Lecture #1 Exam #3: Bone pathology
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
EXTRA CREDIT: Who are the oldest dental surgeons?
Barbers!
EXTRA CREDIT: What famous actor suffered from a facial condition?
Justin Bieber
What is Osteogenesis imprefecta?
A brittle bone disease
How is Osteogenesis Imperfecta characterized?
By a heterogeneous group of heritable disorders marked by osteopenia and bone fragility.
What are the severity classifications of Osteogenesis Imperfecta? (3)
• Mild
• Moderate
• Severe
What does the severity depend on in Osteogenesis Imperfecta? (4)
1. Number of bone fractures
2. Degree of long bone and spine deformity
3. Degree of growth impairment
4. Age at which abnormalities become evident
What type of Osteogenesis Imperfecta is the mildest and most common?
Type I
When do fractures occur typically in Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type I ?
Typically when patient begins to walk
Frequency decreases after puberty
What are the clinical characteristics of Osteogenesis Imperfecta type I ? (3)
1. Variable number of bone fractures
2. Minimal bone deformity
3. Essentially normal growth
What type of Osteogenesis Imperfecta is most severe?
Type II
What is the clinical characteristics of Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type II?
Extreme bone fragility and deformity
➢Most patients die in utero or after birth
o Most common cause of death ✓Respiratory distress
• Small thorax
• Multiple rib fractures
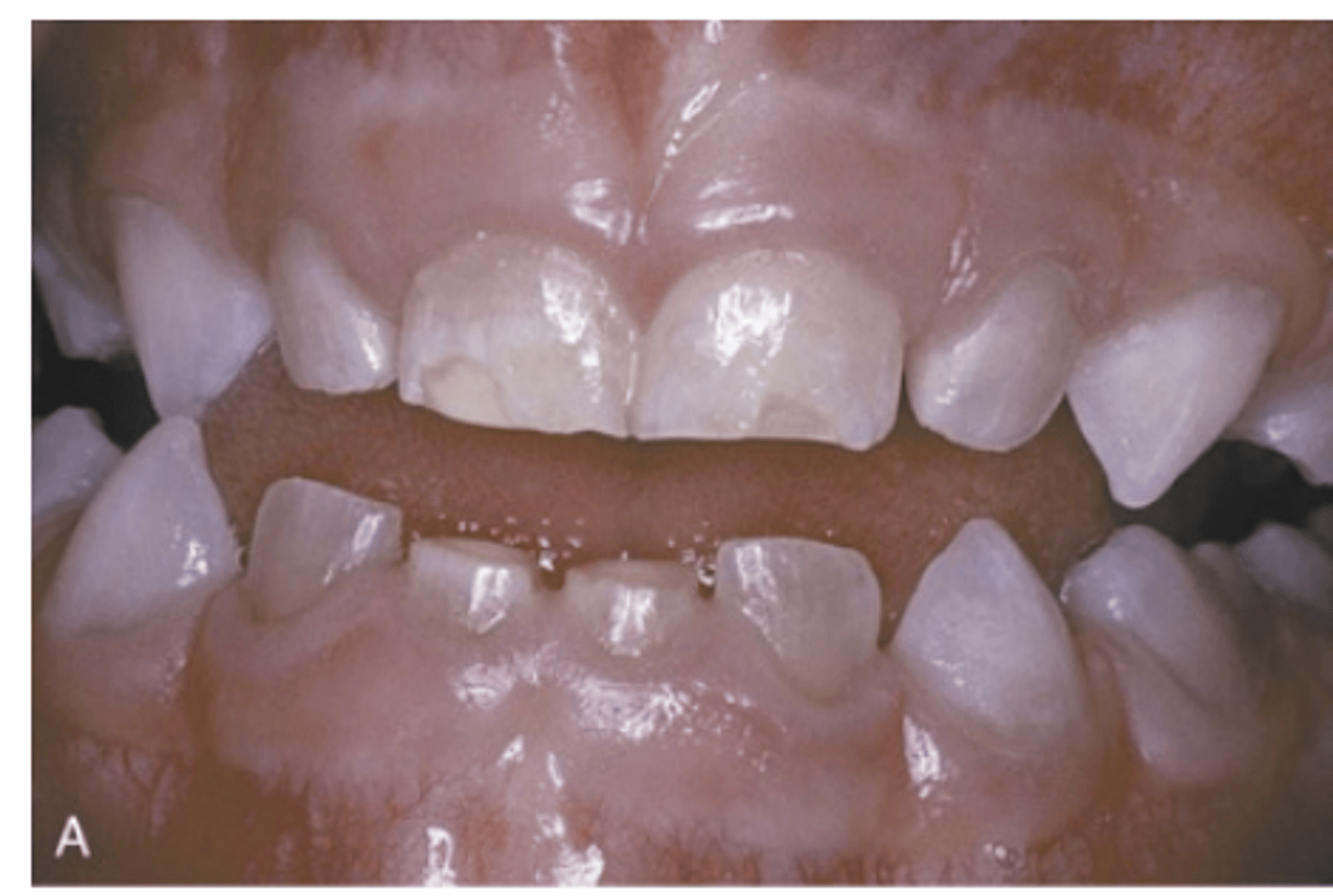
In which types of Osteogenesis Imperfecta are dental alterations more evident?
Types III and IV
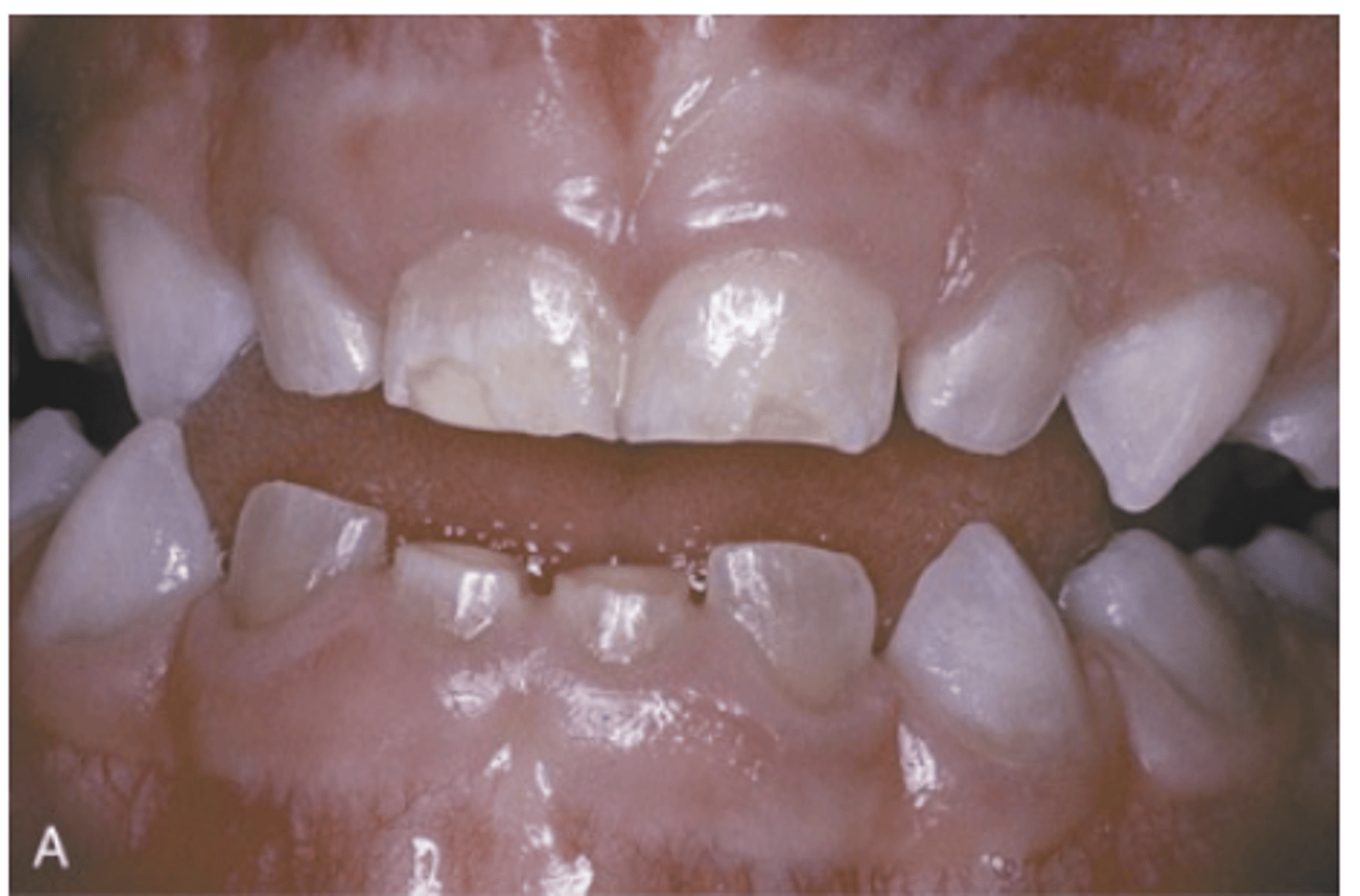
What do dentinal defects in Osteogenesis Imperfecta lead to?
