Lab 11: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the ANS
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Spinal Cord
A continuation of the brain stem located within the vertebral canal that serves mainly as a communication link.
Conus Medullaris
The terminal end of the spinal cord, typically located at the first or second lumbar vertebra.
Cauda Equina
A bundle of spinal nerves and nerve roots extending from the inferior end of the spinal cord.
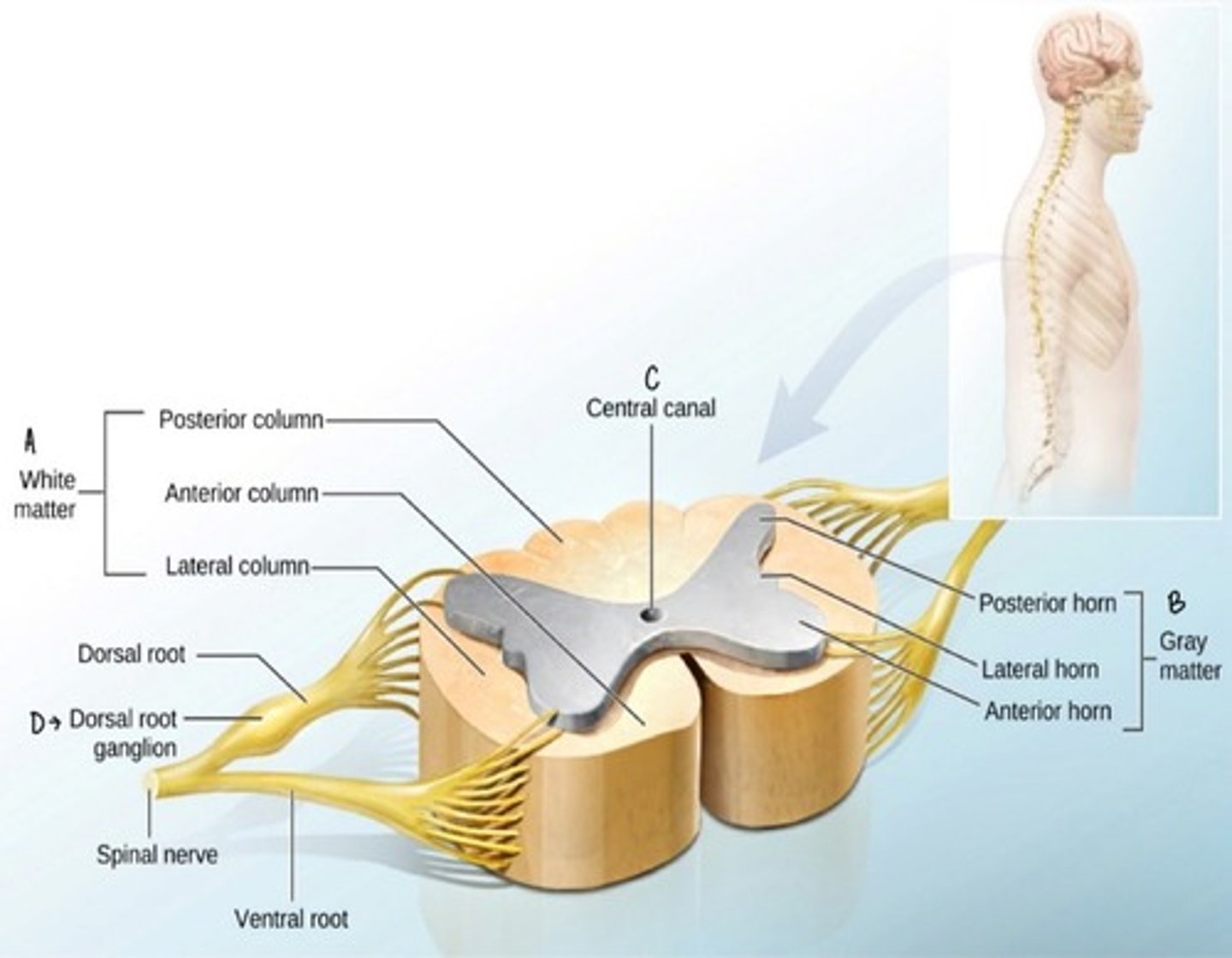
Dorsal Root
The part of a spinal nerve that contains sensory neurons entering the spinal cord.
Ventral Root
The part of a spinal nerve that contains motor neurons exiting the spinal cord.
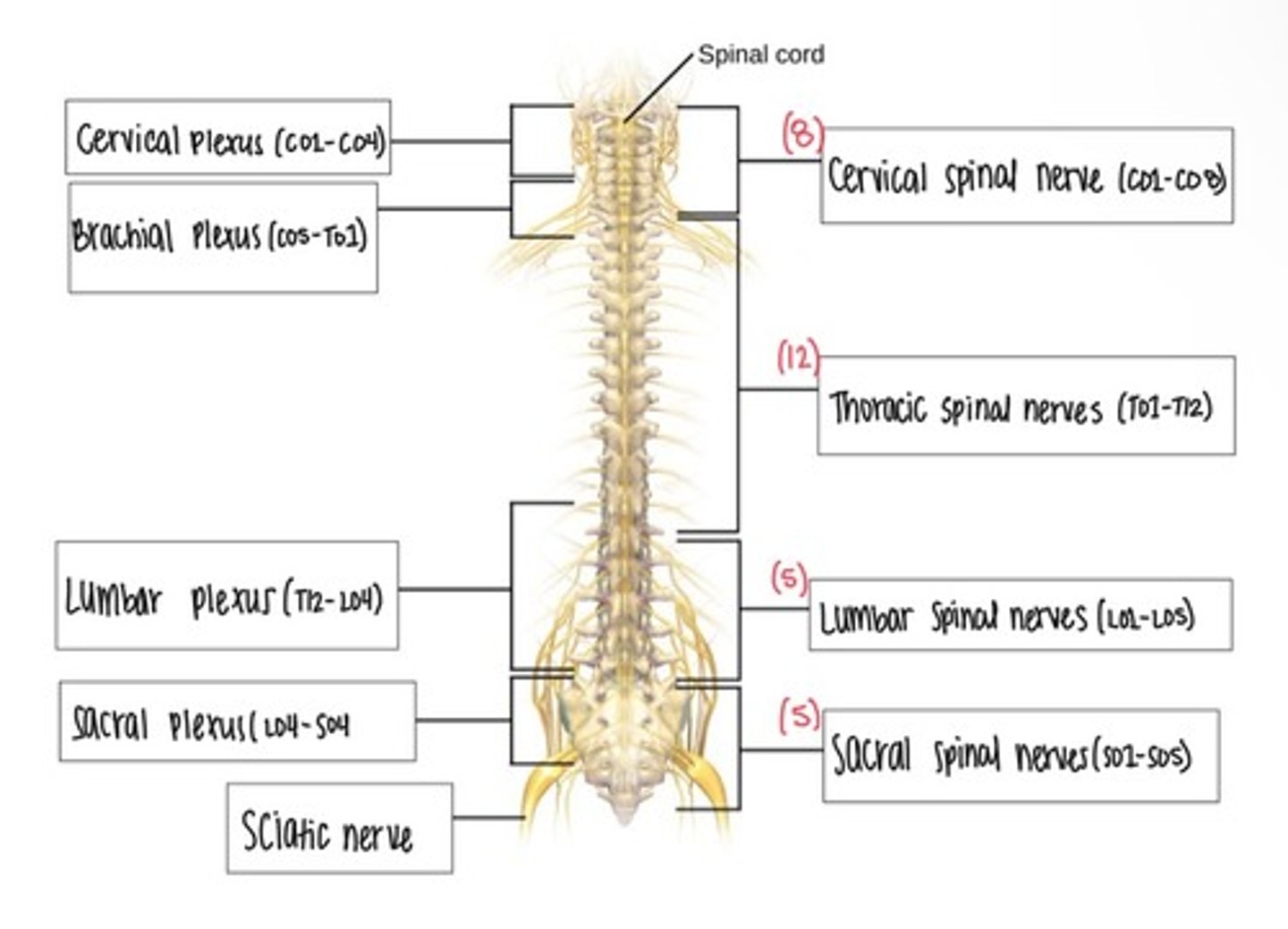
Nerve Plexus
A network of intersecting spinal nerves that supplies nerves to body parts; includes cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral plexuses.
Efferent Pathways
Motor pathways that transmit impulses away from the central nervous system.
Preganglionic Neuron
A neuron that transmits signals from the central nervous system to a ganglion in the autonomic nervous system.
Ganglionic Neuron
A neuron that transmits signals from a ganglion to an effector in the autonomic nervous system.
Sympathetic Nervous System
A division of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
A division of the autonomic nervous system that conserves energy and promotes 'rest and digest' activities.
