Fluid and Acid-Base Balance Overview
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
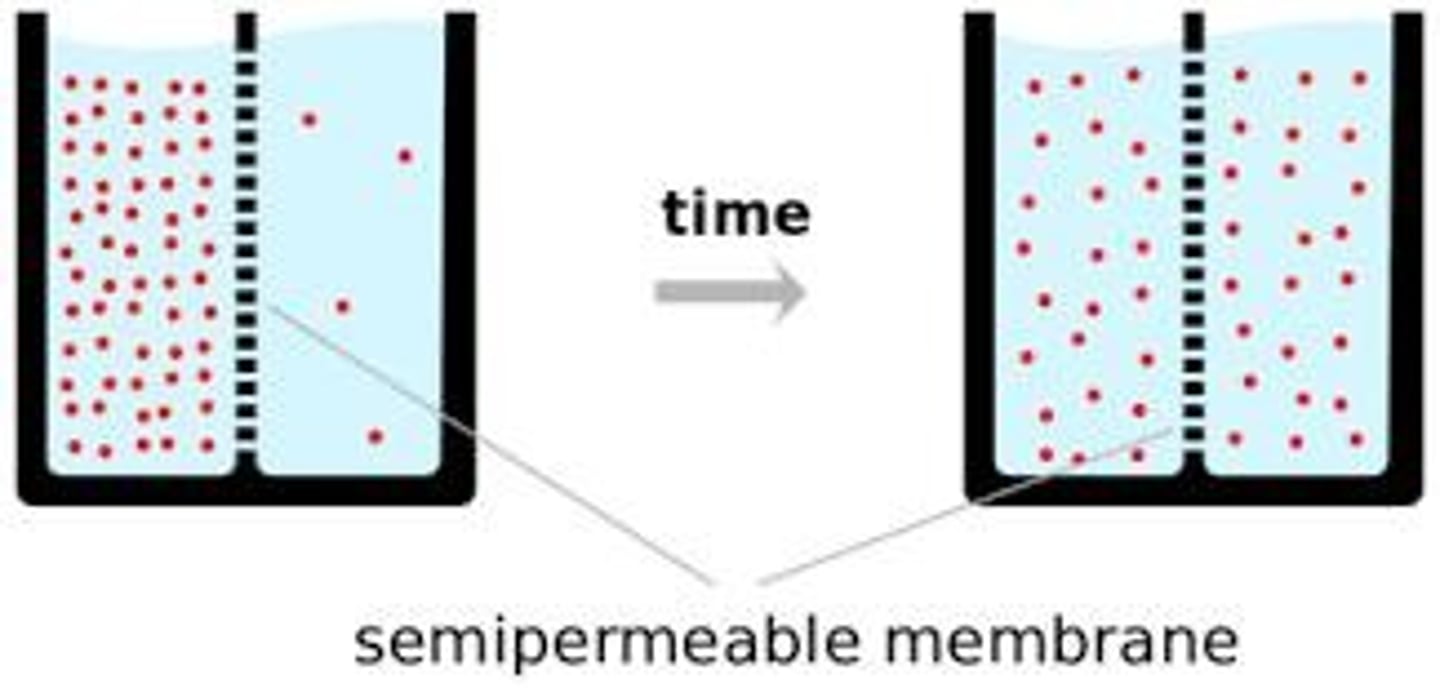
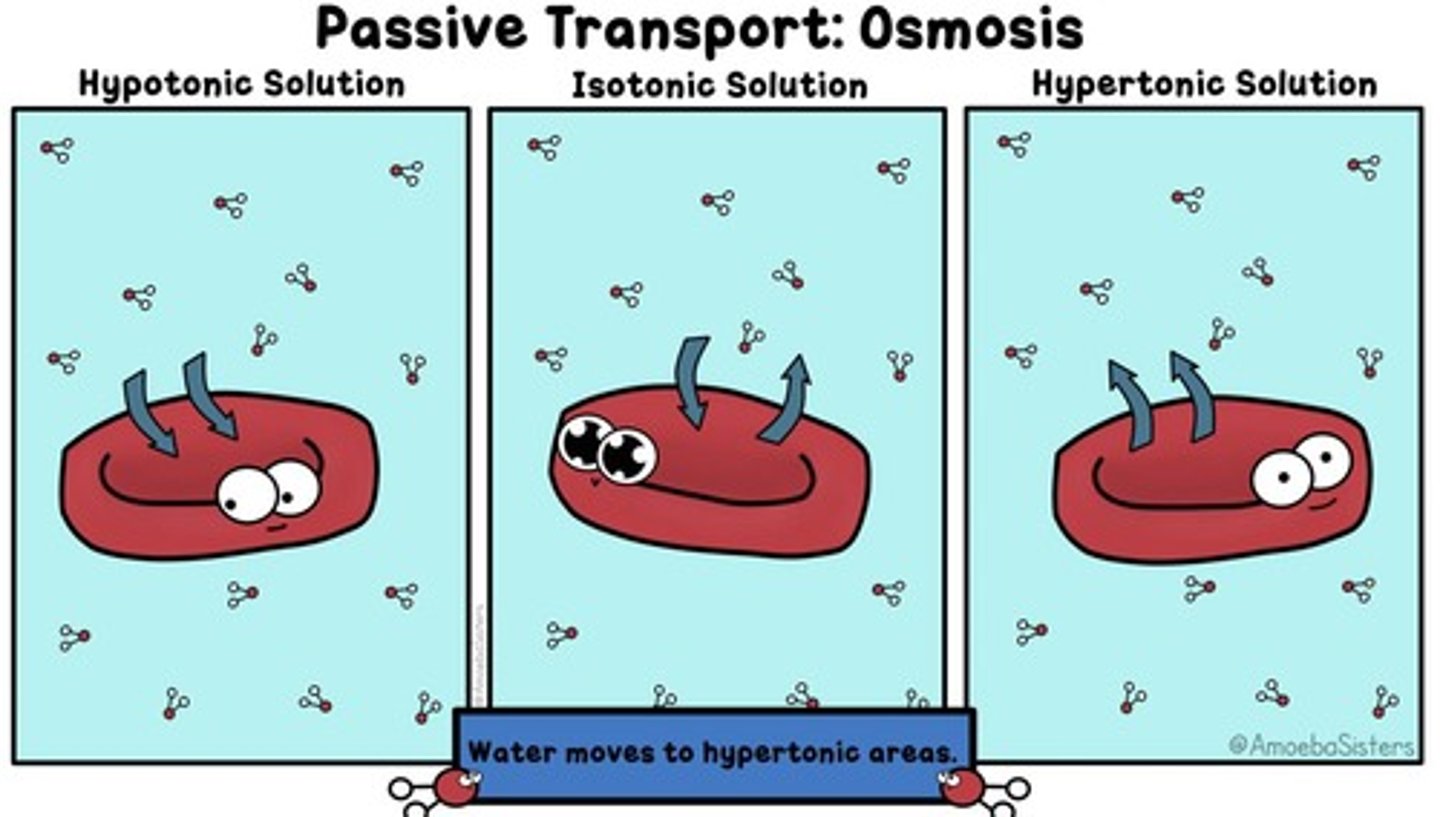
Osmosis
Movement of fluids from an area of low concentration of solutes (lots of water) to an area of high concentration of solutes (less water)
Diffusion
Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration
Hydration
Water balance is regulated by thirst perception and the antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
ADH
Antidiuretic Hormone (also called arginine vasopressin) released from pituitary gland when there is an increase in osmolality or decrease in circulating blood volume; increases water absorption
