L10 - Lymphatic System
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Lymphatic System
Network returning tissue fluid to circulation.
Lymph
Fluid similar to plasma, contains lymphocytes.
Chyle
Lymph from the gastrointestinal tract.
Functions of Lymphatic System
Returns tissue fluid, filters material, produces antibodies.
Lymph Capillaries
Small vessels collecting interstitial fluid.
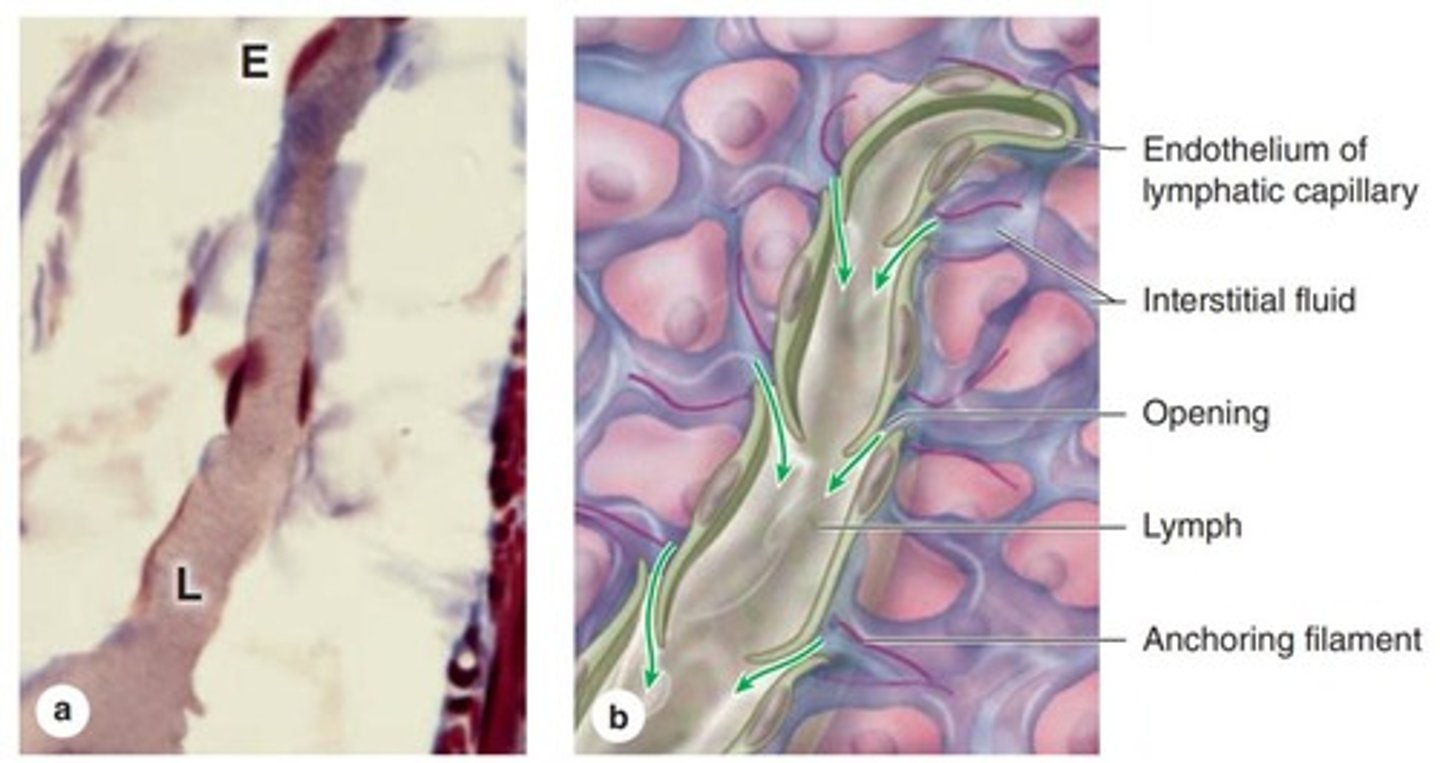
Lymph Vessels
Transport lymph towards larger ducts.
