Fetal Pig Practical
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
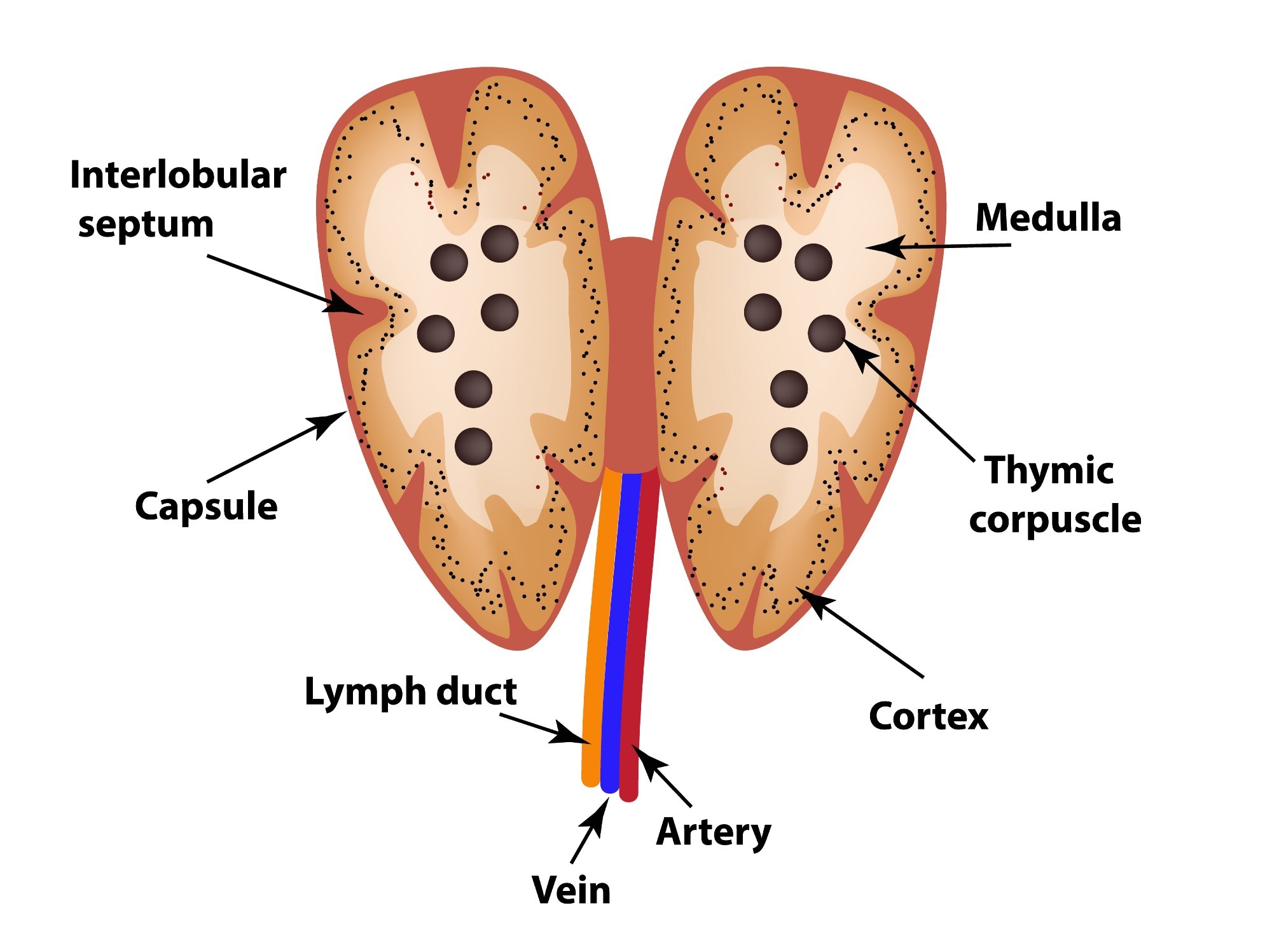
Thymus gland
production & maturation of immune cells
Thyroid gland
produces & releases hormones