Attrition, loss of vertical dimension, and potential tooth loss.
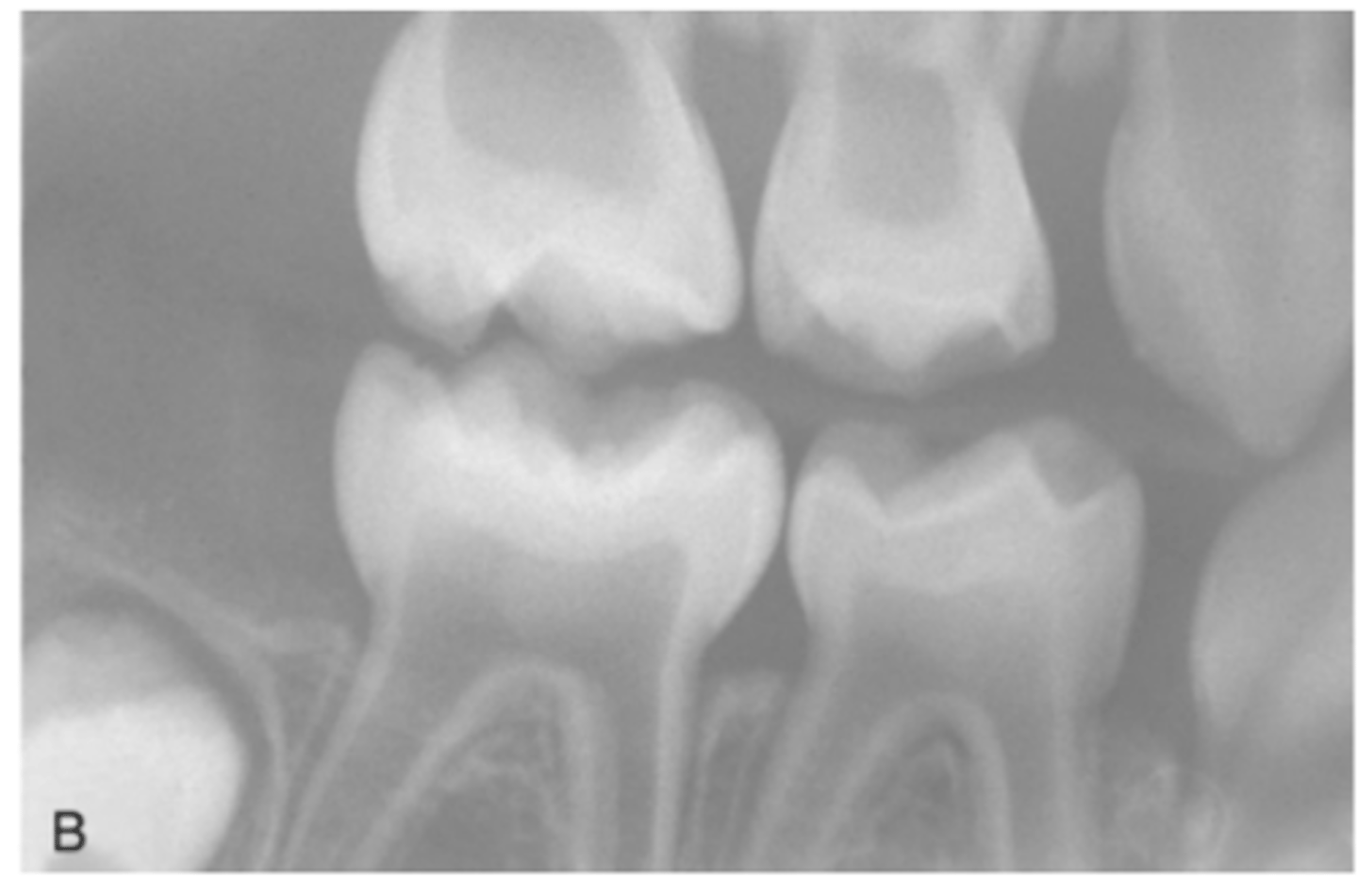
What are some radiographic signs seen in Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Wider pulp chamber
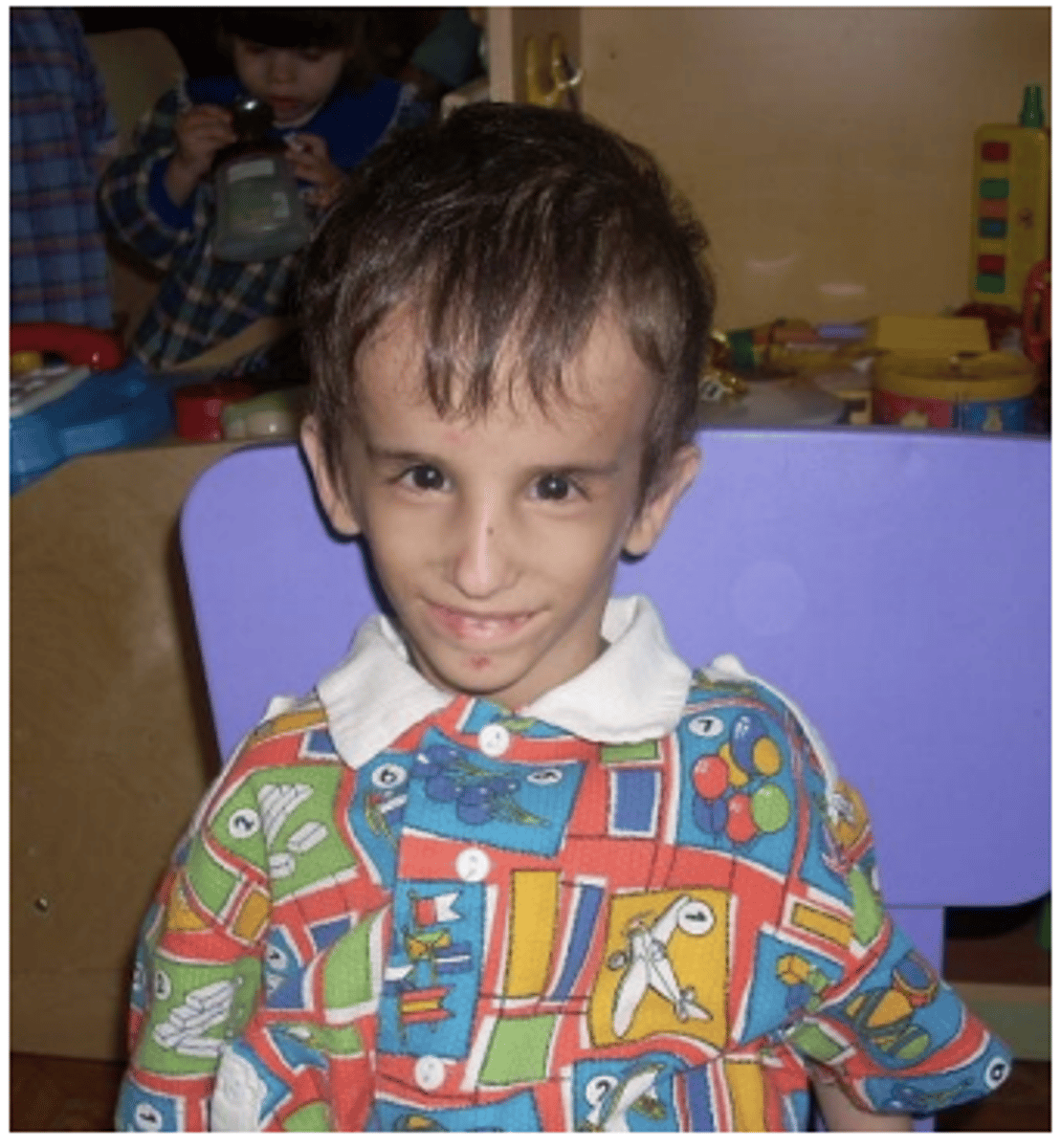
What is a common facial shape seen in patients with Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
Triangular face
What type of malocclusion is more prevalent in Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
Class III malocclusion.