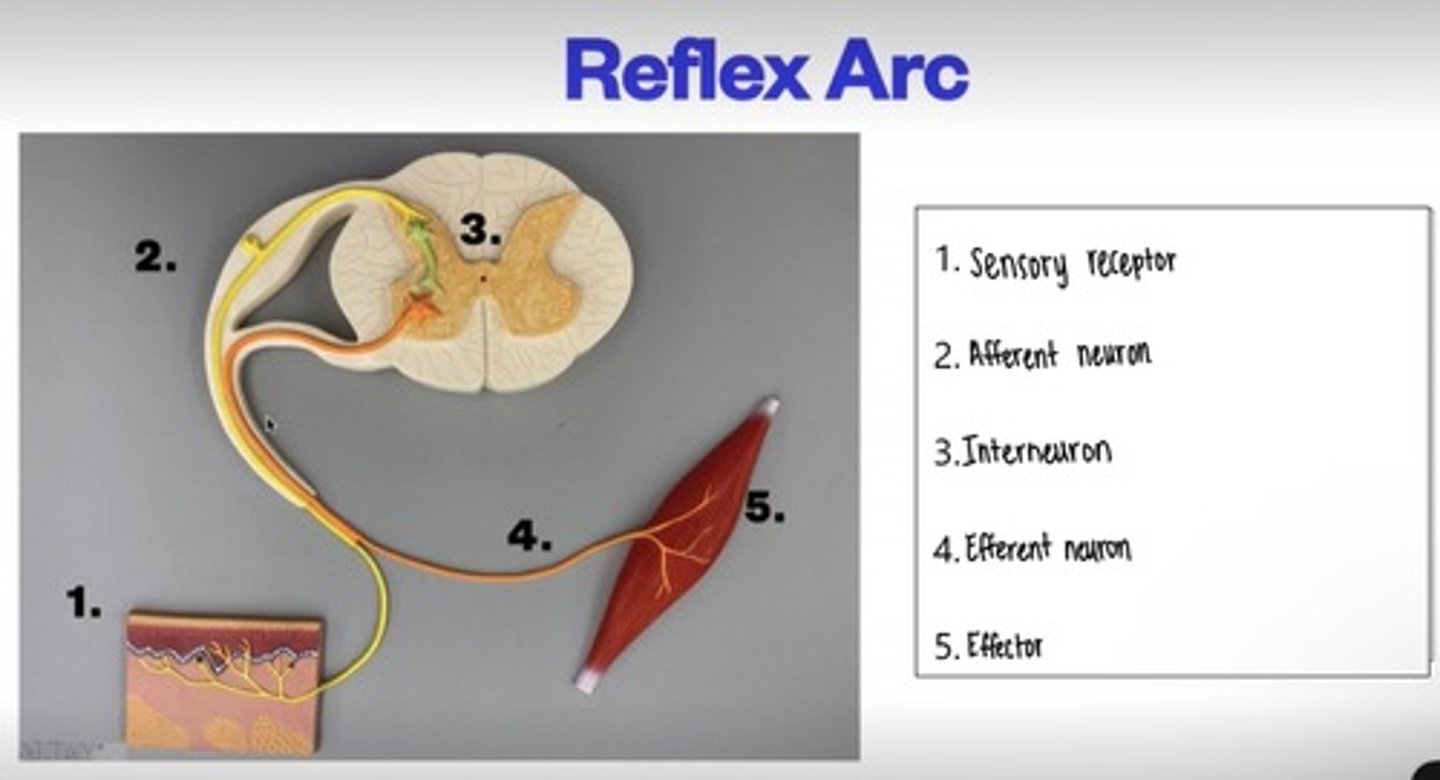
Reflex Arc
The neural pathway that mediates a reflex action, typically comprising a receptor, sensory neuron, integration center, motor neuron, and effector.
Monosynaptic Reflex
A reflex that involves only one synapse between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron.
Polysynaptic Reflex