Esophagus
transport food from the mouth to the stomach

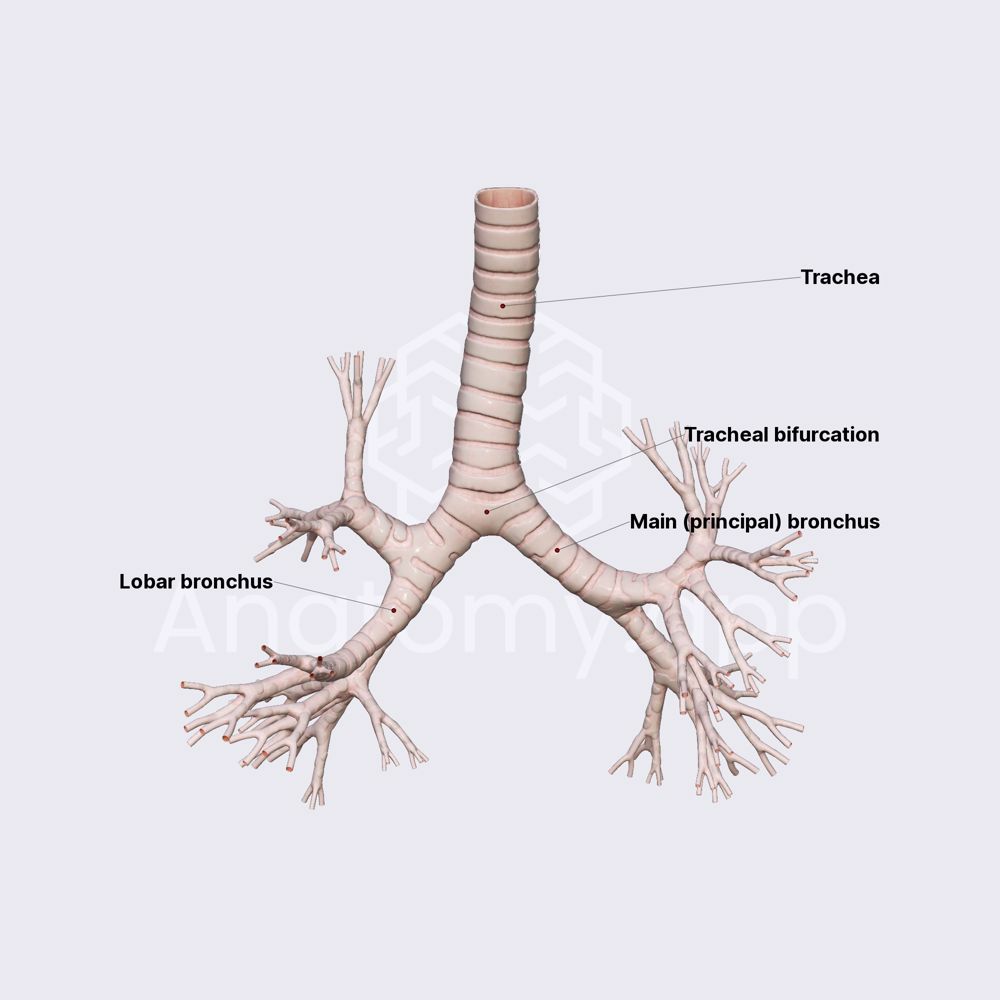
Trachea
transport air from the nasal cavity to the bronchi
Larynx
produce sound & protect the lower respiratory tract from food
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/human-larynx--illustration-1190674300-4ce616b410ea488ab61b6fca58fc992b.jpg)
Kidney
remove waste products from the blood and produce urine

Pleural cavity
protects and produces optimal function of the lungs

Umbilical cord
transports nutrients from the mother to the fetus

Thoracic cavity
protects & houses chest organs & tissues (ex: lungs & heart)