What are common supportive treatments for Osteogenesis Imperfecta? (3)
Physiotherapy
rehabilitation
Orthopedic surgery
What are the goals of treatment in Osteogenesis Imperfecta? (3)
1. Pain management
2. fracture reduction
3. improved mobility.
What pharmacological treatment is commonly used in children with Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
Intravenous bisphosphonates.
What emerging therapies are being researched for Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
- Bone morphogenetic protein modulators
- RANKL inhibitors
- Gene therapy
- Stem cell therapy
What is the treatment for patients with significant malocclusion in Osteogenesis Imperfecta? (2)
1. Orthognathic surgery
2. Orthodontic treatment
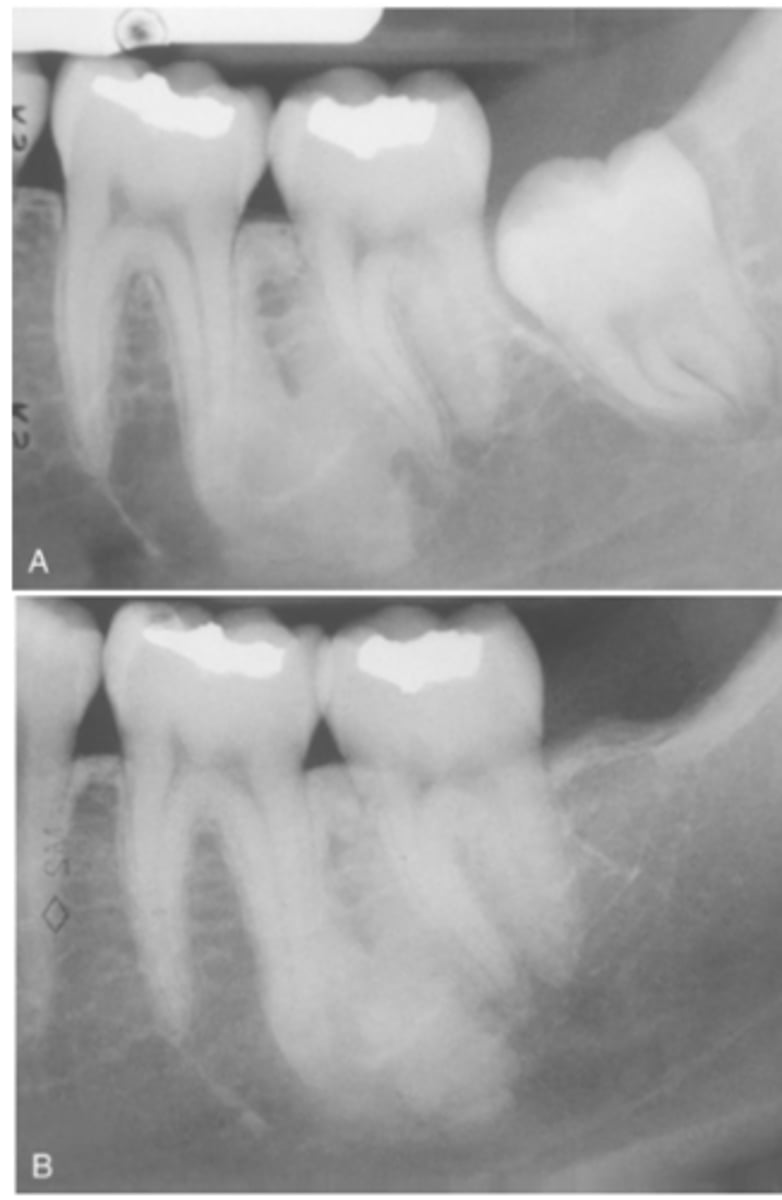
What is Idiopathic Osteosclerosis (dense bone island)
• Focally increased bone density of unknown cause
(Idio means idk, unknown cause)
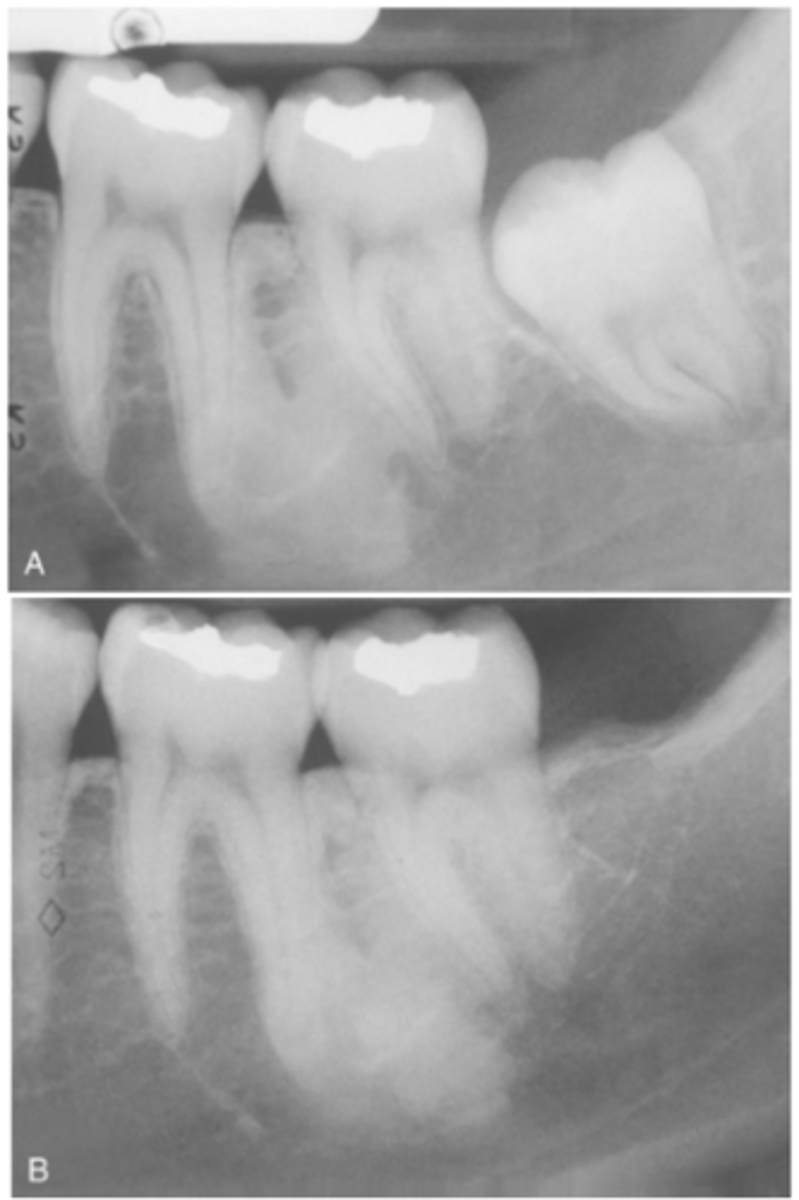
Is Idiopathic Osteosclerosis usually symptomatic or asymptomatic?
