SAM Exam 5 -Ophthalmology
1/112
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Reflex Testing
PLR: CN II (A) + III (E)
Direct: Pupil constricts in the same eye exposed to light
Consensual: Pupil constricts in the opposite eye
Dazzle: CN II + VII + brainstem
Indicates intact retina
Useful even when the animal is blind
Menace: CN II (A)+ VII (E) + retina + brainstem + cortex
Do not use a closed hand
Normal: blink or avoidance movement, Positive at 20/400
Absent: puppies or cortical blindness
Corneal: CN V (A) + VII (E) + VII (E)
Use a wisp of cotton to touch corneal center
Normal: globe retraction + blink
Palpebral: CN V (A) + CN VII (E) + brainstem
Test with brisk touch at medial/lateral canthus
Swinging Light: Detects Marcus-Gunn pupil (RAPD)
Pupil dilates when light swings to affected eye
Visual Field Testing
Light Maze Test (Photopic)
Why: Evaluates cone function (day vision).
How: Performed under normal room lighting.
Results:
Normal: Moves confidently, avoids obstacles.
Abnormal: Hesitant, bumps into objects
Dark Maze Test (Scotopic)
Why: Evaluates rod function (night vision)
How: Performed in dim or dark lighting.
Results:
Normal: Navigates well, minimal hesitation.
Abnormal: Disoriented, collides with obstacles
Cotton Ball Test: Drop a cotton ball silently → check visual tracking
good for dogs, cats often ignore
tear Tests
Schirmer Tear Test (STT)
Why: Measures tear production
Results:
Normal: >15 mm/min
Abnormal: <15 mm/min = KCS
Tear Break-Up Time (TBUT)
Why: Evaluates tear film stability, quality of tears
How: Apply fluorescein dye to cornea and measure time until tear film breaks (dry)
Results:
Normal: >20 seconds
Abnormal: <10 seconds
Nasolacrimal Testing
Irrigation Test
Why: Confirms nasolacrimal duct patency
How: Cannulate punctum and flush with saline or fluorescein solution
Rx: topical anesthesia
Antegrade: all species.
Retrograde: large animals.
Results:
Patent: Fluid exiting opposite punctum or nose
Obx: Reflux through same punctum
Jones Test
Use: Confirms flow of Nasolacrimal System
but not full patency
How: Fluorescein stain
Ocular Stains
Rose Bengal Stain
Why: Detects devitalized or stressed epithelial cells
KCS, viral keratitis, or fungal keratitis
How: use topical anesthetic before application
Causes mild irritation
Results: Positive = Stains damaged cells and mucin-deficient areas
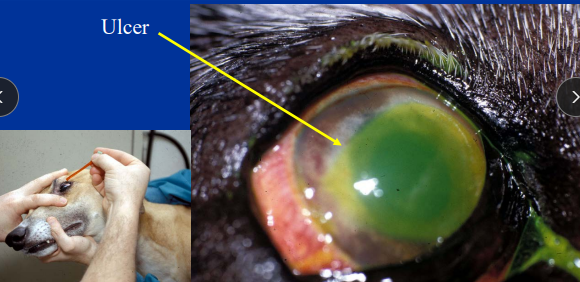
Fluorescein stain
Why: detects ulcers, TBUT, nasolacrimal drainage, Seidel’s test, tear break up time
Normal dog/cat: 15-25mm
Cat: <5-10mm = issues
Result:
Positive: corneal ulcer
exposed corneal stroma
Negative: intact epithelium or Descemet’s membrane
Topical Ocular Anesthetics
Rx: Proparacaine 0.5%
Onset: rapid onset 15-20 sec
DOA: 15-20 min
Prolonged use:
Decreased effectiveness
Delayed corneal healing
Corneal erosions and keratitis
Tonometry
When: Any red/cloudy or painful/blind eye, Breeds that are
predisposed, history of glaucoma in the opposite eye, any medically controlled glaucoma cases, abnormal pupils!!
Why: IOP, glaucoma, uveitis
Only one
Pressure on inner cornea = pressure on retina
Tools:
Indentation (Schiotz): Requires anesthesia, less precise, unreliable - indention
Applanation (Tono-Pen): requires anesthesia Measures corneal flattening, accurate and practical, 6 readings with 3 touches - applanation
Rebound (TonoVet): No anesthesia required, ideal for horses - rebound
Results:
Normal: 10-25 mmHg
High: glaucoma, >40mmHg
Low: uveitis <10mm
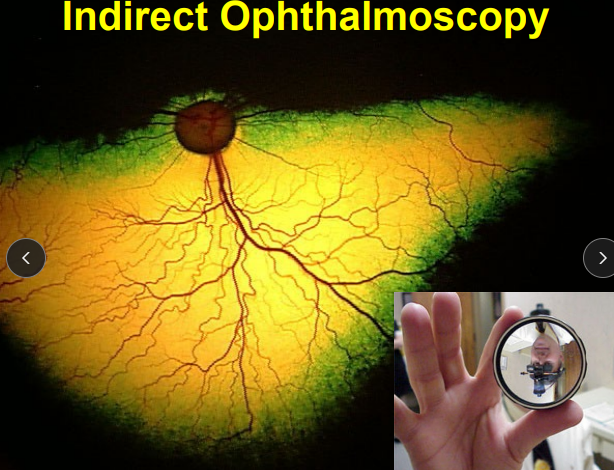
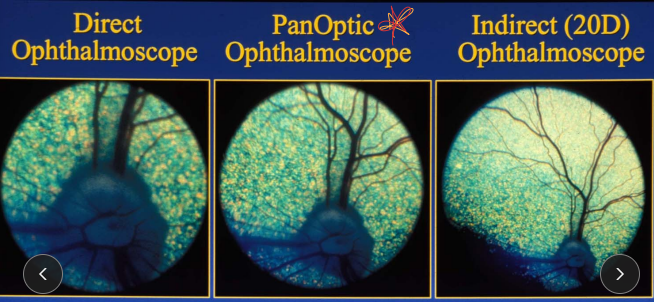
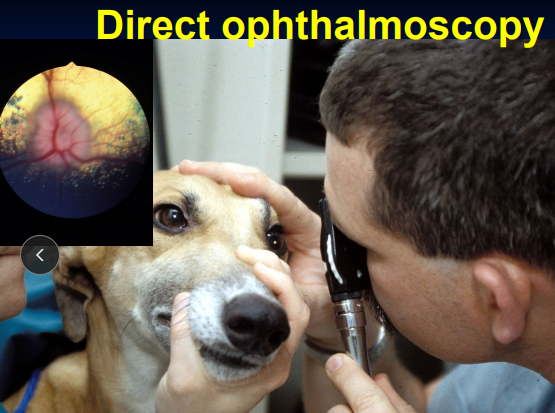
Ophthalmoscopy
Indirect: wide field, image is inverted and reversed
general retinal evaluation
Use magnifying glass
Direct: limited field, upright, magnified image
localized retina or optic nerve lesions
otoscope only
PanOptic: wide field, detailed image
small animals
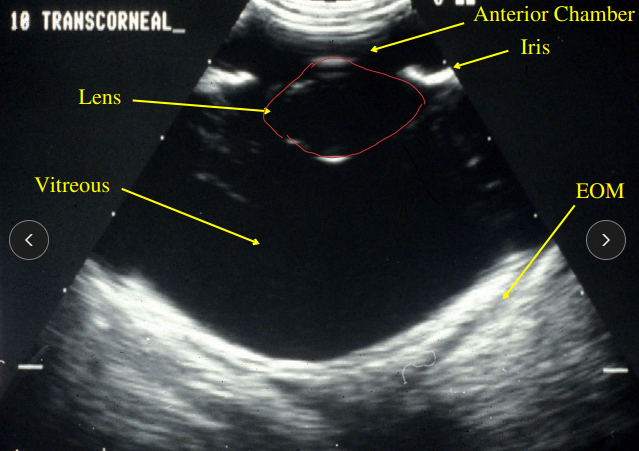
Anterior and Posterior Eye Visualization
Ultrasound
Why: when the posterior segment cannot be visualized - blood or cataracts
Lens, vitreous, retina, optic nerve, and uveal tract
Detects: Lens luxation, Retinal detachment, tumors, uveal cysts, hemorrhage, cataracts
Brightoscopy (Slit lamp)
Use: examination of the anterior eye structures
Adnexa, eyelids, Conjunctiva, cornea, anterior chamber, Iris, lens, anterior vitreous
Electroretinogram
Why: distinguishes retinal from optic nerve blindness
Past cataract Sx, SARDS, unkown blindness
Tools:
Scotopic ERG: Tests rod function (dark-adapted)
Photopic ERG: Tests cone function (light-adapted)
Results:
Cataract with normal ERG: intact retina
Cataract with flat ERG: retinal degeneration
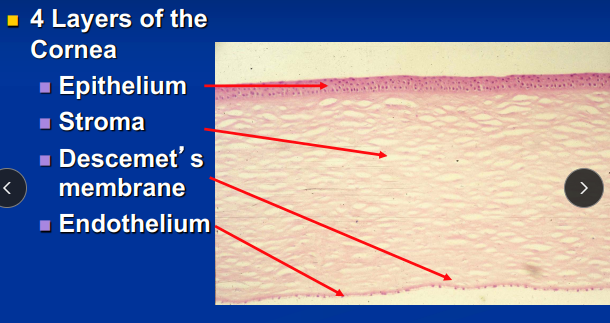
Layers of the Cornea
Cornea Epithelium “english muffin” non-keratinized!