A reflex that involves one or more interneurons in addition to the sensory and motor neurons.
Patellar Reflex
A stretch reflex induced by tapping the patellar ligament, resulting in extension of the knee.
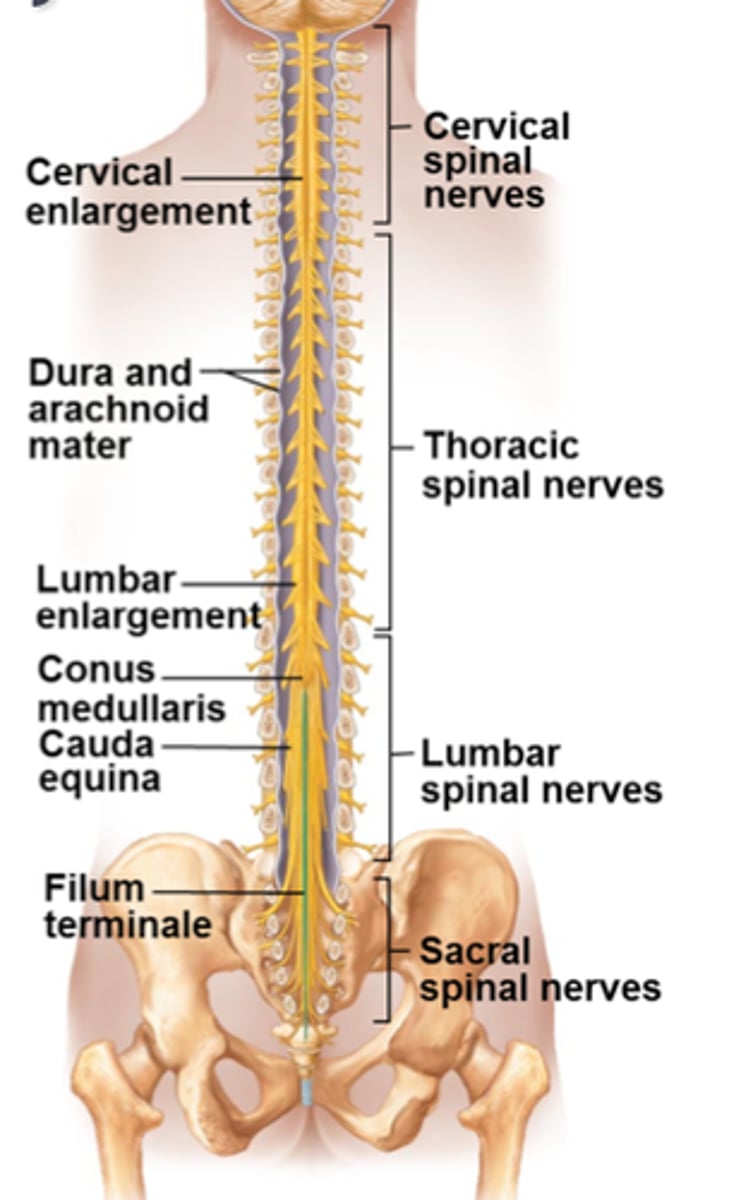
Protection of the Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is part of the CNS that is protected by the meninges and enclosed inside the vertebral column.
