lecture 1
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
what makes up most of cell's dry mass?
- proteins
protein major functions
- storage
- transport
- movement
- structure
- signal transduction
- growth and development
- immune protection
- enzyme activity/catalysis
structure determines...
function
medicinal use of 3D protein structure
- drug design
- predict function of mutated protein
biochemical use of 3D protein structure
- predict MOA
- develop tools to manipulate MOA
biotechnological use of 3D protein structure
- design new enzymes
David Baker
- won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2024 for computational protein design
- generated tools to design proteins
Demis Hassabis
- won nobel prize in chemistry 2024 for protein structure prediction
John M. Jumper
- won nobel prize in chemistry 2024 for protein structure prediction
- AI tools to predict the function of a protein without its structure, so that you can eventually figure out the structure
amino acid
- the building block of proteins
- called residues in an amino acid chain
- 20 exist in nature
classifications of amino acids
- polar acidic/negative
- polar basic/positive
- uncharged polar
- nonpolar
what differentiates amino acids
- R group
parts of amino acids
- alpha carbon
- amino group
- carboxyl group
- hydrogen atom
- R group or side chain
primary structure of proteins
- linear sequence of amino acids
primary structure bonds
- peptide bonds between C-terminus and N-terminus of 2 amino acids
- lose a water molecule in the process
direction of reading amino acid sequence
- N to C terminus
secondary structure of a protein
- regular stretches of a polypeptide chain
- alpha and beta pleated sheets
secondary structure bonds
- Hydrogen bonds between amino acids that are near one another in the linear sequence
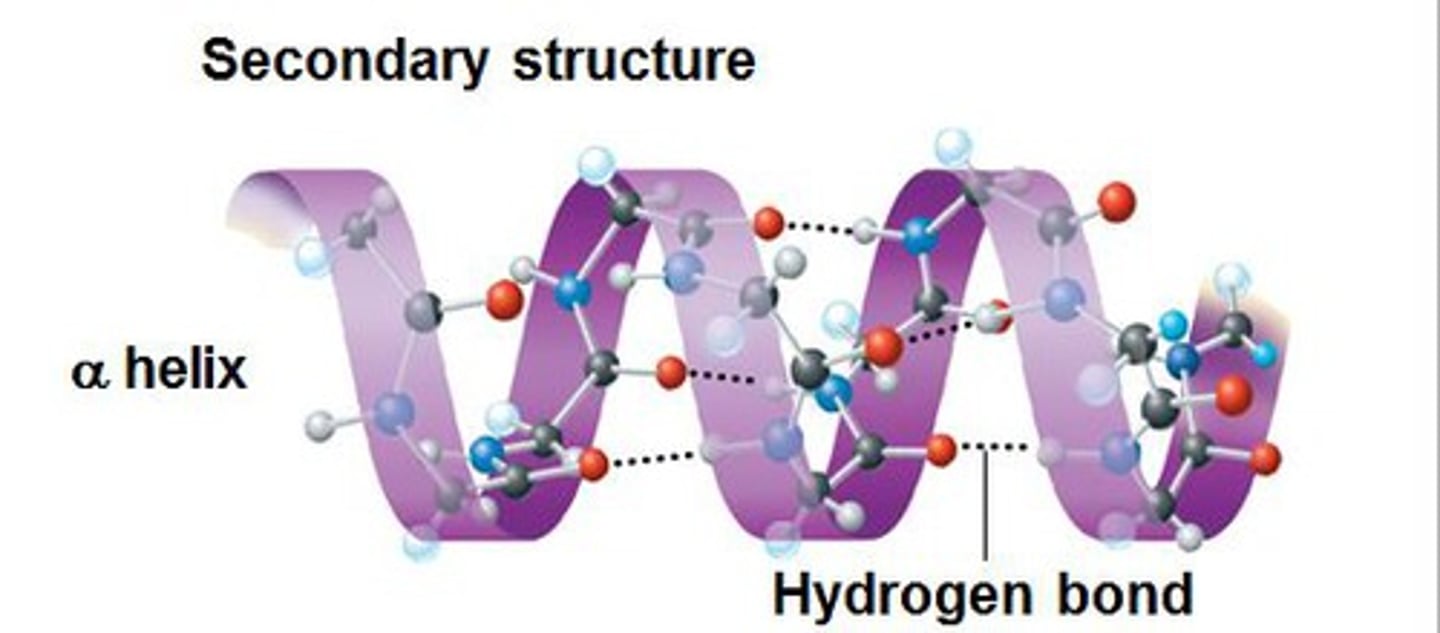
alpha helix
- a single polypeptide chain twists around on itself to form a rigid cylinder
- hydrogen bond every 4th peptide bond
- ferritin
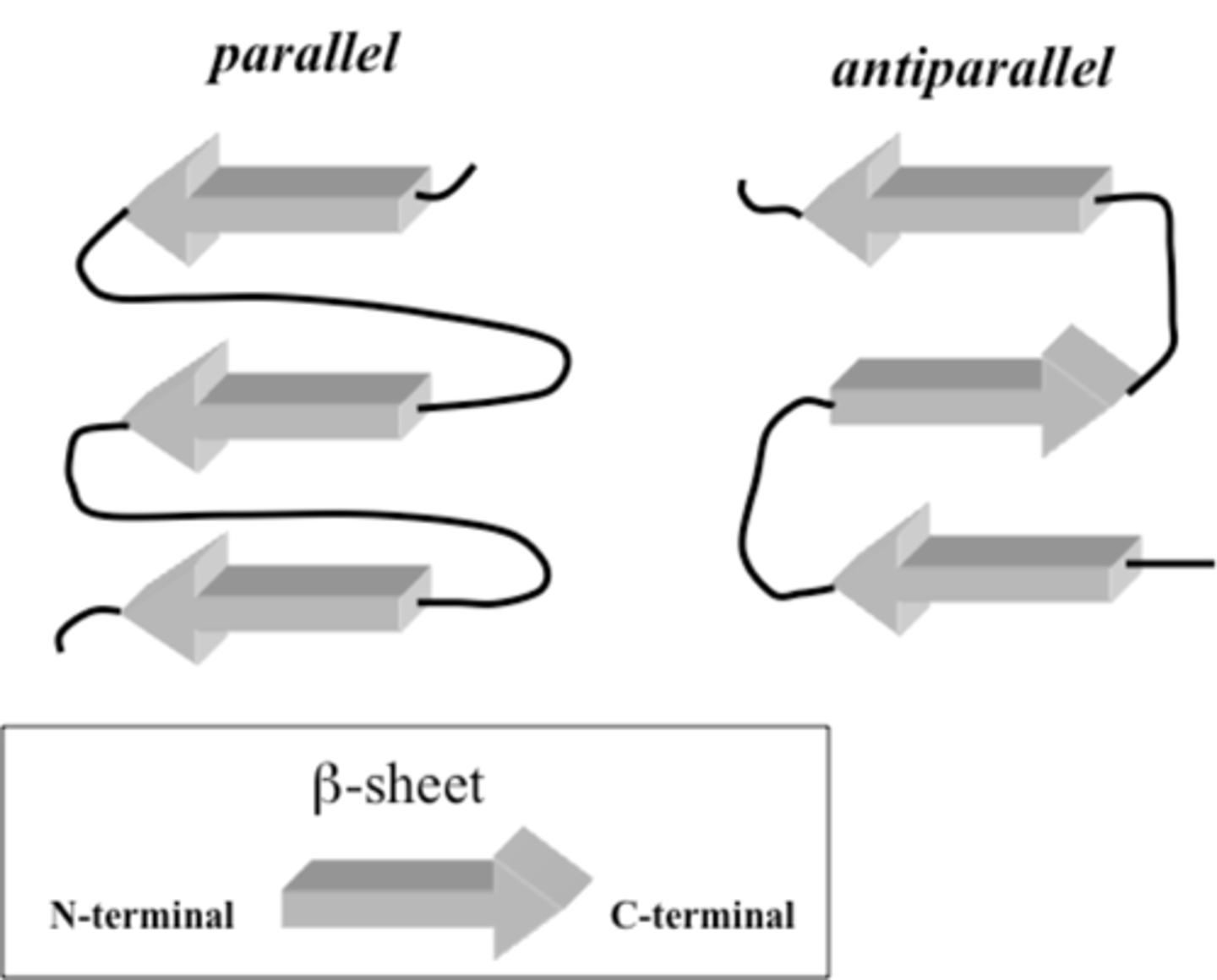
beta sheet
- forms from neighboring segments of the polypeptide backbone that run at the same orientation -parallel- or in the opposite direction to the immediate neighbor -antiparallel-
- fatty acid-binding protein
tertiary structure of a protein
- full 3D organization of a polypeptide chain
tertiary structure bonds
