AP Euro - Unit 5: Conflict, Crisis, and Reaction in the Late 18th Century (1648-1815)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Louis XV (r. 1715-1774)
Grandson of Louis XIV and king of France from 1715 to 1774 who led France into the War of the Austrian Succession and the Seven Years' War (1710-1774).
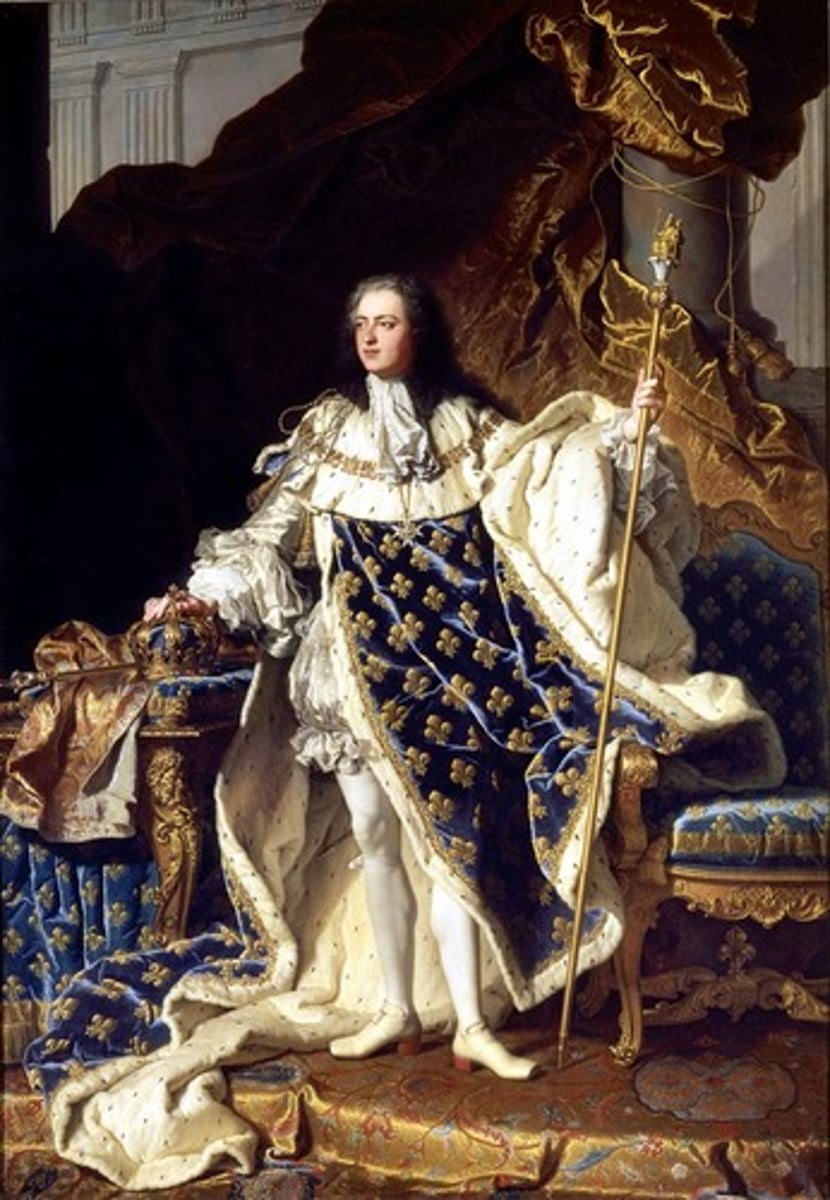

Louis XVI (r. 1774-1792)
King of France (1774-1792). In 1789, he summoned the Estates-General, but he did not grant the reforms that were demanded and revolution followed. Louis and his queen, Marie Antoinette, were executed in 1793.