Dehydration
Water deficit - both sodium and water loss
ICF
Intracellular Fluid - Fluid INSIDE of the cell; Potassium (K+) is the primary electrolyte inside of the cell
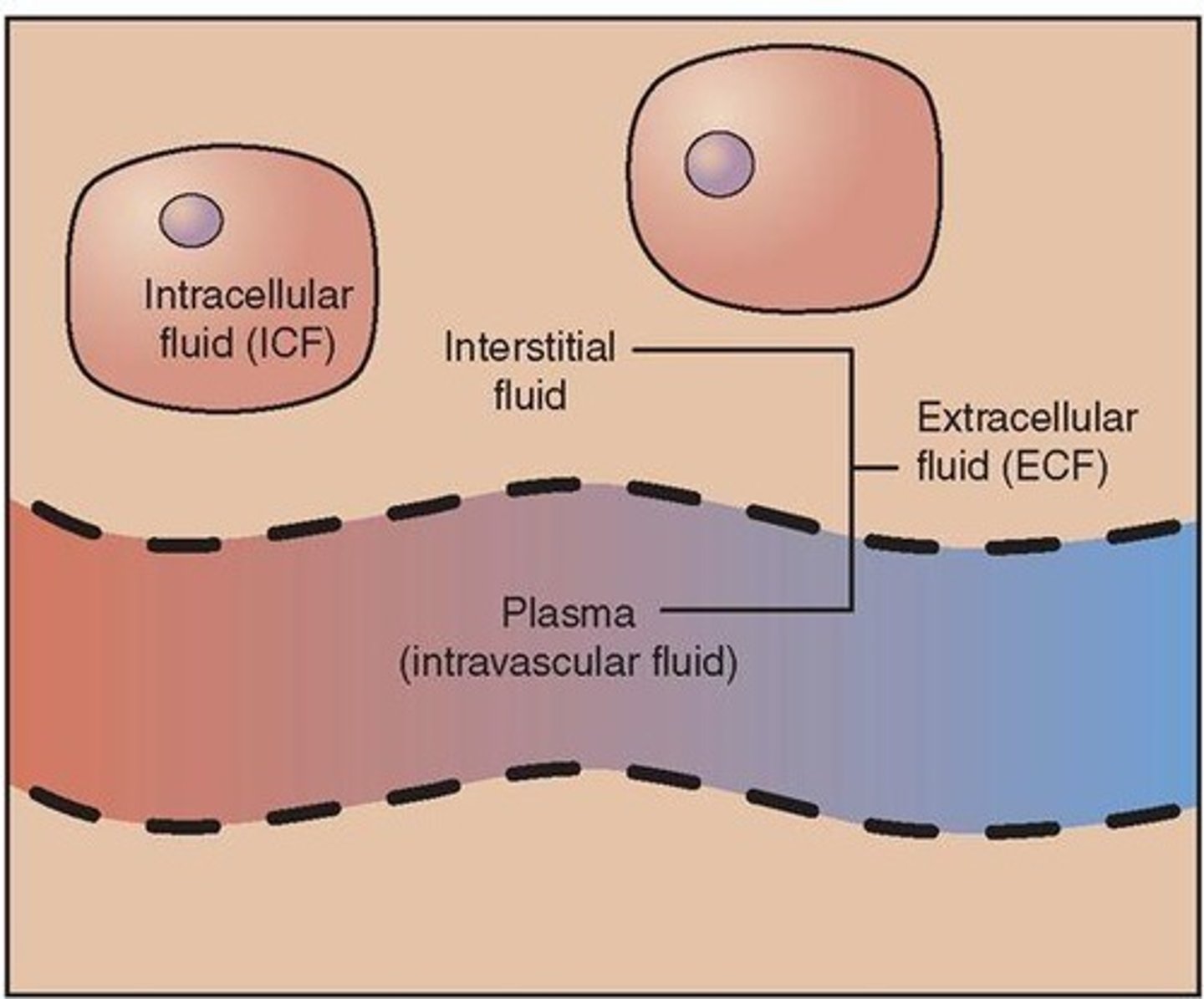
ECF
Extracellular Fluid - Fluid OUTSIDE of the cell; Sodium (Na+) is the primary electrolyte outside of the cell
Interstitial Fluid
Fluid that surrounds the outside of cells
Intravascular Fluid
Fluid located inside the blood vessels; contains blood cells & electrolytes
Homeostasis
Osmatic equilibrium between compartments
Osmolality
Natural body concentration of solutes
Tonicity
Concentration of IV fluid
Isotonic