Right Lymphatic Duct
Drains lymph from right thoracic limb and head.
Thoracic Duct
Main duct returning lymph to venous system.
Cisterna Chyli
Lymph channel associated with abdominal aorta.
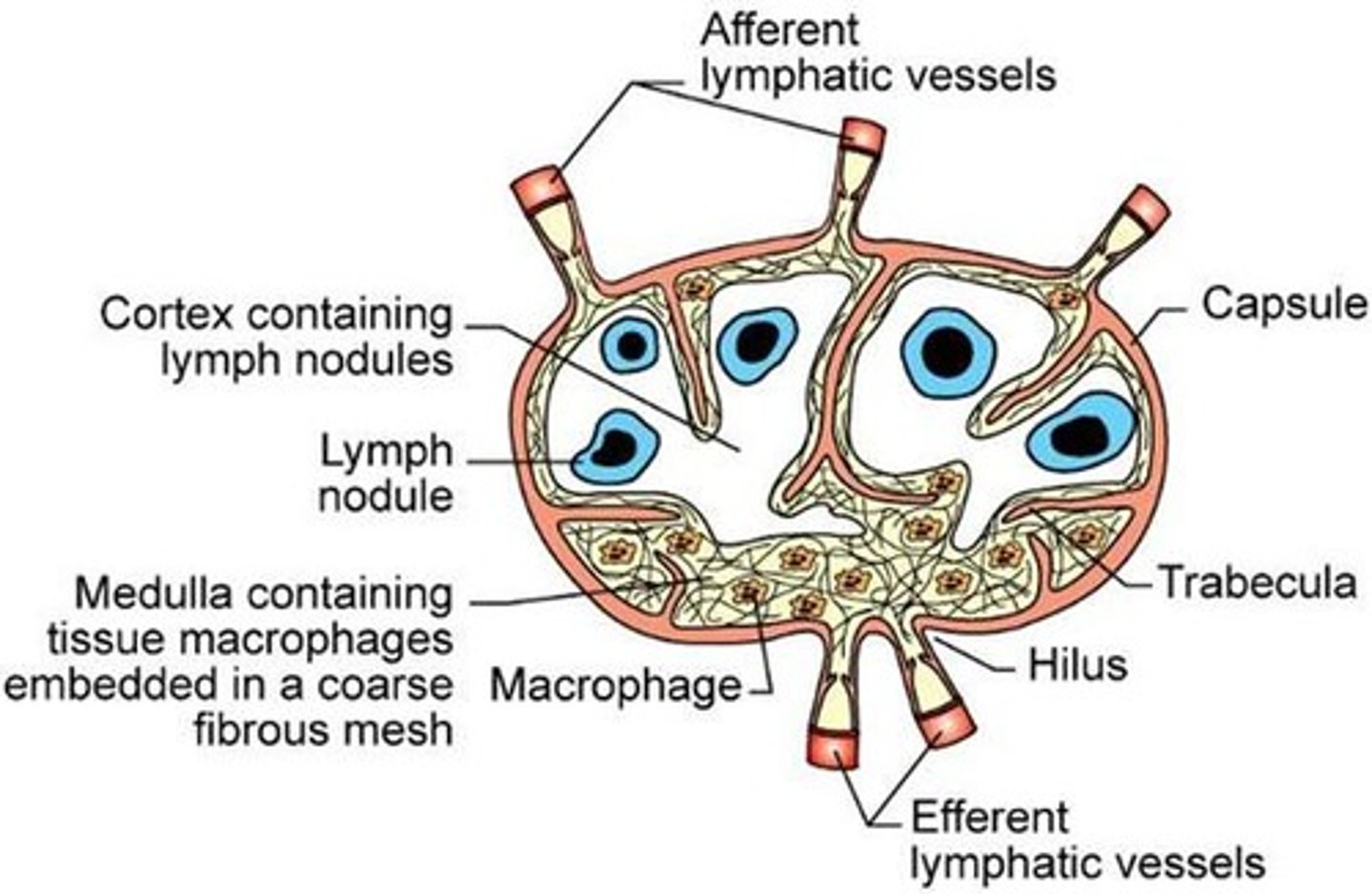
Lymph Nodes
Filter lymph and produce immune responses.