Meninges include three layers:
Dura Mater- thick outer layer (tough structure, protects brain)
Arachnoid Mater- middle layer
Pia Mater- inner layer attached to the spinal cord and brain
External Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
Spinal Nerves
Cervical Plexus
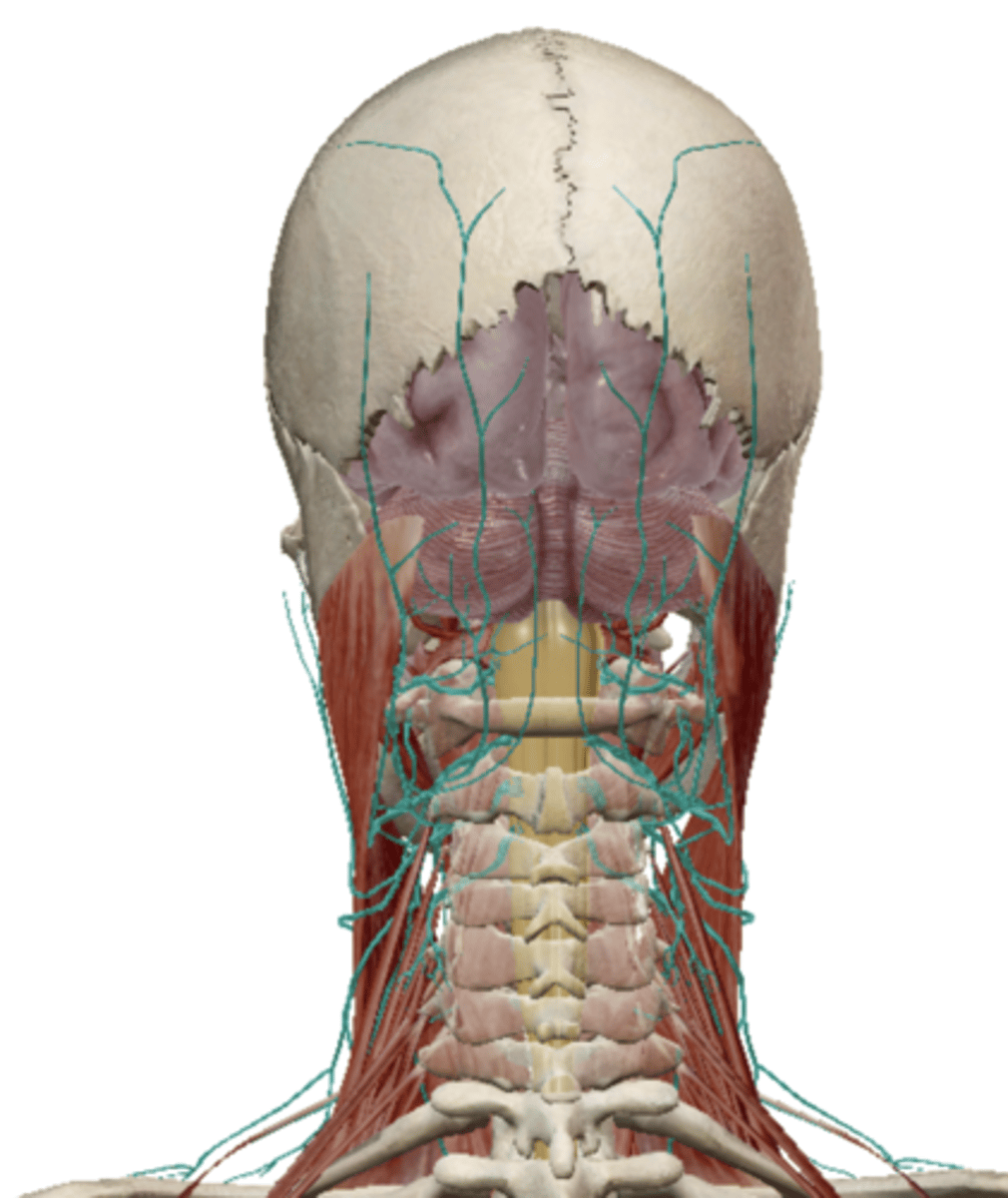
Supraclavicular Nerve (Cervical Plexus)
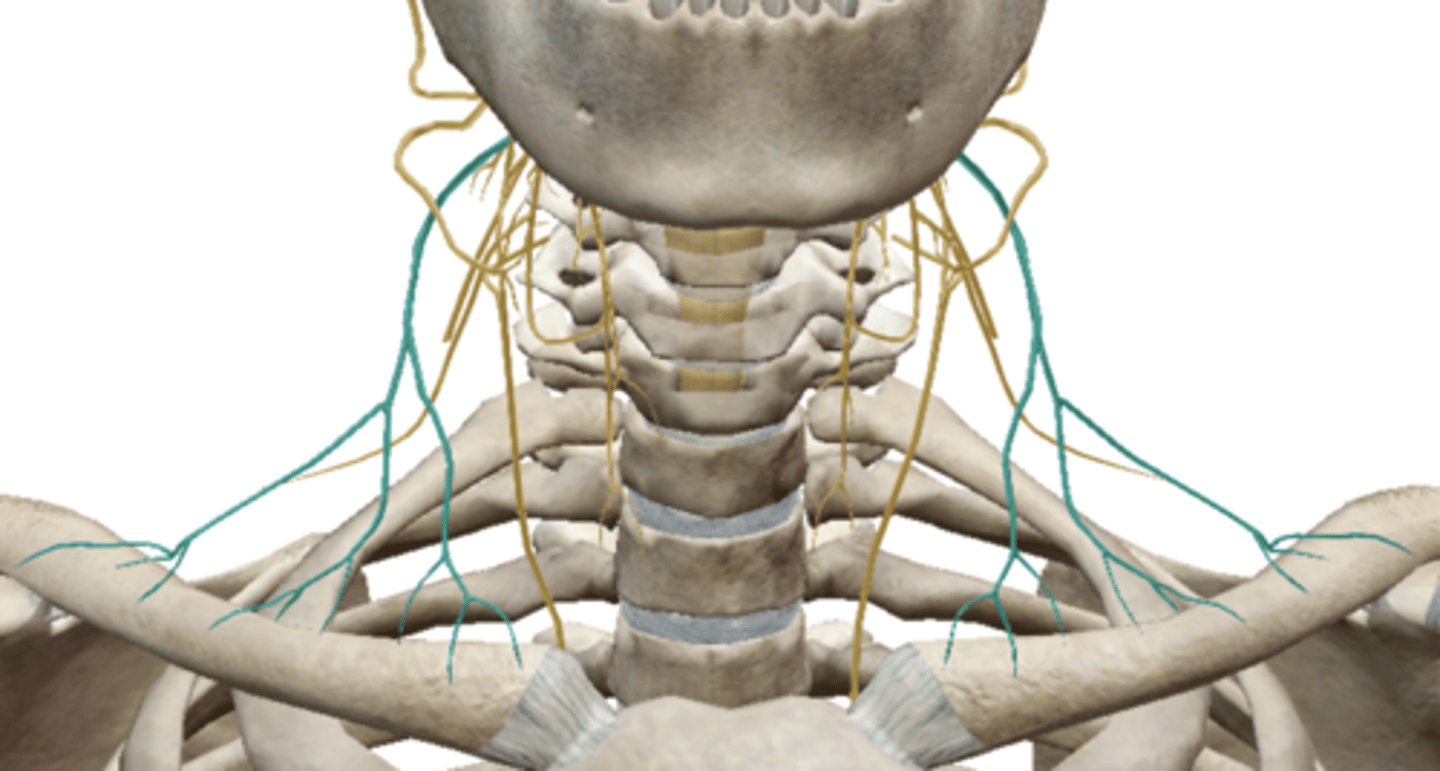