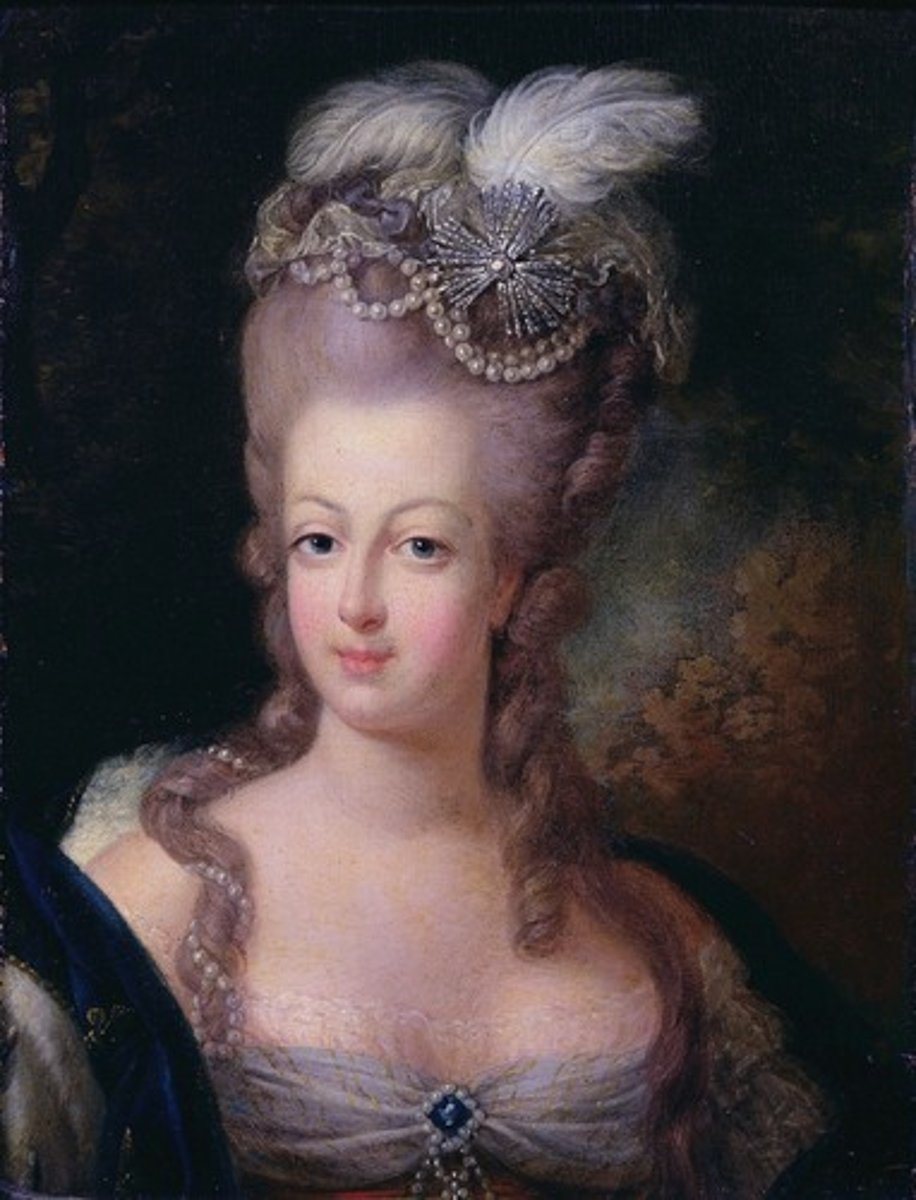
Marie Antoinette
Queen of France (as wife of Louis XVI) who was unpopular due to Austrian background, her extravagance and opposition to reform contributed to the overthrow of the monarchy; she was guillotined along with her husband.

Ancien Regime
The traditional political and social order in Europe before the French Revolution.
Estates General
A legislative body in prerevolutionary France made up of representatives of the three classes, or estates. It was called into session in 1789 for the first time since 1614.
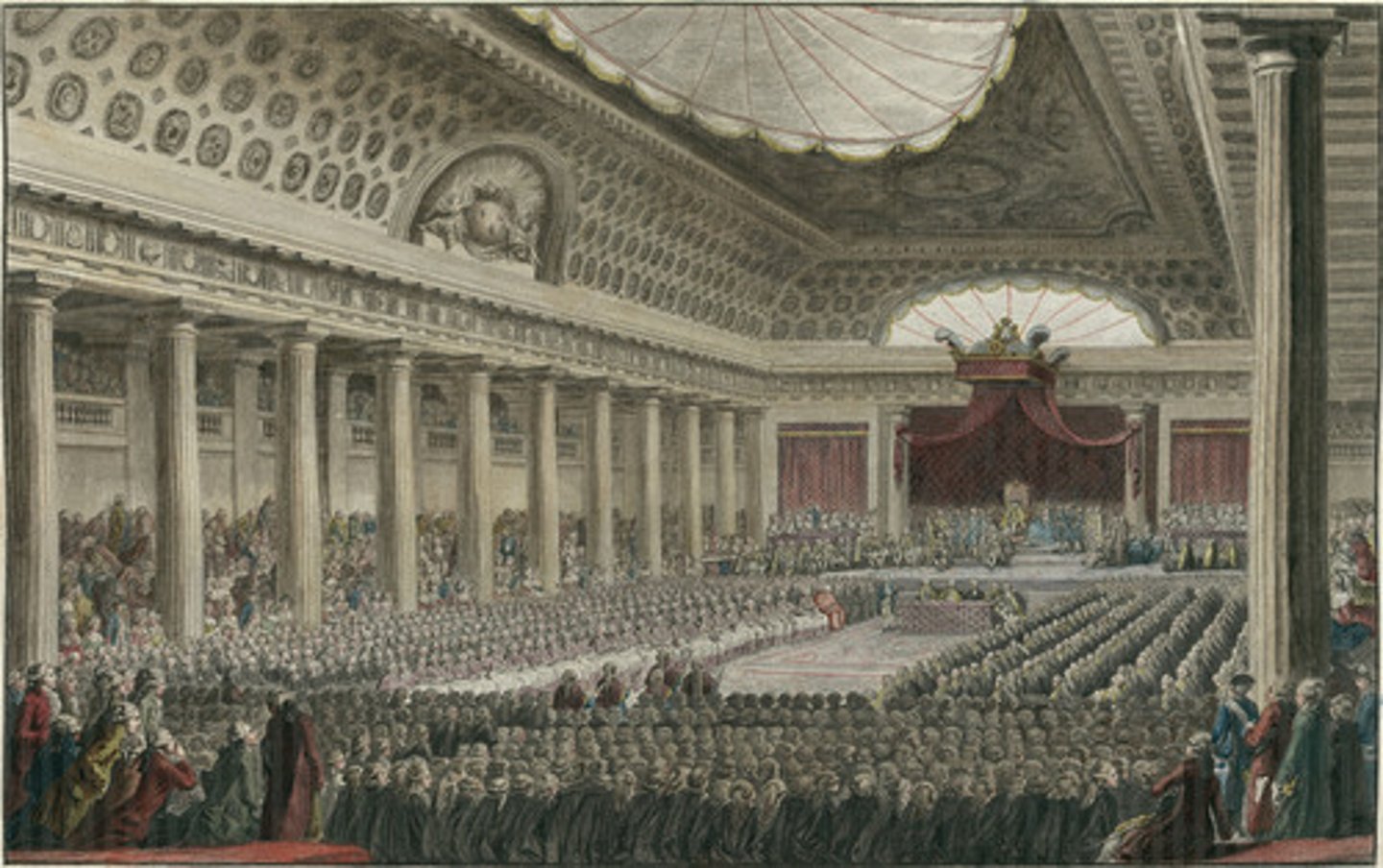
Estates
France's traditional national assembly with representatives of the three estates, or classes, in French society: the clergy, nobility, and commoners. The calling of the Estates General in 1789 led to the French Revolution.
National Assembly
The first French revolutionary legislature, made up primarily of representatives of the third estate and a few from the nobility and clergy, in session from 1789 to 1791.
Abbe Sieyes, What is the Third Estate?
An essay written at the time when the Assembly of Notables was called. It said "What is the Third Estate? Everything. What can it do politically? Nothing. What do they want? To be Something". Since the 3rd estate were not recognized political.