Pericardial sac
reduces friction & protects the heart w/ main vessels

Bronchi
carry air into lungs
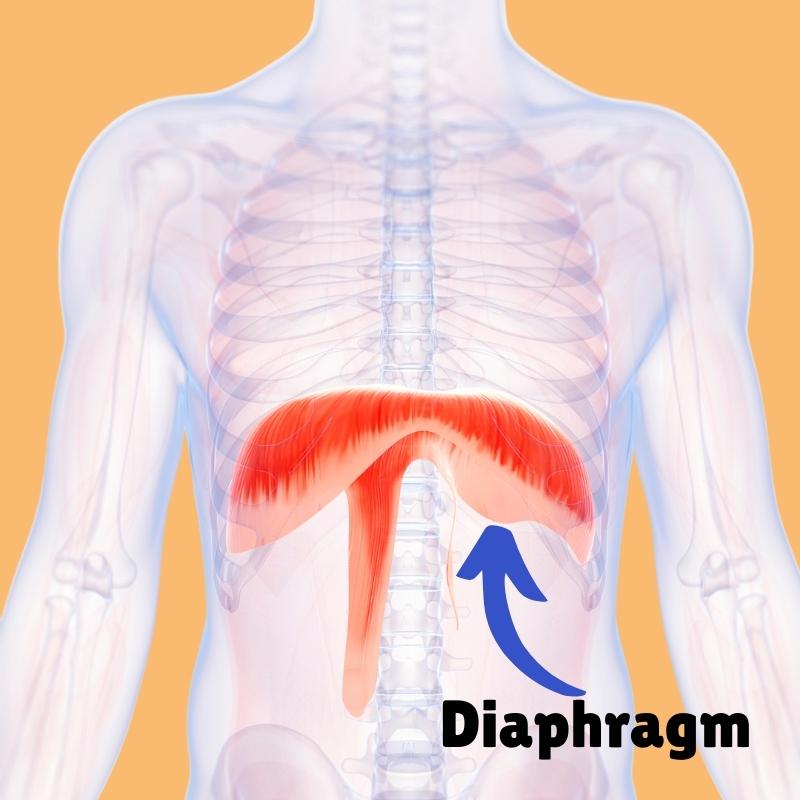
Diaphragm
respiration muscle, aids in breathing
Abdominal cavity
house vital organs of the