- disulfide
- hydrogen
- ionic bonds
disulfide bonds
- covalent bond between 2 thiol groups of Cys residues in one polypeptide chain
- oxidation of 2 SH groups
disulfide bonds extracellular
- often have several
intracellular disulfide bonds
- lack of them
hydrogen bonds
- an electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom, which is covalently bound to a high electronegative atom, to another electronegative atom of the same or different molecules of their close neighborhood
ionic bonds
- chemical bond formed between 2 oppositely charged R groups found close to each other
how many amino acid residues in most natural polypeptide chains/proteins
- 50 to 2,000
average molecular weight of an amino acid
- 110 grams/mol
- 110 daltons Da
average molecular weight of proteins
- 5.5 to 220 kDa
importance of knowing amino acid sequence
- can determine function by predicting its 3D structure
what can alterations in primary structure lead to
- abnormal protein function
- disease
- ex: sickle-cell anemia and cystic fibrosis
types of tertiary structures
- globular
- fibrous
globular proteins
- spherical, water-soluble proteins.
- hydrophobic inside and hydrophilic amino acids outside
- myoglobin
fibrous proteins
- 2 large alpha helices intertwine to make a stronger structure
- more extended compared to globular
- alpha-Keratin
proteins domains
- large proteins consist as a set of these
- a unit in the protein that can fold independently
- 40 to 350 contiguous amino acids
- target specific domain for drug
different domains associated with...
- different functions
cytochrome b562
- a single-domain protein involved in electron transfer in E. coli
NAD binding domain of lactate dehydrogenase
- single binding domain
- binds NAD
antibody light chain
- one domain
- where the antibody will bind to different foreign substances
SH2 domain
- 100 amino acids
- involved in signal transduction
Src protein
- formed from 3 domains
- 536 amino acids
- SH2
- SH3
- catalytic
quaternary structure of a protein
- the complete conformation of a protein that is formed as a complex of more than one polypeptide chain
- each chain is a subunit
dimer/homodimer
- a protein complex containing 2 subunits
what do drugs target is quaternary structure
- dimerization of a protein
- due to some proteins being functional only if their subunits come together and dimerize
