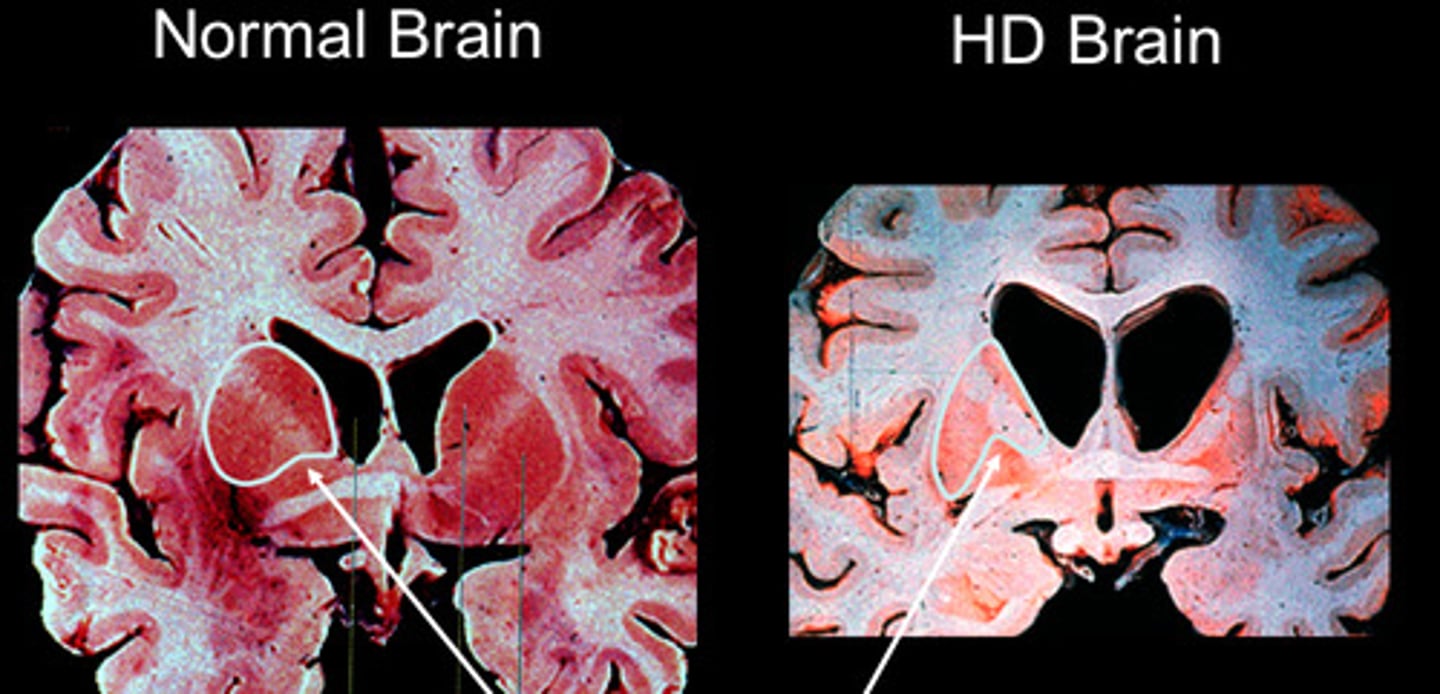
Huntington's disease
a hereditary disease marked by degeneration of the brain cells and causing chorea and progressive dementia
chronic traumatic encephalopathy
form of dementia caused by repeated head trauma such as concussions

concussion
violent shaking up or jarring of the brain
