W4: chapter 12
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
DNA Organization in Chromosomes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
genetic material
responsible for passage of traits from parents → offspring
to do this, must be:
1) stable enough to store info for long periods
2) able to replicate accurately
3) capable to allow evolution
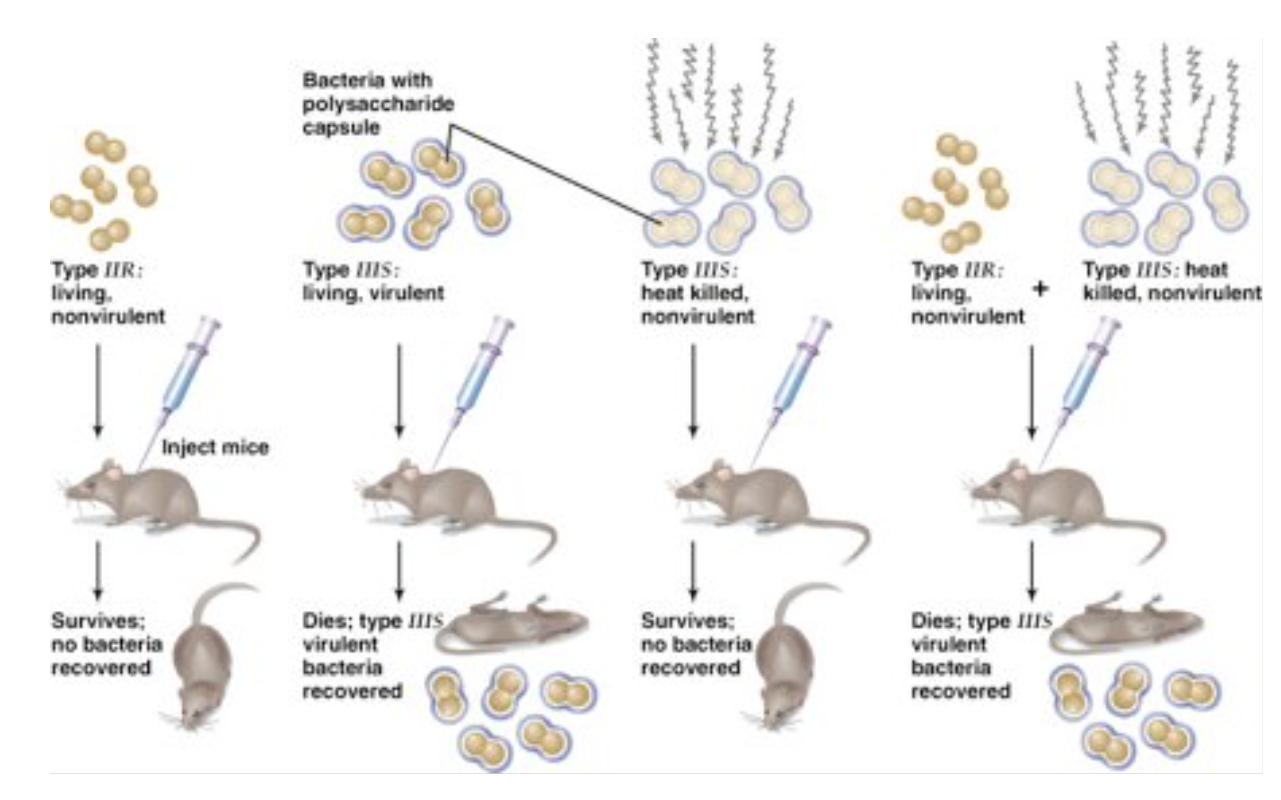
Griffith’s Transformation Experiment
1928 experiment w/ streptococcus pneumoniae in mice showed that something passed from dead bacteria → nearby living ones, allowing them to change their cell surface
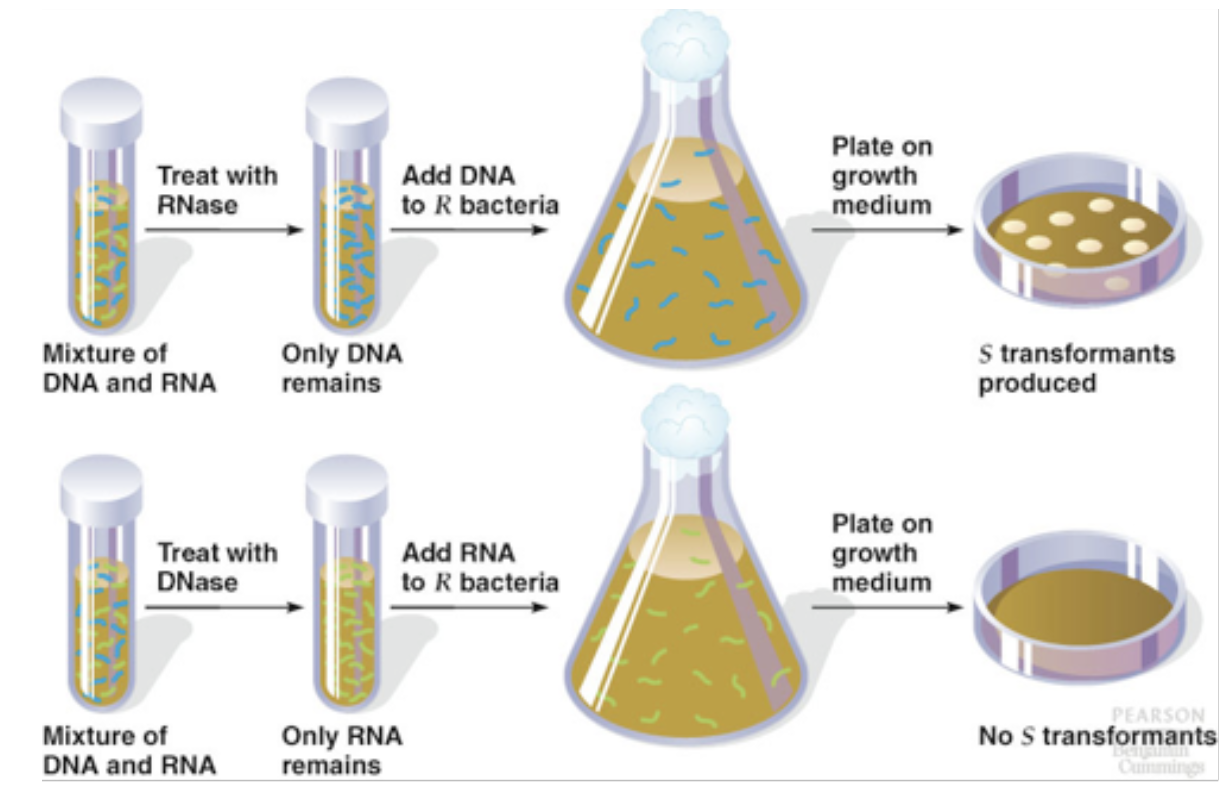
Avery’s Transformation Experiment
Broke open dead cells, chemically separate components (protein & NA), determine which was capable of transforming live S. pneumoniae cells
*only NA transformed bacteria
*supports DNA or RNA as genetic material NOT protein
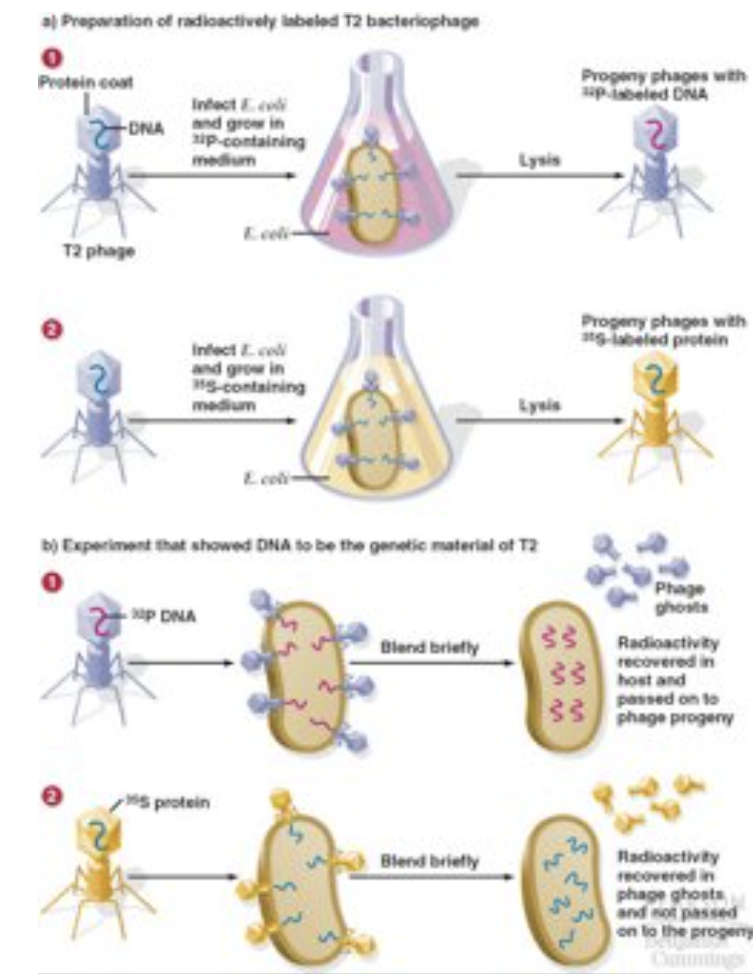