asymptomatic
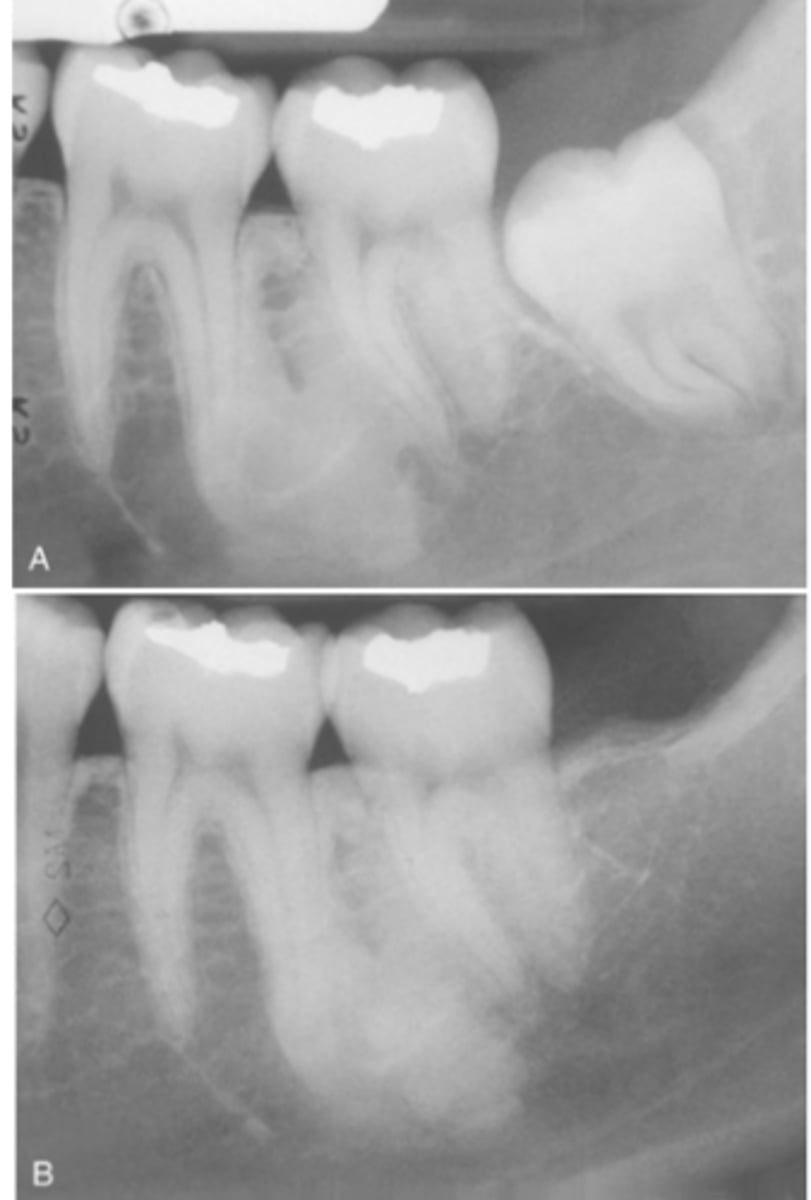
Does Idiopathic Osteosclerosis cause bone expansion?
No, it is nonexpansile.
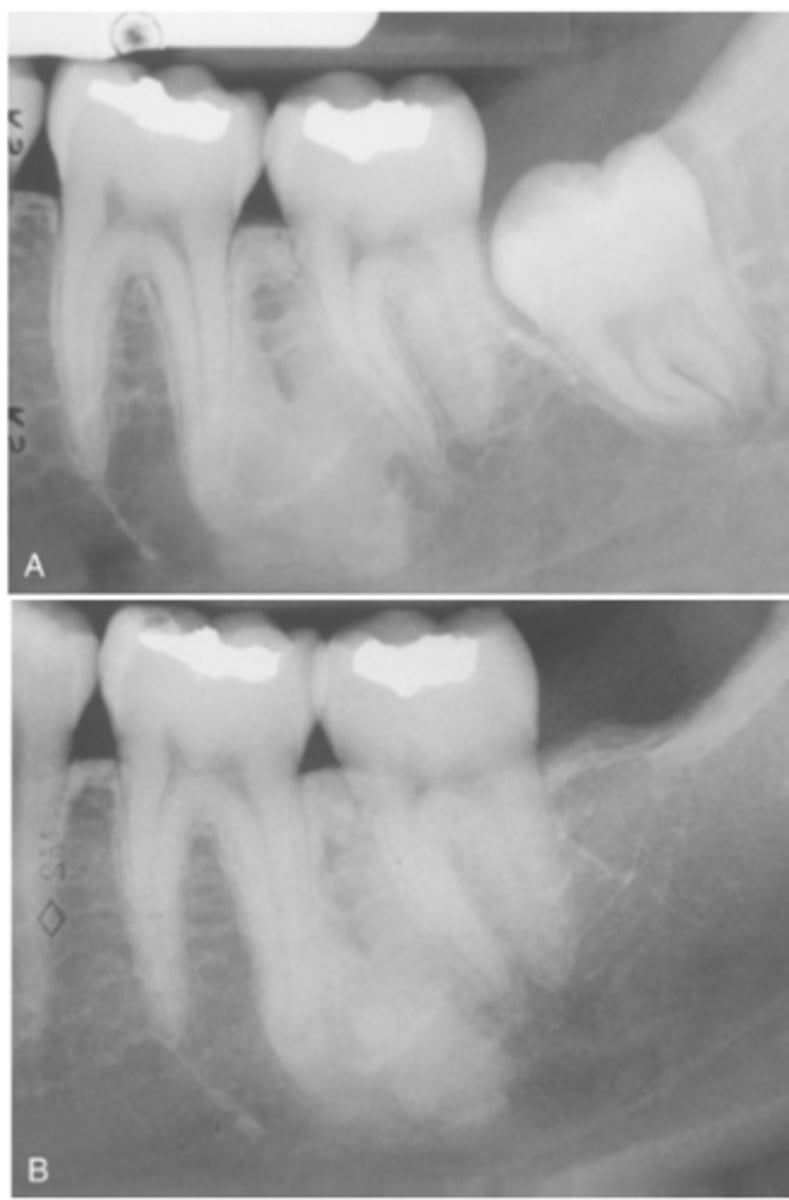
How is Idiopathic Osteosclerosis typically detected?