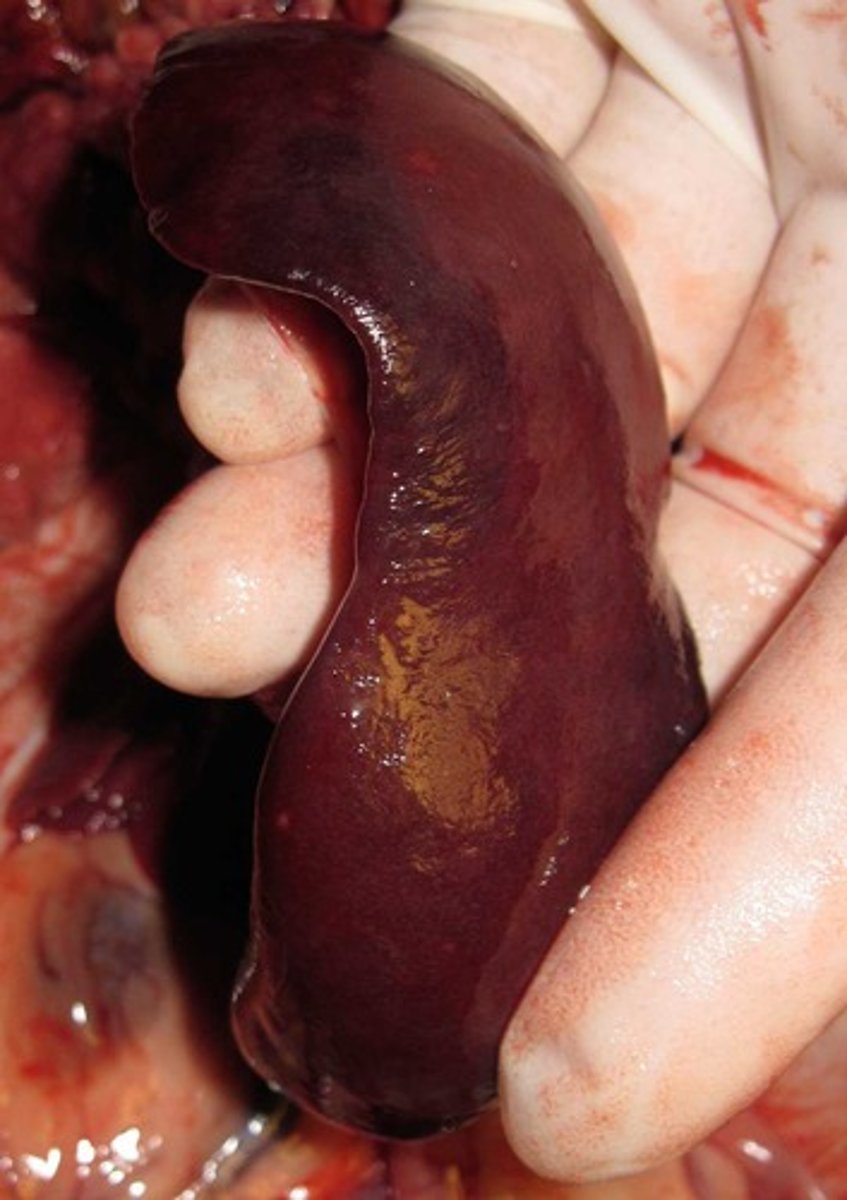
Spleen
Largest lymphoid organ, stores blood, removes old RBCs.
