Anatomy - Unit 2 Concepts 1-2: Support and Motion
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
trabeculae
tiny bone struts that are key for helping the bone to resist stress; also where bone marrow is
hematapoesis
blood cell formation
cartilage
flexible connective tissue
ligament
short bonds of tough, yet flexible connective tissue
tendon
cords of dense connective tissue
joint
junctions between 2 or more bones and included all components to aid in movement and flexiblity of the body
invertebral discs
act as cushioning pads to absorb shock and protect against tension or torsion
sesamoid bones
special type of short bone
osteon
the basic structural unit; long cylinders that act as tiny weight-bearing pillars in the bone
lamellae
a group of hollow tubes
central canal
runs through the middle of each osteon and contains small blood vessels for nourishment and nerve fibers for signaling
lacunae
gaps between the lamellae
osteocyte
release chemical signals to tell osteoclasts to go to the damage
osteoblast
come in and build new bone before they undergo apoptosis
osteoclast
release enzymes there that allow them to digest the calcium phosphate, putting the calcium and phosphate back into the blood
ossification
process of bone tissue formation
fracture
break
living organ
Bone is a rigid but ___ made up of all 4 types of tissues!
connective tissue
the majority is osseous tissue but cartilage and dense connective tissue cover the bone's external surface
osseous tissue
bone tissue
nervous tissue
in its nerves
epithelial tissue
in its blood vessels, which provide nourishment
muscle tissue
skeletal muscle tissue
tendons
Connect muscle to bone
support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell formation, hormone production
functions of the skeletal system
support
framework holding up the entire body
protection