Fxn: mechanical barrier to imbibition of fluid by the stroma
Anatomy: Anchoring fibrils for attachment
lipophilic: fluorescein not absorbed
Healing:
Cell turnover 7 days, ulcers should heal 48-72h hours!!
Damage = focal stromal edema in area of the ulcer
Stroma “dry sponge” No blood vessels
Anatomy: 90% of total corneal thickness, Hydrophilic = absorbs stain/fluid if there is break in epithelium,
CN V trigeminal for outer 3rd innervation - superficial ulcers are more painful then deep ones
Diffuse edema can look blue and cloudy
Descemet’s membrane
Fxn: BM of endothelium
Anatomy: Does not retain fluorescein, Elastic
rim of ulcer will stain but not the center - almost rupture: Emergency
Endothelium: no blood vessels, NO undergo mitosis!
Fxn: physical barrier and metabolic pump to prevent stromal edema
Healing: cellular enlargement and migration, no regeneration, lose with age!!Damage = diffuse edema(blue eyes)
Look like honeycombs
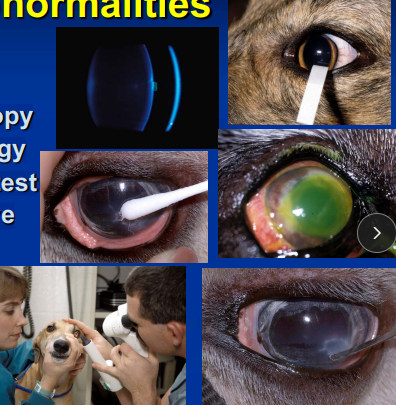
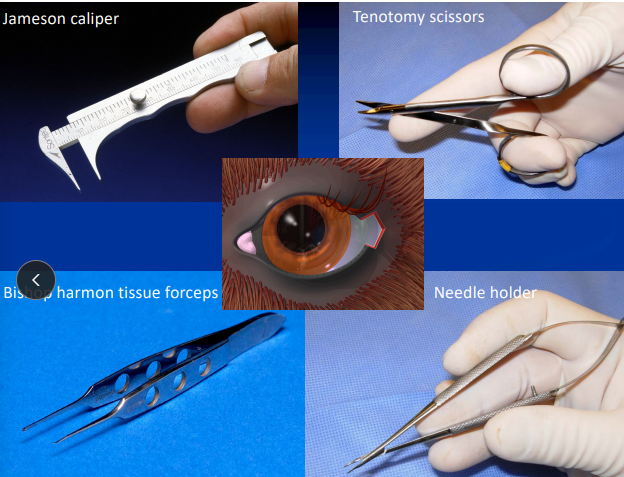
Diagnostic tests for corneal abnormalities
Examination
Finoff
Biomicroscopy
Culture/Cytology
Schirmer tear test
Fluorescein dye
Biopsy
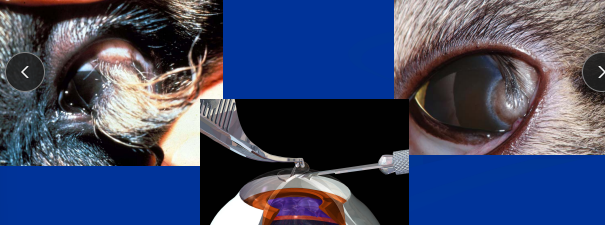
Dermoid (Choristoma)
Et: congenital corneal condition
Cs: Normal tissue in abnormal location
Sig: Dachshund, Dalmatian, Doberman, GSD, Saint Bernard
Tx: Superficial keratectomy - #64 beaver blade
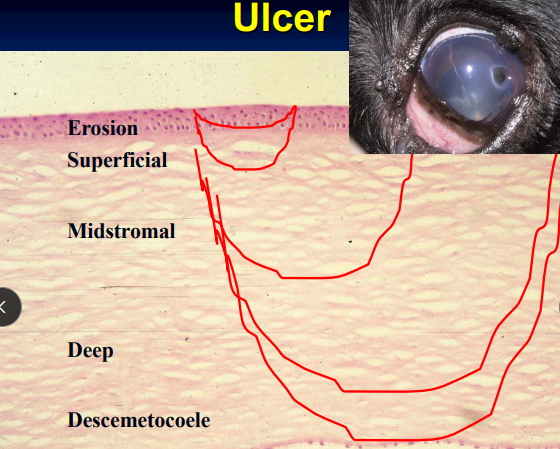
Superficial Corneal Ulcers
Cs: Extreme pain, focal edema
CN 5 trigeminal nerve supplies outer 1/3 of cornea
EXAM #1: Look for eyelid abnormalities, location/size of ulcer, FB, hair, infectious causes
Tx: Heal within 48-72 hours if cause removed
If not healed after 5 days: cause persists, infection present, indolent ulcer present, FHV-1
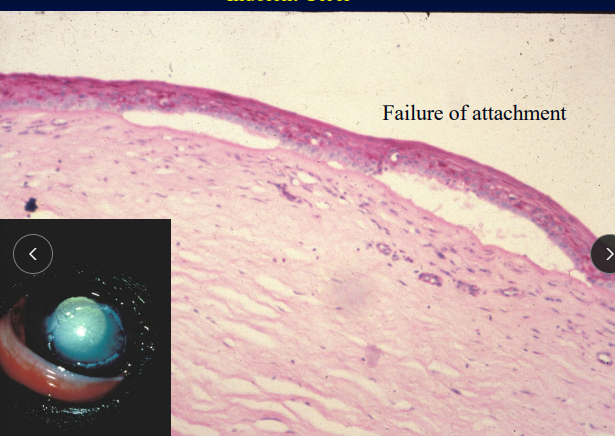
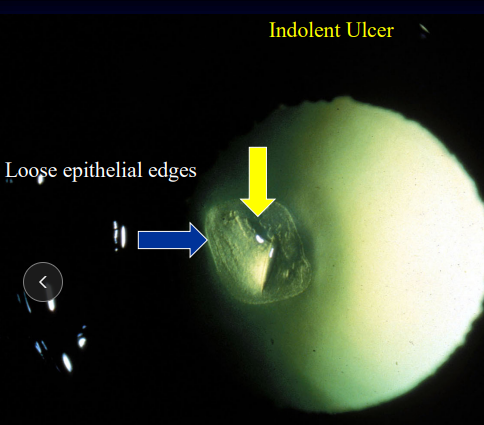
Indolent Ulcer
Et: Recurrent epithelial erosion, failure of BM epithelial attachment
Sig: Old, boxers
Cs: Superficial, mild pain, loose epithelial borders, focal edema, mid aged/older dogs
Chronic
Tx: Client education, debridement, keratotomy (100%), tetracycline(topical), diamond burr (93%)
Recheck every 7-14 days, long term treatment
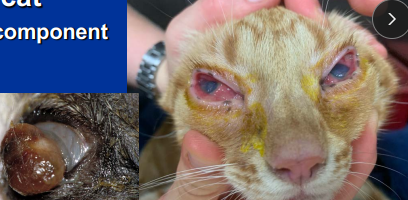
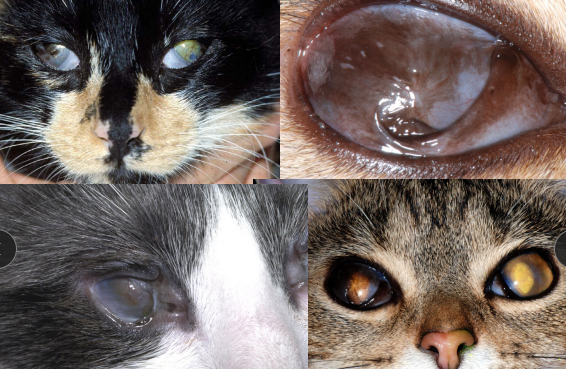
Feline Herpesvirus
Et + Sig: 3 stages
Ophthalmia neonatorum: kittens <4 weeks
Symblepharon – fuses in utero
Adolescent cats: ocular + respiratory
Adult cats: ocular only
Cs: Dendritic(classic) or punctate superficial ulcers, conjunctivitis, keratitis
Dt: History, based on response to therapy + Cs
PCR unreliable and expensive
Tx: Cidofovir(eye drops), Famciclovir (do not compound),l-lysine
Do not taper dose
± Topical mucinomimetic (tear mucus supplement)
Recurrent flare ups w/ stress
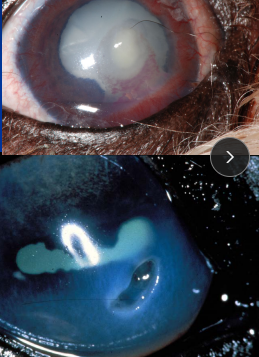
Mid-Stromal Corneal Ulcer
Et: Often with anterior uveitis
