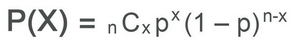AP Stats quiz 6.5-.7
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Requirements for something to be a binomial
BINS → binary (can only be yes or no), independent trials, # of things is fixed, same probability of success
What does each part of the binomial formula mean?
P = probability of success (%), n = # of trials, x/k = # of successful trials
(P)^k
probability of success
(1-P)
probability of failure
N-k
Number of failures
nCk
number of ways to get successes
How to find P(x = k) with calculator
binomPDF (n,p,k)
How to find P(x < k) with calculator
binomCDF (n,p,k)
How to find mean of binomial
Mx = n(p) “after many trials, the average number of successes is (mean)”
How to find the standard deviation of binomial
√np (1-p) “the number of successes typically varies by (SD) from the mean of (m)”
How to find the probability when the equation is NOT a binomial setting
either use the 10% probability or multiply together every successful trial
10% conditional probability
n < (0.10)N, n = sample size, N = population size
How to model a binomial distribution
by using a normal distribution
How to know when something is able to be represented by a normal distribution?
Both equations (n x p) and n(1 - P) must be less than or equal to 10 for a normal distribution to be valid
Equation for binomial formula