Hershey-Chase Bacteriophage Experiment
A 1952 experiment that used radioactively labeled bacteriophages to demonstrate that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material of viruses by showing that only DNA entered bacterial cells during infection.
*proving parents give DNA (genetic material) to offspring NOT protein to offspring
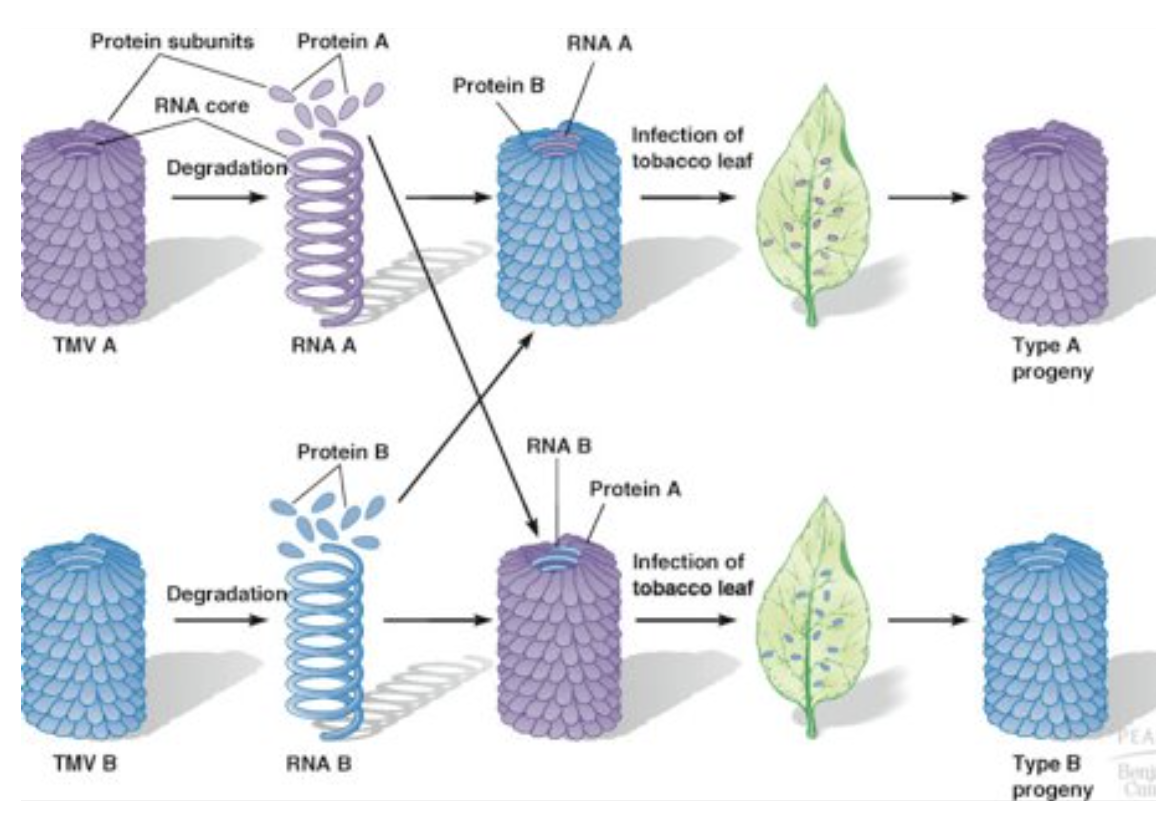
Grierer & Schramm
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) composed of RNA & protein
showed that when purified RNA from TMV directly applied to tobacco leaves → develop mosaic disease
*proves RNA can be genetic material NOT protein
composition & structure of DNA & RNA
monomers → nucleotides
phosphodiester linkage
nucleotide
pentose
N-base
phosphate group
pentose
DNA = deoxyribose
RNA = ribose
N-base
purines
pyrimadines
purines
A & G
dbl ring 9 membered
2 H bonds bt A & T → easier to break
pyrimidines
C, T, & U
1 ring 6 membered