Equal concentration; Example: saline solution for body
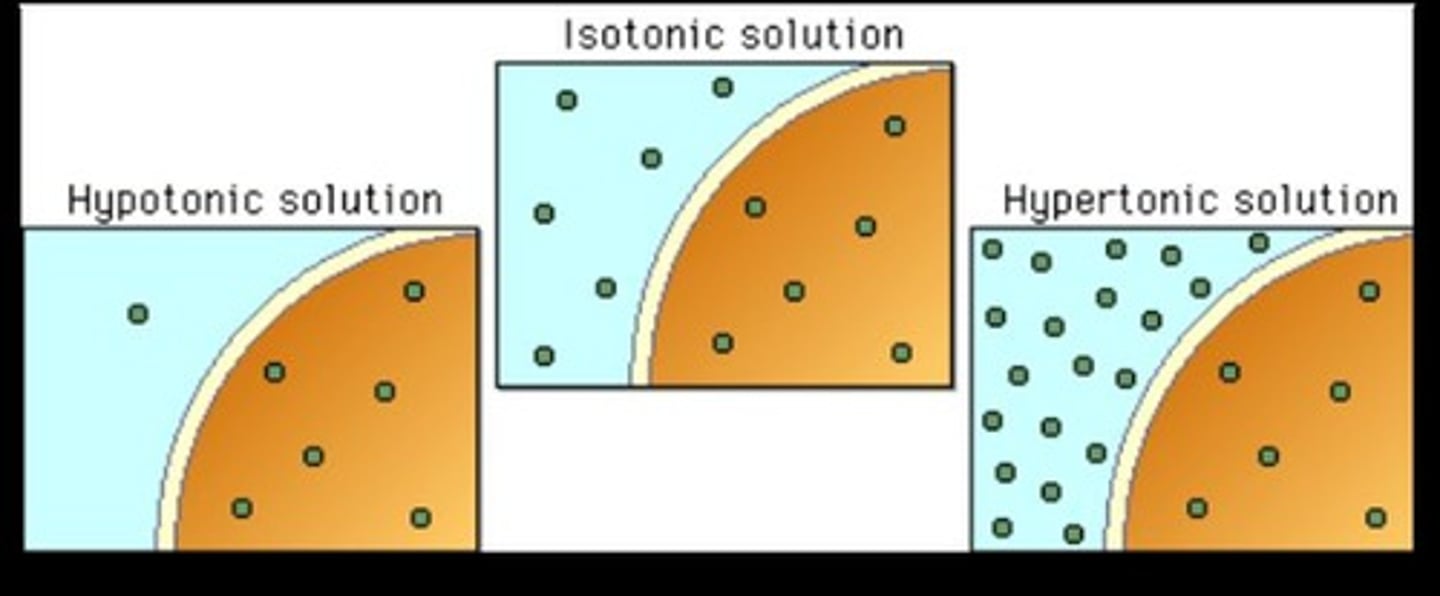
Hypertonic
Lower osmolality than the body
Hypotonic
Higher osmolality than the body
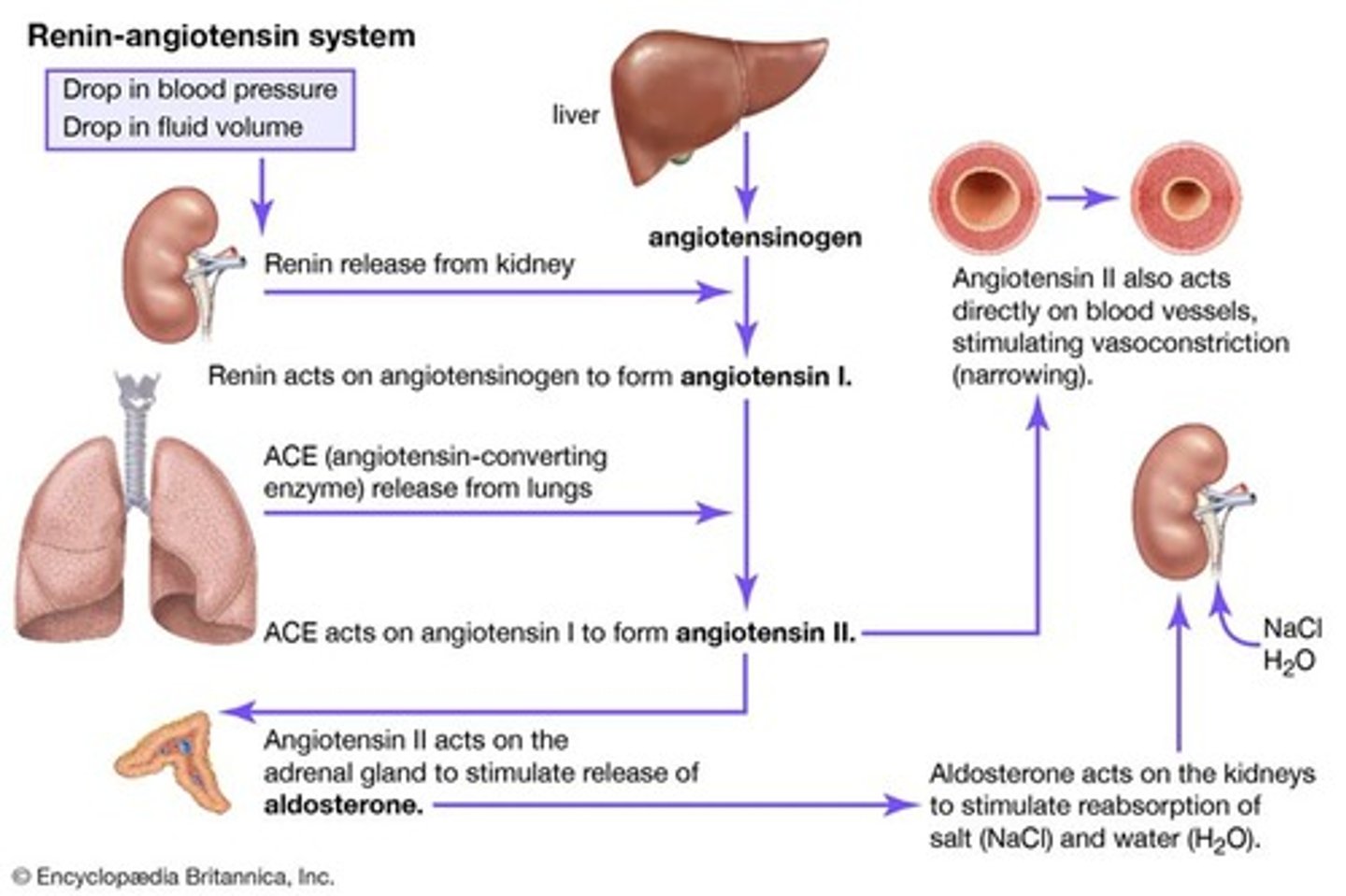
RAAS
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
Renin
Released by the kidney due to low blood pressure
Aldosterone
Hormone that tells the kidneys to reabsorb sodium and water
Angiotensin II
Activated by renin and causes vasoconstriction
Electrolytes
Play a role in the movement of fluid and the process of osmosis
Signs and Symptoms of Dehydration
Low blood pressure, weak pulse, and postural hypotension; Elevated hematocrit and serum sodium levels; Headache, dry skin, and dry mucous membranes
Treatment for Dehydration
Oral fluids and hypotonic saline solution (5% dextrose in water)
Isotonic Alterations
Lose everything (water & sodium) together.
Isotonic fluid loss (FVD)
Loss of total body water (TBW) with proportional change in concentration of electrolytes.
Examples of Isotonic fluid loss
Dehydration & hypovolemia.
Isotonic fluid excess (FVE)
Gain of total body water (TBW) with proportional change in concentration of electrolytes.
Hypertonic Alterations
Related to water loss or sodium gain.
Water deficit
Dehydration - both sodium and water loss.
Manifestations of water deficit
Low blood pressure, weak pulse, postural hypotension.
