Unit 2 Vocab 2020-21
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/19
Last updated 1:07 PM on 10/26/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
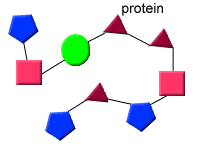
Amino acids
The monomers or building blocks of proteins
2
New cards
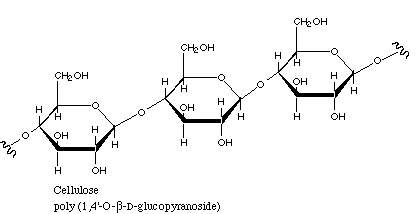
Carbohydrates
Sugars; source of quick energy
3
New cards
Complementary base-pair
The bond between A-T and C-G on the DNA double helix
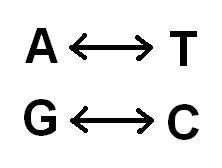
4
New cards
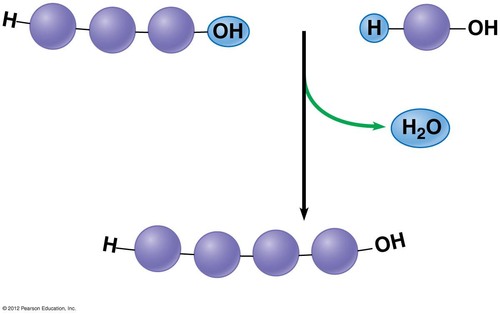
Dehydration Synthesis
Chemical reaction that joins two monomers together releases a molecule of water
5
New cards
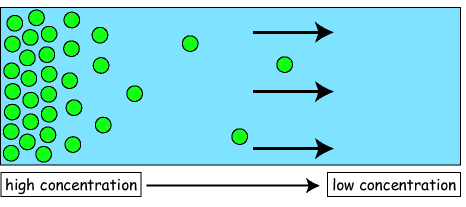
Diffusion
Movement of very small particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, with the concentration gradient.
6
New cards
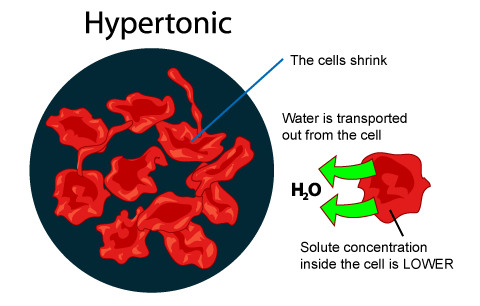
Hypertonic
When there is a higher concentration of dissolved substances outside of the cell than inside, the solution is:
7
New cards
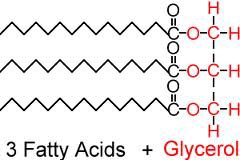
Lipids
These molecules are used for insulation and providing long term energy
8
New cards
Macromolecule
Large molecules, usually 200 atoms or more, bonded together

9
New cards
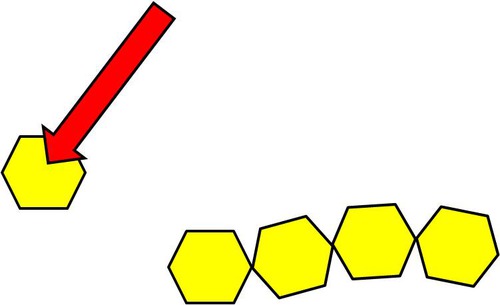
Monomer
A subunit or building block of a larger molecule
10
New cards
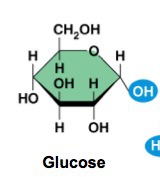
Monosaccharides
The monomers or building blocks of carbohydrates
11
New cards
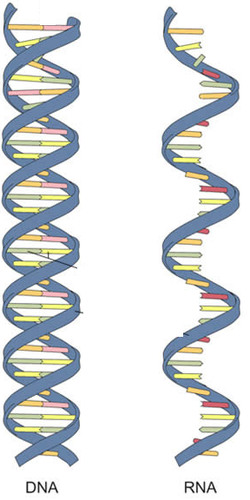
Nucleic acids
Macromolecule that stores information in the form of a genetic code
12
New cards
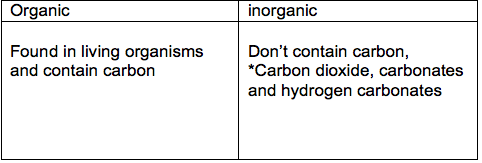
Organic
Molecules that contain the elements hydrogen and carbon
13
New cards
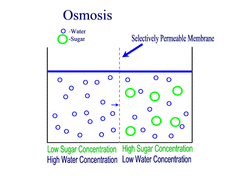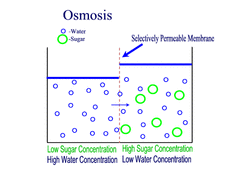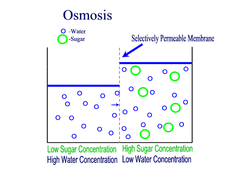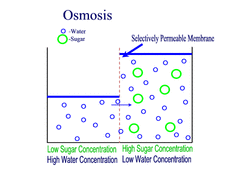
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration, with the concentration gradient.
14
New cards
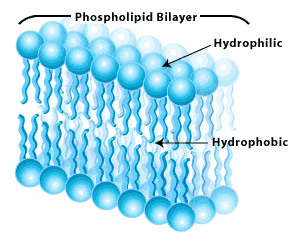
Phospholipid
Type of lipid found in the cell membrane
15
New cards
Polymer
A large molecule formed from smaller molecules
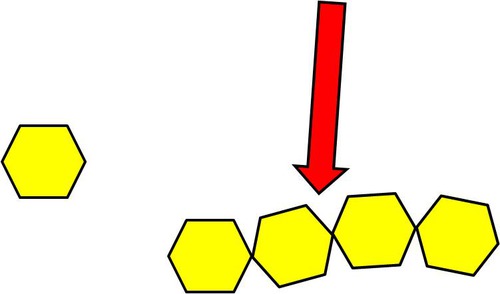
16
New cards
Proteins
These are used in the body for structure, transport, and as catalysts for chemical reactions
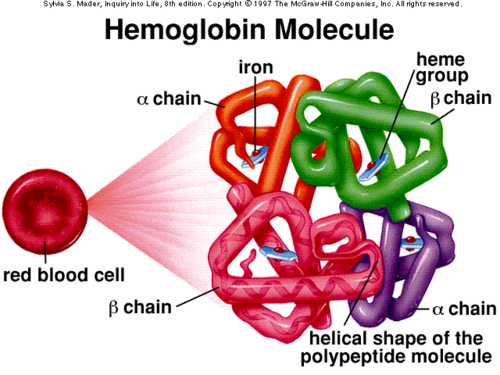
17
New cards
Enzyme
Proteins with a very specific shape that function to speed up, or catalyze, chemical reactions.
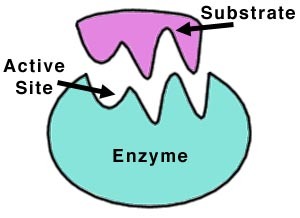
18
New cards
Substrate
The substance that the enzyme is working on
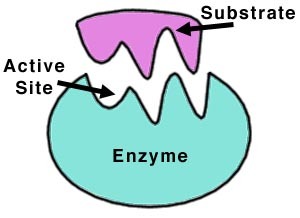
19
New cards
Polar
Molecules that are asymmetrical and have a partial positive side and a partial negative side; like water
20
New cards
Hydrogen Bond
Attraction between the negative oxygen on one water molecule and the positive hydrogen on another water molecule