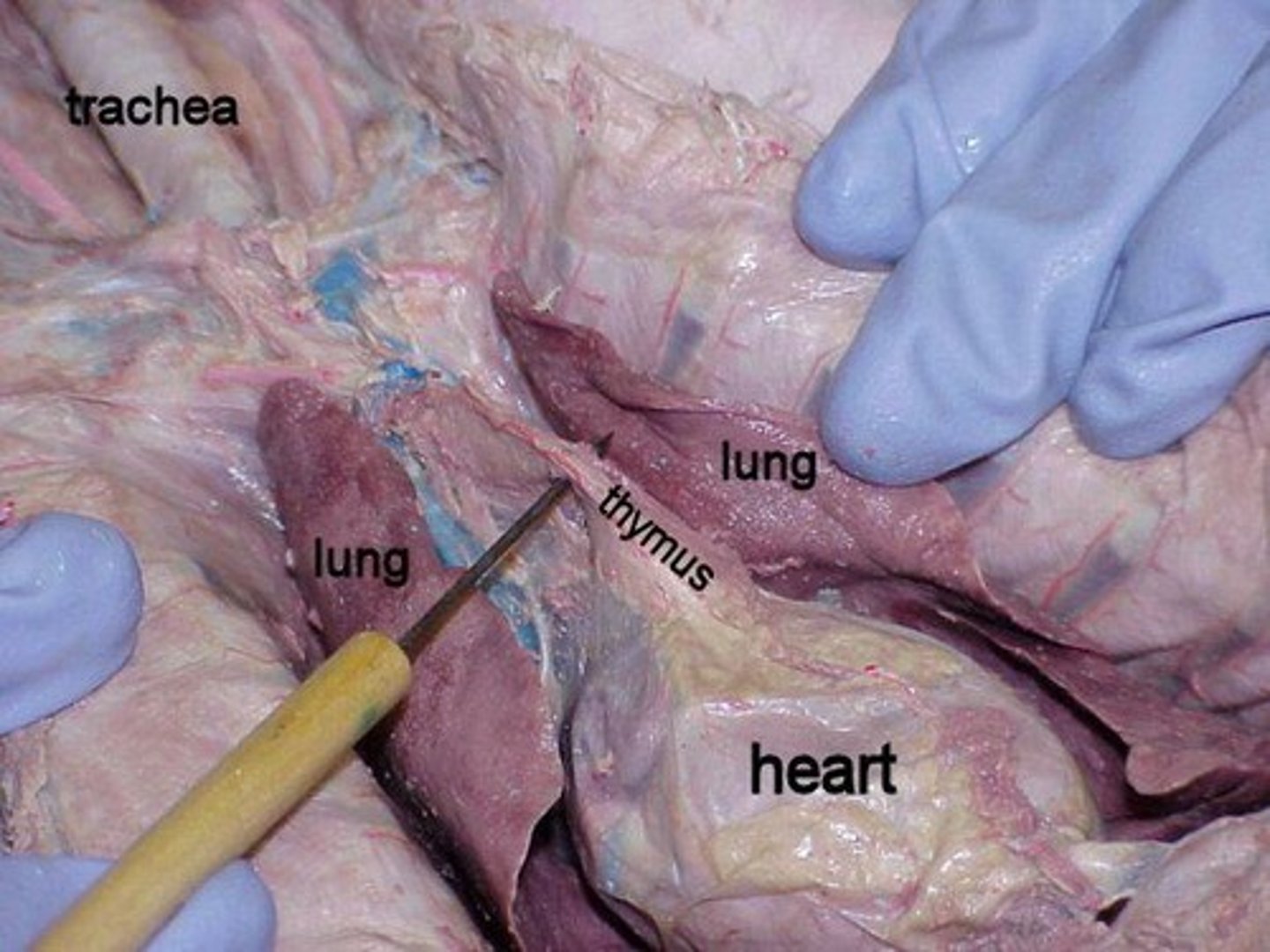
Thymus
Produces T-cells, prominent in young animals.
Tonsils
Lymphoid tissue preventing infection spread.