Treatment for water deficit
Oral fluids, hypotonic saline solution (5% dextrose in water).
Hypernatremia
Serum sodium >145 mEq/L.
Effects of hypernatremia
Water movement from ICF to ECF leading to intracellular dehydration.
Manifestations of hypernatremia
Intracellular dehydration, seizures, muscle twitching, hyperreflexia.
Treatment for hypernatremia
Isotonic salt-free fluids.
Hypotonic Alterations
Free water excess that dilutes sodium.
Hyponatremia
Decreases the ECF osmotic pressure leading to water moving into the cell.
Water excess
Compulsive water drinking leading to water intoxication.
Manifestations of water excess
Cerebral edema, pulmonary edema, cellular edema.
Treatment for water excess
Fluid restriction; may need hypertonic saline solution.
FVD - Fluid Volume Deficit
Causes include fluids shifting in response to concentration of solutes in other compartments.
Signs & Symptoms of FVD
Low BP / Hypotension & Orthostatic Hypotension, compensatory tachycardia, dizziness, dry mouth, thirst, cool clammy skin.
Management of FVD
Fluid restriction, sodium restriction, hypertonic fluids, diuretics.
FVE - Fluid Volume Excess
Causes include fluids shifting in response to the concentration of solutes in other compartments.
Signs & Symptoms of FVE
High BP, bounding pulse, pulmonary congestion, shortness of breath (SOB), jugular vein distention (JVD), later edema.
Common examples of Isotonic fluids
0.9 NS, Lactated Ringers (RS), D5W (Dextrose 5%).
Examples of Hypotonic fluids
0.45% NS, 0.25% NS.
Examples of Hypertonic fluids
D5/0.45 NS, D5% 0.9% NS, Hypertonic Saline (HS) 3% or 5%.
Effects of administering hypo, iso and hypertonic fluids
Do they stay in the veins and arteries? Do they move into the cell? Do they cause fluid to move out of the cell?
Isotonic
No fluid shift; fluid is the same as natural body concentration (same osmolality & tonicity).
Hypotonic
Fluid moves from vascular space into the cells; used for dehydration.
Hypertonic
Fluid moves from cells into the vascular space.
Edema
Accumulation of fluid in interstitium.
Causes of Edema
Hypertonic alterations, increased capillary hydrostatic pressure, decreased plasma oncotic pressure, increased capillary permeability, lymphatic obstruction.
Venous obstruction
A cause of increased capillary hydrostatic pressure leading to edema.
Decreased plasma oncotic pressure
Caused by loss or diminished production of albumin.
Increased capillary permeability
Caused by inflammation and immune response.
Lymphatic obstruction
Can lead to lymphedema.
Manifestations of Edema
Localized vs generalized, dependent edema, pitting edema, 'third space', swelling and puffiness, tight-fitting clothes and shoes, weight gain.
Treatment for Edema
Treat fluid imbalance, elevate edematous limbs, use compression stockings or devices, avoid prolonged standing, restrict salt intake, take diuretic agents.
Electrolyte balance/imbalance
Identify normal levels, signs of deficit and excess, and treatment.
Sodium (Na+)
Normal Levels: 136-145 mEq/L
Sodium Functions
PRIMARY ECF cation, regulates osmotic forces, maintains fluid volume, allows muscle contractions, contributes to nerve impulses.
Signs of Sodium Deficit (<135 mEq/L)
Causes: Plasma hypoosmality, cellular swelling. Manifestations: Lethargy, headache, confusion, seizures, coma, muscle cramping, memory loss, anorexia.
Treatment for Sodium Deficit
Restrict water intake; depends on underlying disorder.
Signs of Sodium Excess (>145 mEq/L)
Causes: Excess water loss, excess Na admin, diabetes insipidus, heat stroke, hypertonic IV solution. Manifestations: Thirst, elevated temperature, dry & swollen tongue, sticky mucosa, neuro symptoms, restlessness, weakness, fluid retention, hypertension, disorientation.
Treatment for Sodium Excess
Hypotonic solution, encourage fluids, restrict sodium.
Chlorine (Cl)
FOLLOWS SODIUM. Function: Primary ECF anion, provides electroneutrality.
Potassium Normal Levels
3.5-5.0 mEq/L
Potassium Functions
Transmission and conduction of nerve impulses, normal cardiac rhythms, skeletal and smooth muscle contraction, regulates ICF osmolality & deposits glycogen in liver and skeletal muscle cells.
Potassium during pH imbalance - Acidosis
Potassium moves from ICF to ECF in exchange for hydrogen.
Potassium during pH imbalance - Alkalosis
Potassium moves from ECF to ICF in exchange for hydrogen.
Signs of Potassium Deficit (<3.5 mEq/L)
Causes: Decreased intake (starvation), shift from ECF to ICF with increased renal loss, v/d. Manifestations: Decreased neuromuscular excitability, skeletal muscle weakness, smooth muscle atony, cardiac dysrhythmias (flattened/depressed T-wave, prominent U-wave).
