CS- introduction to NICE
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What is NICE ?
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an independent public body that helps those working in the NHS, local
authorities and the wider community deliver high quality health and
social care.
Why was nice created ?
to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and cost effectiveness of new medicines, technologies and interventions
-create consistent guideline
-end postcode prescribing
-effective use of resources
What are the types of NICE Guidance ?
Guidelines
-clinical
-social care
-public health
Technology appraisals
-new and existing medicines technologies
Evidence summaries
-best available evidence for selected new medicines
Quality Statements
-set standards of quality
How do they establish clinical effectiveness?
Best available evidence
Recommendations graded based on strength of evidence
Expert opinion of the guideline development group and other
experts considered when there is insufficient evidenceMay decide that there is not enough evidence to recommend
whether a test or treatment is useful or not.
How do they establish cost effectiveness?
Evaluate new medicines using the quality-adjusted life year (QALY) to measure their benefits.
QALYs are estimates that are calculated from a range of sources including questionnaires that ask about factors that impact on a person’s health- related quality of life.
QALYs are used to assess value for money – by assessing how much the treatment costs and how much benefit it produces compared with the next best available alternative. This is expressed as the ‘cost (in £) per quality- adjusted life year (QALY) gained’.
What is the summary of guideline development process?
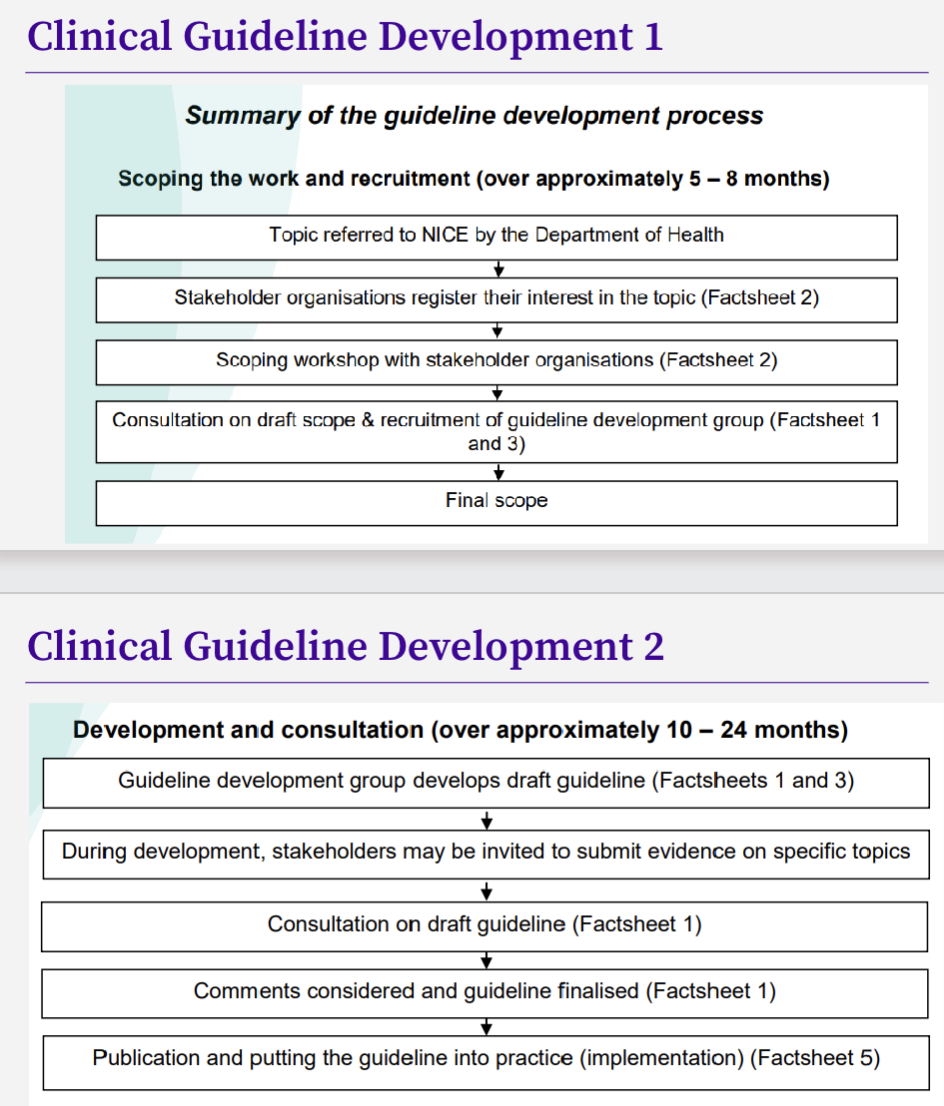
How should NICE guidance be used ?
● Not legally binding but would have to justify non-use
● The recommendations in NICE clinical guidelines should be taken
into account when deciding what treatments to offer people.
Apply the guideline in a person-centred way:
○ Age, frailty
○ Multimorbidity
○ Patient wishes
Wha are some challenges of NICE ?
● Conflict of interest
● Clinical guidelines are often single condition guidelines
● Current process considers cost effectiveness and clinical
effectiveness but not sustainability (except in asthma guidelines)
What other clinical resources can be used ?
● The British National Formulary (BNF)
● The Children’s British National Formulary (cBNF)
● The Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC) website
● The Clinical Knowledge Summaries (CKS) website
● NHS
note - some areas have local formularies
What are some professional resources used
● Community Pharmacy England
● The Royal Pharmaceutical Society
● Centre for Pharmacy Postgraduate Education
● General Pharmaceutical Council
Summary
NICE creates world-leading, evidence-based guidance on safe and cost-effective treatments
Various types of guidance available
Recommendations should be taken into consideration along with patient-specific factors
Local formularies provide medicine-specific
guidance, but should be in line with NICE