It is usually found incidentally during routine radiographic examination.
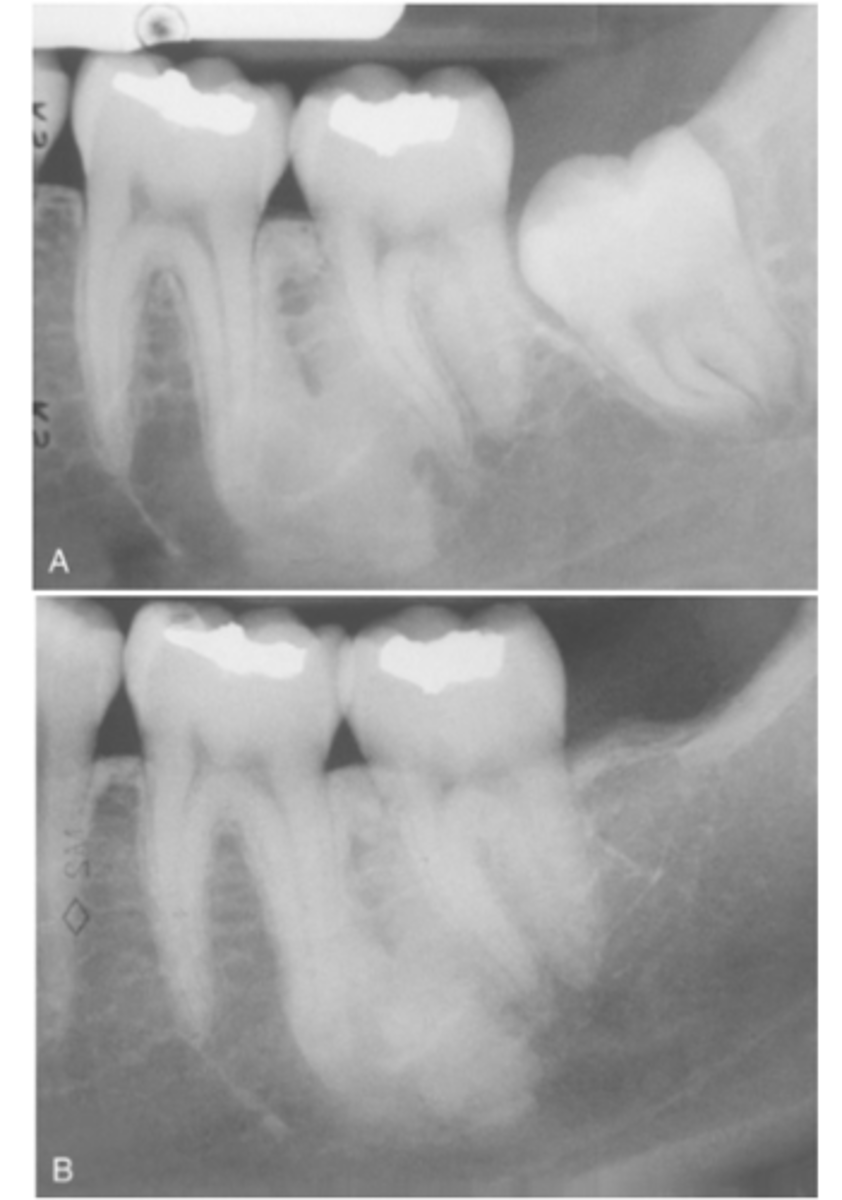
Where are most cases of Idiopathic Osteosclerosis found?
90% of cases affect the mandible
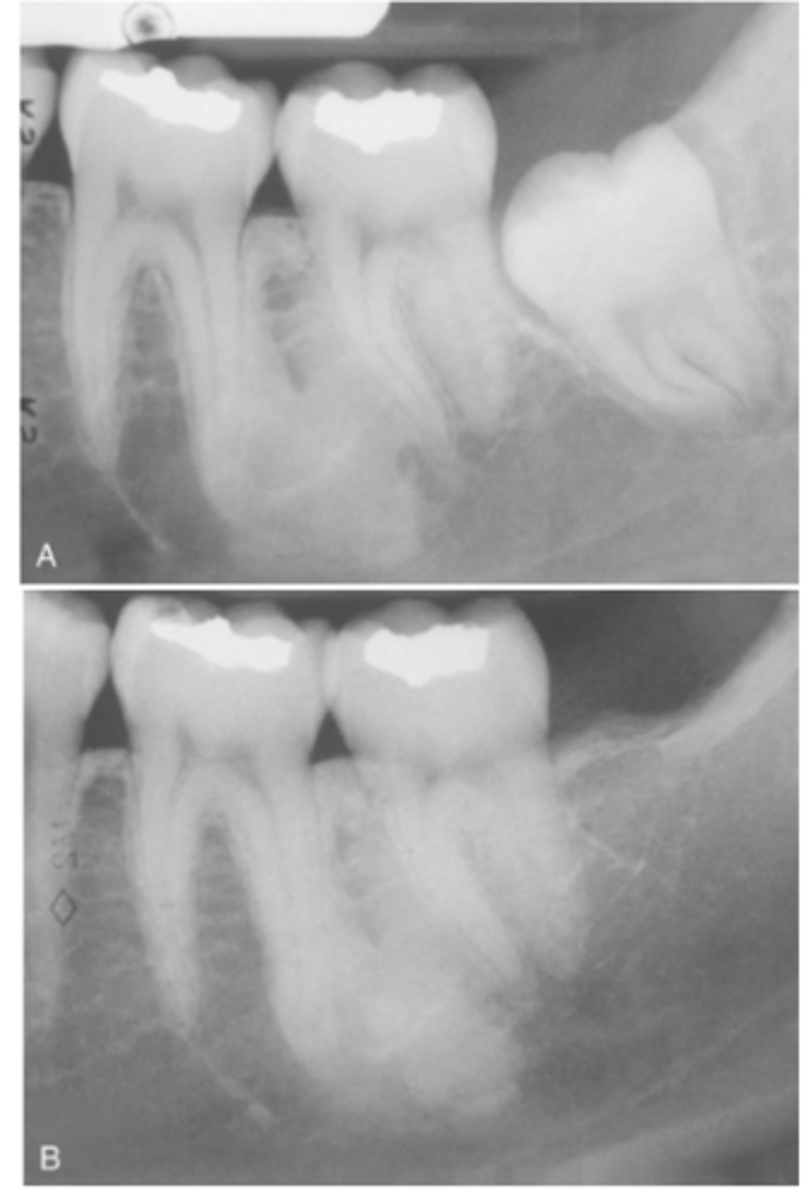
What teeth (in order) in the mandible are most affected in Idiopathic Osteosclerosis
1. First molar area
2. Second molar area
3. Third molar area
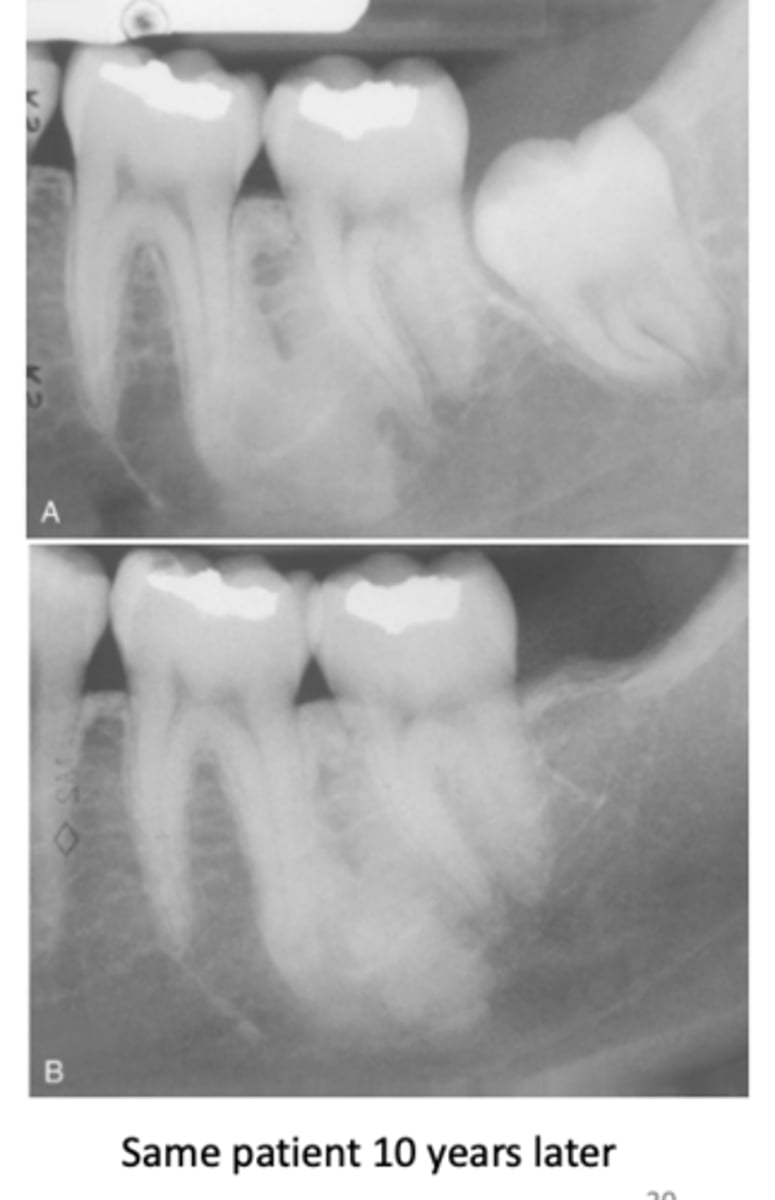
What do radiographic signs show in Idiopathic Osteosclerosis
Well-defined radiopacity
Most are associated to a root apex
If there is signs of cortical expansion in Idiopathic Osteosclerosis what needs to be taken?
biopsy
What is the treatment for Idiopathic Osteosclerosis
Follow-up with radiographs if discovered during adolescence
What is Paget disease of bone?
Abnormal, anarchic resorption and deposition of bone
(said did not need to know for exam just for our information)
What age group does Paget disease of bone primary affect?