Cs: focal edema, pain
Tx: Medically managed, Neomycin–bacitracin–polymyxin, Levofloxacin, Gatifloxacin, atropine (<4x daily), fluxin (horse)
Managed medically
No topical corticosteroids
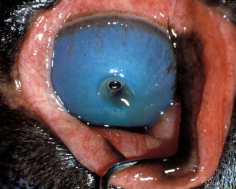
Deep Descemetocele Ulcer
Cs: Perforation imminent, focal edema, pain
Dt: Fluorescein negative centrally
Tx: Conjunctival flap or corneal-conjunctival transposition
Surgery + medical therapy
Do not use third eyelid flap
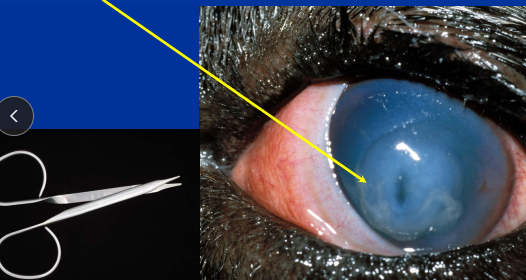
Melting Keratomalacic Ulcer
Deep ulcer - surgery often indicated, debride melting portion
Superficial Keratectomy w/ conjunctival graph
Et: Enzymatic corneal destruction
Involves PMNs, keratocytes, and bacteria
Pseudomonas, β-Strep
Cs: focal edema, pain
Extremely rapid progression
Tx: q 1-2h ofloxacin, levofloxacin, gatifloxacin, serum, tetracycline, debridement
Aggressive: Anticollagenase + antibiotics + surgery
Corneal Edema
Anterior uveitis. glaucoma
Endothelial dystrophy - breed related, age
Anterior lens luxation
CHECK PRESSURE
Loss of Corneal Transparency
Edema
Focal: due to corneal ulcer
Diffuse: due to endothelial damage
Et: Anterior uveitis, Glaucoma, Endothelial dystrophy, Anterior lens luxation
Dt: IOP
Tx: Hyperosmotic therapy, Conjunctival graft, Fresh corneal transplant
Pigmentation
Chronic superficial irritation
Vascularization
Sequestrum or melanoma
Scarring
Et: History of previous ulcer or trauma
Cs: vascularization, absence of pain
Infiltrate
Cellular: inflammatory or neoplastic
Non-cellular: crystalline (cholesterol, mineral)
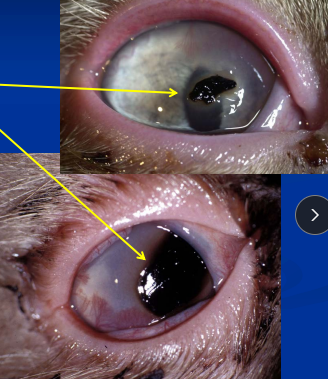
Corneal Sequestration
Et: Associated with herpes keratitis, topical steroids, grid keratotomy
Sig: cats
Cs: Brown-black corneal lesion, pain, may spontaneously slough, often vascularized
Dt: Fluorescein negative
Tx: Superficial keratectomy
Post-op antibiotics, atropine, artificial tears following sx
This dz could happen w/ steroids and grid keratotomy
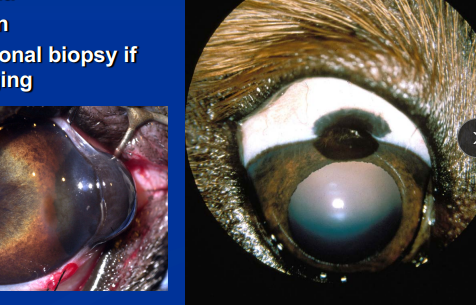
Melanoma
Corneal Epibulbar (limbal):
Benign pigmentation
Excisional biopsy if enlarging
Eyelid: dogs, horses, benign
Conjunctival
Dogs: benign
Cats: Melignant
Intraocular:
Canine: benign, Labs, GSDs
Feline: malignant, high mitotic index
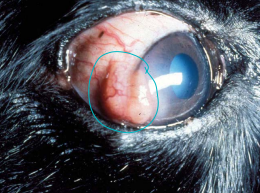
Nodular Granulomatous Episclerokeratitis (NGEK)
immune mediated
Et: Non-neoplastic inflammation mass at temporal limbus (1 or both eyes) - Lateral canthus
Lymphocytes, plasma cells, histiocytes
Sig: Cocker Spaniels, Collies
Cs: Loss of Corneal Transparency
Tx: topical Dexamethasone, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, systemic: very rare - azathioprine, cyclosporin
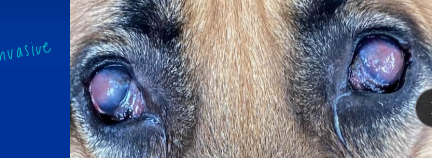
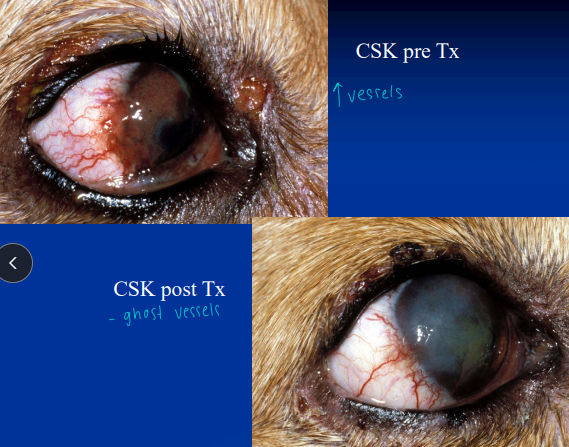
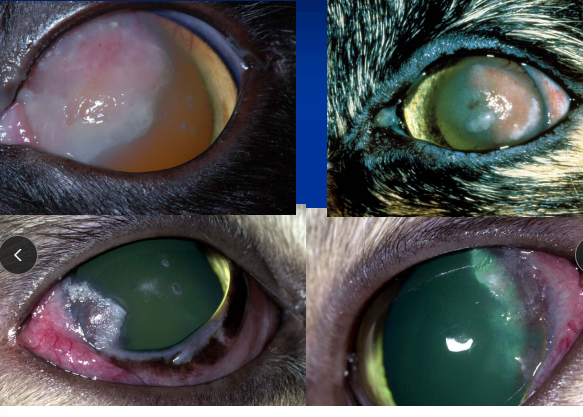
Chronic Superficial Keratitis (Pannus)
“degenerative pannus”