guards the body's most vital organs, like the skull protecting the brain and rib cage protecting the heart
movement
skeletal muscles are connected to bones via tendons and use bones as levers at joints to produce movements
pull
muscles can only _____
storage
stores minerals like calcium and phosphate, which can be released into the blood when needed
yellow bone marrow
stores energy in the form of fat in the ________________
blood cell formation
in red bone marrow of certain bones
hormone production
critical for helping maintain homeostasis
osteocalcin
secreted by bones helps to regulate insulin secretion, glucose levels, and energy usage
blood calcium
hormone production helps to regulate ____________ levels
location; shape
bones are classified by their ______ and ______
location
in the axial vs. appendiuclar skeleton
function
a bone's shape dictates its __________
long, short, flat, irregular
4 types of bones
long bones
longer than they are wide
shaft; wider
long bones tend to have a long _______ with either end being a bit ______
limbs
long bones are mostly in the ________
levers; movement
long bones act as ______ to aid in _______
arm bones, hand bones, leg bones, foot bones
examples of long bones
short bones
more cubes shaped
wide; long
short bones tend to be as _______ as they are _______
support; stability
short bones provide ____________ and ______ with little movement
wrists and ankles
examples of short bones
cubed
sesamoid bones are not as ________ shaped as short bones (more like a sesame seed)
tendons
short bones are embedded with ______ to create a strong joint
knee cap
example of a sesamoid bone
flat
thin and flat bones
curve
flat bones often have a bit of a _______
surface area; muscles
flat bones have a large ____________ for attaching to __________
sternum, shoulder blades, ribs, most of the cranial bones in the skull
examples of flat bones