Tennis Court Oath (1789)
Oath taken by representatives of the Third Estate in June 1789, in which they pledged to form a National Assembly and write a constitution limiting the powers of the king.
Storming of the Bastille (July 14, 1789)
-events erupted into revolution
-crowd gathered outside the prison
-demand weapons
-commander fired on the crowd, killing many
-mob broke through
-freeing prisoners
-fall of the Bastille challenged the existence of the ancient régime
-Revolution Begins
Great Fear of 1789
A period of panic and riot by peasants and others amid rumors of an "aristocratic conspiracy" by the king and the privileged to overthrow the Third Estate.
Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen
Statement of fundamental political rights adopted by the French National Assembly at the beginning of the French Revolution.
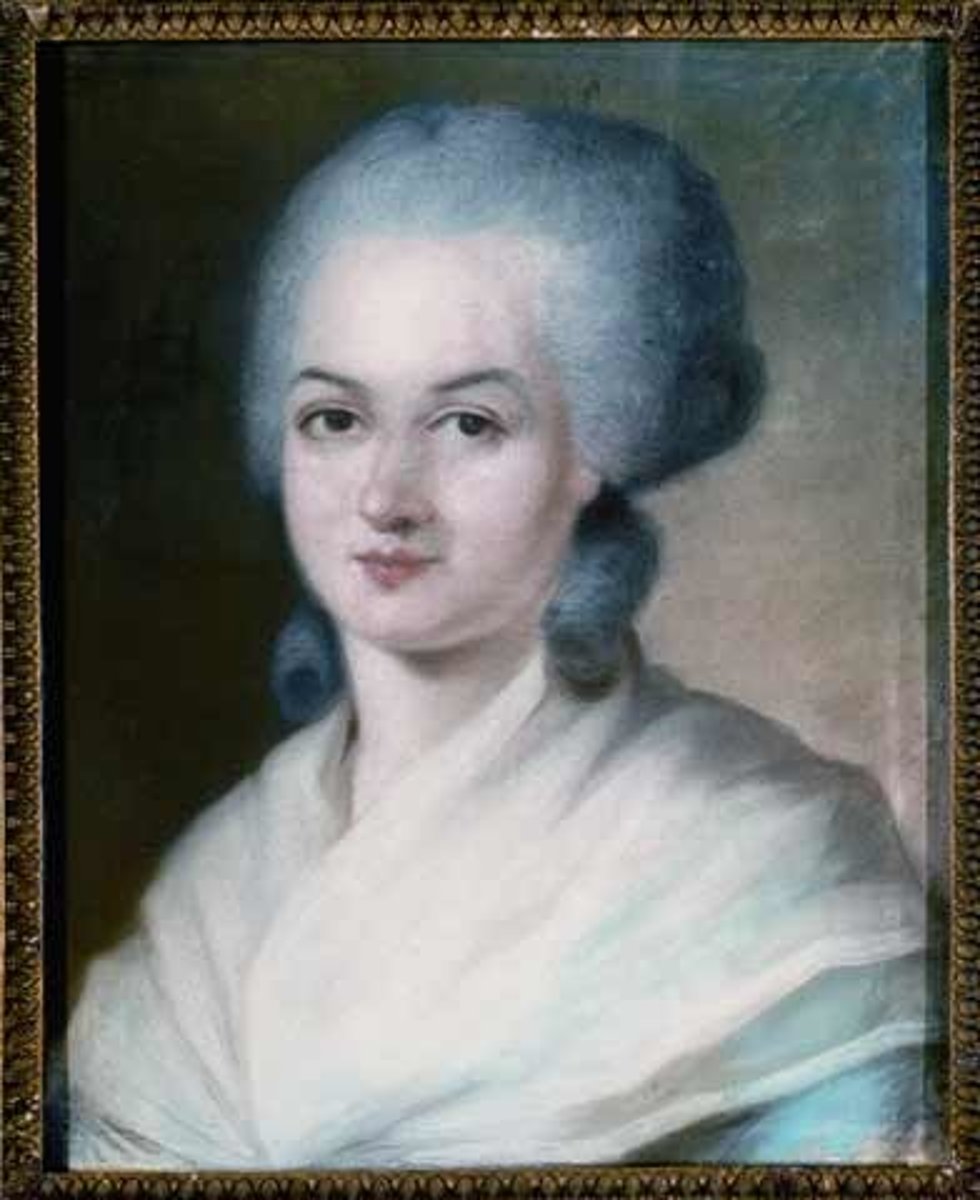
Olympe de Gouges (1748-1793)
A French feminist and reformer in the waning years of the Enlightenment who articulated the rights of women with her Declaration of the Rights of Woman and the Female Citizen (1791). Eventually executed during the French Revolution.