digestive, urinary, endocrine, exocrine, circulatory, and parts of the reproductive system
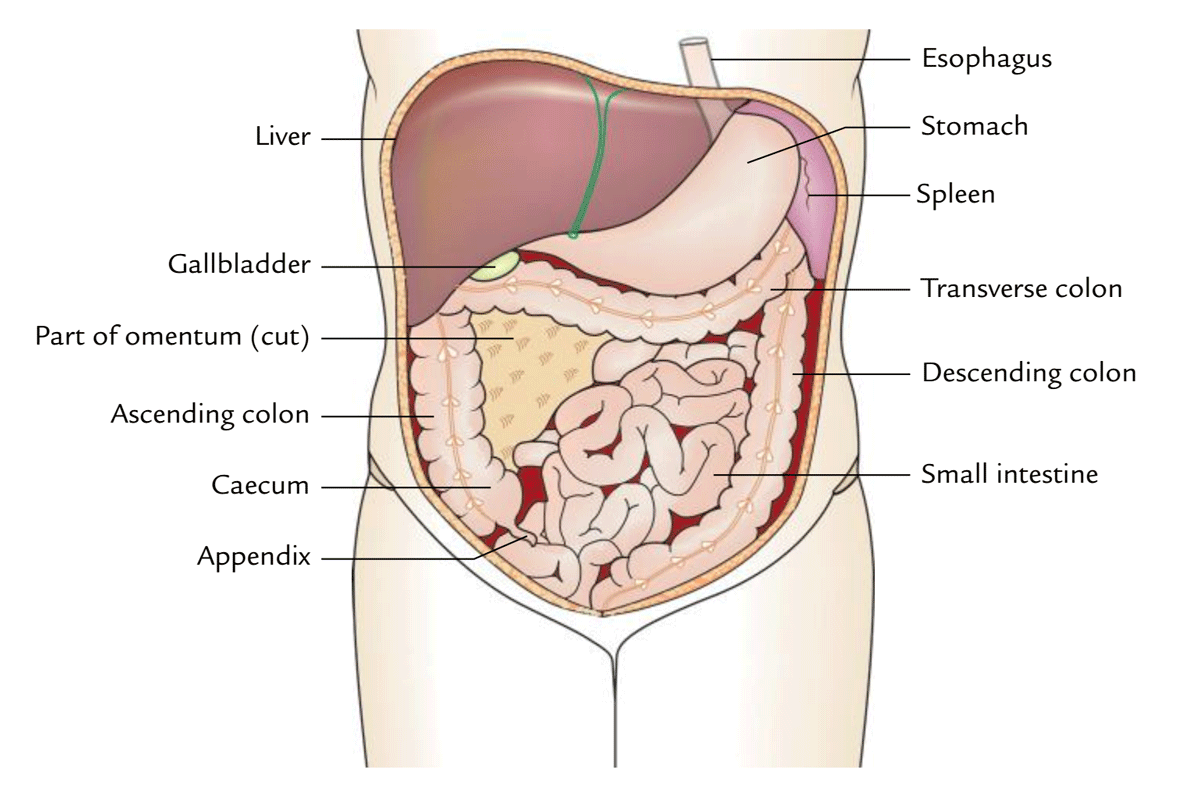
Cecum
store food where bacteria can break down cellulose
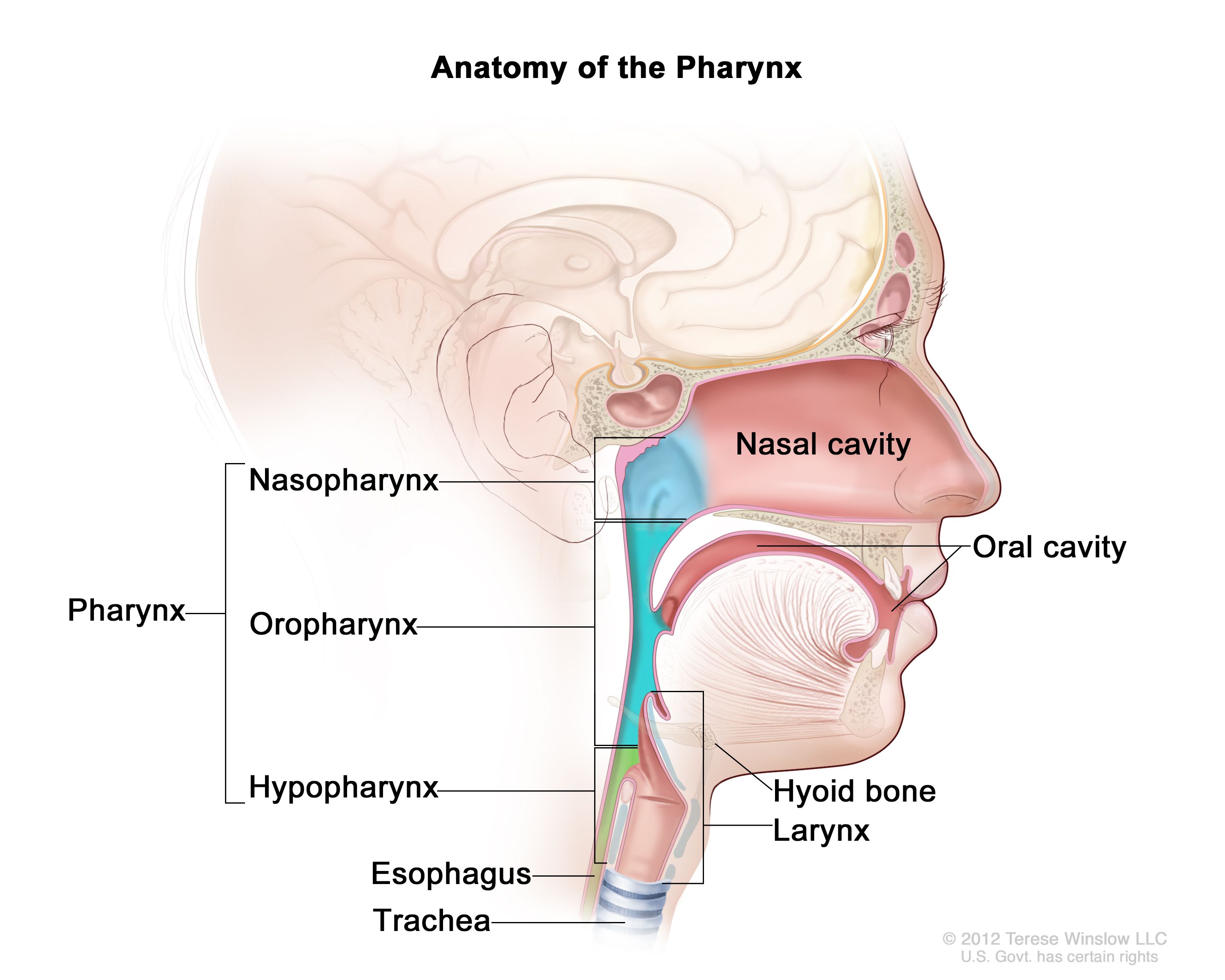
Pharynx