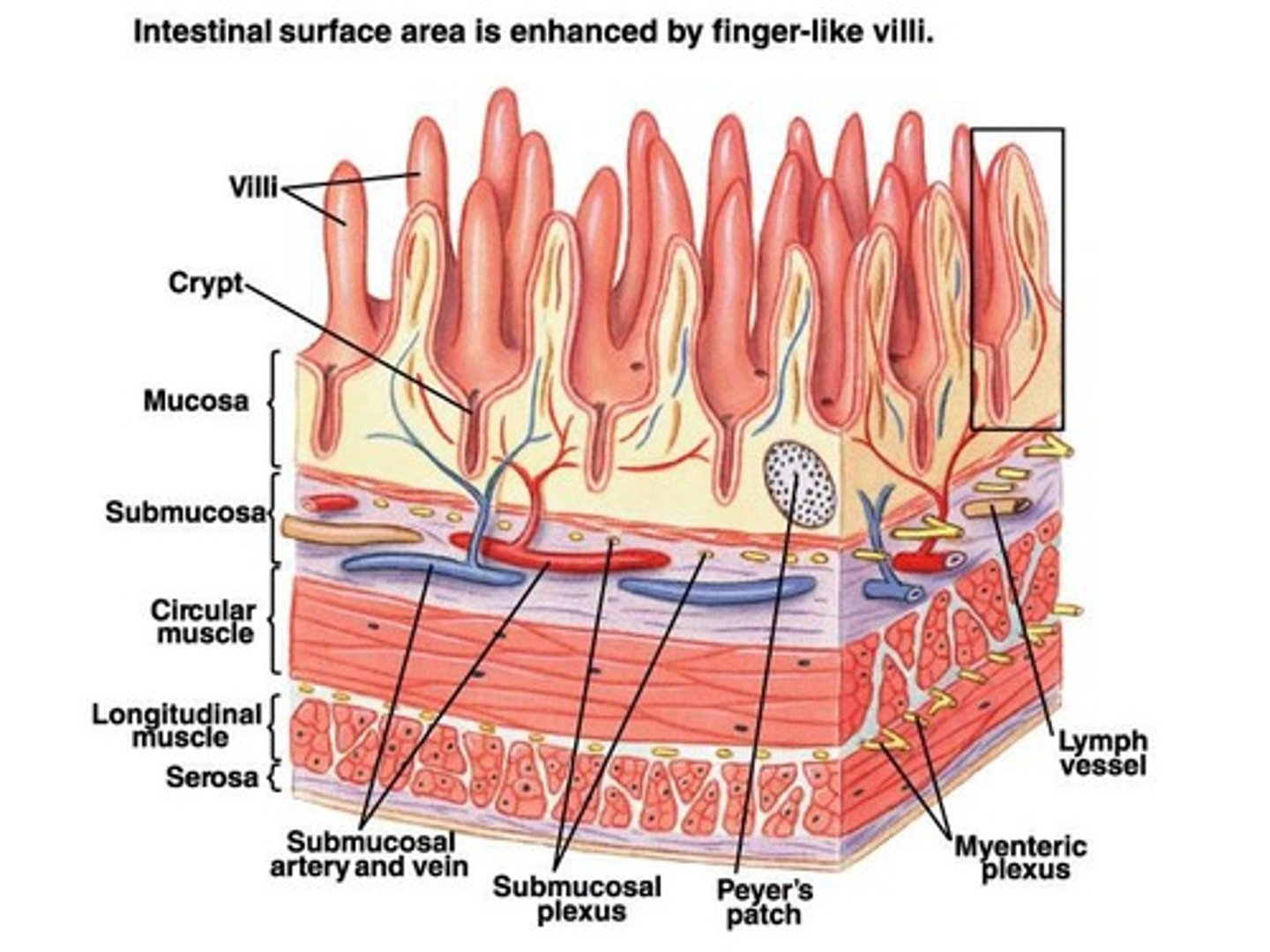
Gut Associated Lymph Tissue (GALT)
Lymphoid tissue in intestinal mucosa.
Peyer's Patches
Lymphoid tissue in intestinal wall combating antigens.
Lymph Node Anatomy
Bean-shaped, contains cortex and medulla.
Lymph Formation
Fluid from capillaries accumulates in tissues.
Interstitial Fluid
Fluid between cells, excess drained by lymphatics.
Lymphatic Valves
Prevent backflow in lymphatic vessels.