irregular bones
everything else
highly specialized
irregular bones have a _____________ shape and structure
hip bones, vertebrae, clavicles
examples of irregular bones
compact; outside; spongy; inside
a dense and smooth layer of _________ (cortical) bone tissue on the ___________ surrounding the more porous _______ bone tissue on the ________
haversion canal
runs through the middle of each osteon and contains small blood vessels for nourishment and nerve fibers for signaling
central canal
another name for haversion canal
salts; collagen fibers; torsion stress
lamella are filled with tiny _____ and _______ that allow the bone to resist _____________
Made of osteons which containt lamellae that surround the haversion canal
structure of compact bone
osteon
orange bracket
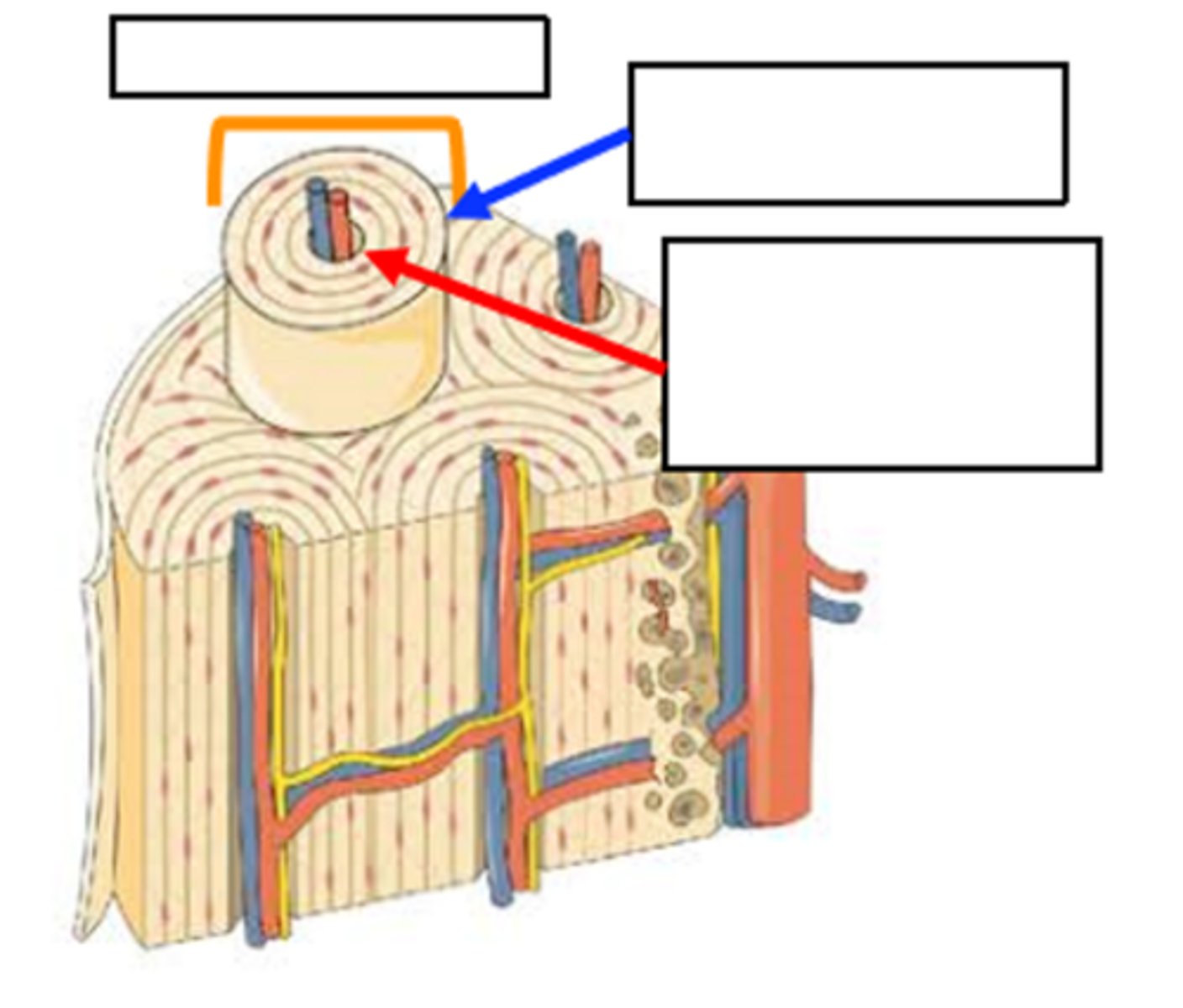
lamella
blue arrow
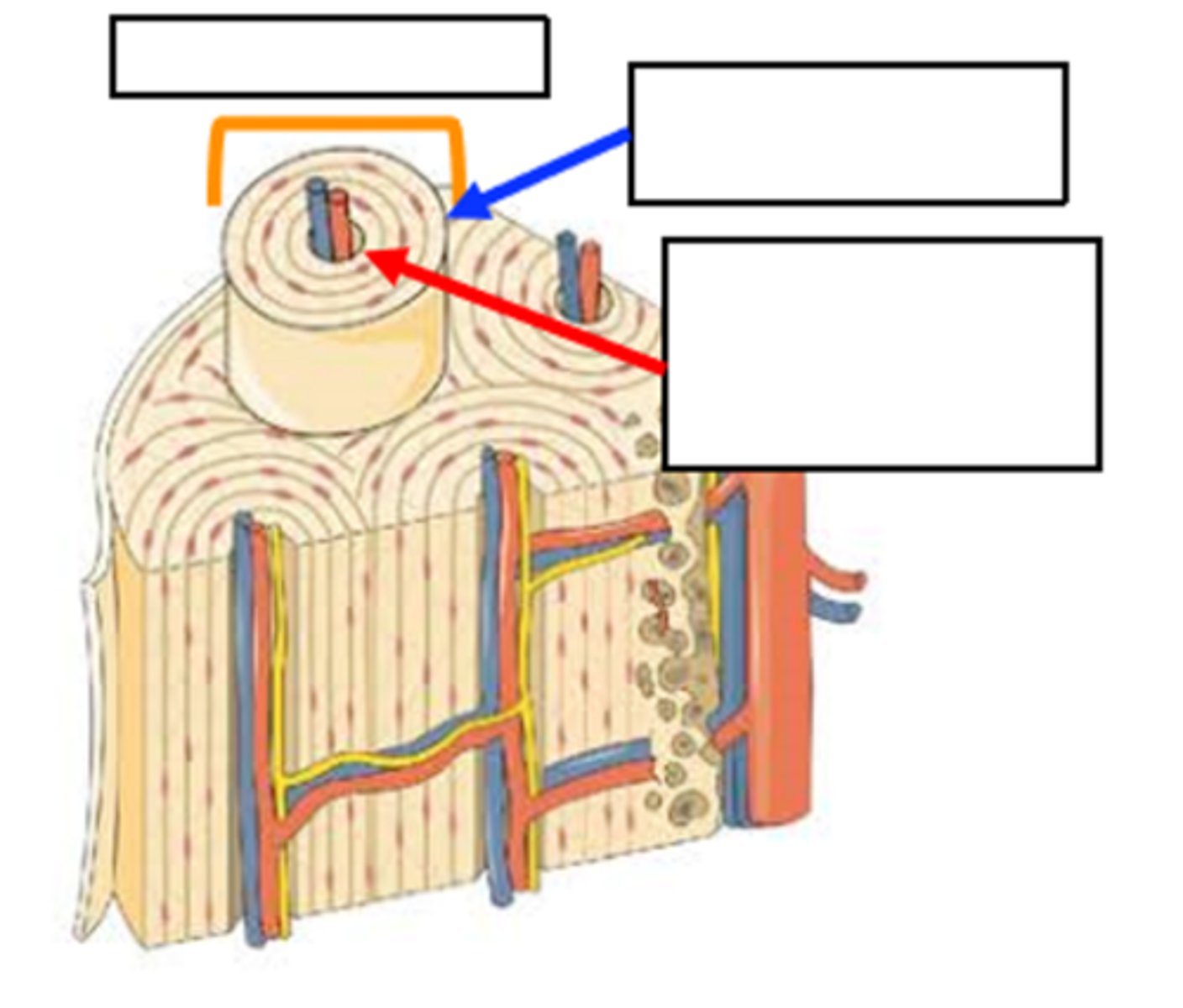
Haversion (central) canal
red arrow
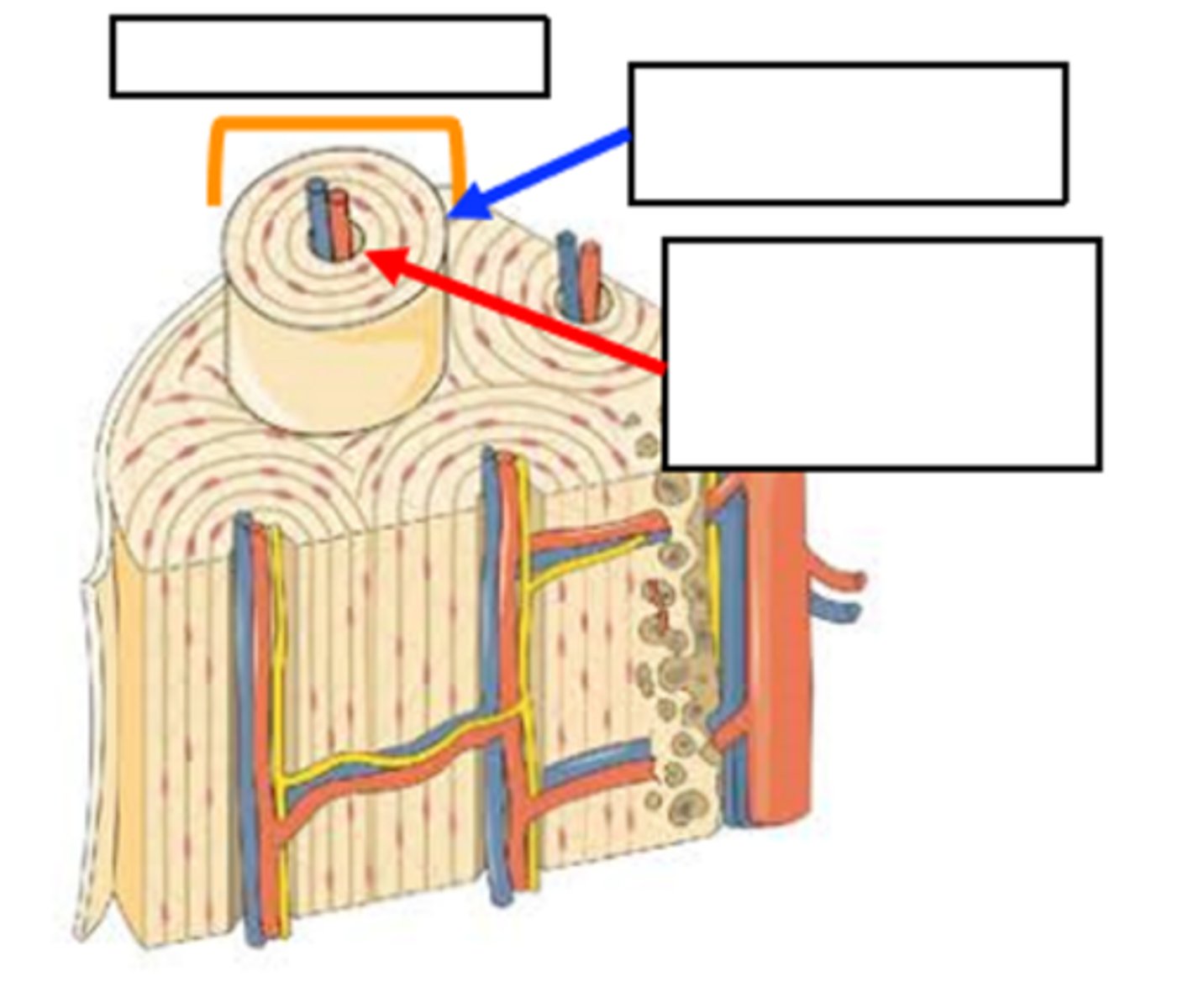
less organized, no osteons, have trabeculae
strucutre of spongy bone
trabeculae
where is bone marrow found
blood cells; stores energy
red bone marrow makes __________, yellow bone marrow _________________ in the form of fat
lightweight
spongy bone is small but __________
bone markings
the external surface of a bone is rarely smooth, and often has distinct ______________
muscles; ligaments; together
bone markings correspond to how the bone and its attached ________ and _________ work __________
projections, surfaces, depressions and openings
3 types of bone markings
projections
where muscle and ligaments attach
cheekbones
ex of projections
surfaces
that form joints
depressions and openings
allow blood vessels and nerves to run through
sinuses, eye sockets, nasal cavity
examples of depressions and openings
osteocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts
3 types of bone cells
housed
