Enzymes - Chemistry 107
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Describe enzymes and their role in enzyme-catalyzed reactions
accelerate chemical reactions
lowers activation energy needed for the reaction to occur
What are the seven types of enzymes and what are their names?
Oxidoreductases - catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions
Transferases - transfer a functional group from one molecule to another
Hydrolases - break a chemical bond by adding a molecule of water
Lyases - break chemical bonds in a way that forms a double bond or adds a group to a double bond w/o the use of water
Isomerases - rearrange the atoms within a molecule to form an isomer
Ligases - join two molecules together to form a larger one, often with the use of ATP
Translocases - catalyze the movement of ions or molecules across a membrane
Describe the effects that changes of temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, and substrate concentration have on enzyme activity
Temperature affects the speed of molecules.
Low temperature - slow, high temperature - fast, too high causes denaturation, which creates a dramatic drop in activity. optimum temperature, the molecule is moving at maximum rate
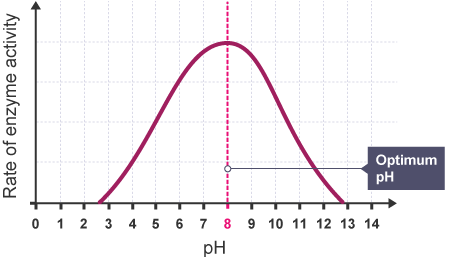
pH affects the activity of the enzyme
optimum pH - enzyme is most active, too high or too low - enzyme ceases all or most activity due to severely altered structure
Concentration determines reaction rate
high concentration - faster reaction rate (if substrate is in sufficient amount)
Substrate also determines reaction rate
Has a saturation point where it will reach its maximum, and adding any more substrate will not increase the reaction rate.
Describe the role of allosteric enzymes, feedback control, and covalent modification in regulating enzyme activity
Allosteric enzymes