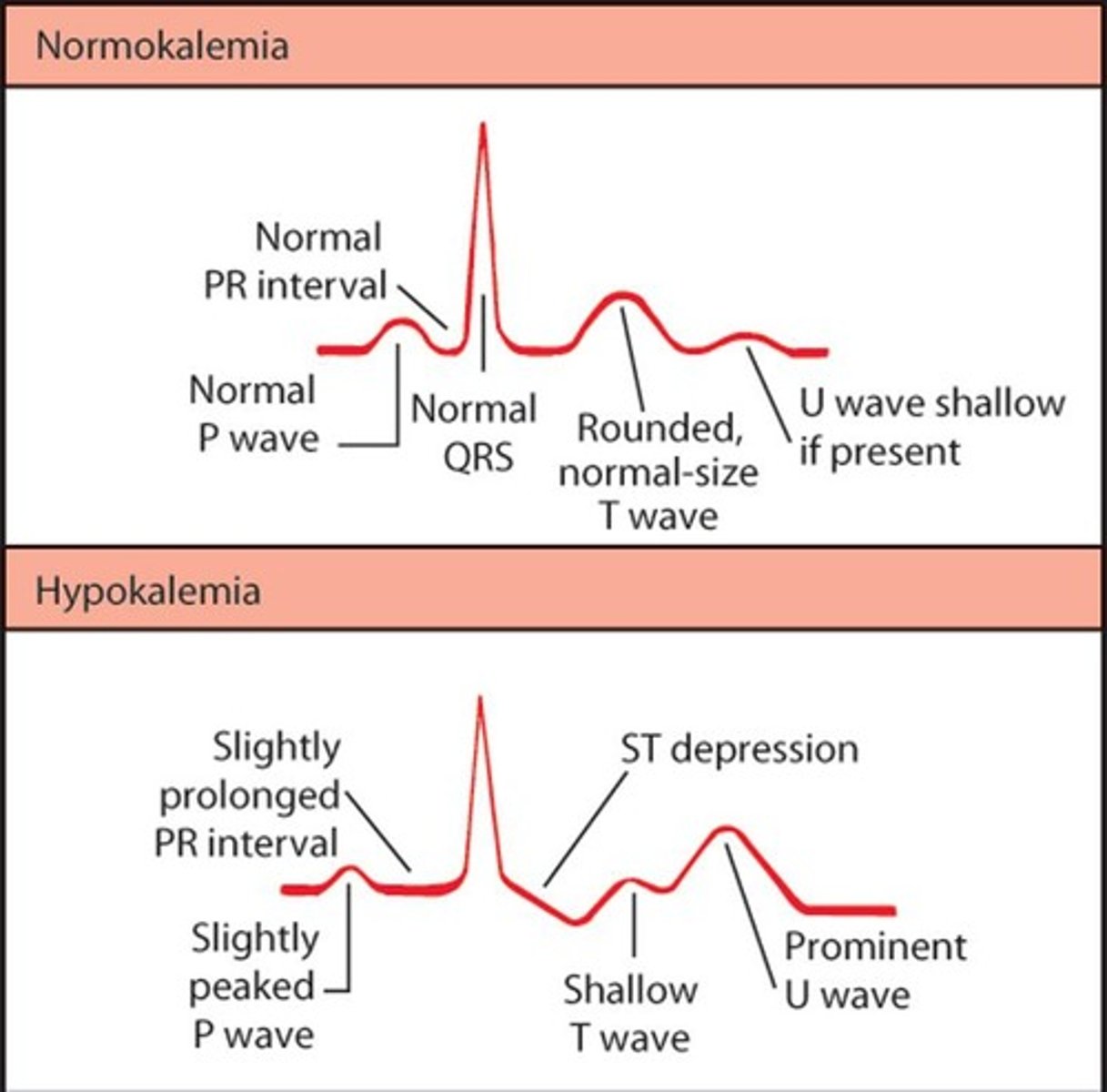
Treatment for Potassium Deficit
Replace potassium orally and/or intravenously; dietary sources include bananas, oranges, dried fruits, tomatoes, avocados, dried peas, meats, broccoli, dairy products, meat, whole grains, potato.
Signs of Potassium Excess (>5.0 mEq/L)
Causes: Increased intake, shift from ICF to ECF, decreased renal loss, metabolic acidosis, insulin deficiency, cell trauma. Manifestations: Mild attacks (tingling of lips and fingers, restlessness, intestinal cramping and diarrhea, peaked T-waves on ECG), severe attacks (muscle weakness, loss of muscle tone, paralysis).