human hemoglobin
- composed of alpha2beta2 tetramer
- since each subunit can hold a heme group, it increases oxygen capacity
complex assemblies
- some proteins may come together to form different ones
- myosin interacts with actin to form sarcomere
- many sarcomeres come together to form myofibril
- many myofibrils come together to form muscle fiber
native protein
- a protein in its folded and active form
denatured protein
- when a protein is converted into a randomly coiled peptide without its normal activity
- primary structure is not affected
how do proteins get denatured
- any treatment that disrupts weak, non-covalent bonds stabilizing the tertiary structure
- happens with heating, chemical denaturants, oxidizing, or reducing agents
Chemical denaturants
- urea
- guanidinium chloride
protein biosynthesis
- translation of nucleotide sequences into amino acid sequences
- a conserved process
ribosomes
- responsible for protein biosynthesis
- molecular machines that coordinate the interplay of aminoacyl-tRNAs, mRNA and proteins
- on the rough ER but not smooth
- large subunit
- small subunit
membrane bound vs free ribosomes
- structurally and functionally identical
A of ribosome
- aminoacyl-tRNA
- where the tRNA brings the amino acid
P of ribosome
- peptidyl tRNA
peptidyl transferase center
- region of the large ribosomal subunit that catalyzes peptide bond formation between the aminoacyl tRNA in the P site and the aminoacyl tRNA in the A site
E ribosome
- where the mRNA enters
- where the tRNA is released from the ribosome and exits
Francis Crick 1961
- described a set of rules defining how the four-letter code of DNA is translated into the 20-letter code of amino acids
Codon
- a set of 3 letter combinations of nucleotides, each of which corresponds to a specific amino acid or stop signal
methionine
- AUG
- all amino acids start with this codon
stop codons
- UAA
- UAG
- UGA
transfer RNA
- the adaptor molecule in protein synthesis
- contains an amino-acid-recognition site
- template-recognition site/anticodon
what pattern can each tRNA be rearranged into
- cloverleaf
- secondary structure RNA
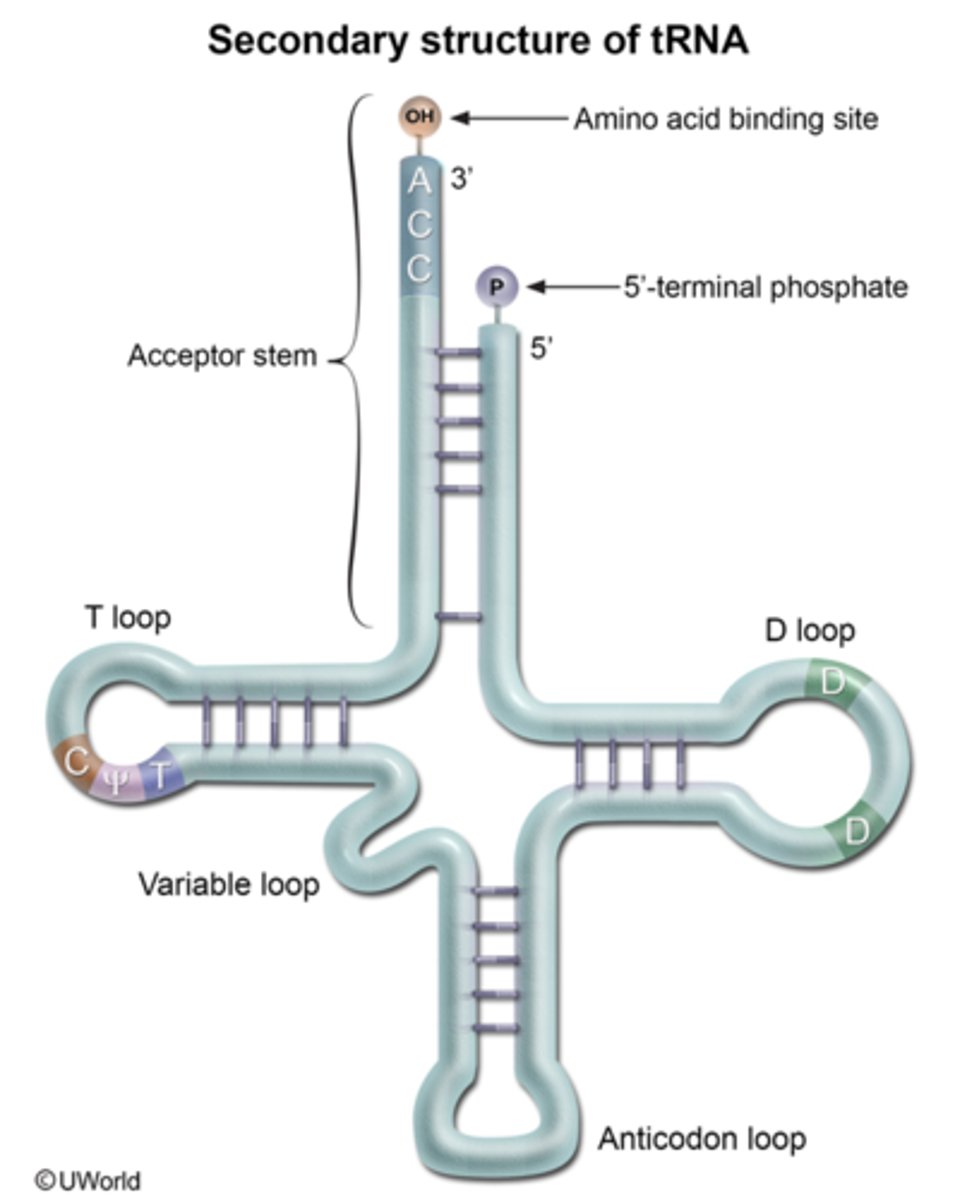
where is activated amino acid attached to in tRNA
- hydroxyl group of the adenosine residue in the amino-acid-attachment site of CCA at the 3' end
anticodon loop
