EXAM 03 - CHEST, ABDOMEN, AND PELVIS ANATOMY
1/655
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
656 Terms
anterior abdominal wall
anterior abdominal wall (contents)
skin
subcutaneous fat
aponeurotic/tendinous sheaths
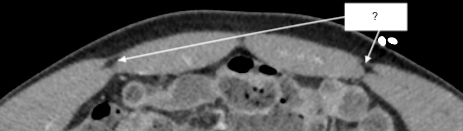
rectus abdominus
transversalis fascia
linea alba
skin
subcutaneous fat
aponeurotic (tendinous) sheaths
encase muscles and tendons
rectus abdominus
transversalis fascia
fascial layer deep to rectus abdominus
linea alba
semilunar line
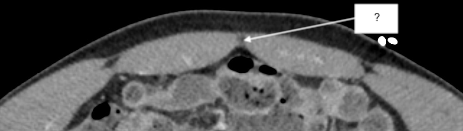
anterolateral abdominal wall
anterolateral abdominal wall (contents)
skin
subcutaneous fat
aponeurotic/tendinous sheaths
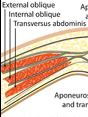
external oblique
internal oblique
transversus abdominis
transversalis fascia
external oblique
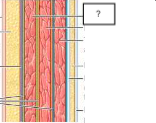
internal oblique
transversus abdominis
transversalis fascia
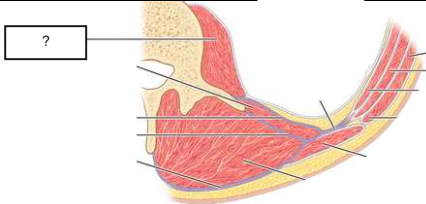
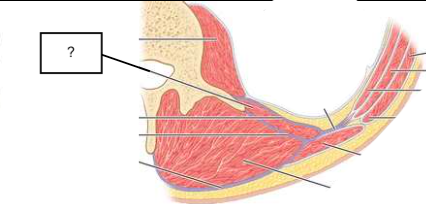
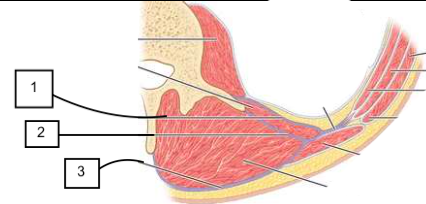
posterior abdominal wall
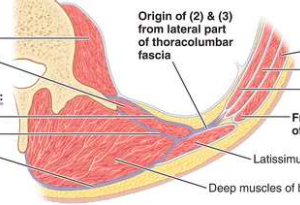
posterior abdominal wall (contents)
psoas
quadratus lumborum
latissimus dorsi
deep muscles of back
thoracolumbar fascia (anterior, middle, posterior layers)
psoas
quadratus lumborum
thoracolumbar fascia (1. anterior layer, 2. middle layer, 3. posterior layer)
latissimus dorsi
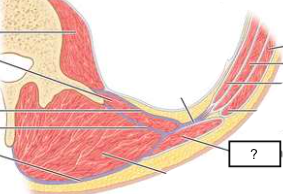
deep muscles of back
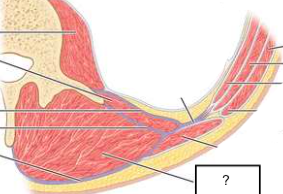
indirect inguinal hernia
pelvic contents travel through deep inguinal ring into inguinal canal
located lateral to inferior epigastric artery
may extend into scrota sac/labia majora
more common in males
indirect inguinal hernia
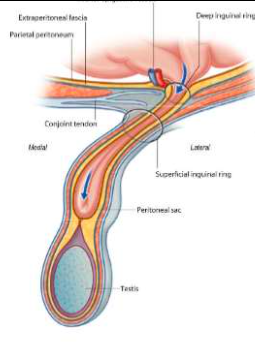
direct inguinal hernia
pelvic contents bulge through a weak part of pelvic wall fascia called the Inguinal (Hesselbach’s) triangle
located medial to inferior epigastric vessels
may extend through superficial inguinal ring
direct inguinal hernia
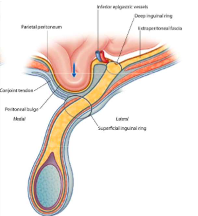
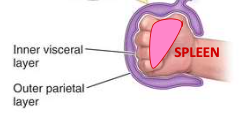
intraperitoneal
completely surrounded by visceral peritoneum
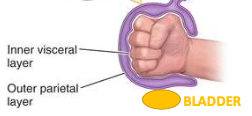
retroperitoneal
partially covered by parietal peritoneum
posterior to intraperitoneal structures
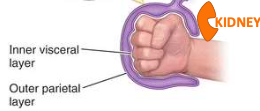
extraperitoneal
partially covered by parietal peritoneum
inferior to intraperitoneal structures
intraperitoneal structures
stomach
1st portion duodenum
jejunum
ileum
transverse colon
sigmoid colon
liver
spleen
uterus
ovaries
retroperitoneal/extraperitoneal structures
2nd, 3rd, 4th portions duodenum
cecum
ascending colon
descending colon
pancreas
kidneys
abdominal aorta
bladder
intraperitoneal
stomach is…
intraperitoneal
1st portion duodenum is…
intraperitoneal
jejunum is…
intraperitoneal
ileum is…
intraperitoneal
transverse colon is…
intraperitoneal
sigmoid colon is…
intraperitoneal
liver is…
intraperitoneal
spleen is…
intraperitoneal
uterus is…
intraperitoneal
ovaries are…
retroperitoneal
2nd, 3rd, 4th portions duodenum are…
retroperitoneal
cecum is…
retroperitoneal
ascending colon is…
retroperitoneal
descending colon is…
retroperitoneal
pancreas is…
retroperitoneal
kidneys are…
retroperitoneal
abdominal aorta is…
extraperitoneal
bladder is…
lesser omentum (composition)
fat, vessels, and lymphatics extending from stomach to liver
lesser omentum (function)
contains collections of macrophages
physical barrier to prevent spread of disease
lesser omentum
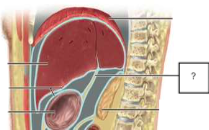
lesser omentum
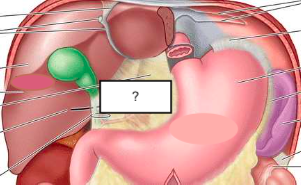