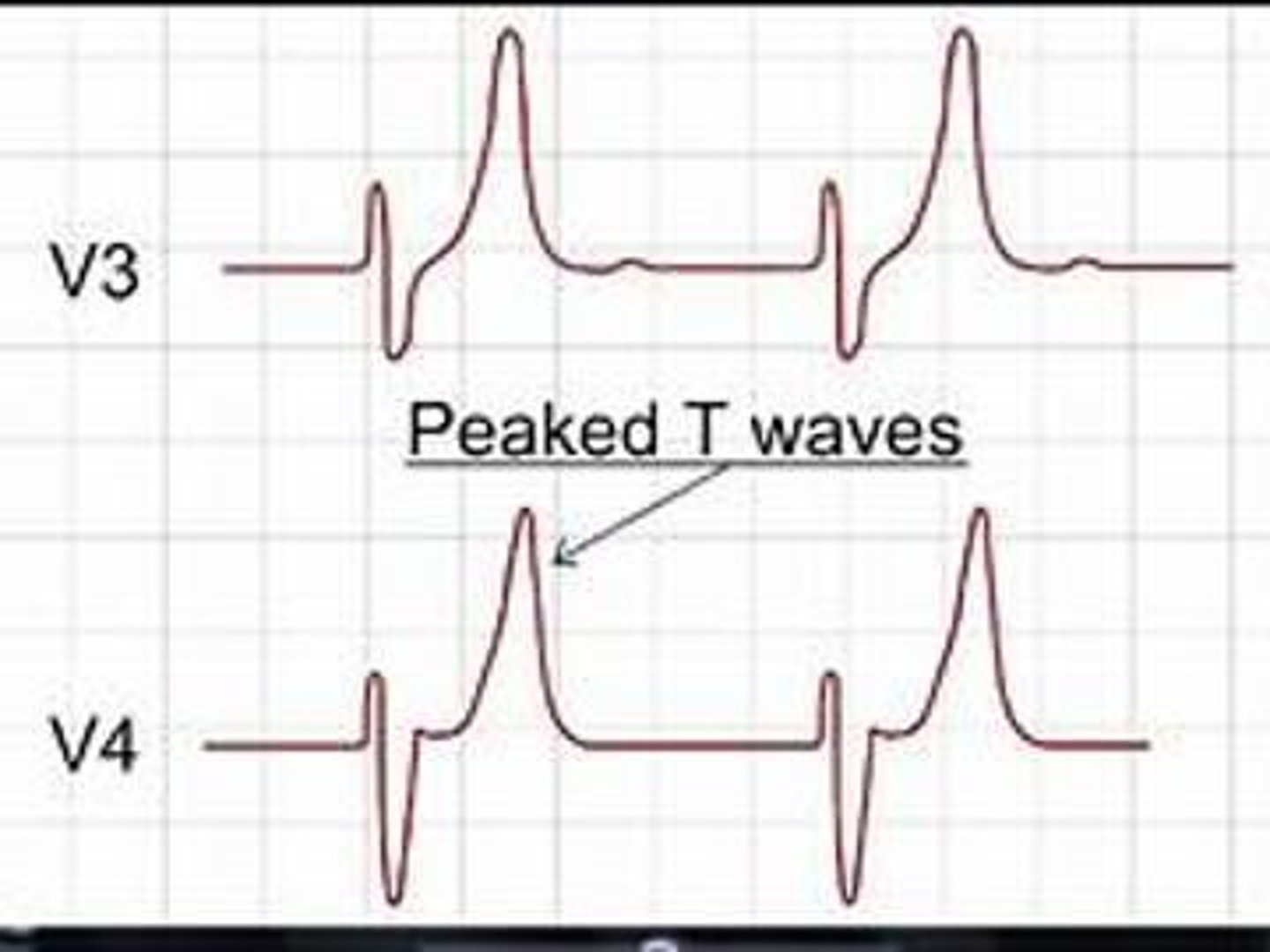
Treatment for Potassium Excess
Polystyrene sulfonate (kayexalate); if bowels do not work, limit dietary K+, calcium gluconate + insulin + buffered solution (bicarb), dialysis.
Normal pH
7.35-7.45
Abnormal pH
<6.8 & >7.8
Body Fluid Normal pH - Gastric Juices
1.0-3.0
Body Fluid Normal pH - Urine
5.0-6.0
Body Fluid Normal pH - Blood
7.35-7.45
Body Fluid Normal pH - Cerebrospinal Fluid
7.28-7.32
Body Fluid Normal pH - Pancreatic Fluid & Bile
7.8-8.0
Body Fluid Normal pH - Small Intestine
6.8-7.5
ABG - Arterial Blood Gas
Normal, acidosis, and alkalosis arterial blood pH levels are obtained through ABG sampling.