- makes the 3 bases that constitute the anticodon accessible for interaction with mRNA codon
step one in amino acid to tRNA
- formation of adenylated amino acid
step 2 amino acid to tRNA
- the attachment of the amino acid to the corresponding tRNA
activated tRNA
- when an aa is coupled to its respective tRNA molecule
animoacyl-tRNA synthetase
- enzyme that catalyzes the aa activation reaction and linkage of aa to tRNA
- most cells have a different synthetase for each amino acid
what direction is mRNA read through ribosome
- 5' to 3'
bacterial vs eukaryotic ribosomes
- Bacterial: 70S
- Eukaryotic: 80S
- mitochondria and chloroplast have ribosomes more similar to bacteria
antibiotics and ribosomal differences
- the differences between eukaryotic and bacterial ribosomes can be exploited for the development of antibiotics
- bind and block protein synthesis in bacteria, so they could also have an effect on mitochondria
streptomycin and other aminoglycosides
- inhibit initiation and cause the misreading of mRNA
- bacteria
tetracycline
- binds to the 30S subunit and inhibits the binding of aminoacyl tRNAs
- bacteria
chloramphenicol
- inhibits the peptidyl transferase activity of the 50S ribosomal subunit
- bacteria
cycloheximide
- inhibits translocation
- eukaryotes
erythromycin
- binds to the 50S subunit and inhibits translocation
- bacteria
Puromycin
- causes premature chain termination by acting as an analog of aminoacyl-tRNA
- bacteria and eukaryotes
posttranslational modifications
- alterations in the structure of a protein after it has been synthesized in the cell
- covalent attachment of groups to amino acid side chains
- cleavage or modification of the polypeptide backbone
Hydroxyproline
- hydroxyl groups in many proline residues stabilize fibers of newly synthesized collagen
vitamin C deficiency
- results in insufficient hydroxylation of collagen because it is a cofactor essential in hydroxylating proline
- abnormal collagen fibers unable to maintain normal tissue strength
- scurvy
Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP)
- a protein found in certain species of jellyfish that glows green when excited by certain wavelengths of light (fluorescence)
- source of fluorescence is a group formed by spontaneous rearrangement and oxidation of the sequence Ser-tyr-gly within the center of the protein