Civil Constitution of the Clergy, 1790
Established by National Assembly in dealing with issue of Church. Clergy to be elected by the 50,000 electors. Protestants, Jews and agnostics could take part. Number of diocese reduced from 130 to 83 and were to be coterminous with the new departements. No papal approval of appointments was necessary. State was to pay salaries. Abuses such as pluralism were ended. Significance - many did not approve and became counterrevolutionaries. Created big division. Left the Catholic laity terrified and puzzled. Many of peasantry were still devoutly catholic and found this aspect of revolution difficult to accept.
Vendee Revolt
During the French Revolution, the 1793- 1796 uprising in the Vendee, variously known as the Uprising, Insurrection, Revolt, Vendean Rebellion, or Wars in the Vendee, was the largest internal counter-revolution to the new Republic.
Jacobin Club
A political club in revolutionary France whose members were well-educated radical republicans.
Second Revolution
From 1792 to 1795, the second phase of the French Revolution, during which the fall of the French monarchy introduced a rapid radicalization of politics.
The National Convention, 1792
Declares France a republic and abolished the monarchy.
Brunswick Manifesto (1792)
Prussian Duke said that if the French royal family was harmed, Paris would be leveled- this branded the French royal family as traitors and caused the 2nd French Revolution.
Girondists
A moderate group that fought for control of the French National Convention in 1793.
The Mountain (Montagnards)
Led by Robespierre, the French National Convention's radical faction, which seized legislative power in 1793.
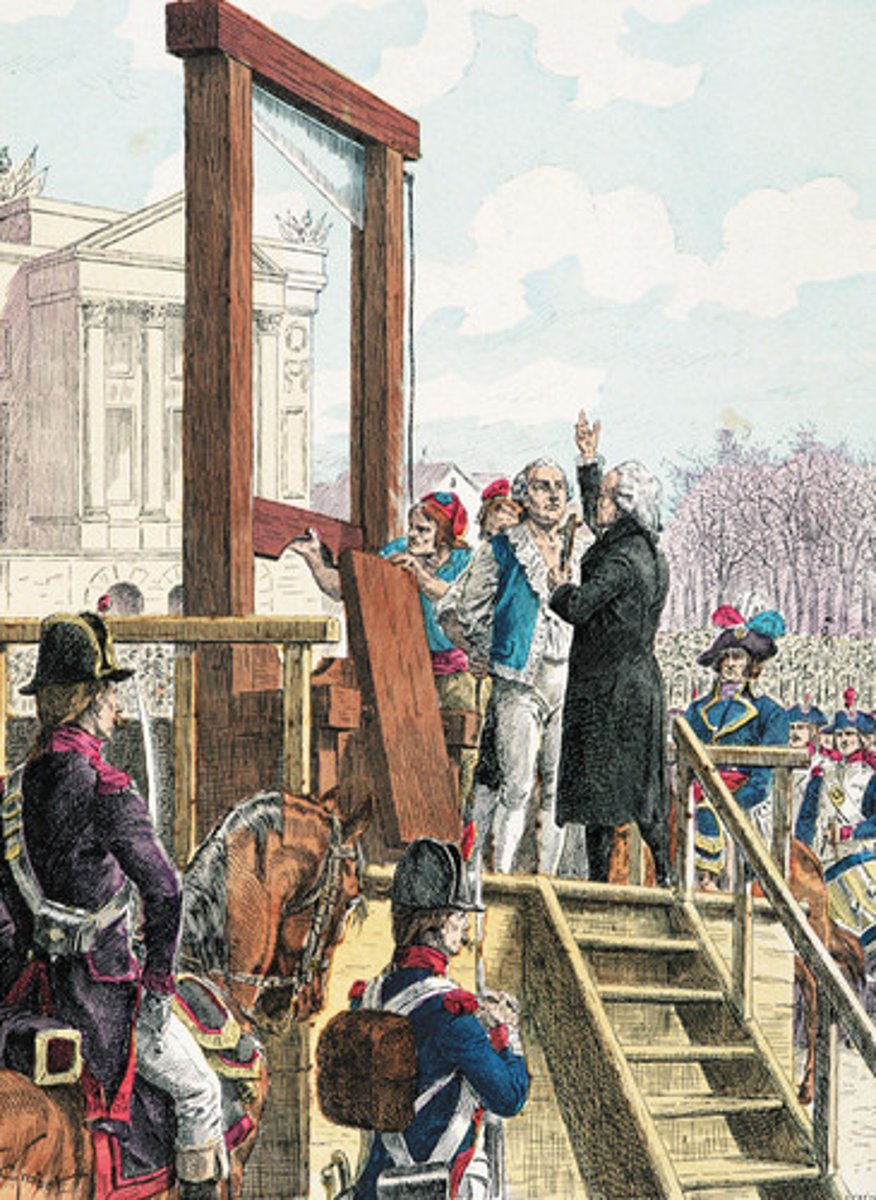
Maxmilien Robespierre
One of the most radical revolutionaries of the French Revolution. Leader of the French government that put King Louis XVI on trial. Created and ran the Reign of Terror.
Sans-Culottes
In the French Revolution, a radical group made up of Parisian wage-earners, and small shopkeepers who wanted a greater voice in government, lower prices, and an end of food shortages
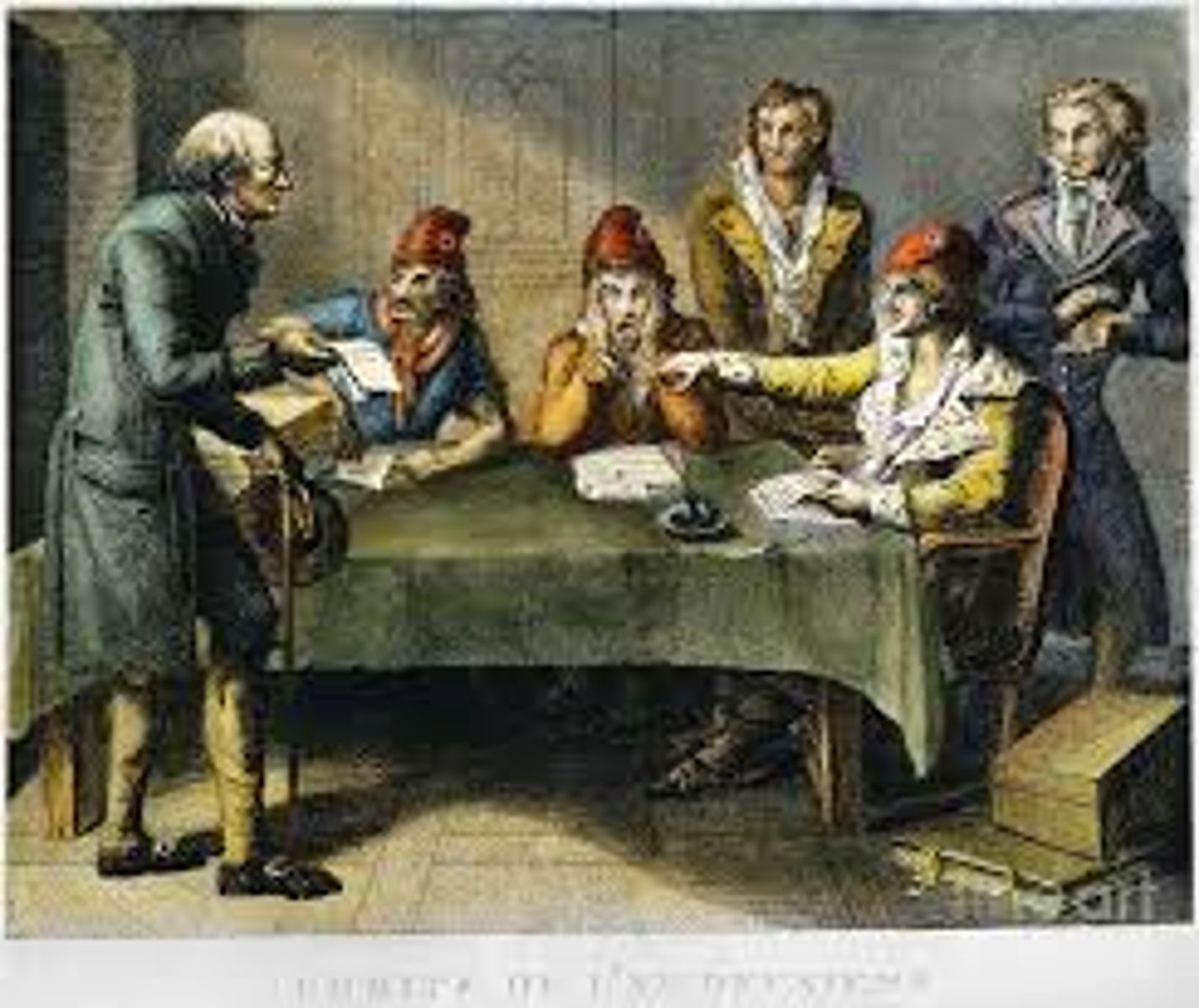
Reign of Terror
The period from 1793 to 1794 during which Robespierre's Committee of Public Safety tried and executed thousands suspected of treason and a new revolutionary culture was imposed.