Primarily affects older patients
What are the causes of pain in Paget disease of bone? (2)
1. Increased bone turnover
2. Secondary complications ✓Osteoarthritis
✓Spinal stenosis
✓Pathologic fracture ✓Pseudofracture
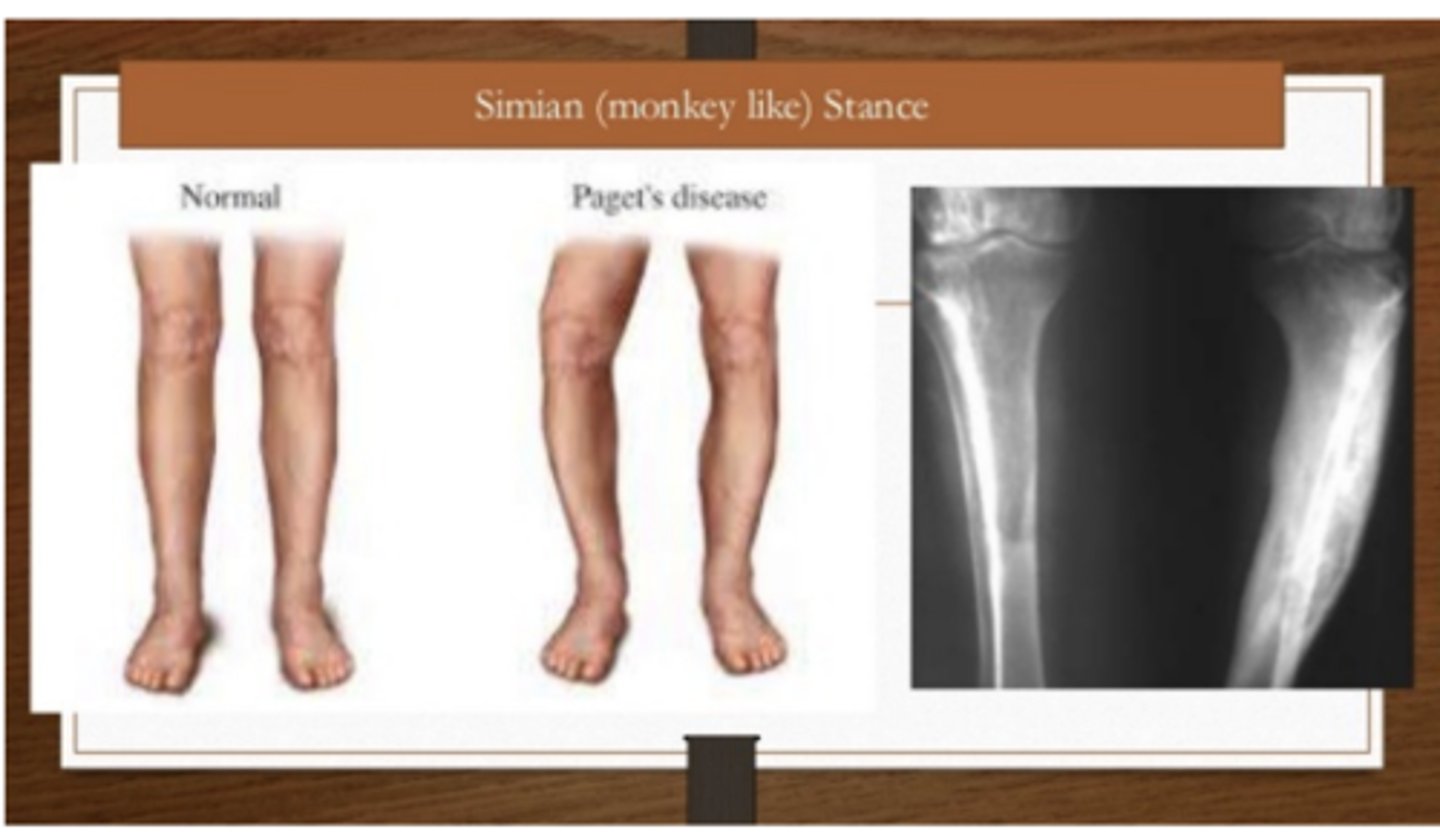
What are some clinical manifestations of Paget disease of bone
Weight-bearing bones
• Bowing deformity
o “Simian (monkeylike) stance”
What type of lesion is a Central Giant Cell Granuloma?
An intraosseous lesion.
What is the main controversy surrounding the nature of Central Giant Cell Granuloma?
Whether it is a reactive process or a benign neoplasm.
Where is the most frequent location of Central Giant Cell Granuloma?
70% occur in the mandible
What area of the mouth is Central Giant Cell Granuloma more common?
More common in anterior portion of jaws
What are the two categories of Central Giant Cell Granuloma based on clinical and radiographic features?
Nonaggressive lesions and Aggressive lesions.