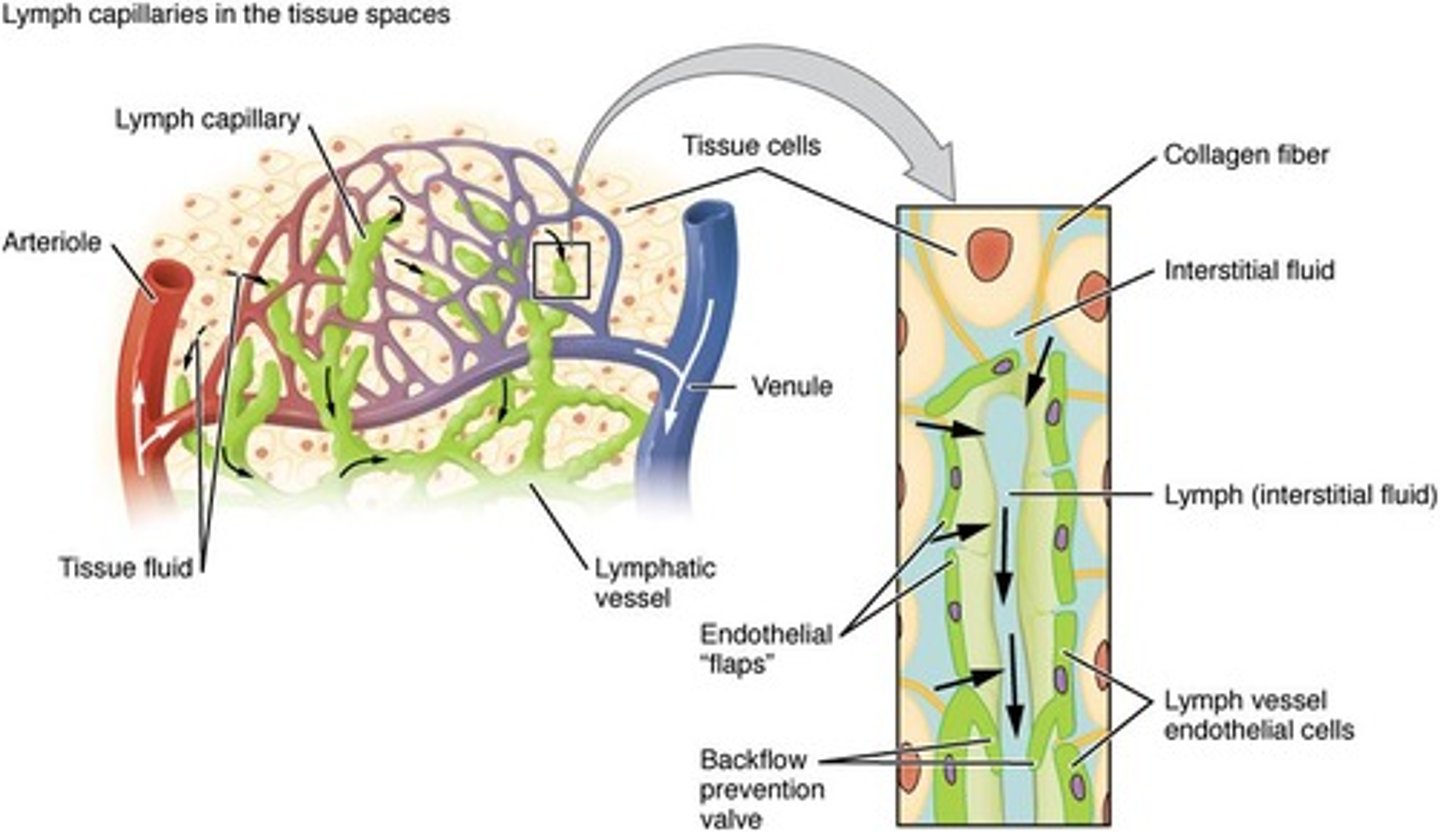
Unidirectional Flow
Lymph moves only towards the heart.
Splenectomy
Surgical removal of the spleen.
Lymphocyte Production
Lymphocytes produced in lymph nodes and thymus.
Major Lymph Nodes
Include parotid, mandibular, axillary, and inguinal.