Public Committee of Safety
Instituted by National Convention, killed anyone suspected of being against French Revolution, The Riegn of Terror, led by Maximilien Robespierre and Jacobins, used the guillotine.

Temple of Reason
The new name for the Cathedral of Notre Dame during the Radical Phase of the French Revolution.
Revolutionary Calendar
Created by the National Convention, it established after the French Revolution -day one was the first day of the French Republic
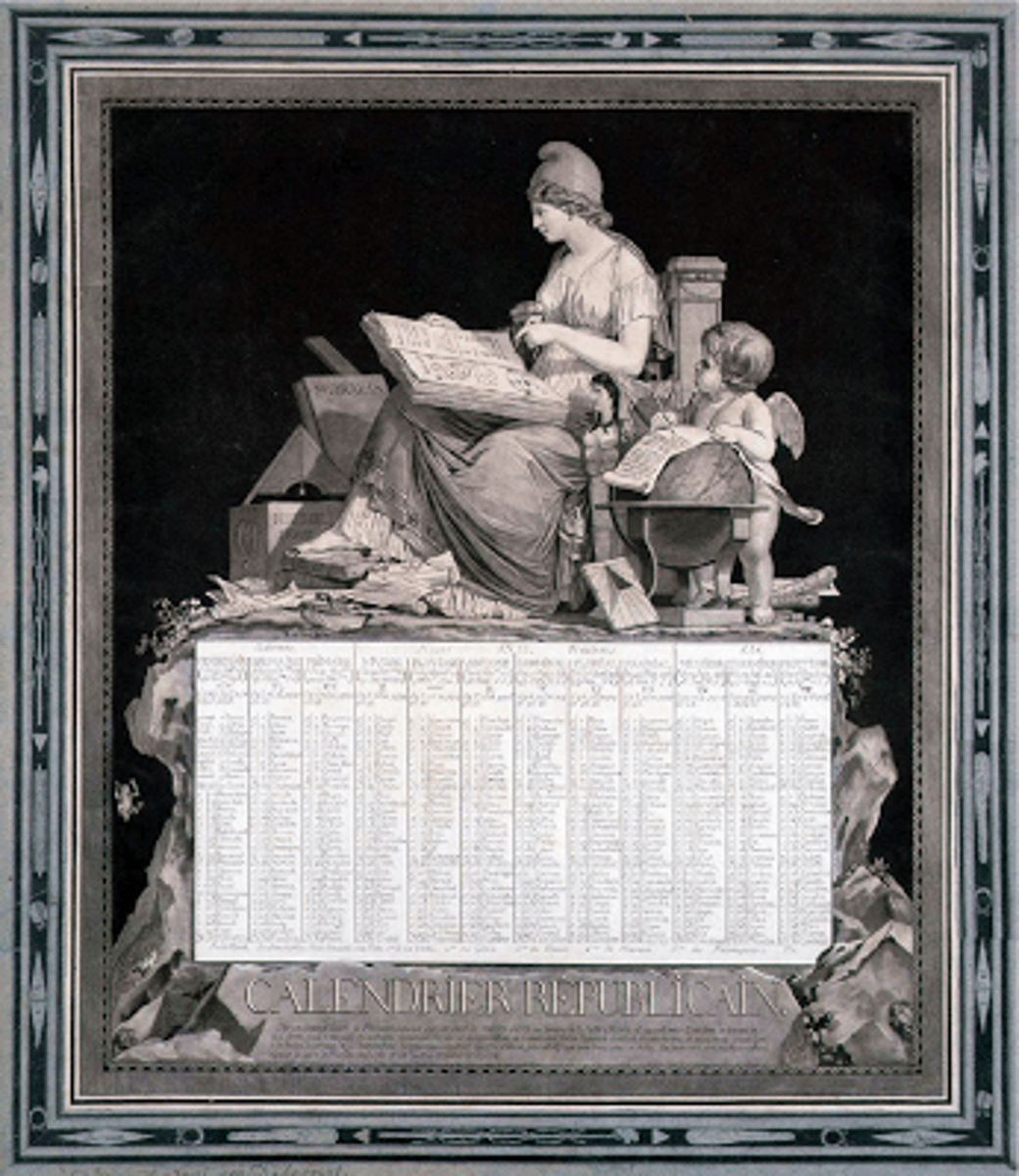
Thermidorean Reaction
A reaction against the violence of the Reign of Terror in 1794. Robespierre was executed and the loosening of economic controls.