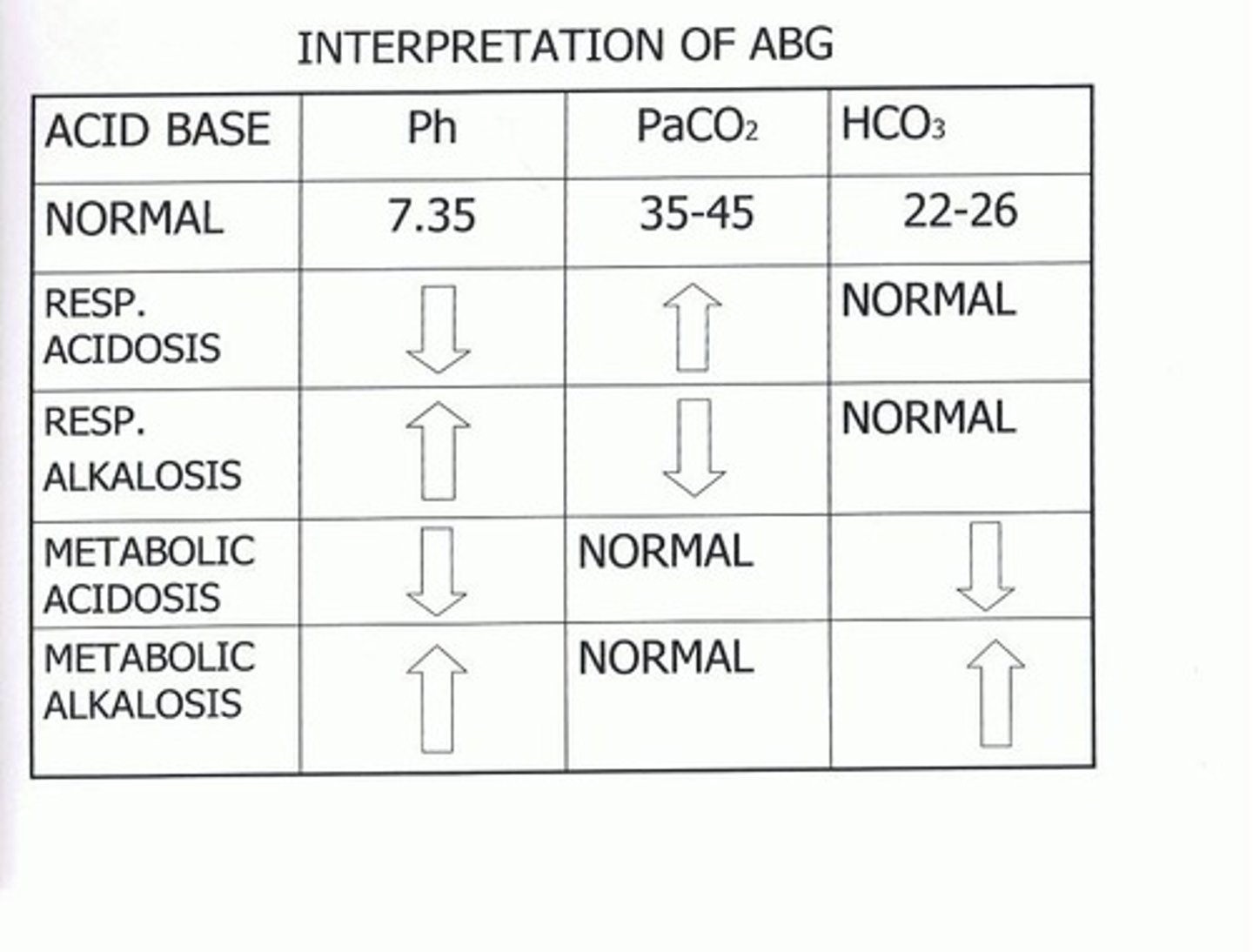
Acidosis
pH < 7.35
Alkalosis
pH > 7.45
Reading ABGs - CO2
If CO2 matches = Respiratory; High = acid/acidosis.
Reading ABGs - HCO3
If HCO3 matches = Metabolic; High = base/alkalosis.
Systems that help regulate acid-base balance
Bones, Lungs, Kidneys.
Lungs Function in Acid-Base Balance
Lungs can decrease carbonic acid by exhaling carbon dioxide; compensate in minutes to hours by increasing or decreasing ventilation.
Kidneys Function in Acid-Base Balance
Kidneys can reabsorb bicarbonate or regenerate new bicarbonate; compensate in hours to days by producing more acidic or alkaline urine.
Metabolic Acidosis
pH < 7.35, PaCO2: normal, HCO3 < 22mEq/L; causes include lactic acidosis, renal failure, diabetic ketoacidosis, diarrhea, starvation.
Treatment for Metabolic Acidosis
Buffering solution administration (sodium bicarb), treat underlying causes, correct sodium and water deficits.
Metabolic Alkalosis
pH > 7.45, PaCO2: normal, HCO3 > 26 mEq/L; causes include prolonged vomiting or gastric suctioning, excessive bicarbonate intake, hyperaldosteronism with hypokalemia, diuretic therapy.
Treatment for Metabolic Alkalosis
Sodium chloride, potassium, chloride IV (chloride replaces HCO3).
Respiratory Acidosis
pH < 7.35, PaCO2 > 45 mmHg, HCO3: normal; causes include depression of the respiratory center, respiratory muscle paralysis, disorders of the chest wall and lung tissue.
Treatment for Respiratory Acidosis
Restore adequate ventilation; may need mechanical ventilation, oxygen therapy.
Respiratory Alkalosis
pH > 7.45, PaCO2 < 35mmHg, HCO3: normal; causes include high altitudes, hypermetabolic state, early salicylate intoxication, anxiety/panic disorder.
Treatment for Respiratory Alkalosis
Paper bag (treats hypoxemia & hypermetabolic states).