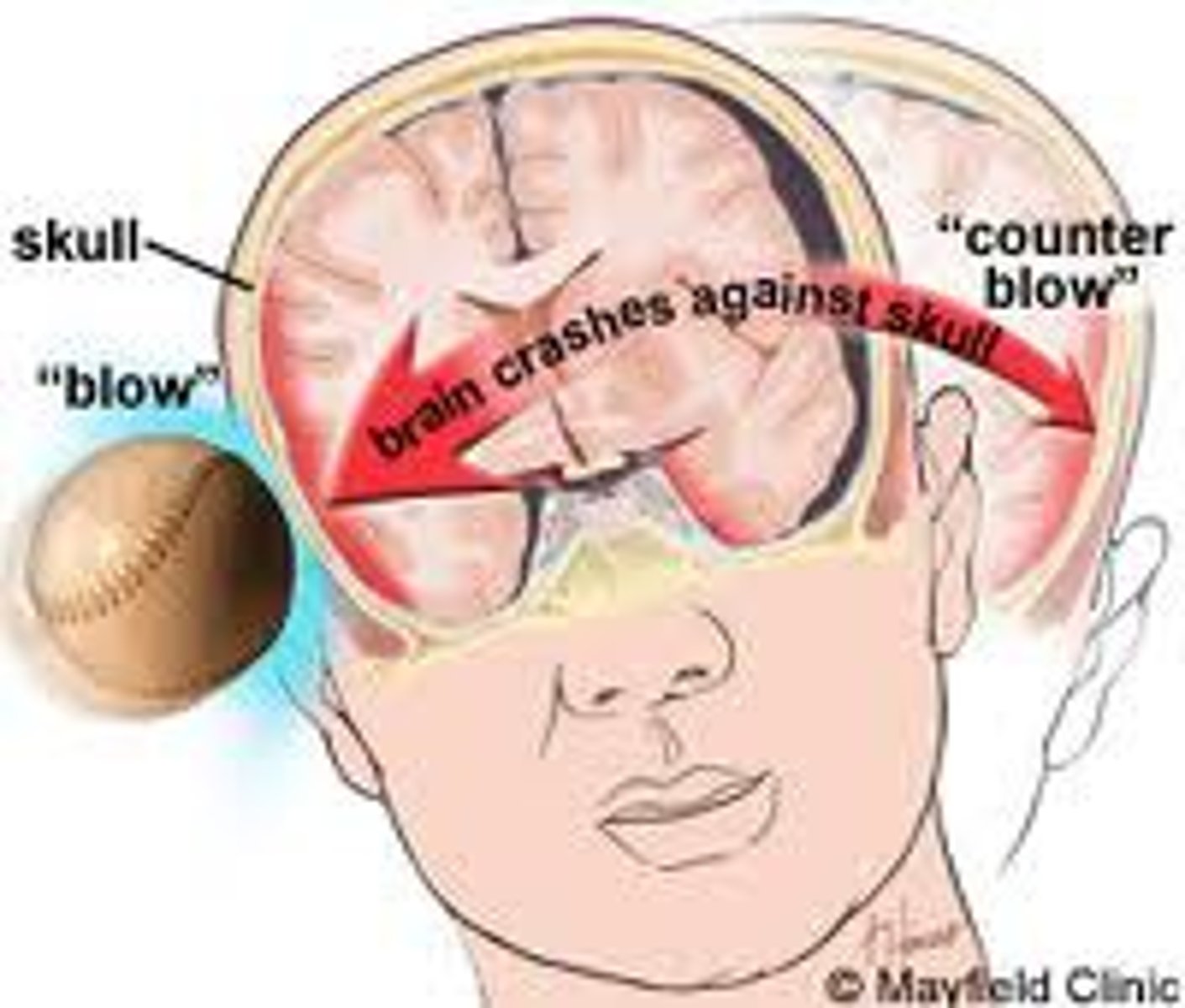
tauopathy
any disease that is associated with abnormal accumulations of the protein Tau, forming neurofibrillary tangles that impair the normal function of neurons
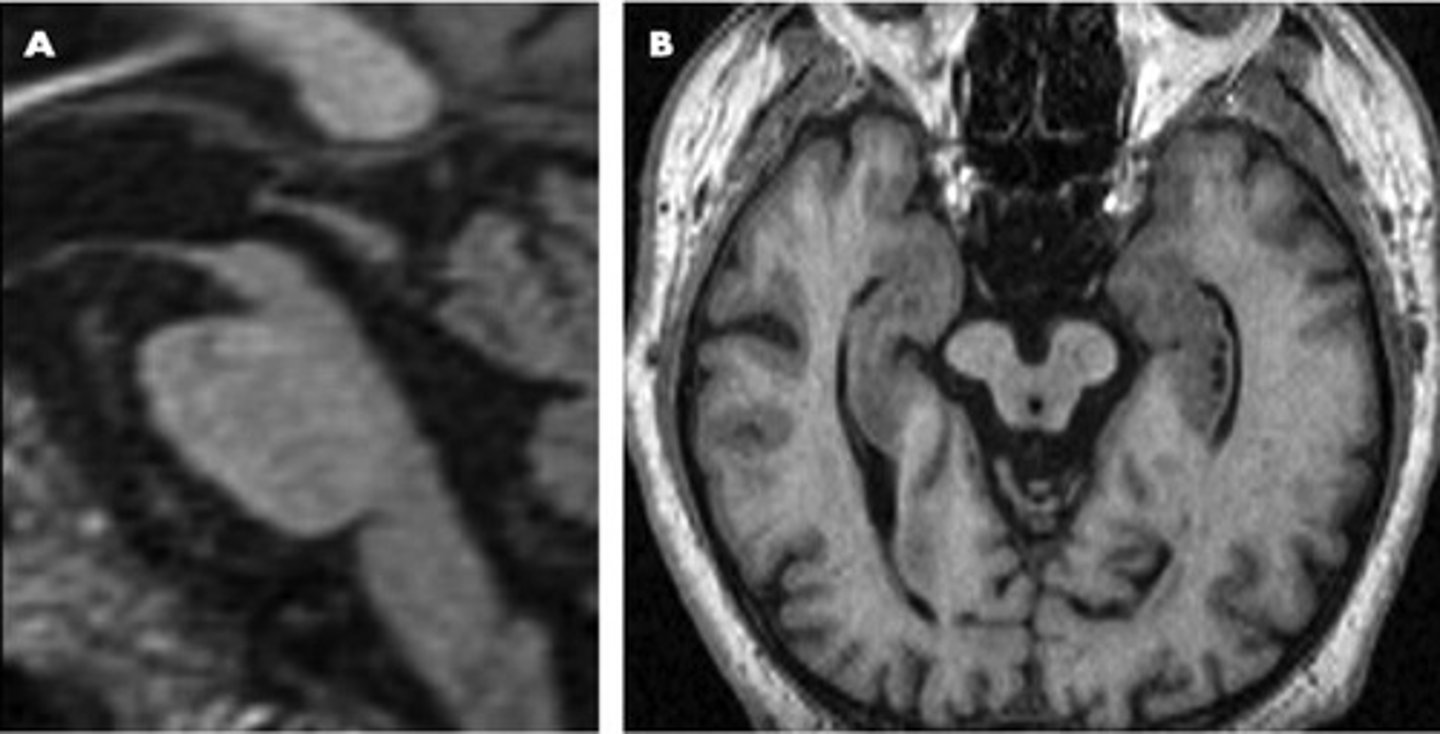
tau protein
part of the intracellular support structure of axons