Phrenic Nerve (Cervical Plexus)
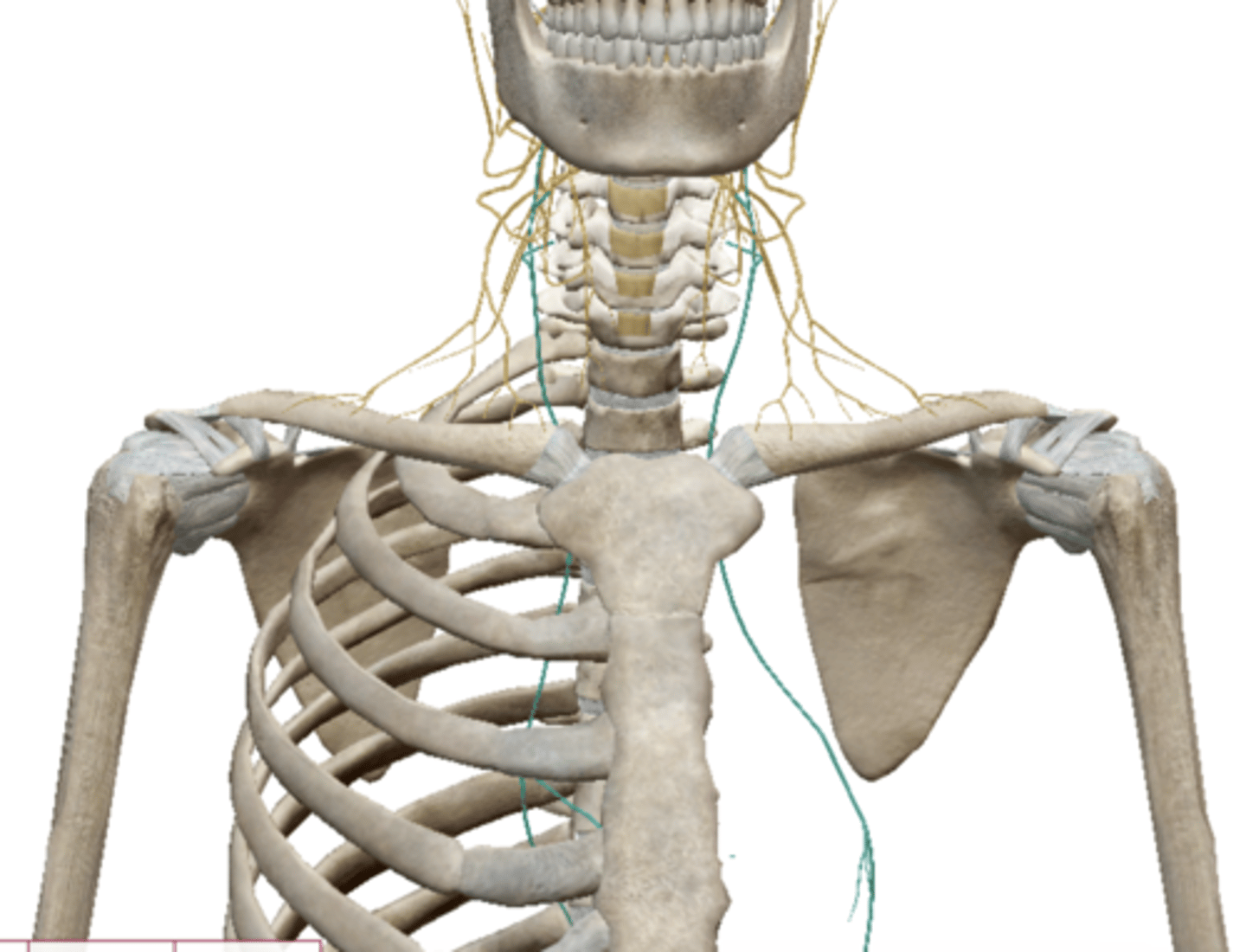
Brachial Plexus
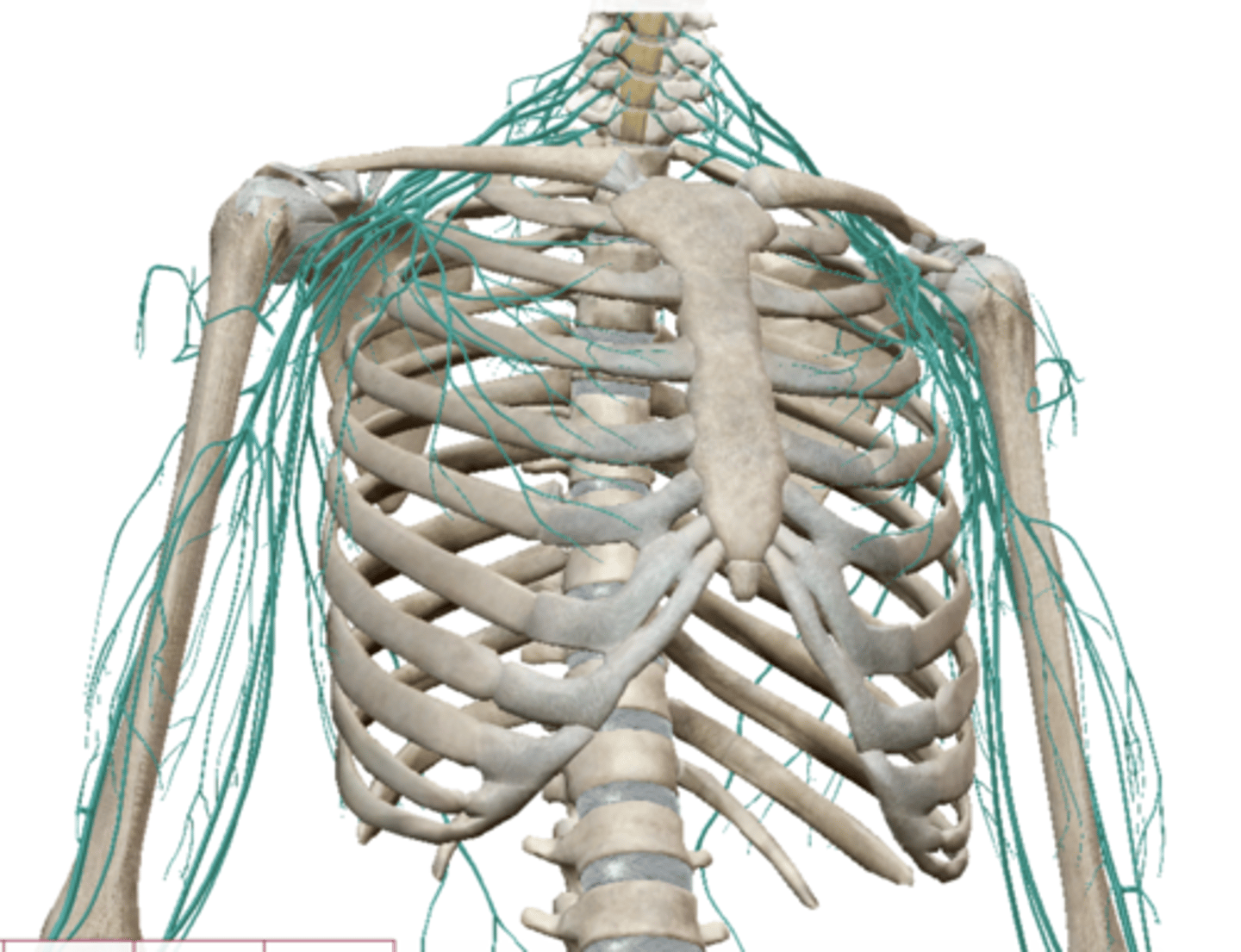
Axillary Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
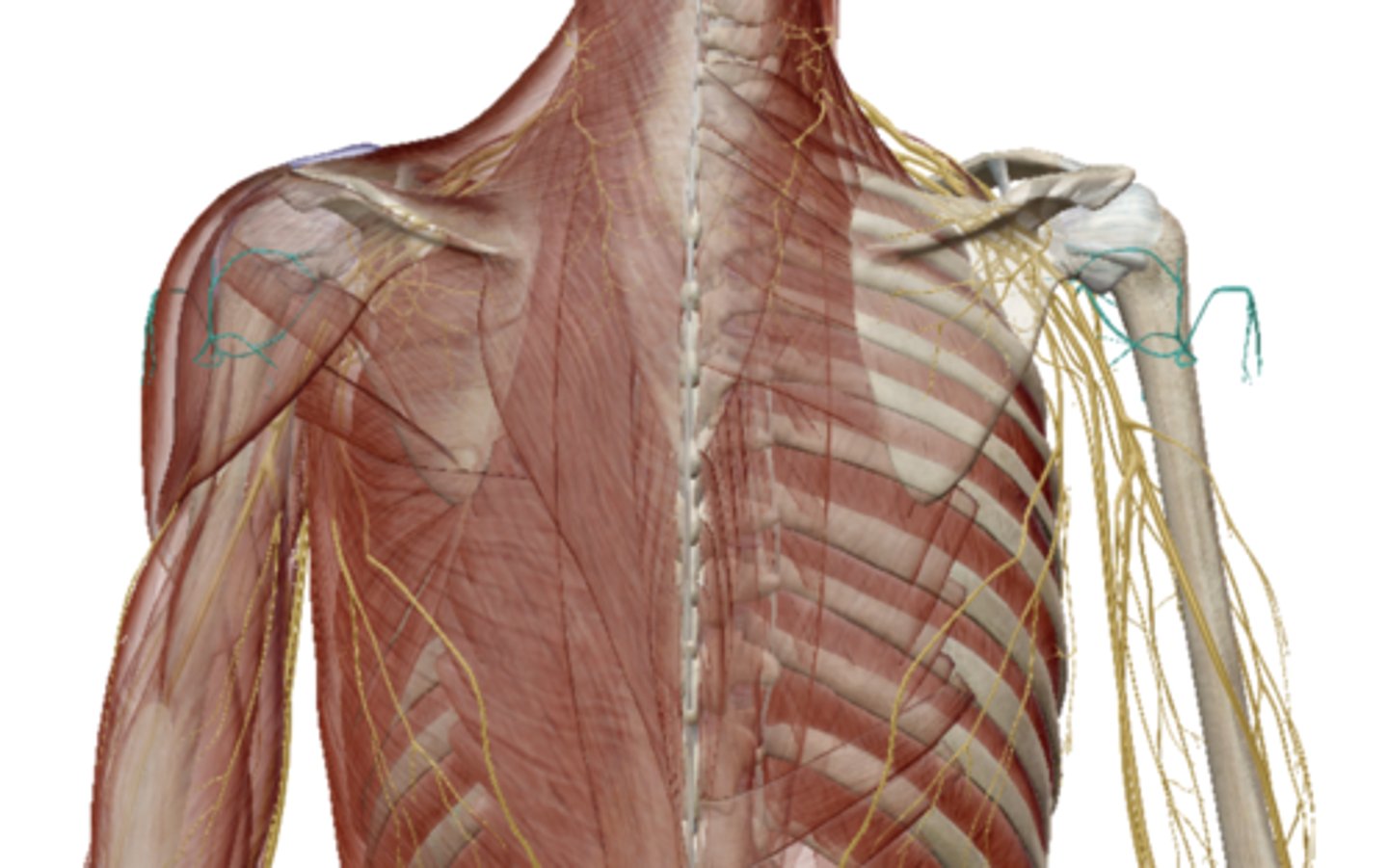
Radial Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
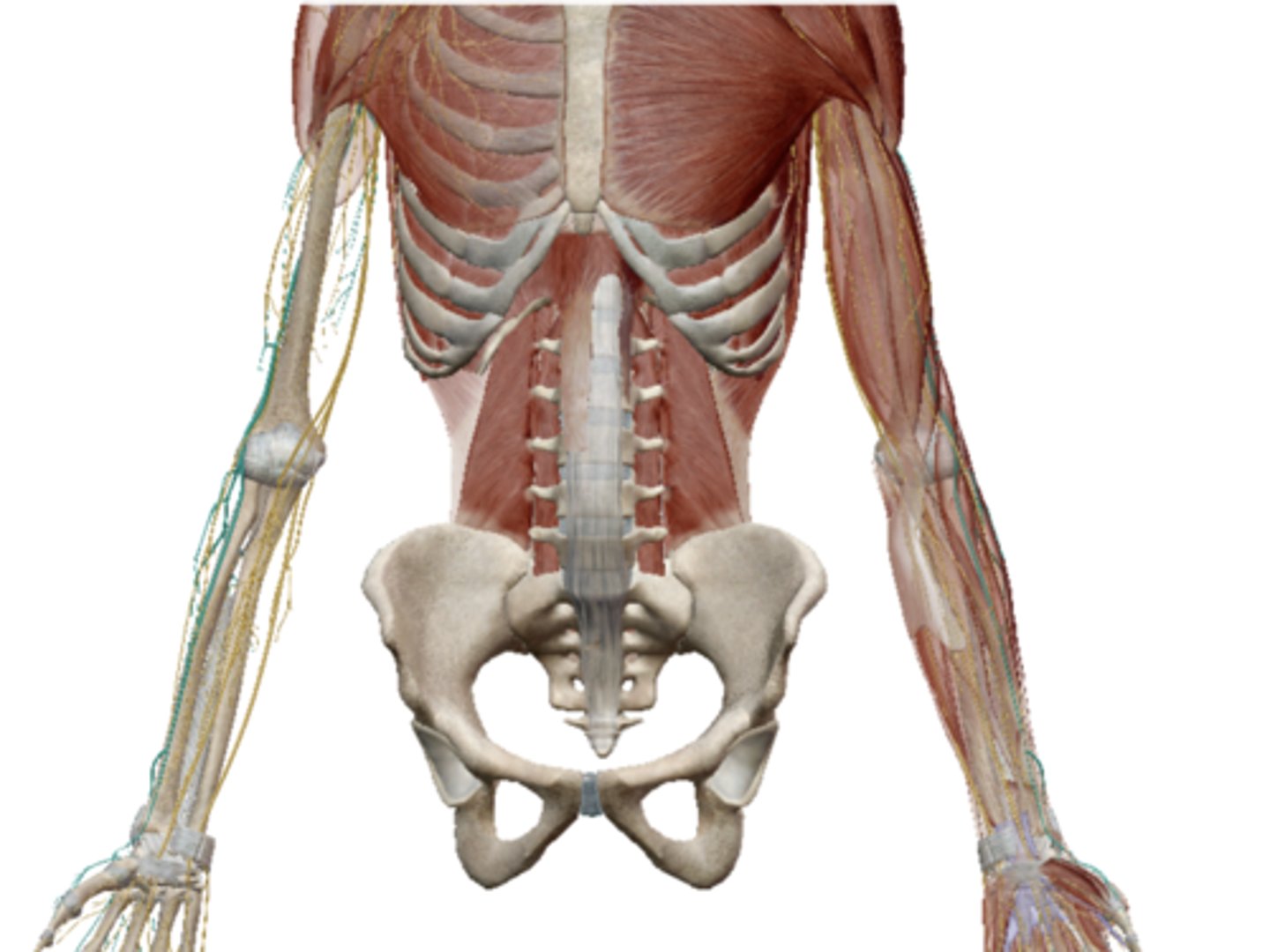