passageway for air to enter the larynx and lungs and food and liquid to enter the esophagus
Liver
filters blood & removes pathogens
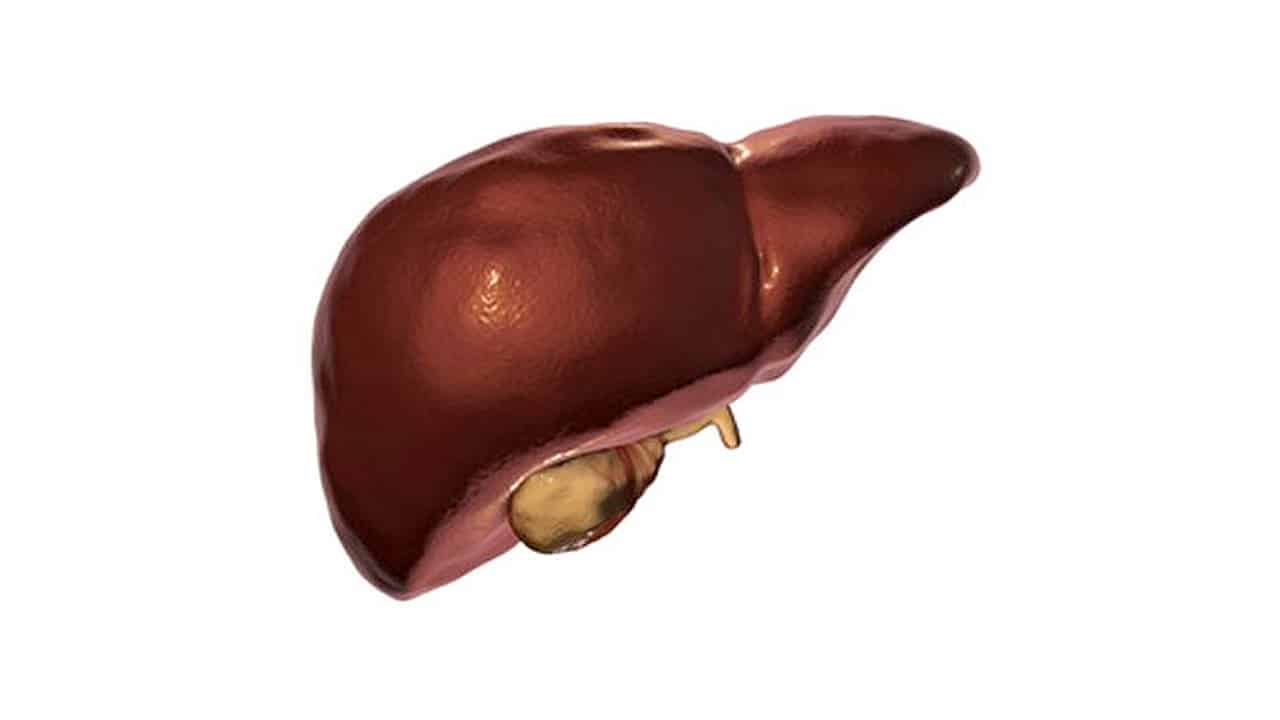
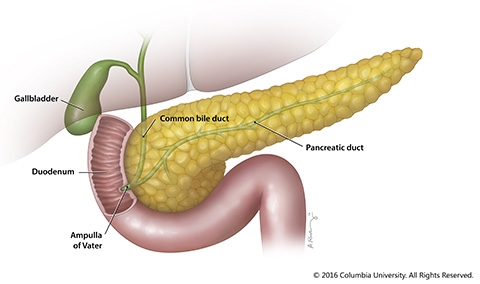
Gallbladder
stores and concentrates bile from the liver