The Directory
Established after the Reign of Terror / National Convention; a five man group as the executive branch of the country; incompetent and corrupt, only lasted for 4 years.
Napoleon Bonaparte
Overthrew the French revolutionary government (The Directory) in 1799 and became emperor of France in 1804. Failed to defeat Great Britain and abdicated in 1814. Returned to power briefly in 1815 but was defeated and died in exile.

Napoleonic Code (Civil Code)
French civil code created in 1804 that reasserted the revolutionary principles of the equality of all male citizens before the law and the absolute security of wealth and private property as well as restricting rights accorded to women by previous revolutionary laws.
The Consulate
Form of government which followed the directory -established by Napoleon-ended when Napoleon was crowned emperor.
Grand Empire
The empire over which Napoleon and his allies ruled, encompassing virtually all of Europe except Great Britain and Russia.
Continental System
Napoleon's policy of preventing trade between Great Britain and continental Europe, intended to destroy Great Britain's economy.
Napoleonic Wars
A series of wars fought between France (led by Napoleon Bonaparte) and alliances involving England and Prussia and Russia and Austria at different times (1799-1812).
Congress of Vienna
Following Napoleon's exile, this meeting of European rulers in Austria established a system by which the balance of power would be maintained, liberal revolutions would be repressed, as would imperial expansion, and the creation of new countries in Europe.
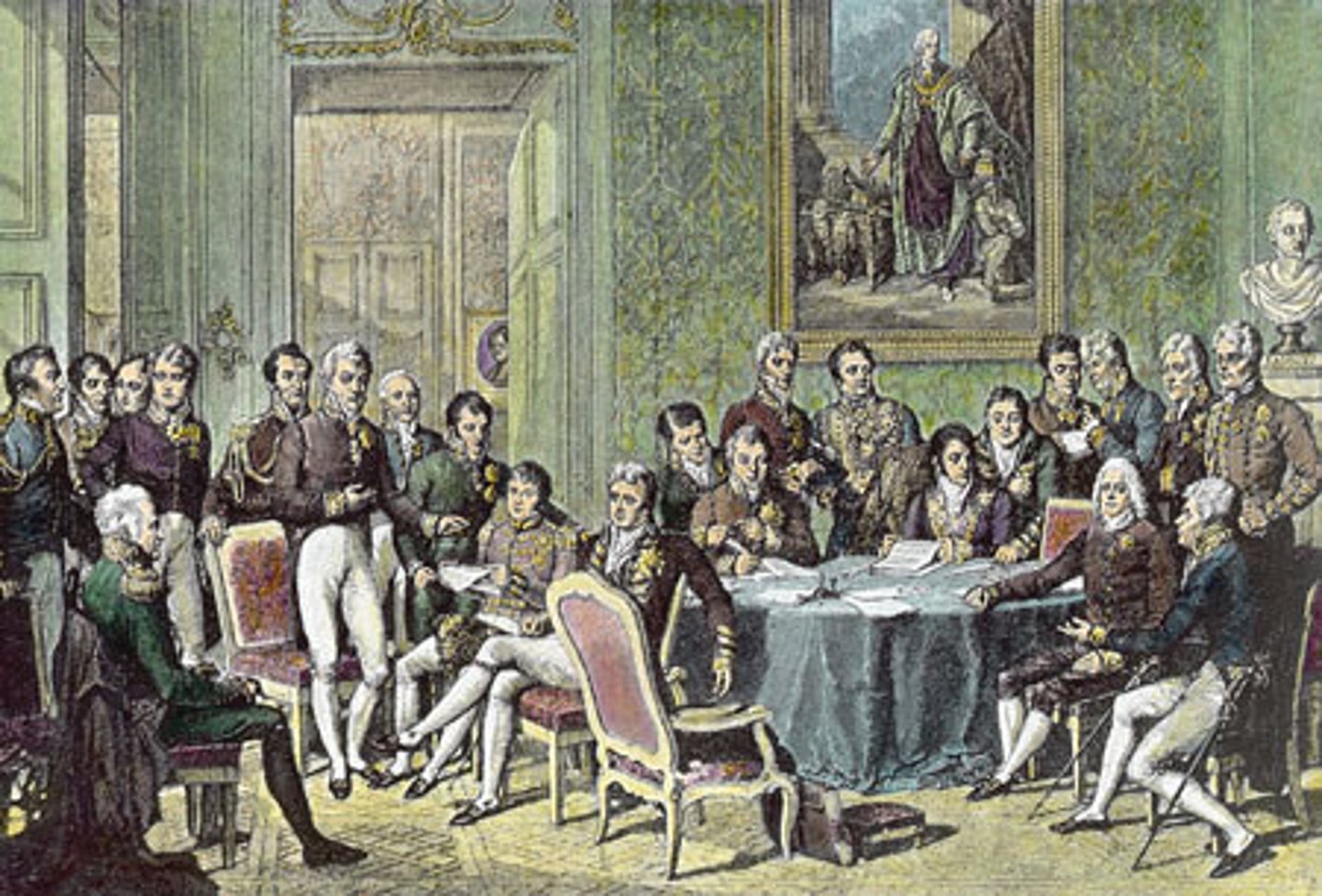
Klemens von Metternich
This was Austria's foreign minister who wanted a balance of power in an international equilibrium of political and military forces that would discourage aggression

Concert of Europe
A series of alliances among European nations in the 19th century, devised by Prince Klemens von Metternich to prevent the outbreak of revolutions.
