Anatomy: Planes, Positions, and Body Regions
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
Vertical
up and down, north to south
Horizontal
side to side, east to west
S-O-F-T
sagittal, oblique, frontal, transverse
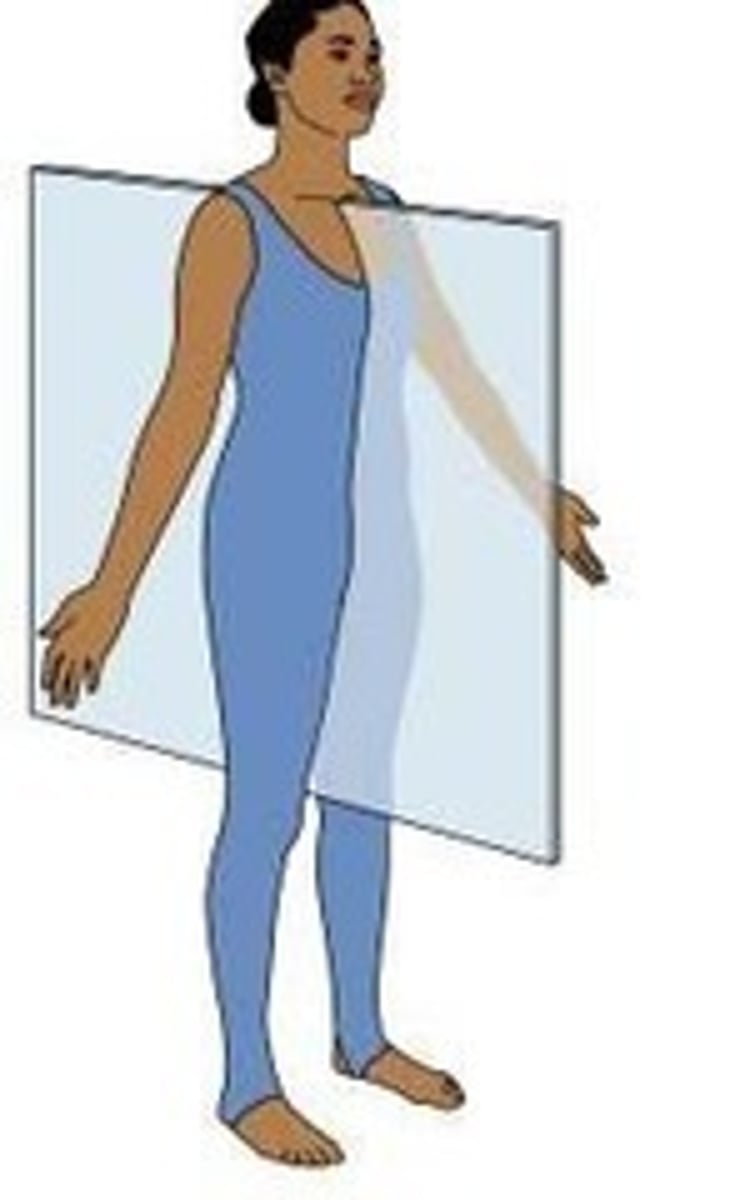
Sagittal plane
splitting the body into left and right
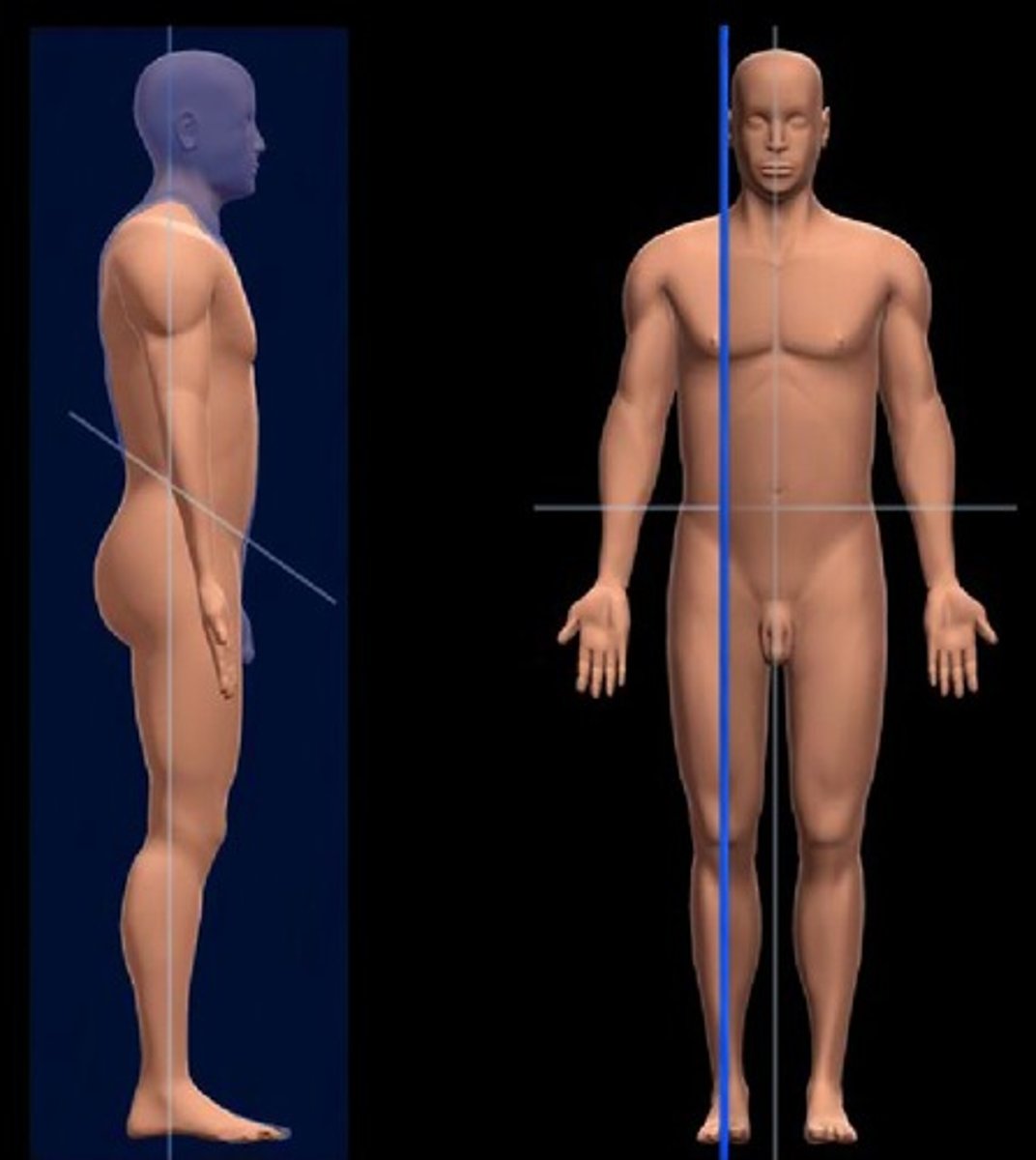
Mid-sagittal plane
divides the body into equal right and left halves