(CUT PY)
3 H bonds bt C & G → harder to break
who discovered double helix?
Watson and Crick
Chargaff’s rule
States that in DNA, the amount of adenine equals thymine and the amount of guanine equals cytosine.
A - DNA
dehydrated form of DNA
B - DNA
what we talk abt
10 bp 1 turm
right-handed helix
Z - DNA
left - handed helix
existence in living cells not proven
viral chromosomes
NA, ds/ss DNA or RNA
circular or linear molecules
viral genetic material inert until released into host cell
able to package DNA into small volume
bacterial chromosomes
circular, ds DNA compacted into nucleoid
readily replicated & transcribed
plasmid = minor chromosome is dispensible to the life of the cell
both viral and bacterial chromosome (prokaryotes)
single NA molecule
largely devoid of associated proteins
much smaller than eukaryotic chromosome
contain less genetic info
topoisomerase
enzyme that cuts 1 or both strands of DNA
unwind/wind helix before resealing ends
chromatin
@ interphase → eukaryote chromosomes uncoil and decondense into chromatin
C value paradox
The C value paradox refers to the observation that the genome size (C value) does not correlate with the organism's complexity. It highlights how different species can have vastly different amounts of DNA that do not equate to the number of genes or organismal complexity.
histones
(+) proteins associated with chromosomal DNA in eukaryotes
types: H1, H2, H3, H4
contain large amounts of lysine and arginine
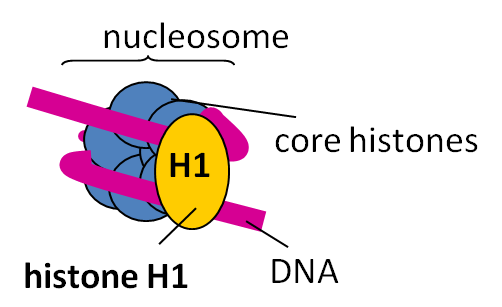
nucleosome
DNA wrapped around octomer of a histone
‘beads on a string’
C-banding
only centromere takes up stain
G-banding
differential staining along length of each chromosome
karyotype
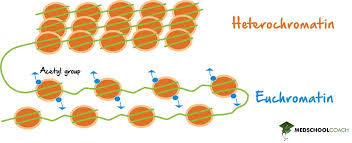
heterochromatin
condensed areas mostly inactive
lacks genes/repressed genes
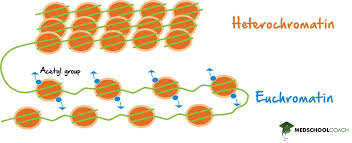
euchromatin
uncoiled and inactive