Median Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
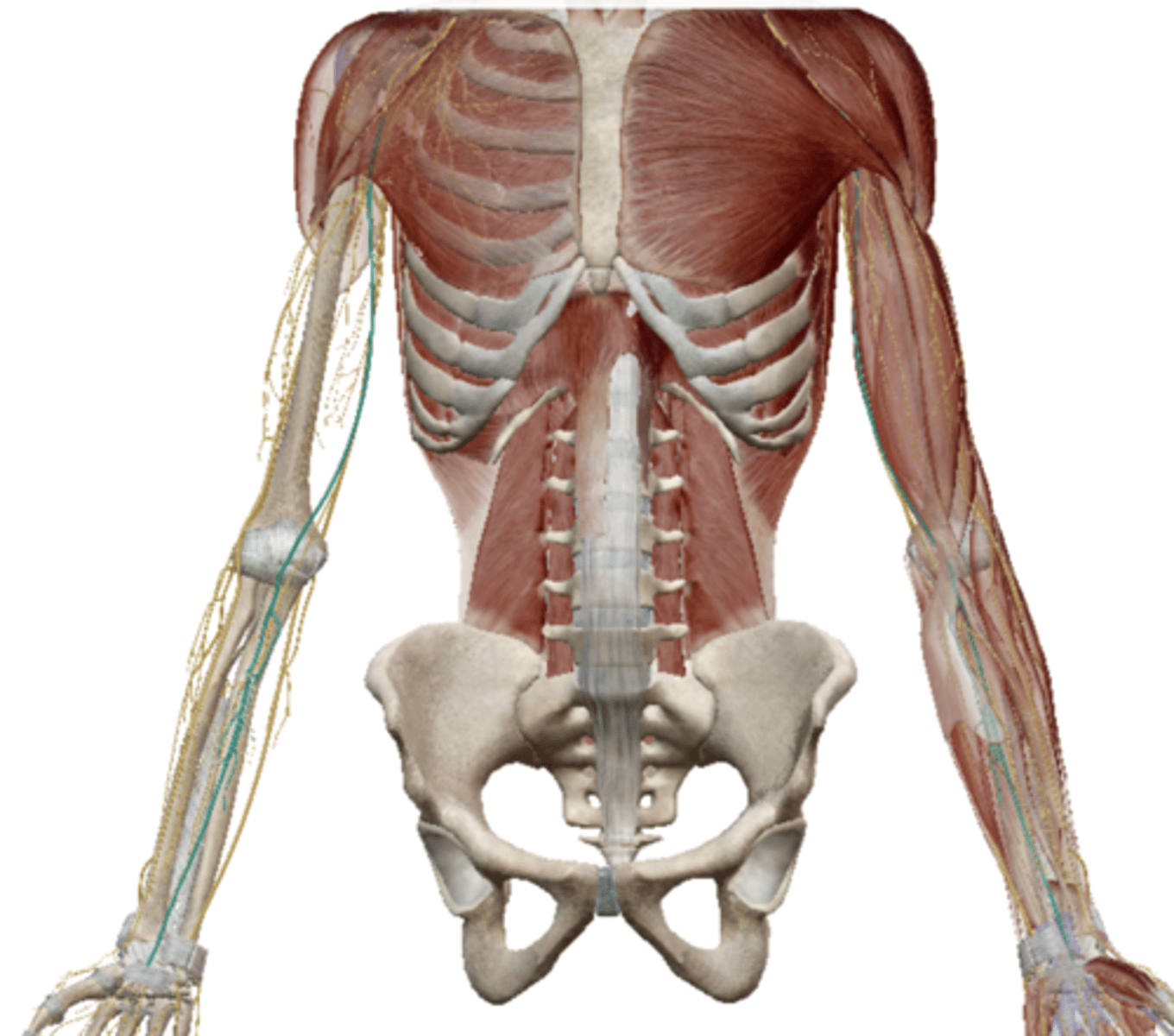
Musculocutaneus Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
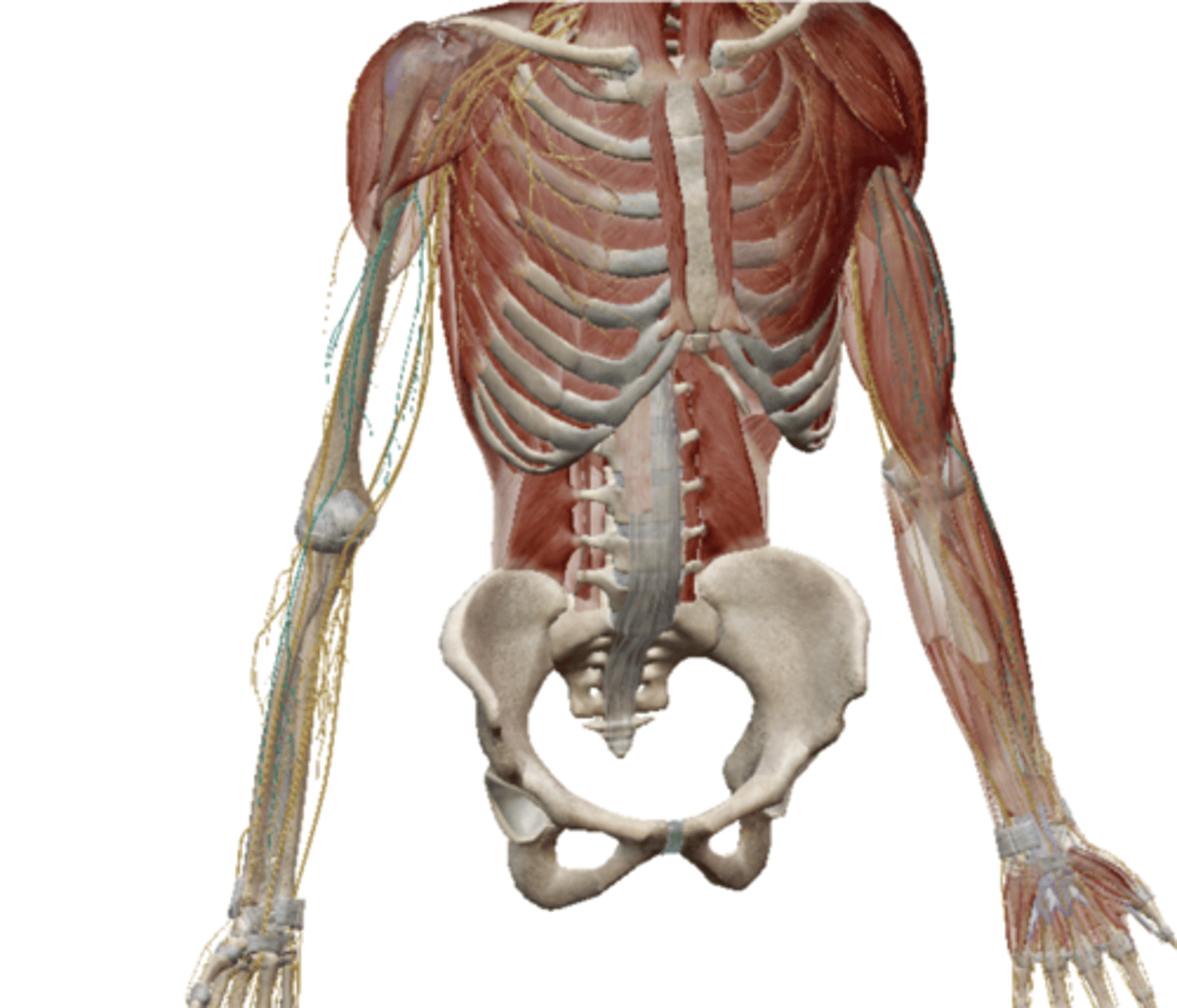
Ulnar Nerve (Brachial Plexus)
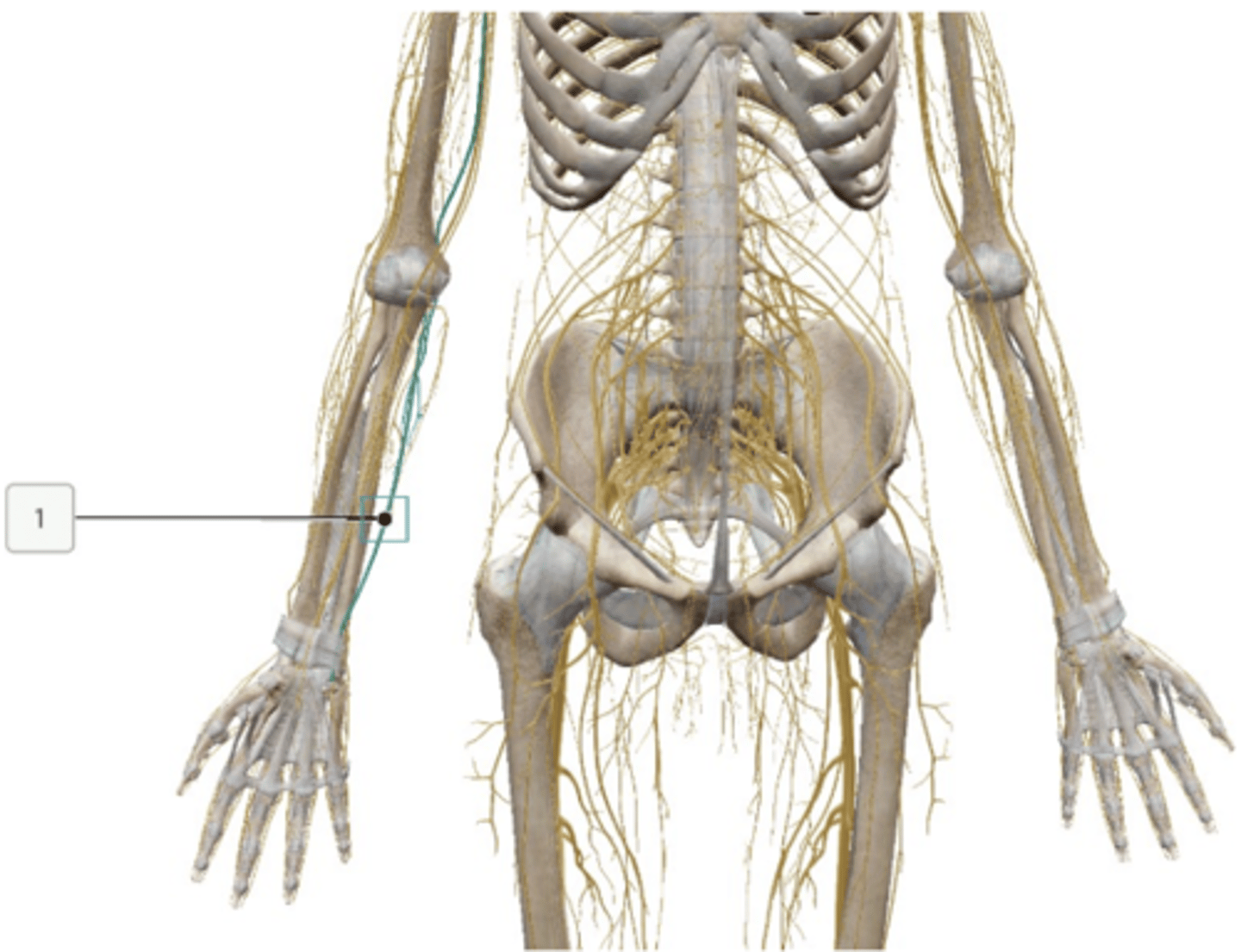
Lumbosacral Plexus
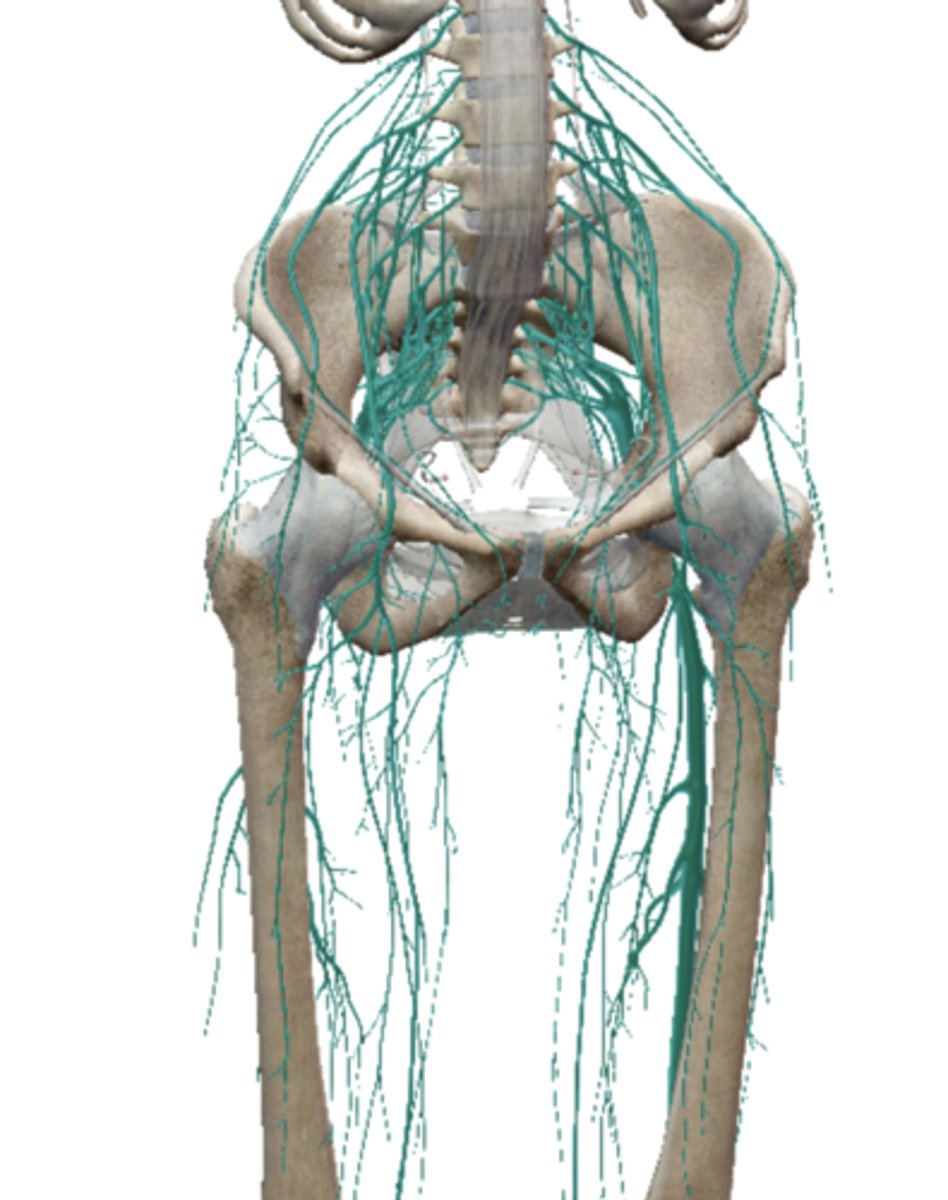
Femoral Nerve (Lumbar Plexus)
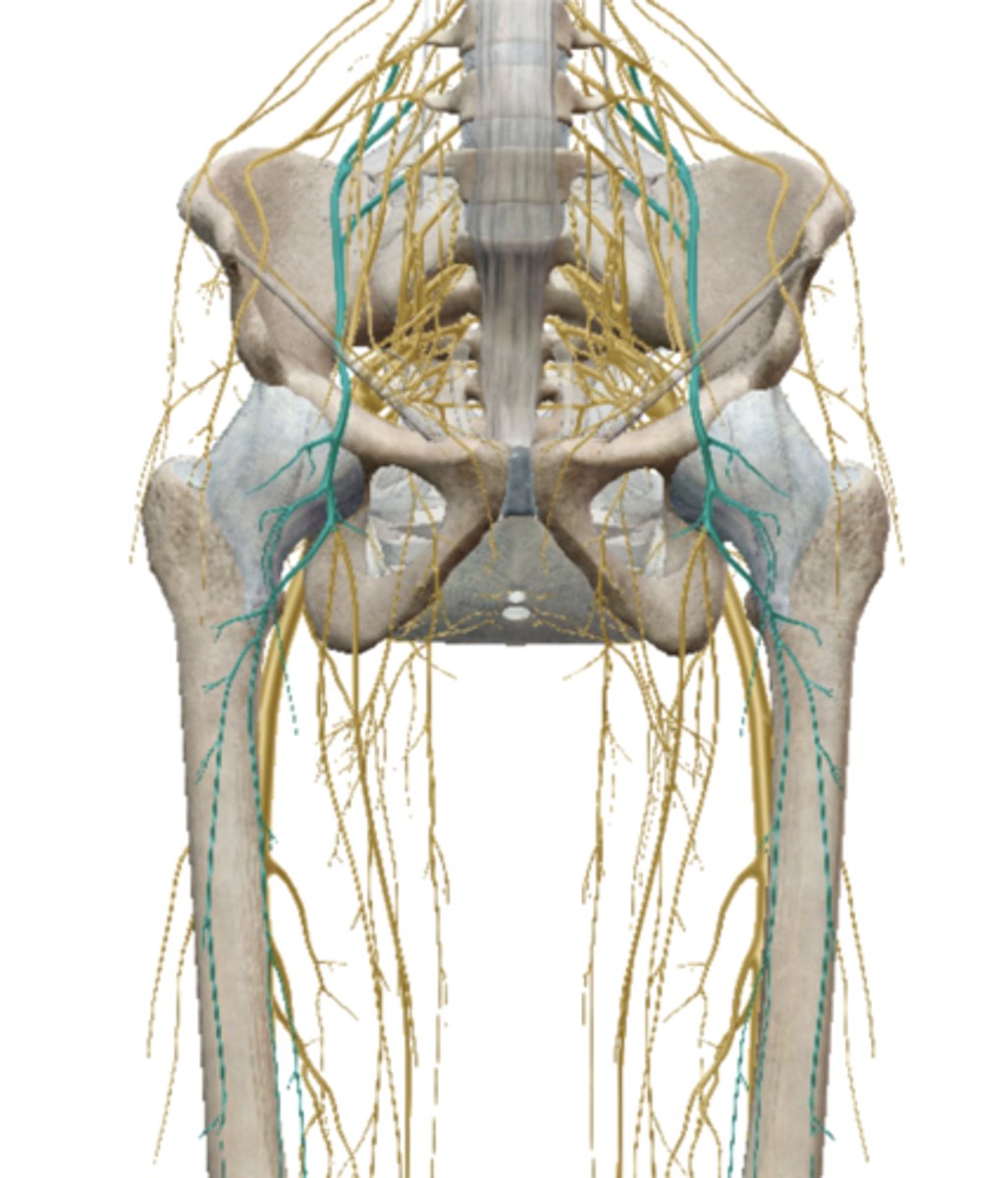