Et: Immune mediated
Sig: GSD, Greyhounds
Cs: progressive corneal vascularization and pigmentation beginning at inferior-temporal limbus - will progress over entire cornea
starts in lateral canthus then progresses
Tx: topical dexamethasone, Cyclosporine, tacrolimus, Reduce UV exposure: doogles
Eosinophilic Keratitis
Cats, lateral limbus
Et: Limbal orientation of mast cells and eosinophils (one or both)
Cs: Loss of Corneal Transparency
Tx: Topical Cyclosporine, corticosteroids(herpes risk), Oral: Ovaban® (megestrol acetate, Cats) #1 but best to be topical
7d then taper to lowest dose
Ovaban side effects: DM, weight gain, cancer, behavior changes
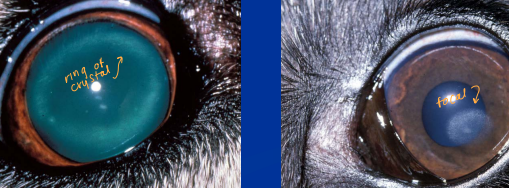
Corneal Dystrophy and Degeneration
Non-cellular corneal infiltrates
Crystalline materials: cholesterol or mineral
Dystrophy
Cs: Non-painful, Non-vascularized, Bilateral, Loss of Corneal Transparency
Tx: No treatment needed, steroids make it worse
Degeneration
Et: Secondary to inflam, cushings, hypothyroid, hypercalcemia, DM, steroid use
Cs: Loss of Corneal Transparency, deposits/crystals in eye
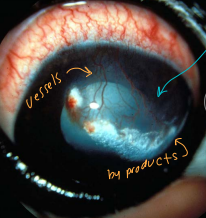
Corneal Trauma
Sharp: leaks, deflates, reparable
Ex: cat claws
Blunt: explodes, compresses
Ex: Horses
Poor Prognosis Indicators
Limbus involvement
Significant hyphema (blood in front of eye)
Lens perforation
US if poor visibility of virtuous
Large Uveal prolapse - remove eye
No consensual PLR
Chemical Injuries
Et: Soaps (mild), Acids (severe), Alkalis(critical/worst)
Severity = duration and concentration
Tx: irrigate sterile eyewash
Lacerations/perforations:
Perforating: punctures, pupil mis-shaped : double layer
Remember: corneas don’t bleed only: iris or lens
Non-perforating: flap - cut it off or suture back on
Adnexa
“Everything but the globe”
Extraocular muscles
Eyelids
Eyelids protect and serve the cornea.
Corneal diameter averages 16 mm.
Meibomian glands - sebaceous glands
Lacrimal system
Efferent + Parasympathetic: CN VII.
Afferent: CN V
2 puncta: except rabbits (only one).
Tear production + drainage: 2 canaliculi → nasolacrimal duct → nasal vestibule.
Conjunctiva
Goblet cells: Produce mucin component of tear film
Palpebral: lines inner eyelid
Bulbar: covers sclera
Third eyelid (nictitating membrane)
Reflection (fold) of conjunctiva.
Has T cartilaginous support
Responsible for 50% of aqueous tear film production.
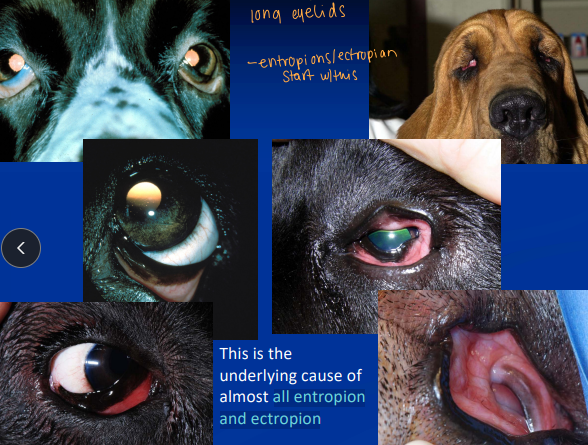
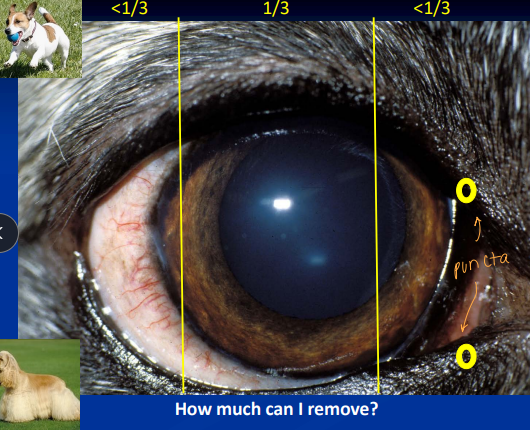
Macroblepharon
Long eye lids
Et: Abnormally large eyelid opening (palpebral fissure).
Cs: cause of nearly all entropion and ectropion cases
Dt: maximum canthus-to-canthi distance measurement under GA
Normal = 24-26 mm
Tx: Permanent Lateral Canthoplasty
surgical shortening improves corneal protection
Look where the canthus collapses & notching at the fold .
Ends should be tucked away from the cornea.