- serve as markers within cells, as they have been engineered to absorb and emit light across the entire visible spectrum
folding of a newly synthesized protein
- protein begins to fold while it is still being synthesized
- chaperones
- heat shock proteins
chaperone
- a protein that interacts with stabilizes, or helps another protein to acquire its functionally active conformation without being present in its final structure
- the most abundant protein
heat shock proteins hsp
- Chaperones upregulated under stress conditions
- when the temperature is too high and denatured proteins need to be refolded
what is protein misfolding and aggregation associated with
- neurological disease
- Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's disease
amyloid fibrils
- also called amyloid plaques
- improperly folded proteins and deposition of protein aggregates in extracellular space
- seen in Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's disease
- when normally soluble proteins are converted into insoluble fibrils
what are fibrils rich in
- Beta-sheets
improper folding of protein can lead to
- protein failing to achieve its functional conformation or reach required location in the cell
cystic fibrosis
- the most common lethal genetic disease affecting Caucasians
- caused by defects in CFTR - cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
CFTR
- channel for chloride ions
- comprised of 1480 amino acids
deletion of Phe residue at position 508 in CFTR
- most common mutation in greater than 90% of CF patients
- improper folding of the protein and CFTR does not reach the cell membrane
drug discovery strategies that restore protein folding and function
- small molecule pharmacological chaperones
- inhibition of aggregation
small molecule pharmacological chaperones
- stabilizing specific misfolding-prone or mutant proteins and pulling them towards a lower free energy minimum
- CFTR correctors
CFTR correctors
- Lumacaftor
- tezacaftor
Lumacaftor
- the first medicine to trear underlying cause of CF in people 12yrs or older with 2 copies of F508del mutation
- FDA approved in 2019
Tezacaftor
- FDA approved in 2019
- stabilize CFTR by filling an internal cavity
- prevent CFTR premature degradation
CF treatment inhibition of aggregation
- of a specific amyloid-prone protein that stabilizes the native state or the partially folded state
- prevents the formation of oligomers or amyloids