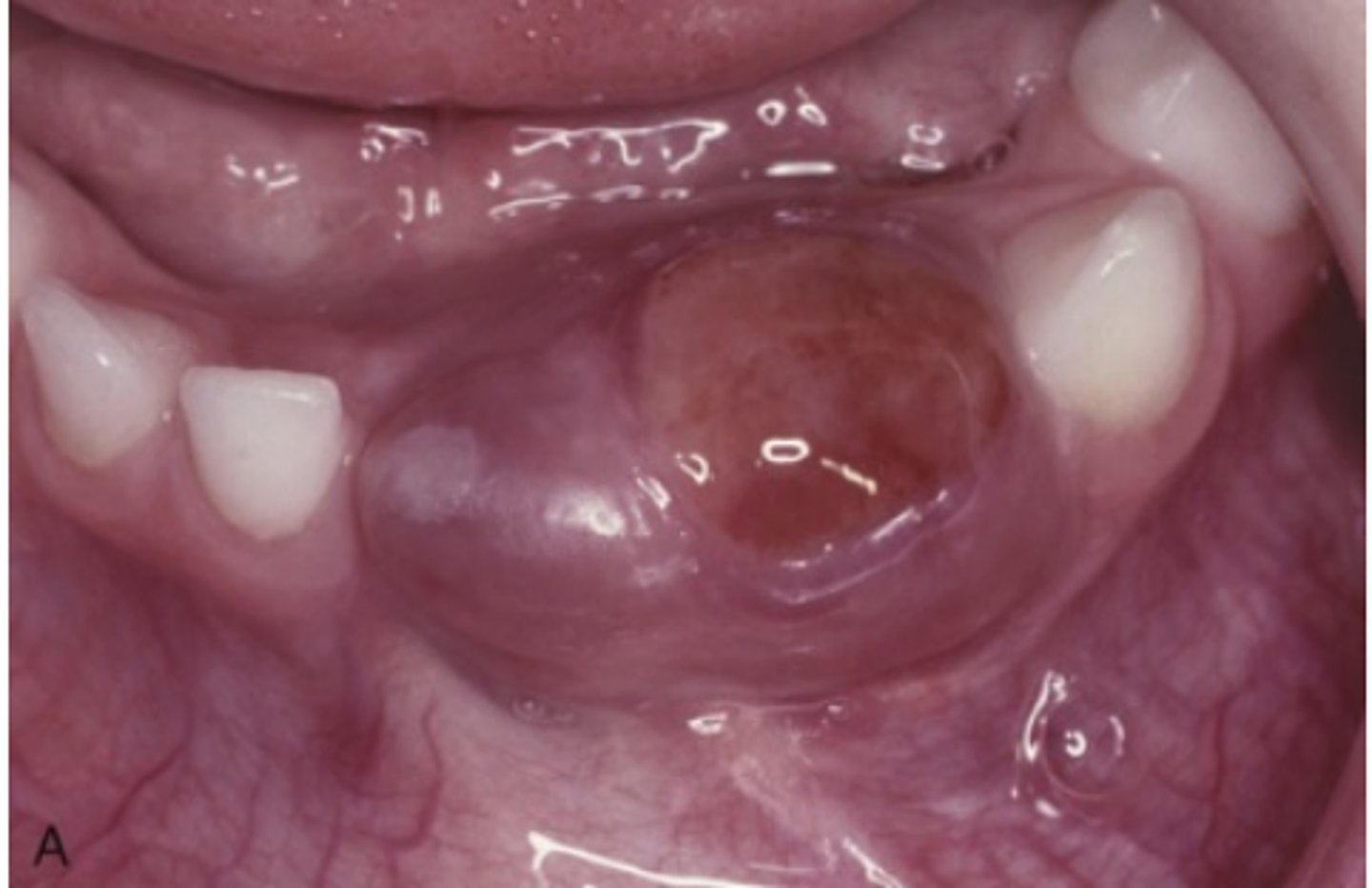
What are typical characteristics of nonaggressive Central Giant Cell Granulomas?
Relatively small, few or no symptoms, slow growth, no cortical perforation or root resorption, usually discovered during routine radiographs or due to painless jaw expansion.
How do aggressive Central Giant Cell Granulomas typically present?
Pain, rapid growth, cortical perforation, root resorption, tooth displacement, paresthesia, soft tissue extension, and mucosal ulceration.
What is the treatment for Central Giant Cell Granuloma
Thorough curettage
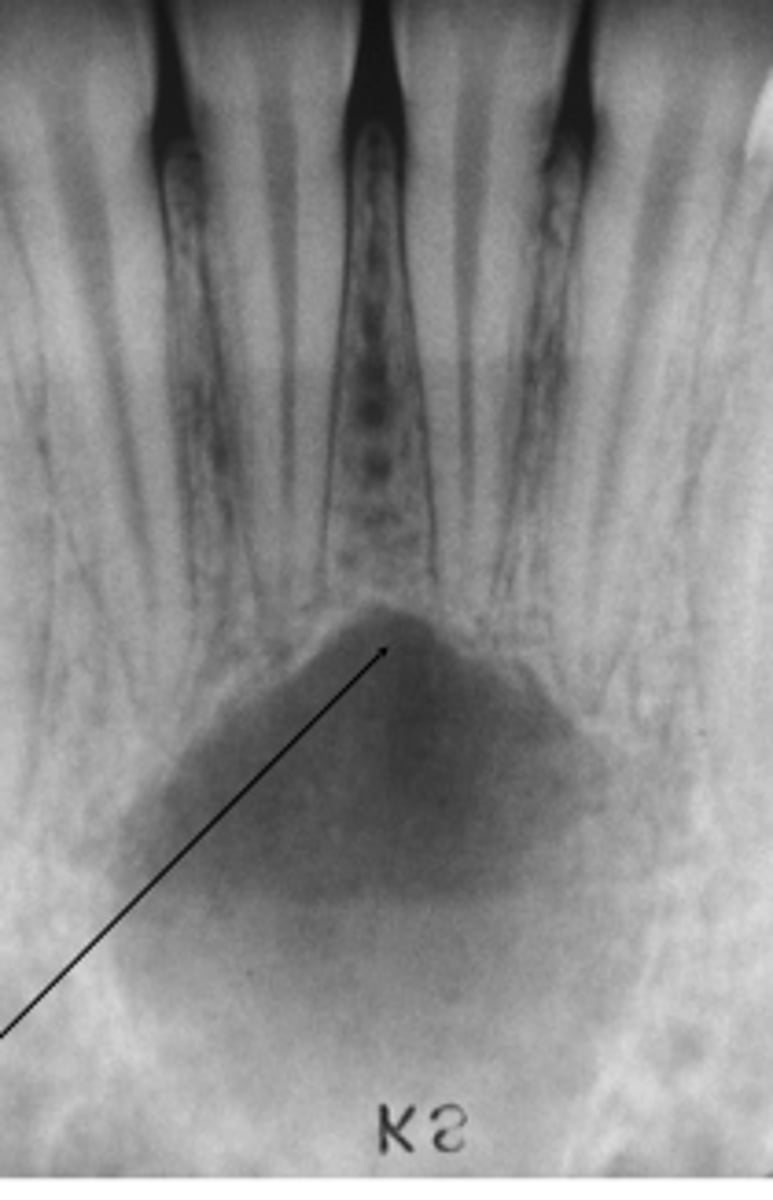
What is a simple bone cyst?