Obturator Nerve (Lumbar Plexus)
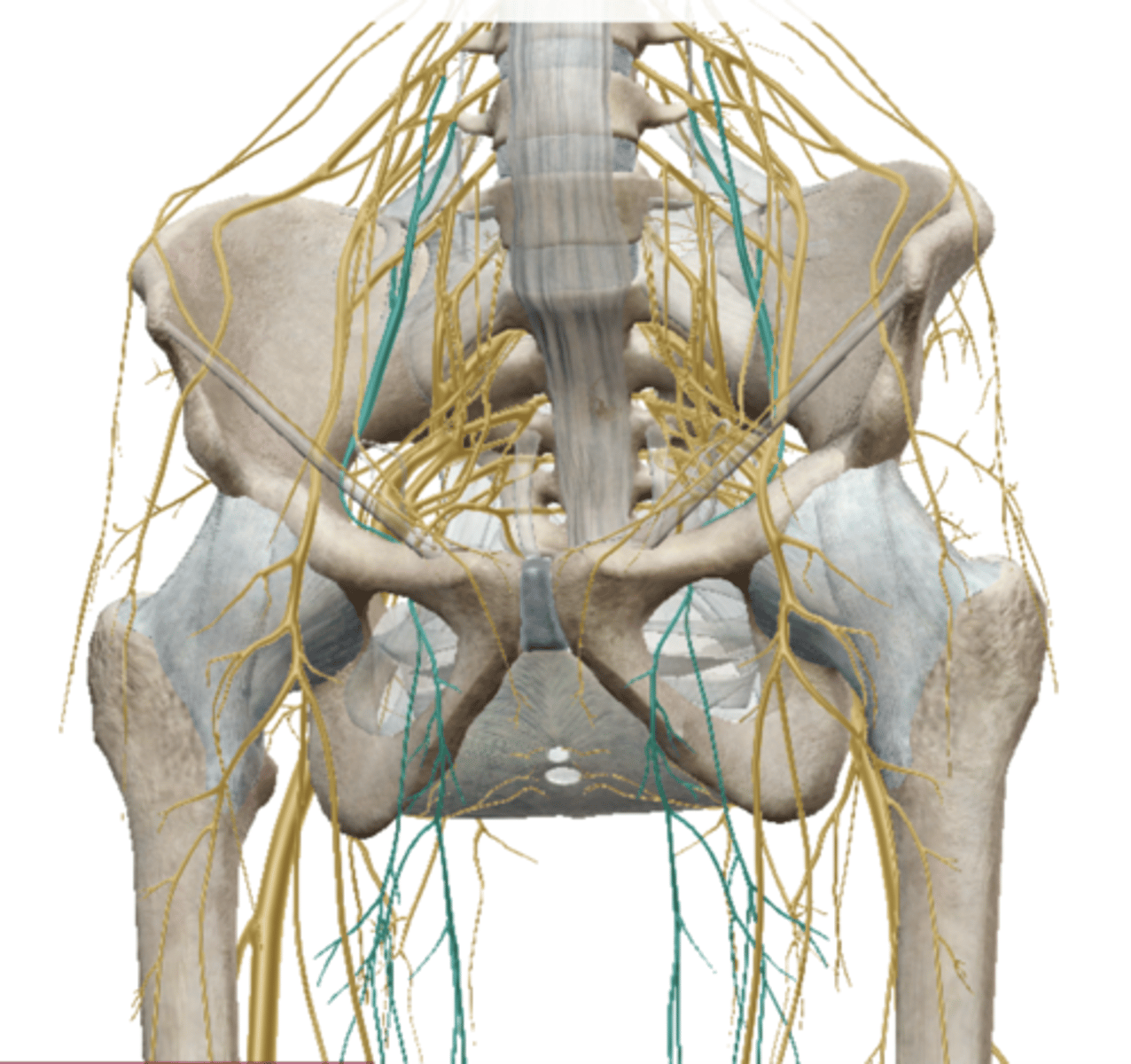
Sciatic Nerve (Sacral Plexus)
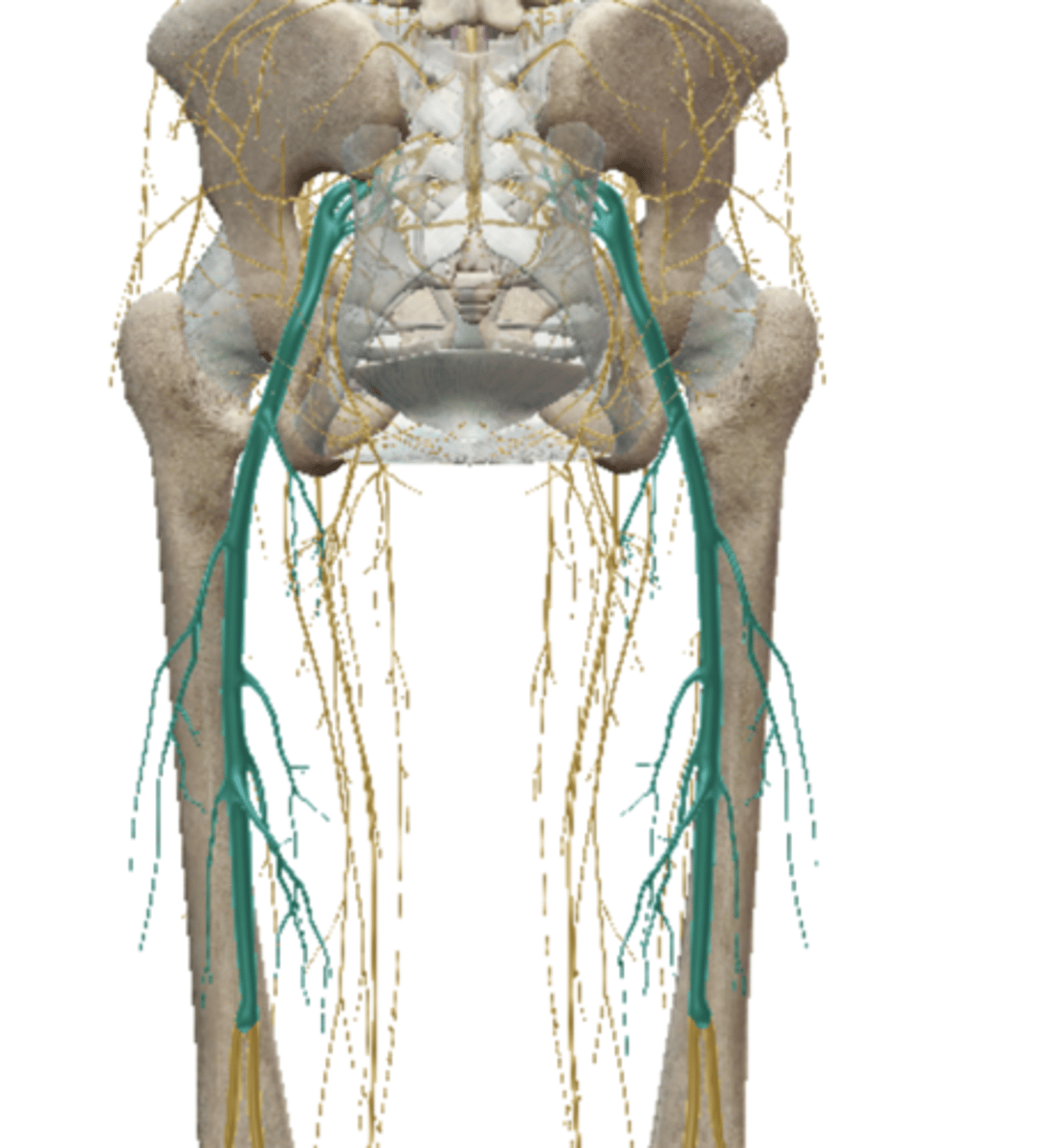
Gluteal Nerves (Sacral Plexus)
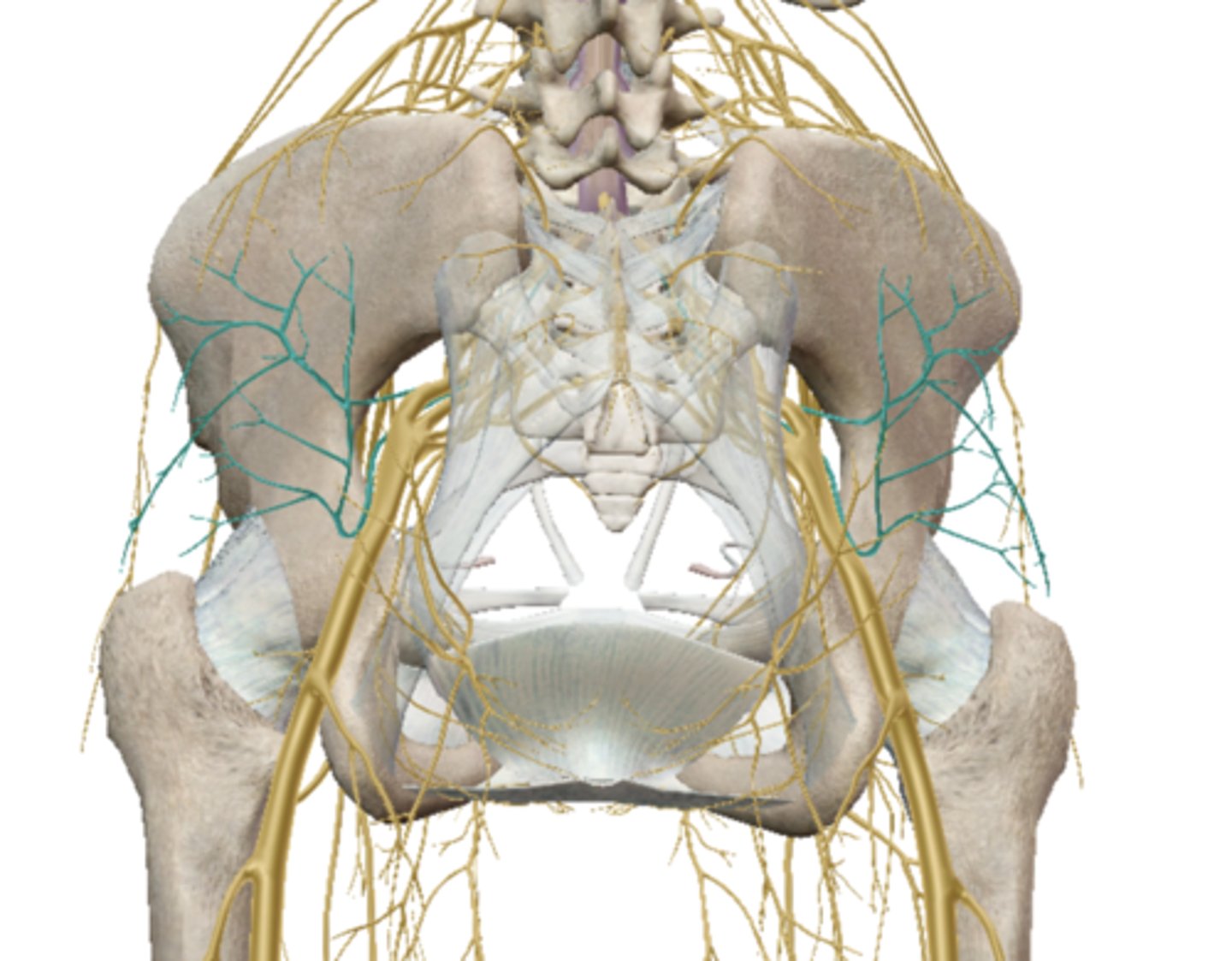
Common Fibular (peroneal) Nerve
Superficial Fibular (peroneal) - VB
(Sacral Plexus)
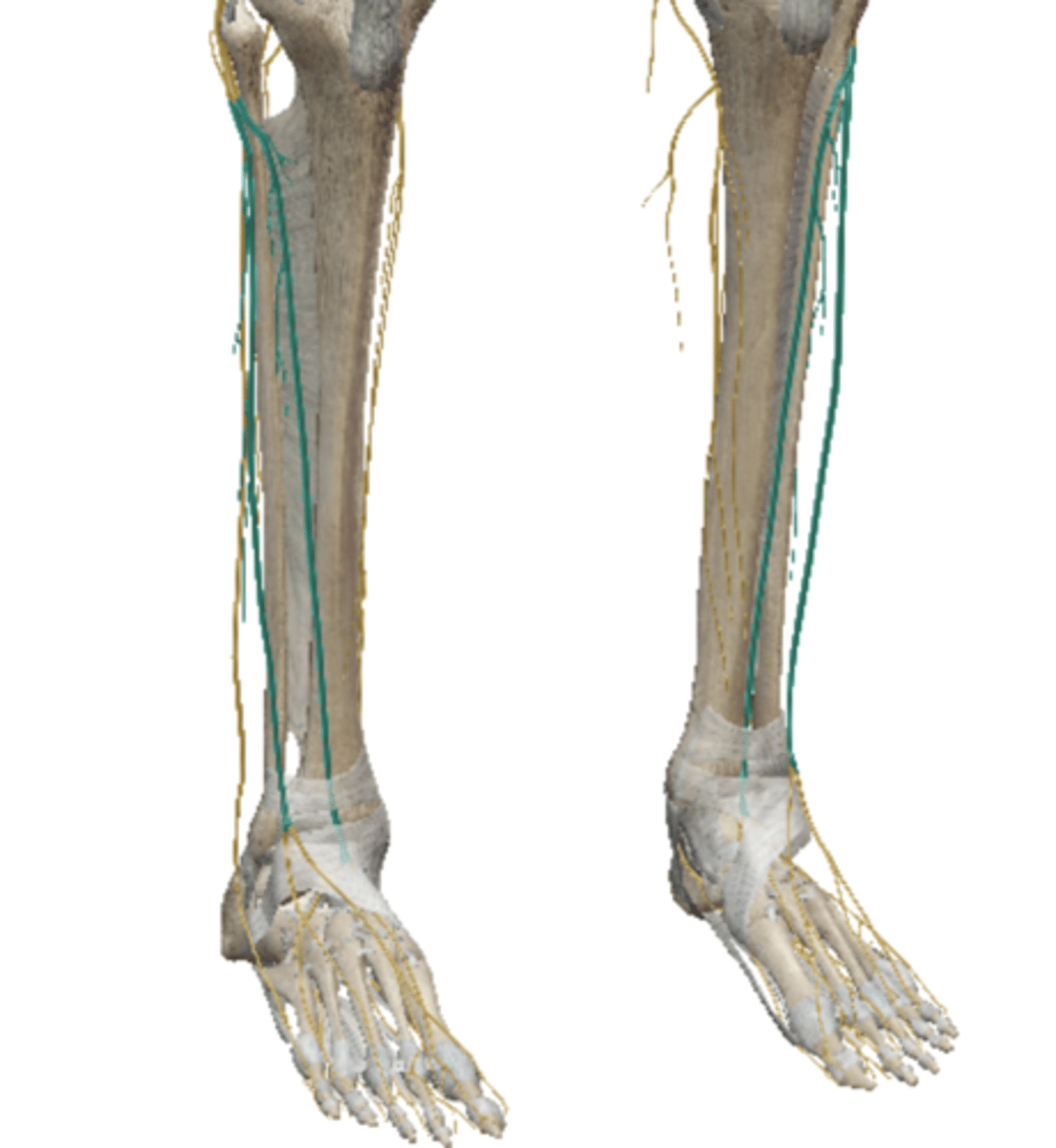
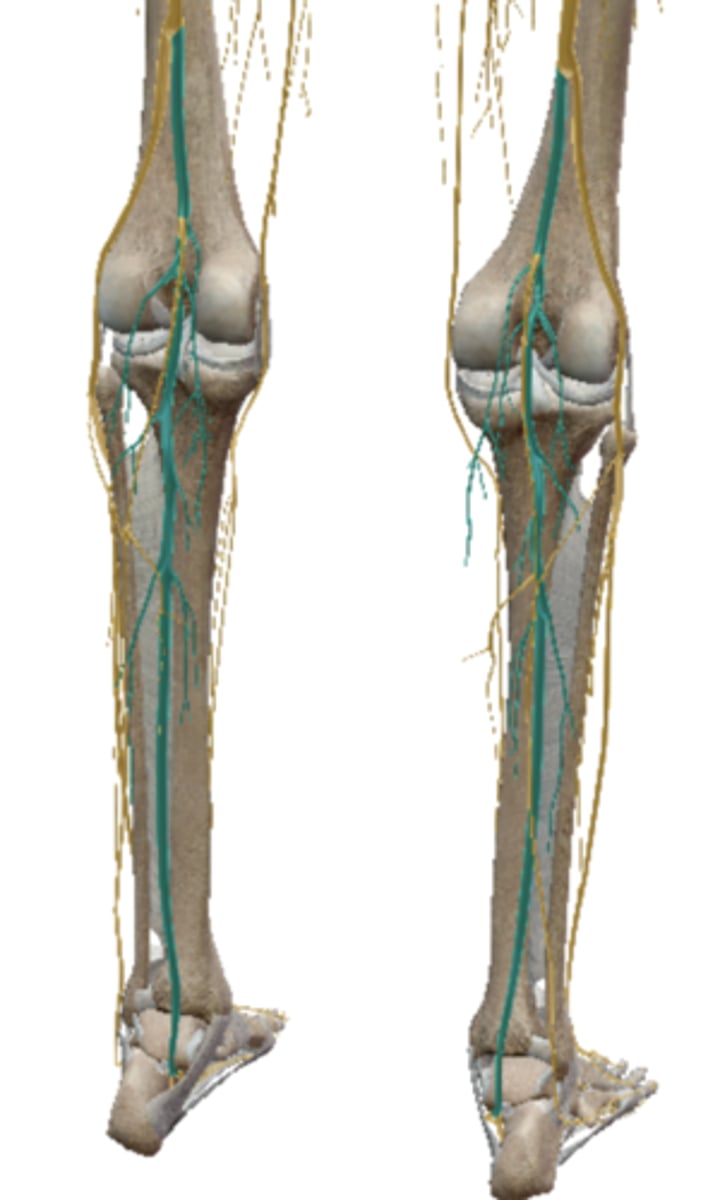