Double layer closure, second layer cruciate
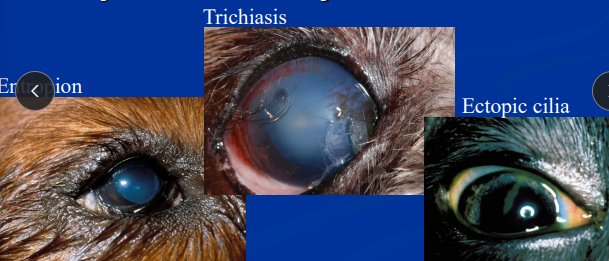
Entropion
Et: Inward rolling of the eyelid margin
Cats: lateral canthal, unilateral
Sm dogs: medial canthal
Cs: corneal irritation
Tx:
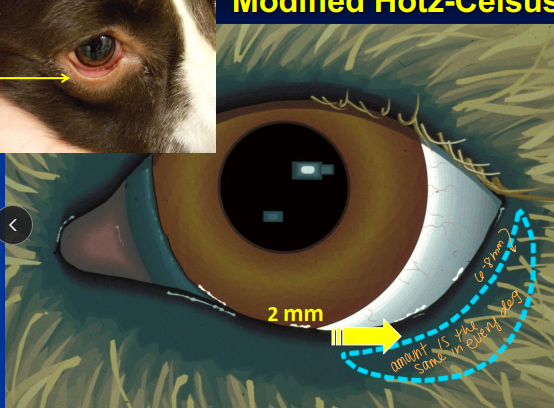
**Modified Hotz-Celsus Procedure: Permanent
Incision made approximately 2 mm from eyelid margin(hairline)
Small elliptical section of skin is removed
6-0 Surgilene in simple interrupted pattern(start in the middle)
Permanent Lateral Canthoplasty: lateral canthal entropion
Ends should be tucked away from the cornea
Permanent Medial Canthoplasty: Medial Canthal Entropion Pugs
Excision of caruncular tissue, reduces eyelid length medially
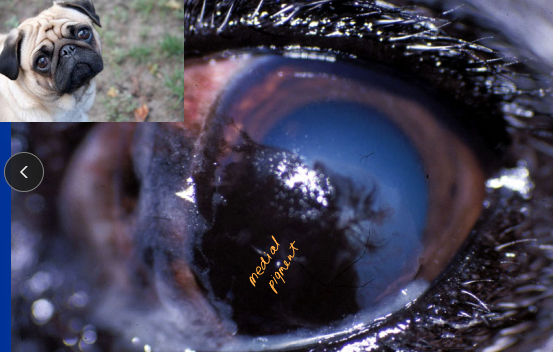
1st Q - How old is the dog? fix them while you can
remove the caruncle
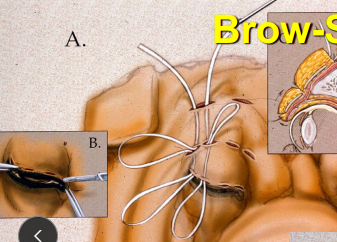
Advanced Cosmetic Surgical Eyelid Procedures
Brow Sling - shar pei
Used when excessive skin or drooping brow causes eyelid malposition
Lifts upper eyelid region and corrects sag
Rhytidectomy (Facelift/forehead Technique)
Tightens periocular skin to reposition eyelids
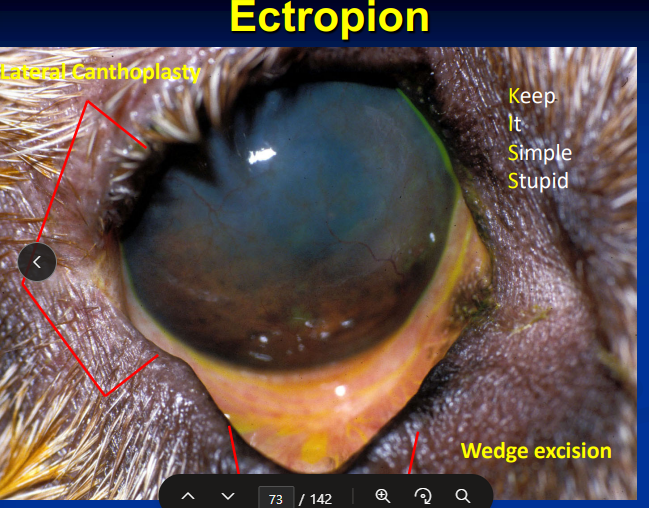
Ectropion
Et: Macroblepharon
Cs: Outward rolling of eyelid margin
Tx: Lateral canthoplasty, Wedge excision
“KISS” — Keep It Simple, Stupid
Abnormal eyelid hair emergence
Distichia - tx if bothering pet
Et: Hairs emerging from Meibomian gland openings
Tx: kill the follicle, Epilation (temp), cryosurgery, Electroepilation, CO₂ laser
Ectopic Cilia - always need tx
Et: Hairs emerging from palpebral conjunctiva
Cs: irritating to the cornea
Tx: surgical removal or ablation
Eyelid Agenesis
Et: Lack of upper eyelid development
Usually superior-temporal
Often bilateral
Tx: Lip-to-lid transposition, Rotational grafts
Eyelid Neoplasia
Dog: Histiocytoma, BCT, Melanoma, Adenoma, MCT, GCT
Common, benign
Cat: SCC, MCT, Fibrosarcoma
Aggressive
Horse: Sarcoid, SCC, Melanoma, MCT, Lymphosarcoma, BCT, Papilloma - ASK age and purpose of the horse
SCC: older horses, locally aggressive, low metastasis rate
Sarcoid: younger horses
Intralesional chemo - medial canthus
Tx: Benign neglect(dogs), excisional biopsy, Cryosurgery, CO₂ laser, Chemo, Radiation
Can remove 1/3 of the eye lid @ 6/12 o’clock for equal closure
double layer closure, 2nd layer w/ cruciate (identical on both sides)
Eyelid Reconstruction
H-plasty
Used for larger excisions
Preserve as much conjunctiva as possible
Incisions diverge
Z-plasty
Lateral canthal reconstruction
Repositions tension lines
Common in feline eyelid tumor repairs
Axial pattern flap
Cutaneous artery and vein for blood supply
Medial canthal reconstruction
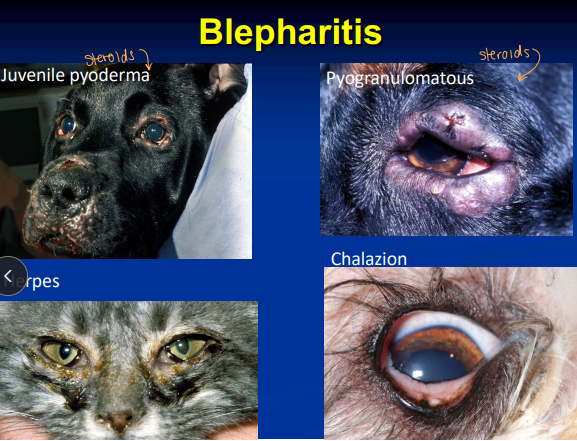
Blepharitis
Et: Juvenile pyoderma, Herpes, Chalazion (Meibomian gland blockage), Pyogranulomatous inflam
Tx: systemic antibiotics, steroids, compress
Approach as derm condition
Eyelid Lacerations and resection
Two layer closure, 2nd layer cruciate
Conjunctiva: 5-0 to 6-0 absorbable, horizontal mattress
Skin: 5-0 to 6-0 nonabsorbable, cruciate at margin + simple interrupted
Avoid excessive debridement
Never amputate an eyelid pedicle!!!