Duodenum
helps to further digest food coming from the stomach
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-585996538-b7755be0a8e849ff93b516e8aa43bfc4.jpg)
Pancreas
produces enzymes that help to digest food, particularly proteins
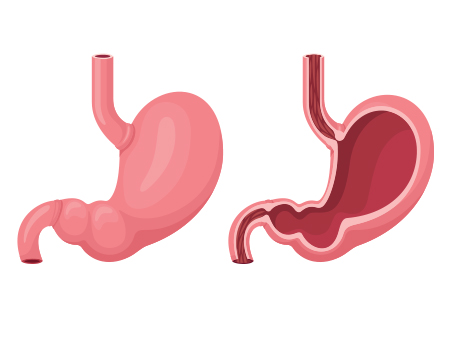
Stomach
holds the food and mixes it with acid and enzymes that continue to break the food down into a liquid or paste
Lungs
take in O2 for the body while getting rid of CO2
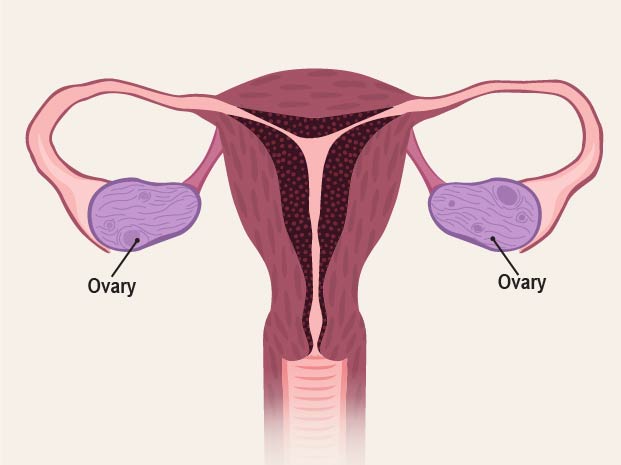
Ovaries
produce eggs for fertilization and they make the hormones estrogen and progesterone
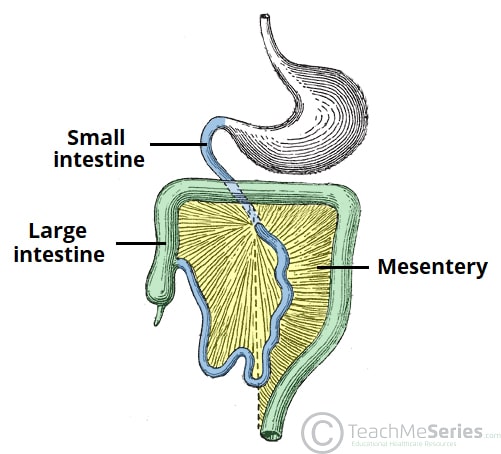
Mesenteries
keeps your intestines in place, preventing it from collapsing down into your pelvic area
Villi
absorb nutrients, increase SA of small intestines
Small intestines
further digests food from stomach
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-GettyImages-1435918094-48e2c5ec776d4ae8a938ba6338801846.jpg)
Large intestines
absorbs water, forms fecal matter
Rectum
expell feces