Romanticism
An artistic movement at its height from about 1790 to the 1840s that was in part a revolt against classicism and the Enlightenment, characterized by a belief in emotional exuberance, unrestrained imagination, and spontaneity in both art and personal life.
William Wordsworth (1770-1850)
Major English Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romantic Age in English literature with the 1798 joint publication Lyrical Ballads.

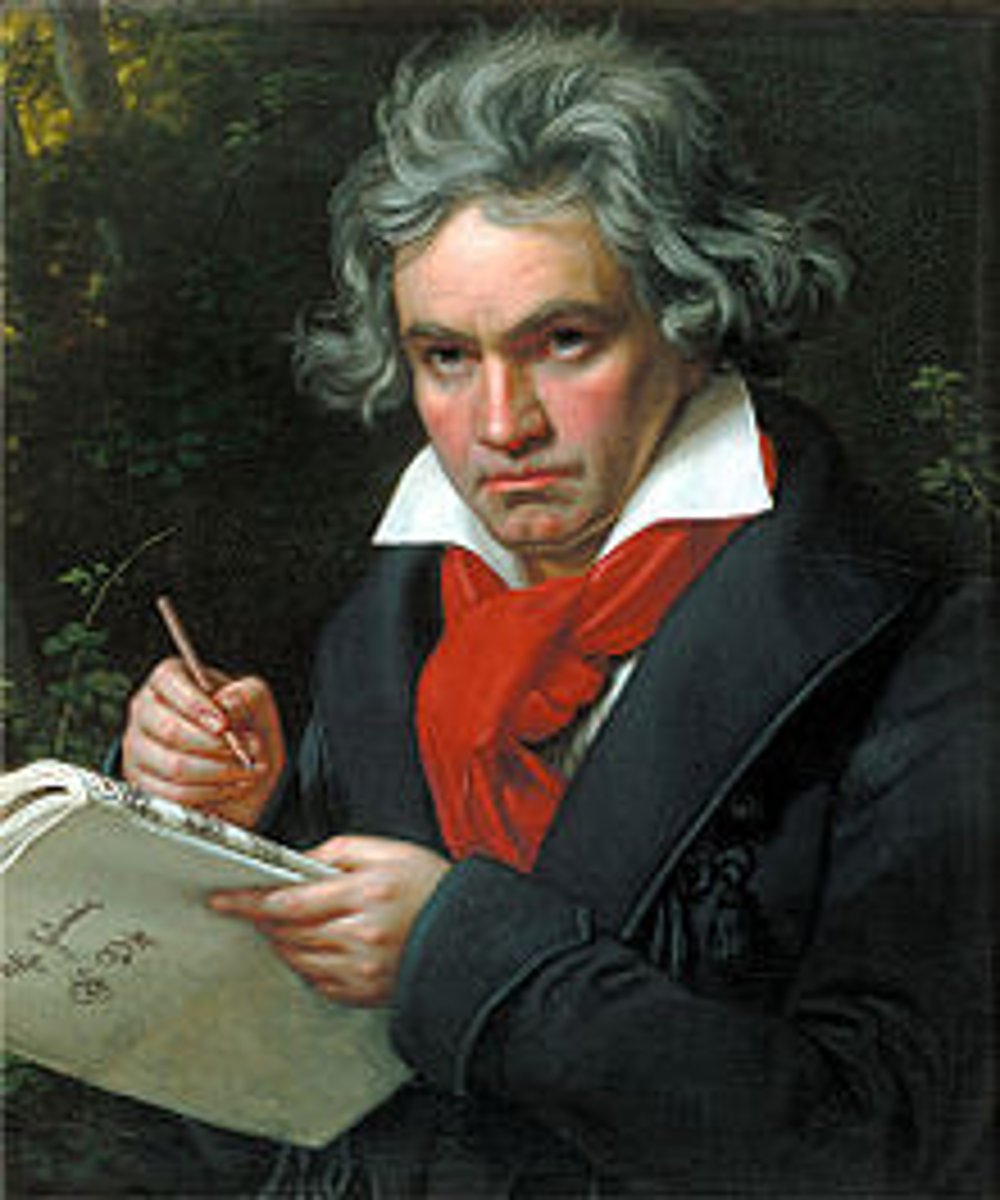
Ludwig van Beethoven (1770-1827)
This pianist was considered the master of Romanticism music.