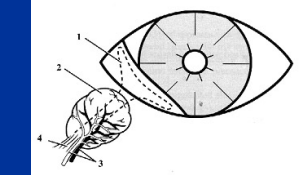
Nictitating Membrane
Reflection of conjunctiva
Cartilagenous support
“T” cartilage
Gland of the nictitans
Aqueous portion of tear film
Clinical signs of conjunctivitis
Conjunctival hyperemia
Chemosis
Lymphoid follicles
ocular discharge
Dx: Complete ophthalmic examination
Schirmer Tear Test
Cytology
Biopsy
Culture and sensitivity
Vital stains
3rd eyelid Follicular Conjunctivitis
Et: non-specific inflammatory response
seasonal
Sig: young dogs
Cs: Conjunctival hyperemia (redness), Chemosis (swelling), Lymphoid follicle formation, Ocular discharge
Tx: steroids
May resolve with age
Allergic Conjunctivitis
diagnosis of Exclusion
Et: non-specific inflammatory response
Seasonal or atopy/skin allergies
Sig: young dogs, rare in cats
Cs: Conjunctival hyperemia (redness), Chemosis (swelling), Lymphoid follicle formation, Bulbar conjunctival follicles , Epiphora (tearing), Mucoid discharge
Dt: Diagnosis of exclusion
Tx: antihistamines, anti-inflammatorys
Chlamydophila felis
Et: zoonotic
Sig: cats
Cs: conjunctivitis
Dt: elementary bodies in conjunctival epithelial cells (cytology)
Tx: Tetracycline, Erythromycin, macrolides
Parasitic conjunctivitis
Et: non-specific inflammatory response
Thelazia, Onchocerca, or Habronema
Sig: horses
Cs: Conjunctival hyperemia (redness), Chemosis (swelling), Lymphoid follicle formation, Ocular discharge
Eosinophilic Keratitis + Conjunctivitis
Et: non-specific inflammatory response
Seasonal, IM
Sig: horses
Cs: Conjunctival hyperemia (redness), Chemosis (swelling), Lymphoid follicle formation, Ocular discharge
Dt: cytology
Tx: Superficial keratectomy, diamond burr debridement
Scroll Cartilage
Et: Curved or everted cartilage of the third eyelid
Tx: Thermal cautery
Prolapsed Gland of the Third Eyelid
Cs: Cherry Eye
Tx: Surgically replace (Morgan Pocket or anchoring), benign neglect, remove
all KCS risk: Monitor STT for life
Third Eyelid Neoplasia
Adenocarcinoma
Dog
Papilloma
SCC
Equine: Excisional biopsy, Cryosurgery
Lymphosarcoma
Inflammation of the Nictitans (Plasmoma)
Et: Chronic IM inflam of the third eyelid
Tx: steroids, immunomodulators
keratoconjunctivitis sicca
Et: IM, Cherry eye Sx, Irradiation, drugs, DM, hypothyroid, facial denervation or palsy,
Qualitative: Goblet cell loss or dysfunction and decreased Mucin Production
Quantitative: Decreased Aqueous Production
Sig: small dogs and brachycephalic breeds
Cs: Discomfort, Mucopurulent discharge, Blindness, conjunctivitis
Ulceration, Vascularization, Pigmentation, Keratinization, SCC
Dt:
Quantitative: STT <15 mm/min
Qualitative: TBUT <10 seconds
Tx: Lacrimogenics, tear supplements, anti-inflammatories, Parotid Duct Transposition
Lacrimogenics: Cyclosporine A, Optimmune, Tacrolimus → Tear stim
PDT: Reroutes parotid salivary duct to the conjunctival fornix
Treat before STT values drop severely, do not wait
Tear Overproduction
Et: Usually secondary to irritation or pain
Tear Outflow Abnormalities
Cs: May result in epiphora (overflow tears)
Congenital Nasolacrimal Abnormalities
Missing lower punctum: dogs
Dacryops: congenital duct malformation
Imperforate nasal meatus: equine, camelids
Medial trichiasis: misdirected hair causing drainage interference
Imperforate Punctum
Et: involves inferior punctum of nasolacrimal system
Tear Outflow Abnormalities
Sig: Cocker Spaniels
Tx: irrigate superior punctum and surgically open inferior punctum
Atresia of Nasal Opening
Et: Tear Outflow Abnormalities
Sig: equines and camelids
Dt: lack of fluorescein exit from nostril after ocular application
Tx:
Pass catheter to nasal vestibule
Incise nasal mucosa to expose punctum
Leave silicone tubing in place 6 weeks post-surgery
Acquired Nasolacrimal Obstruction
Et: Dacryocystitis, FB
Tear Outflow Abnormalities
Tx: flushing, imaging, surgical repair
Structures of the Vascular Tunic
Iris
Regulates the amount of light entering the posterior portions of the eye
Blood Aqueous Barrier
Ciliary body
Located posterior to iris
Source of aqueous humor, Lenticular zonules(holds the lens in place)
Blood Aqueous Barrier
Choroid: posterior portion of eye
Provides nutrition:
Outer portions (rods & cones) of retina in dog, cat, cow
All of retina in horse
Tremendous blood flow → cools retina
The eye has the highest blood flow (by weight) of any organ
Contains Tapetum
Muscles of the Eye
Sphincter Muscle
Smooth muscle in Mammals
Striated muscle in Birds
Miosis = constriction
CN III parasympathetic control
Dilator Muscle
Smooth muscle in Mammals
Striated & smooth in Birds
Sympathetic control
Mydriasis = Dilation of pupil
Horner’s Syndrome
Et: Denervation of sympathetic nerve supply to eye
1st order: CNS neoplasia, trauma, inflammation
2nd order: spinal cord, thoracic mass, cervical mass/trauma, iatrogenic
3rd order: otitis, guttural pouch disease, endocrine disorder, orbital disease, idiopathic
Cs: Miosis, Ptosis, Enophthalmos, Prolapse of third eyelid, Ocular hyperemia
Unilateral sweating → Horses
Dt:
PE: Radiographs, Otic exam, CT of tympanic bulla, Guttural pouch endoscopy
Phenylephrine Response:
Rapid, strong response → 3rd order lesion
No response = likely 2nd order lesion
Persistent Pupillary Membranes
Et: Remnants of fetal iridal vascular arcades
Originate from collarette zone of iris
Attach to cornea, iris, or lens
Sig: Basenji
Tx: None
Different from Synechia: pupils edge
Heterochromia
Et: genetic
Alone = no significance
May associate with ocular/systemic abnormalities
white coat / deafness in cats
Sig: blue merle, appaloosa, Siamese, harlequin
Cs: colour variation within or between irides, iris stroma lacks pigment - multi colored blue eyes
Coloboma
Sig: Notch defect in iris
usually inferonasal
Dt: Differentiate from iris atrophy(Swiss cheese/spiderweb eyes)
Rottweilers
Iris Cyst
Et: Cystic accumulation of aqueous humor within posterior iris or ciliary body epithelium
Acquired lesion
Can maintain attached or floating around
Dt: Transilluminates
Tx: Neglect, laser ablation
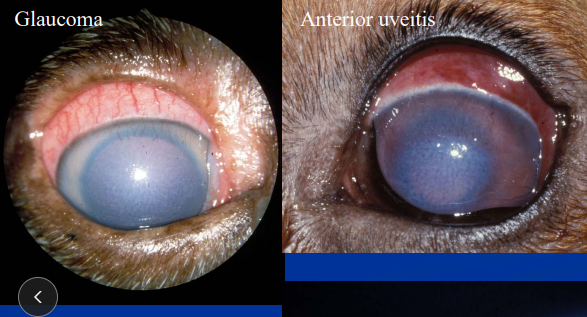
Anterior Uveitis
Prostaglandins play a huge role!!