Spleen
filters your blood, removes waste products and produces white blood cells to fight infections
Scrotal sacs
protects testes
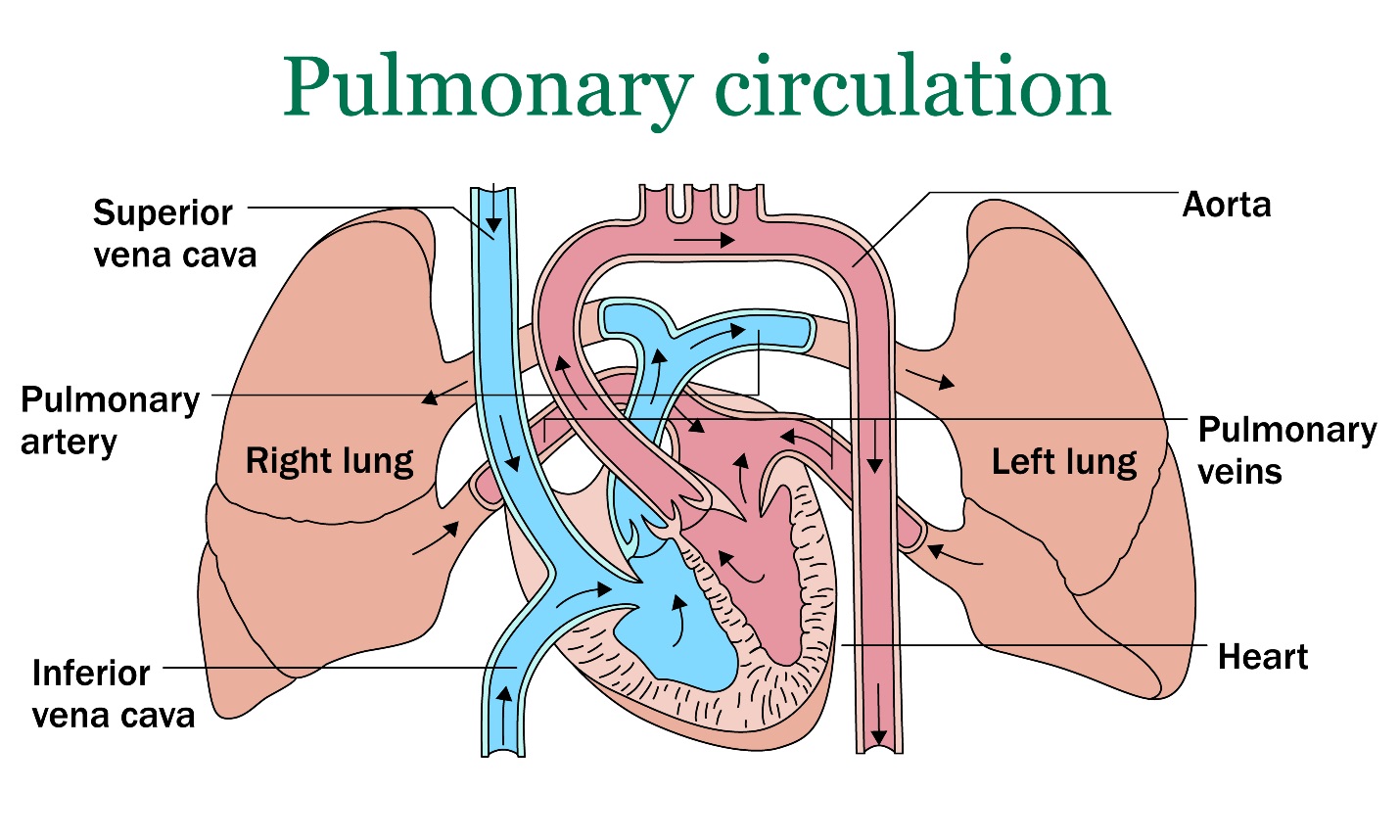
Pulmonary/Systemic system
move fresh air into your body while removing waste gases