Empty or fluid-containing bone cavity
Pseudocyst (lacks epithelial lining)
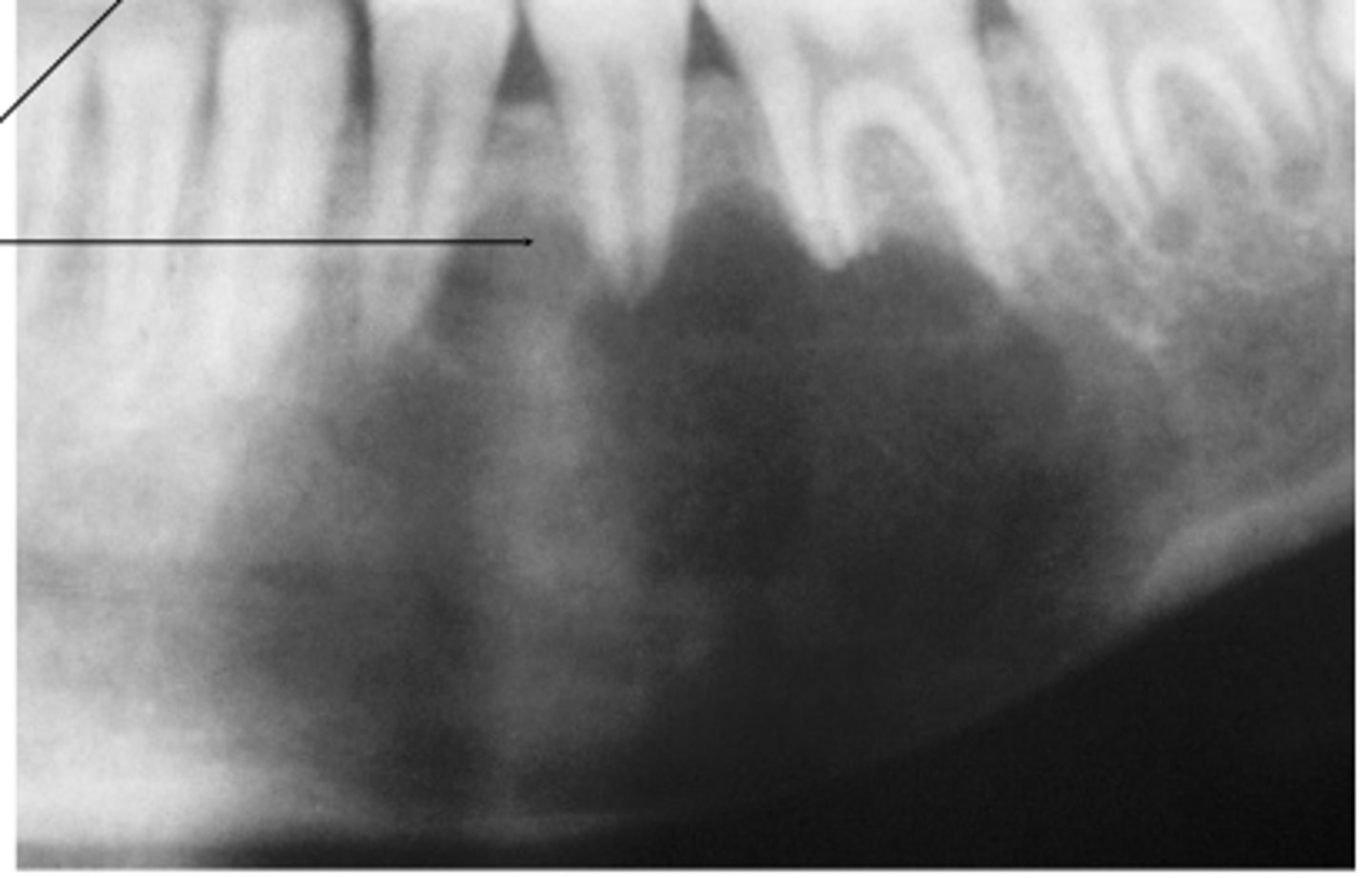
Where does simple bone cysts typically occour?
Marked mandibular predominance
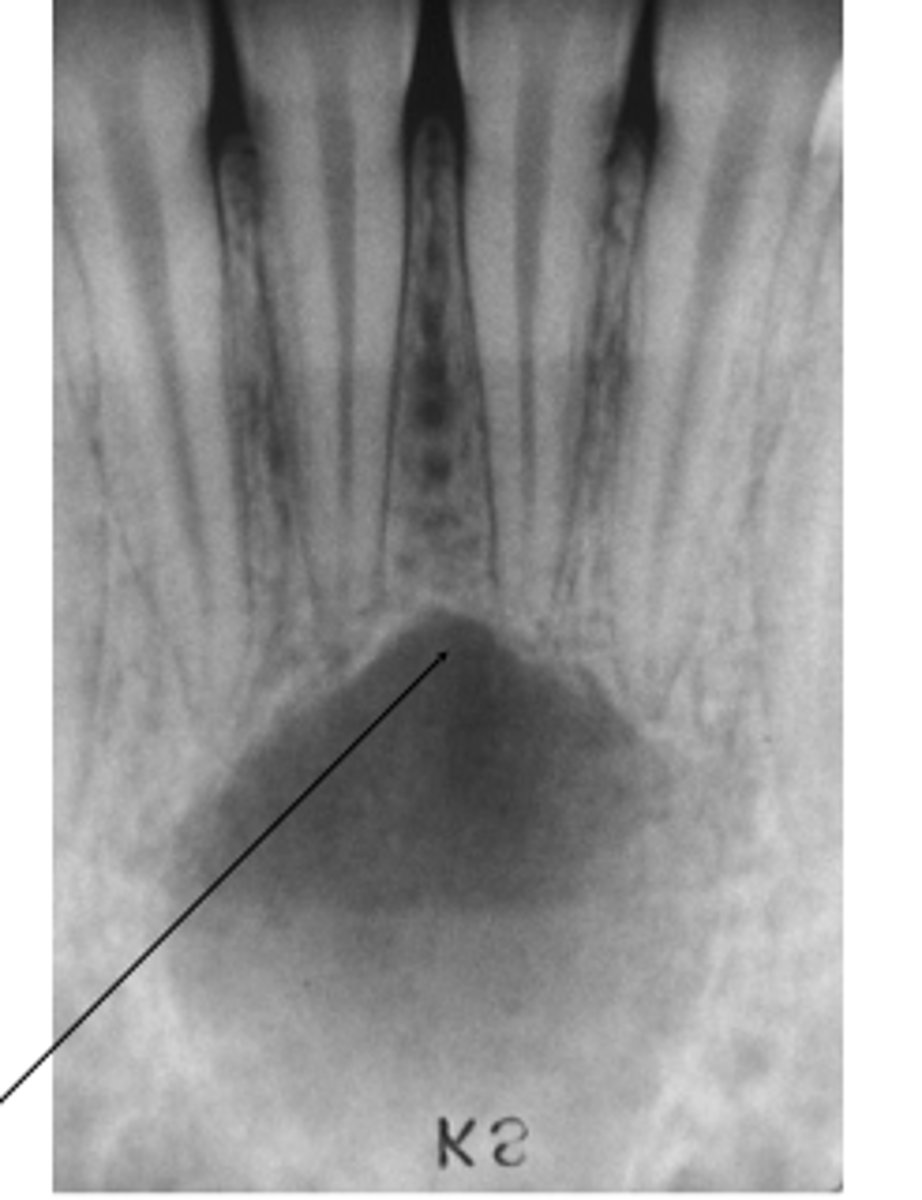
What is a clinical manifestation associated with simple bone cysts?
20% of patients present painless jaw swelling
Jaw lesions are normally asymptomatic.
diagnosed by radiographic examination.
what is the diagnosis for simple bone cyst?
Radiographic signs are not specific
• Surgical exploration is required