Rule out other ocular/systemic causes #1 ~ 50% have systemic dz
Et: idiopathic, Corneal ulceration, lens induced, trama, cancer, IM, bacteremia, viremia, septicemia
Dogs systemic: Tick dz, fungal dz, ICH, Brucella, Uveo-dermatologic syndrome (depigmenting), HW
Cats: FeLV, FIP, Toxo(2 titers), FIV, Crypto, Bartonella, Lymphosarcoma (#1 tumor), Melanoma(primary tumor)
Cs: Miosis, Flare(sunrays), Redness, Photophobia, Pain, Keratic precipitates, Hypotony
Dt: histo/culture, US, CBC, IgG + IgM titer
Remember coinfections
Tx: Stop the inflammation #1, Antimicrobials, Immunotherapy, Chemo, Atropine(no more then x4), steroids, NSAIDs
Systemic or topical
Posterior Uveitis
Systemic dz!
Et: Bacteremia, septicemia, mycotic infections, disseminated neoplasia
High choroidal blood flow → predisposed to blood-borne disease
Cs: edema, exudate, granulomatous/non-granulomatous, hemorrhage, neoplasia, retinal thinning, depigmentation, vascular loss
Dt: color change on fundic exam, histo/culture, US, CBC, blind eye=vitreocentesis
Tx: NSAID, steroids(if know cause), immunosuppressives
Requires systemic meds
Hyphema
Blood filled sac
Et: Blood in anterior chamber
Coagulopathies/vascular disorders, Trauma, Neoplasia, Hypertension, Anterior uveitis
Dt: IOP #1, US #2
Tx: Treat underlying cause(if known), Cage Rest
Do not drain hemorrhage!
Lipid Aqueous
Fat inside the eye, tomato soup w/ milk
Et: systemic lipemia - dont feed fatty foods
No ocular abnormality required
Cs: Flare appears milky, non-painful
Iris Atrophy
Et: Swiss cheese / spiderweb eye
Primary: dogs, Poodles
Secondary: Uveitis, glaucoma
Cs: abnormal PLR
Affects iris sphincter
Tx: none, make sure this is the dz
Intraocular Tumors
Et: Primary = happy, 2ndary = pissed off
Melanoma: Primary, threatens the eye
Canine: benign
Feline: malignanthigh mitotic index, flat yellow
Ciliary Adenoma: Primary, remove eye!
Feline Spindle Cell Sarcoma: Primary, remove eye!!
highly malignant, metastasizes via optic nerve, post-traumatic, uveitis
Secondary:most common Lymphosarcoma, sarcoma, carcinoma
Cs: Hemorrhage, Uveitis, Lens displacement/luxation, Cataract, Glaucoma, Retinal detachment
Tx:
Primary: enucleation if symptomatic
Secondary: Treat prime disease, enucleation
Eye = bystander
Aqueous Production
Production: Ciliary body
Involves carbonic anhydrase, ATP, glucose, and local environment
Inhibited pharmacologically by carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs)
Outflow Pathway: Ciliary epithelium → between iris and lens → pupil → anterior chamber → Iridocorneal angle → trabecular meshwork → scleral venous plexus
Pharmacologic Effects on Aqueous Outflow
Pilocarpine:
Contracts ciliary muscle → ↓ resistance → ↓ IOP
Contraindicated in uveitis
Atropine:
Paralyzes ciliary muscle → ↓ outflow → ↑ IOP
Contraindicated in glaucoma
Glaucoma
Genetic or 2ndary
prime: bilateral w/in 2y, 2nd: unilateral besides: lens luxation terriers
Increase in IOP w/ decreased outflow - no atropine!
Cs: Redness, Corneal edema, Engorged episcleral vessels, Dilated pupil, absent PLR**, Corneal striae, Retinal degeneration, Cupped disc, Buphthalmos, Pain
Chronic = Not an emergency – vision loss irreversible
Acute = Emergency– vision loss reversible
Dt: increased IOP >40 mmHg !!
Rx:
Acute: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (Methazolamide/Dorzolamide/Brinzolamide/Cosopt), Prostaglandins (Latanoprost) #1!!!, passive paracentesis
Horse: timolol, cosopt
Chronic: eyes blind! Evisceration with prosthesis, Enucleation
Sx:
Acute: Laser surgery (vision saved)(TransScleral CycloPhotocoagulation)
Chronic: Intravitreal Injection of Cidofovir or Gentamicin, enucleation(most common), prosthesis
Lens Anatomy
Embryo: Originates from surface ectoderm
Path: Lens is not perceived as part of self
Exposure to lens proteins results in inflammatory response → Lens-induced uveitis
Physio:
Avascular: depends on aqueous humor for nutrients and waste removal, issue = cataract
Growth: anaerobic glycolysis (hexokinase), continues to grow throughout life(compact/dense)
Composition: 35% protein, 65% water
Capsule:anterior(Y) thick / posterior (thin)
Epithelium: anterior
Cortex: anterior/posterior
Nucleus: central
Zonules: 360°, Anterior “Y” suture + 50–70 μm, Posterior 2–4 μm
Lenticular Sclerosis
Normal w/ aging
Et: increased central density
Normal senile chage
Sig: All dogs and cats >6 years old
Cs: Bilateral, symmetrical, transparent
Surgically Harder Lens
Dt: Does not prevent fundus/retina exam
Tx: no treatment required
Cataracts
loss of transparency, Irreversible! Ghost eyes
Will NEVER interfere w/ afferent arm PLR!!**
Et: Hereditary, Metabolic, Inflam, Traumatic, Toxic, Nutritional, Radiation, Electric, DM
Equatorial: #1, very progressive, worst place!!
Hypermature: cant see in/out, no menace!
Undergoing liquefaction in all or part of the lens: dries out
Lens proteins exposed → immune response → Lens-induced uveitis
Sig:<6 years (developmental)
>6–9 years (senile)
Dt: US, Electroretinogram
Retinal detachment: Immature < Mature < Hypermature
PLR unaffected
Tx: Early Referral
None: highest failure
Rx: Anti-inflammatory treatment
Sx: #1, Phacoemulsification + IOL (Artificial lens)
Lens Luxation
Et: genetic, trauma, glaucoma, uveitis
Sig: Terries (primary)
Cs: Iridodonesis (iris tremor), Phacodonesis (lens wobble), Aphakic crescent, Corneal edema
Anterior luxations: painful, epiphora, blepharospasm, redness
Posterior luxations: may have no overt signs
Dt: IOP
Tx:
Anterior luxation: w/in 24h: Sx(acute, 1mary), artificial lens
Best treatment = referral
No latanoprost!
Posterior luxation: Sx, miotic agents (latanoprost!!/pilocarpine, manage IOP
Orbit Anatomy
Carnivors: Incomplete, Forward placed globe
Herbivour: Complete, Laterally placed globe
Extraocular muscles: (LR6SO4)3
4 rectus muscles → CN6
2 oblique muscles→ CN4
Retractor muscle → CN3
Levator muscle → CN3
Glands:
Lacrimal gland
Zygomatic salivary gland(floor of orbit)
Gland of the 3rd eyelid
Harderian gland (cow, pig, rabbit)
Abnormalities: Exophthalmos, Enophthalmos, Strabismus(lazy)
Intraconal: bug eyes
extraconal: sideways eyes
PE: retropulsion of both eyes!