Tibial Nerve (Sacral Plexus)
Reflex Arc
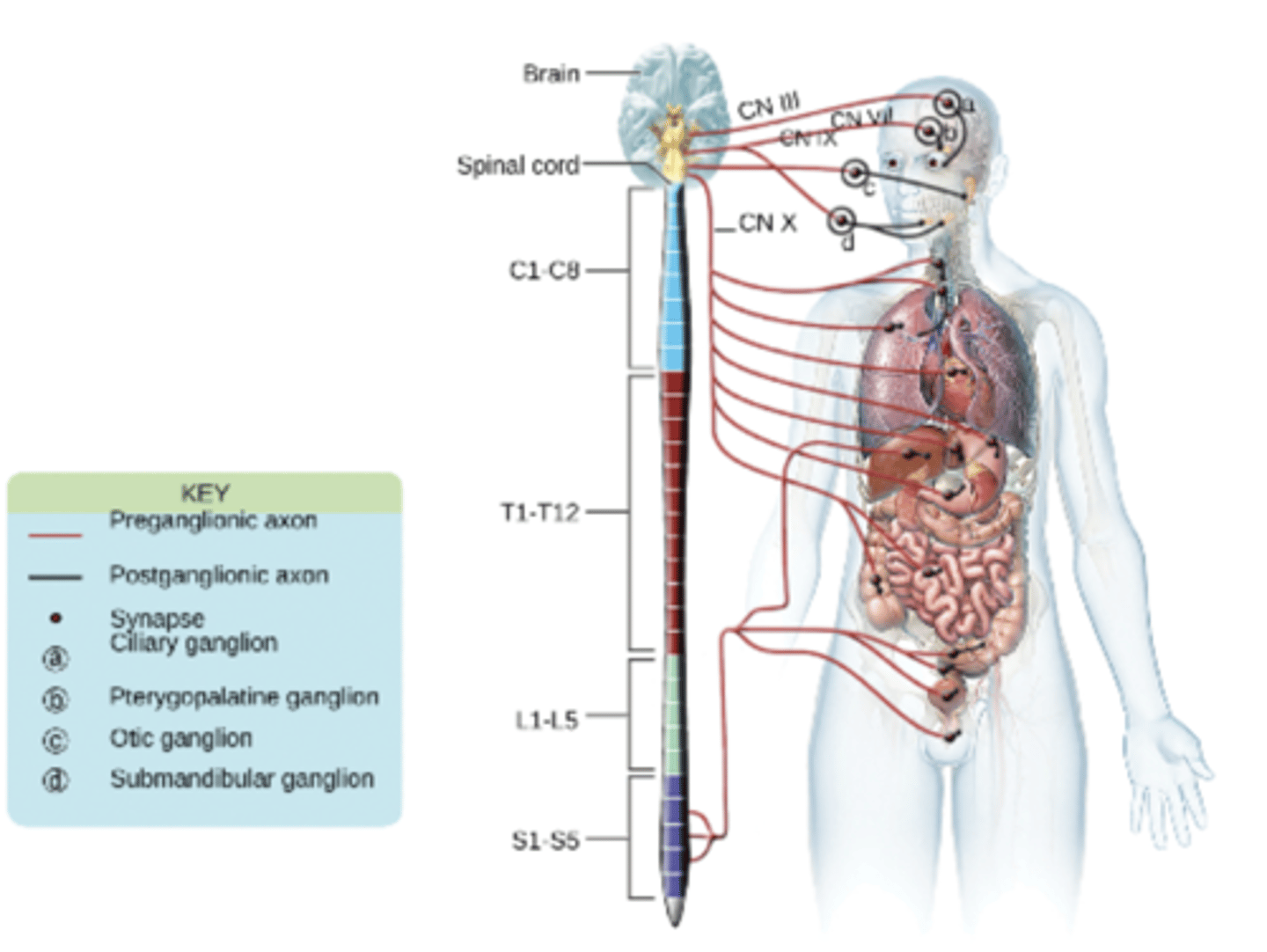
Parasympathetic Nervous System
will NOT cause the heart rate to increase
(the heart rate decreases)
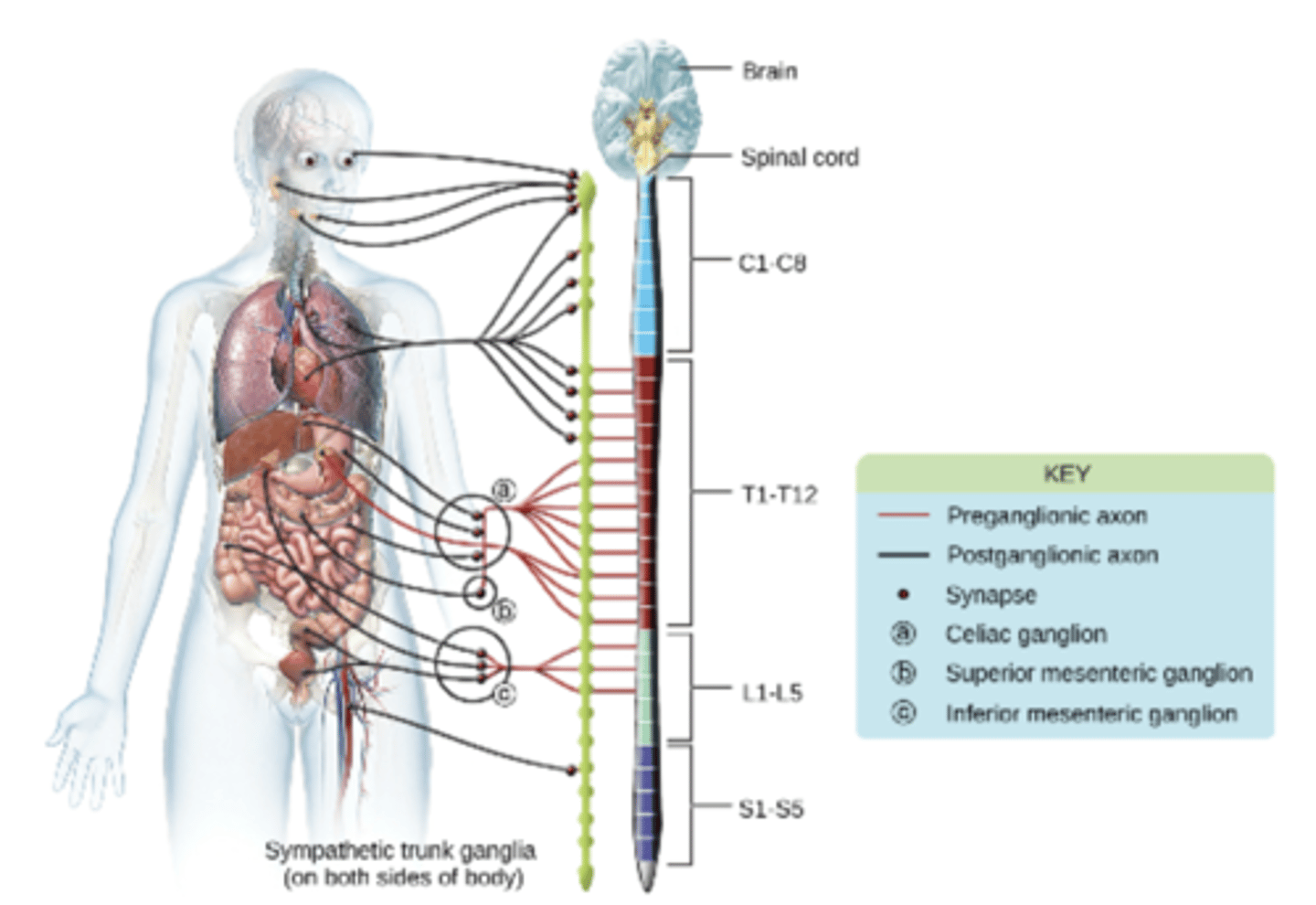
Sympathetic Nervous System
stimulates the fight or flight responses
Subarachnoid Space
the area/space around the spinal cord that contains CSF.