osteocytes are _______ in the lacunae
calcium
osteoblasts make sure that ______ is distributed
breakdown; rebuild
osteoclasts ______ a fracture to then _________
osteogenesis
Another name for ossification
forming your skeleton
ossification is key for __________
bone growth
ossification is essential for _____ from childhood up until early adulthood
bone modeling and repair
later in life ossification is used for ___________
intramembranous and endochondral
2 types of ossification
intramembranous ossification
bone develops from a fiborous membrane
membranous bone
what kind of bone develops from intramembranous ossification
clavicle and skull bones
examples of membranous bone
endochondral ossification
bone develops by replacing cartilage
endochondral bone
what kind of bone develops from endochondral ossification
all other bones (not clavicle and skull)
example of endochondral bone
articular cartilage and epiphyseal plates
cartilage remains in 2 places - the __________ on the ends of bones and the _________ which is where bone growth comes from as bones elongate
when a bone is bruised and old
when does bone remodeling occur
when a bone is fractured
when does bone repair occur
remodeled
bone is constantly being ______
the calcium in our bones would crystallize and make the bones more brittle
why is it important for our bones to keep remodeling
resorption
putting calcium and phosphate back into the blood
osteocytes; signals; osteoclasts; enzymes; blood; macrophages; remodeling; osteoblasts; apoptosis
BONE REMODELING PROCESS
__________ release chemical ______ to tell the osteoclasts to go to the damage. _________ release ______ there that allow them to digest the calcium phosphate, putting the calcium and phosphate back into the ______. __________ promote bone tissue __________. __________ come in and build new bone tissue before undergoing ________