Orbital Abscess and Cellulitis
Acute
Et: Possible extension from adjacent tissues (mouth, sinus, salivary gland)
Cs: sudden onset: Painful opening mouth, exophthalmos, elevated 3rd eyelid, fever, LN enlargement, leukocytosis, swelling behind last upper molar in mouth
acute
Tx: Systemic antibiotics, Soft food, Corneal protection, Surgical drainage
Do not probe or irrigate!!
Orbital Myositis
Et: IM
Sig: Usually bilateral exophthalmos
Cs: Exophthalmos, 3rd eyelid elevation, difficulty opening mouth, swollen muscles of mastication and extraocular muscles
Tx: immunosuppression steroids (Prednisolone, Azathioprine)
Orbital Neoplasia
Chronic
Et: malignant >90% dog/cats
Dog Primary: osteosarcoma
Secondary: adenocarcinoma
Feline Primary: osteoma
Secondary: SCC
Cs: Exophthalmos, Globe indentation, unilateral, Slow progression, Less painful opening mouth
Dt: FNA, biopsy, US, Rads, CT, MRI
Tx: enucleation, exenteration, radiation, chemo
Px: grave
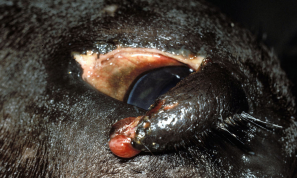
Proptosis
Et: Incomplete orbit in dogs and cats
Sig: squish face
Cs: Acute exophthalmos with eyelid entrapment behind the globe, severe chemosis, subconjunctival hemorrhage, blindness, keratitis/corneal ulcer, hyphema, rectus muscle avulsion (shortest muscle), periorbital trauma
sequela: Lateral or dorsolateral strabismus, Neurotrophic keratitis, Lagophthalmos, KCS), Blindness (optic nerve atrophy), Phthisis bulbi
Tx: good prognosis <2 EOM tear, pupils miotic. replace #1 or enucleate (can enucleate later, Water-soluble lubricant on cornea, Lavage, Warm compresses, Antibiotics, NSAID
50% of replaced canine globes are blind
No topical steroids
No cats regain vision
Retina Anatomy
Nerve fiber layer
Ganglion cells
Inner + Outer plexiform
Inner + Outer nuclear
Photoreceptors
Rods: Night vision, Motion
Cones: Day vision, Color
Retinal pigment epithelium
Pathways in the Eye
Light:
Light → Vitreous → Retina → Choroid/Sclera
Afferent PLR CN II
Retina → Optic nerve → Chiasm → Optic tract → Pretectal nucleus → Edinger–Westphal nucleus → CN III → Ciliary ganglion → Pupil constrictor
Efferent PLR CN III
Edinger–Westphal nucleus → CN III → ciliary ganglion → short ciliary nerves
Vision
Retina → Optic nerve → Chiasm → Optic tract → Lateral geniculate → Optic radiation → Visual cortex
Progressive Retinal Atrophy
Et: Breed-specific, inherited, progressive disease
Cs: Tapetal hyperreflection, Pale optic disc, Vascular attenuation, Dilated pupils, slow/incomplete PLR, Night blindness (nyctalopia), total blindness
Retinal Detachment
Et: Hypertension, Inflam, Fungi, Crypto, Cataracts, Congenital, Breed-associated, Trauma, Uveo-Dermatologic Syndrome, Lymphoma
Sig: Akita, Samoyed, Siberian Husky, Bichon Frise, Shih Tzu
Cs: acute blindness, pupils fixed and dilated, Veil of tissue posterior to lens
Dt: Complete systemic exam mandatory
Tx: Amlodipine, Enalapril, Diode laser barrier retinopexy
Retinal Dysplasia
Et: Developmental abnormality of retinal differentiation/proliferation
Sig: dogs
Forms:
Folds → mild
Geographic → moderate
Complete → severe, non-attachment, blindness)
Tx: None, do not be bred
Sudden Acquired Retinal Degeneration Syndrome (SARDS)
Et: unknown
mild Cushing’s or hepatic disease
Cs: Acute blindness, “Swiss cheese retina” seen within 3 weeks, PU/PD, polyphagia, weight gain
Dt:
Labs: Elevated ALP, cholesterol, or liver enzymes
Fundus exam: Initially normal fundus → after 2–3 months generalized retinal degeneration
ERG: differentiate from optic neuritis or cortical blindness
Tx: none
Enrofloxacin Toxicity
Et: Occurs at therapeutic doses
Sig: cats
Cs: Acute blindness
Irreversible
Micropapilla and Optic Nerve Hypoplasia
Et: Congenital optic nerve abnormality, smaller optic nerve in a visual eye
Sig: GSD, Min Poodle
Cs: blindness
Tx: None
Coloboma
Et: Congenital pit or defect in optic nerve and sclera
Sig: Collie Eye Anomaly
Cs: non-vision-threatening
Must differentiate from chronic glaucoma
Tx: Affected animals should not be bred
Papilledema
Et: Non-inflammatory optic nerve swelling
Elevated CSF pressure
Mass lesions compressing optic nerve
Cs: Not always vision-impairing
Papillitis or Optic Neuritis
Et: Inflammation of optic nerve
intraocular or retrobulbar
Cs: Decreased or absent PLR, sudden vision loss, hyperemic optic disc, peripapillary hemorrhage, retinal detachment
Dt: ERG
differentiates from SARDS
Optic Nerve Atrophy and Degeneration
Et: Secondary to Inflam, Trauma, Chronic glaucoma
Cs: Gray, flat optic nerve, vascular attenuation, glaucoma, peripapillary hyperreflectivity
Optic Nerve CNII
Use: vision, sensory
Afferent: PLR, Dazzle, Vision
Dz: Blindness, Mydriasis, Absent PLR + Dazzle reflex + menace response
Dt: Optic Nerve Exam, Maze Test
Oculomotor Nerve CN III
Motor Fxn: (LR6SO4)3
Dorsal, ventral, medial rectus muscles
Ventral oblique muscle
Levator palpebrae (elevates upper eyelid)
Parasympathetic Fxn:
Ciliary body muscle
Iris constrictor muscle
Dz: Down and out” strabismus, Dilated pupil
Trochlear Nerve CN IV
Motor Fxn:
Superior oblique muscle
Rotates dorsomedially, deviates ventrally
Dz: Strabismus (“out and up”), star gazing
PEM
Trigeminal Nerve CN V
Branches: Ophthalmic, Maxillary, Mandibular
Sensory Fxn: Cornea and eyelid sensation
Afferent: palpebral reflex, oculocardiac reflex → bradycardia
Dz: Masseter muscle atrophy / enophthalmos, Neurotrophic keratitis, Decreased tears, Decreased blink on touch
Abducens Nerve CN VI
Motor Fxn: (LR6SO4)3
Lateral rectus
Retractor bulbi
Dz: Medial strabismus, Reduced ocular motility, Inability to retract globe
Facial Nerve CN VII
Motor Fxn:
Muscles of facial expression
Orbicularis oculi
Efferent for palpebral reflex
Parasympathetic Fxn: Lacrimal gland
Dz: Facial paralysis, KCS, Lagophthalmos, Ptosis, Facial asymmetry
Vestibulocochlear Nerve CN VIII
Sensory Fxn: Afferent for ocular position
Dz: Abnormal globe motility, Nystagmus
Peripheral: horizontal or rotary, fast phase away from lesion
Central: vertical or variable, can be overridden