greater omentum
fat extending from anterior aspect of stomach which folds in on itself and connects to transverse colon
greater omentum
perirenal space
(green space)
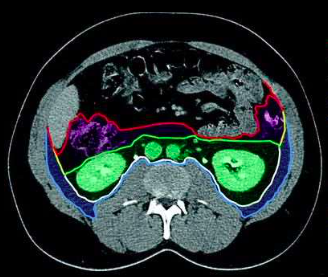
anterior pararenal space
(purple space)
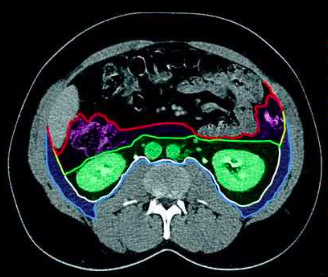
posterior pararenal space
(blue space)
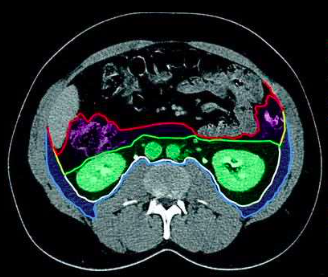
parietal peritoneum
(red outline)
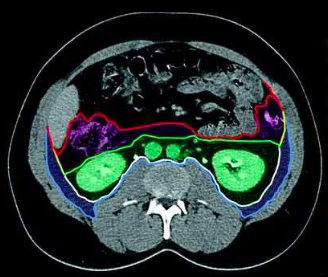
Gerota’s fascia (anterior renal fascia)
(green outline)
Zuckerkandl’s fascia (posterior renal fascia)
(white outline)
transversalis fascia
(light blue outline)
lateroconal fascia
(yellow outline)
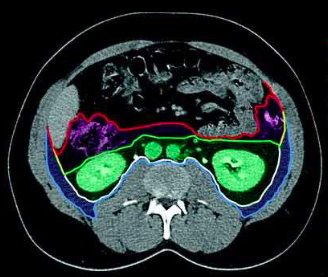
retroperitoneal spaces
perirenal space
anterior pararenal space
posterior pararenal space
retroperitoneal space boundaries
parietal peritoneum
Gerota’s fascia
Zuckerkandl’s fascia
transversalis fascia
ascend (move superiorly and rotate 90°)
kidneys ____ during development
kidney ascension
kidneys move superiorly, rotate 90°
vascular supply/drainage changes during this process
excessive renal arteries
change in vascular supply of kidneys during ascension can result in…
accessory renal artery
may result in obstruction of ureter at uretero-pelvic junction and hydronephrosis
important in living kidney donors
retroperitoneal
kidneys are ____ structures
2 layers of fat
kidneys are surrounded by…
fascia
fat layers separated by…
Gerota’s fascia
fat layers are separated by ______ anteriorly
Zuckerkandl’s fascia
fat layers are separated by ______ posteriorly
renal sinus (contents)
fat
arteries
veins
nerves
lymphatics
hilum
entry point into the renal sinus
capsule
envelops kidney
enclosed potential space
important in hemorrhage originating from the kidney
composed of the same structures
renal cortex and columns are…
renal papilla
empty urine into calices
ureter
forms a tunnel in the bladder wall
closed off
as urine expands the bladder, ureter is…
vesicoureteral reflux
abnormal angle/length of the tunnel (uretero-vesical junction) prevents closure and results in…
vesicoureteral reflux
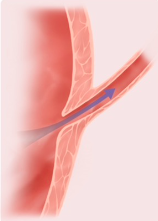
tunnel closure (urine expansion of bladder)
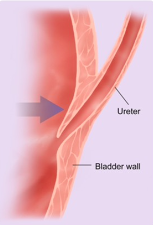
intra- and extraperitoneal
bladder is… (peritoneum relation)
intraperitoneal
dome of bladder is…
bladder trigone
developmental remnant of obliterated structures
ureteral orifices at upper corners of upside-down triangle
bladder
empties via contraction of detrusor muscle
contraction of detrusor muscle
parasympathetic response to stretch sensors in bladder wall
male urethral segments
intramural/preprostatic
prostatic
membranous
spongy urethra
intramural urethral segment (males)
associated with internal sphincter
membranous urethral segment (males)
highest risk of traumatic injury because it’s fixed
associated with external sphincter
segments of spongy urethra (males)
bulbous
penile/pendulous
fossa navicularis
female urethral segments
no organization of detrusor muscle to form internal sphincter
no segmental divisions
paraurethral (Skene) glands homologs of prostate
greater vestibular (Bartholins) glands homologs of Cowper glands
retroperitoneal
adrenal glands are…
superomedial
adrenal gland location relative to kidneys
adrenal gland shapes
pyramidal on right
crescentic on left
flat if kidney doesn’t ascend
adrenal cortex
secretes corticosteroids and androgens
comprised of zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis
zona glomerulosa
secretes aldosterone (Na+ regulation —> BP regulation)
zona fasciculata
secretes glucocorticoids (e.g. cortisol)