Right/left atrium
receives blood into the heart and drives it into a ventricle, or chamber, for pumping blood away from the heart

Anterior (superior) vena cava
deliver oxygen-depleted blood from the head and upper body to the right side of the heart
Posterior (inferior) vena cava
carries blood from the torso and lower body to the right side of the heart

Right/left ventricle
receive blood from the heart's upper chambers (atria) and pump it to the rest of the body
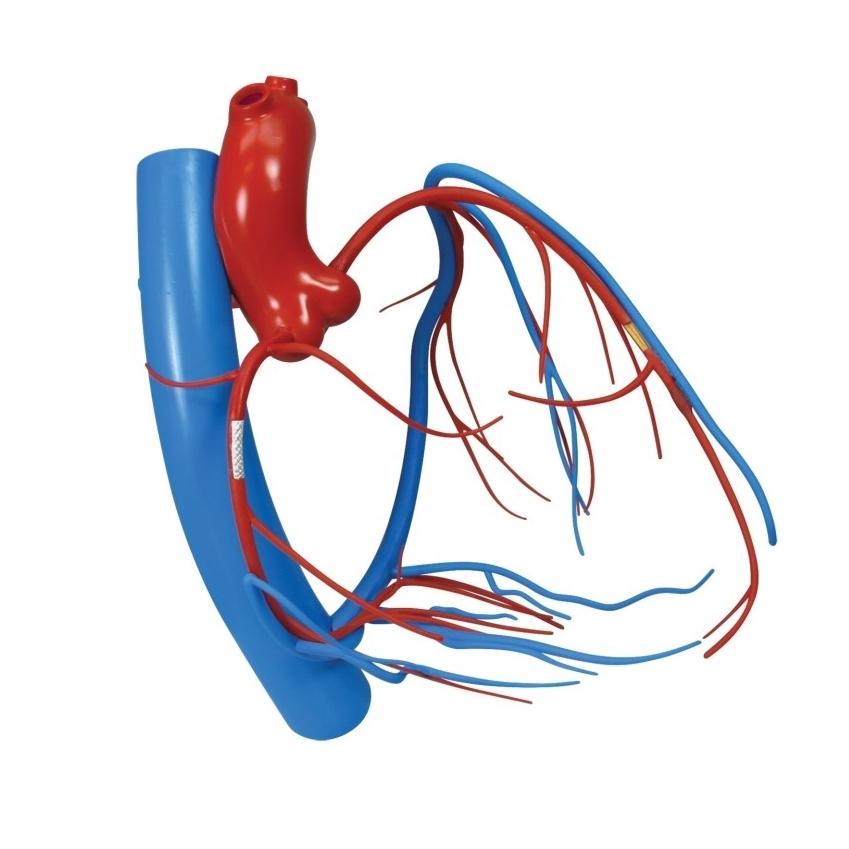
Pulmonary trunk
carry blood from your heart to your lungs
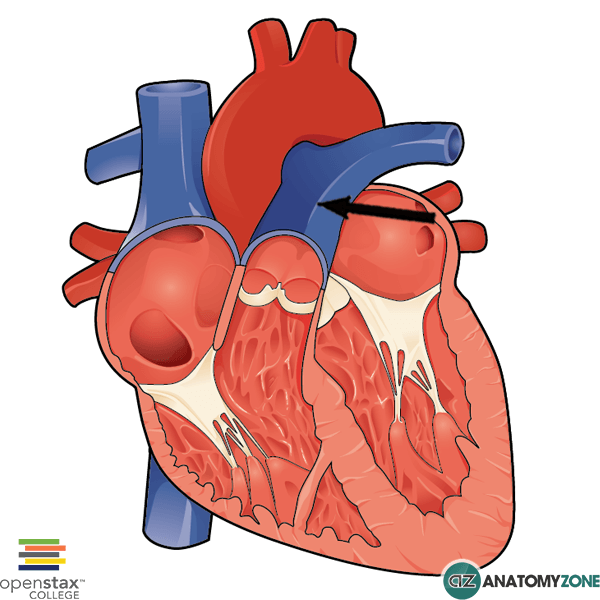
Pulmonary artery/vein
carry oxygen-poor blood from your heart to your lungs & carry oxygenated blood back to the heart
Foramen ovale
connects the atriums to allow blood to circulate through the fetus w/o going to the lungs first

Ductus arteriosus
connects the aorta to the pulmonary artery in a fetus to prevent blood from going to the lungs

Aorta
transporting oxygen rich blood from your heart to the rest of your body

Coronary artery/vein
provide the main blood supply to the heart