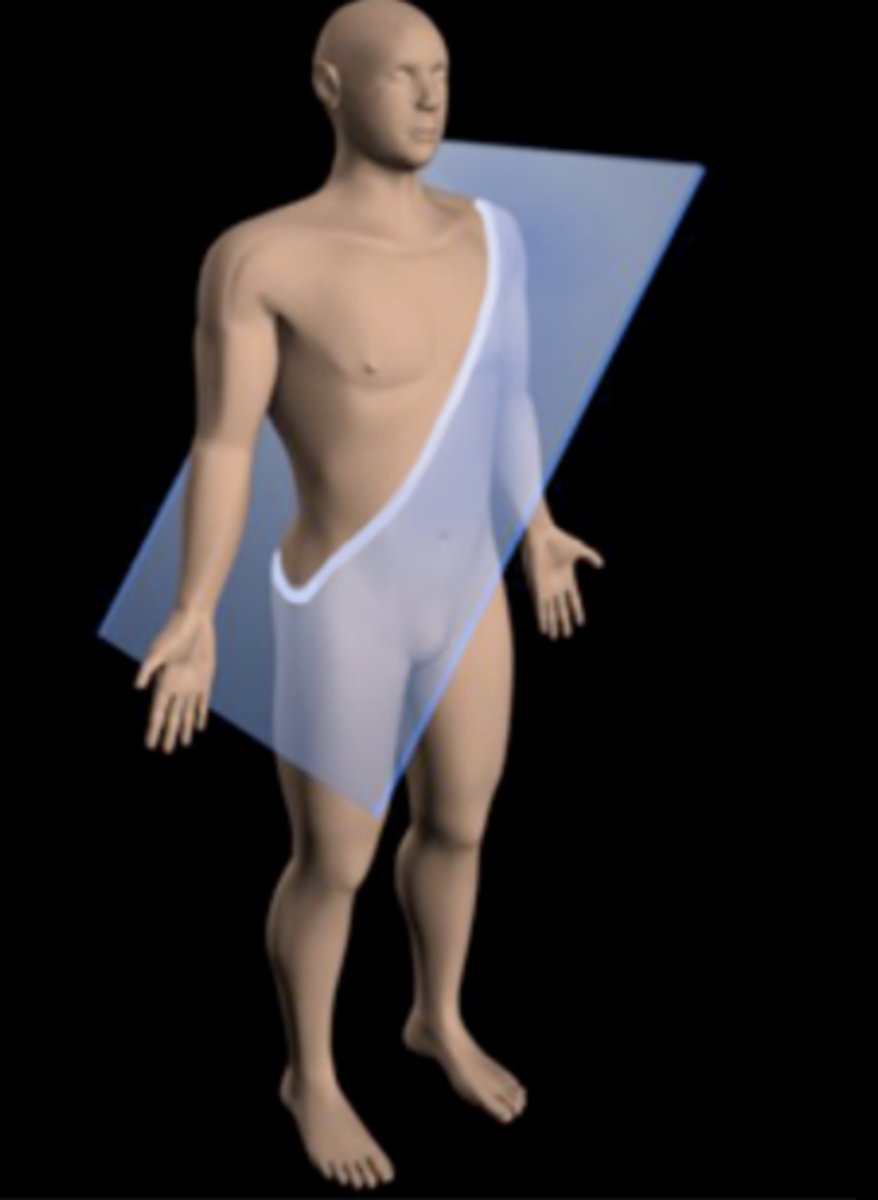
Oblique plane
cutting through at an angle

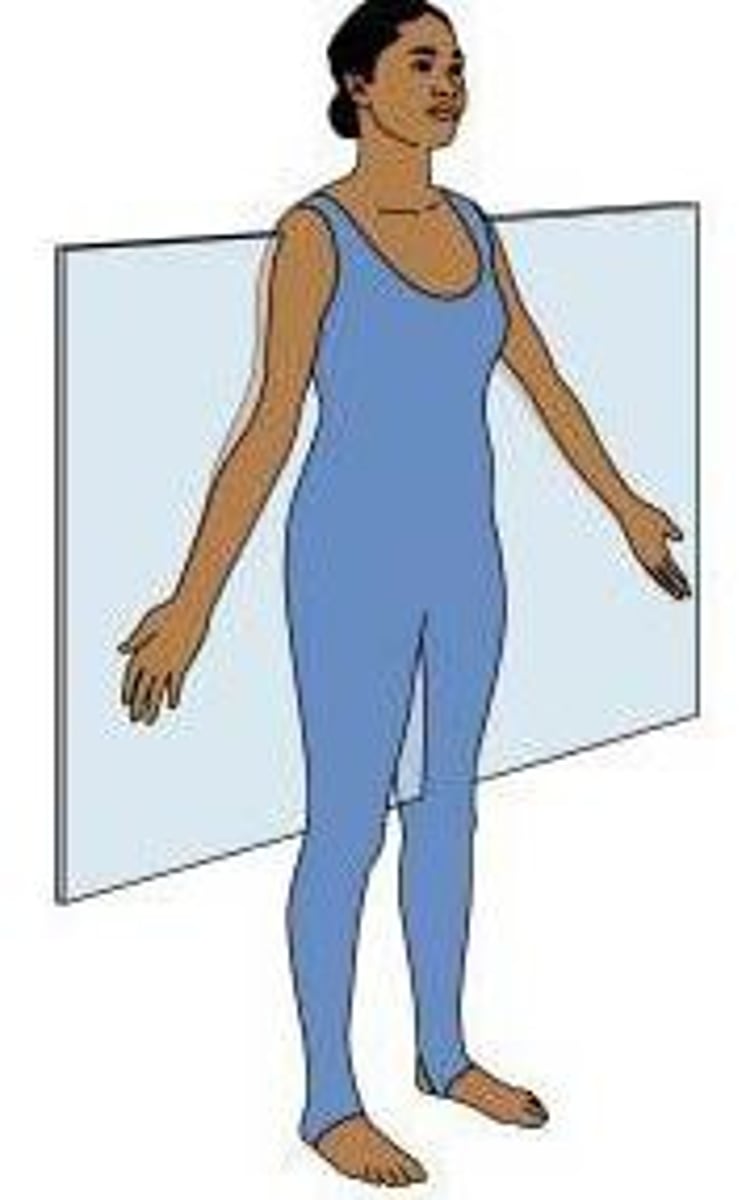
Frontal plane (coronal plane)
a cross-section dividing the body into front and back half
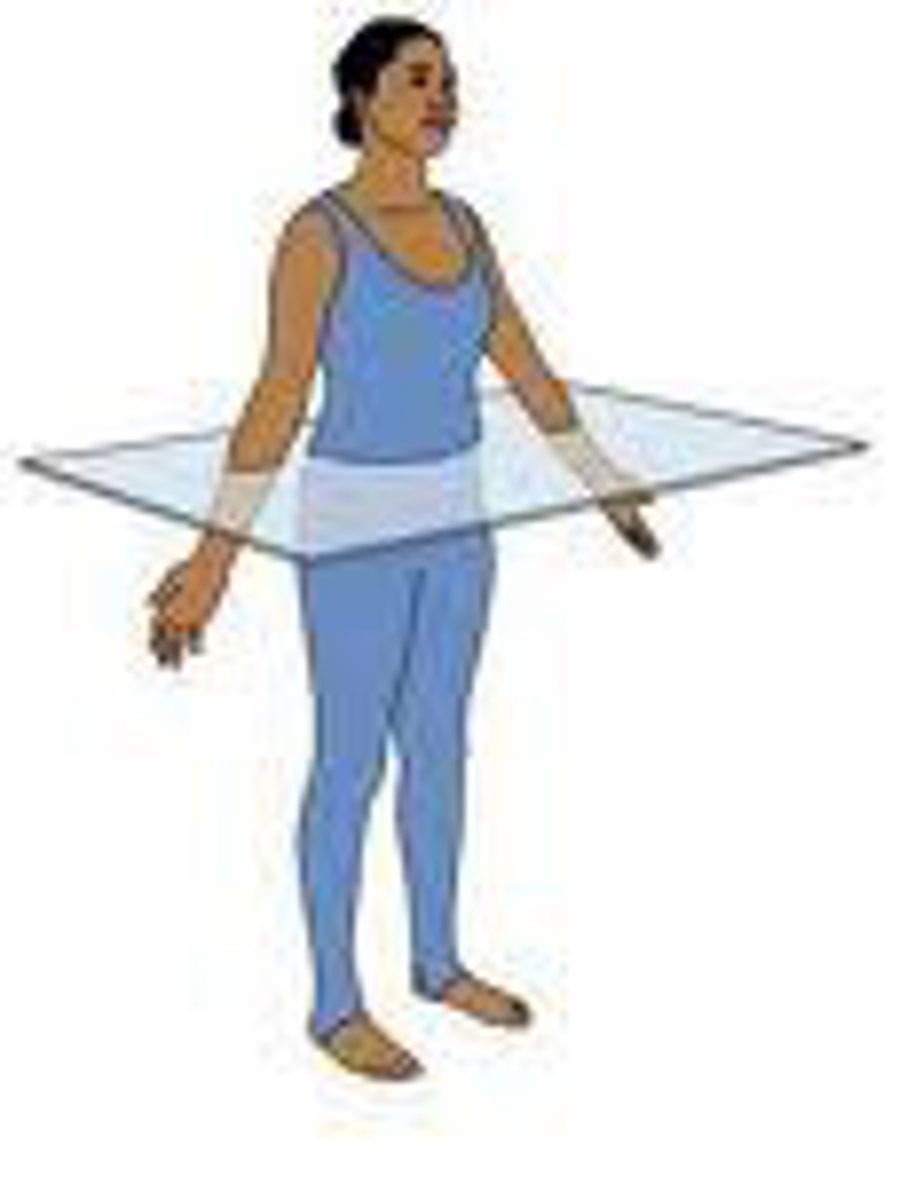
Transverse plane
line that divides the body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior) sections
Anterior or Ventral
nearer the front of the body
Posterior or Dorsal
nearer to the back of the body
Proximal
nearer to the point of origin or attachment
Distal
further from the point of origin or attachment
Medial
nearer to the median plane
Lateral
further from the median plane
Superior or cephalic
nearer to the top of the head
Inferior or caudal
nearere to the bottom of the feet
Superficial
towards the surface of an organ or the body
Deep
towards the center of an organ or the body
External
away from the center of an organ or cavity, towards the surface
Internal
closer to the center of an organ or cavity
Rostral
describe a portion with respect to the nose
Cranial
towards the head
Caudal
towards the tail or coccyx
Central
at or near the center or midpoint
Peripheral
away from the center or midpoint
Ipsilateral
same side
Contralateral
opposite side
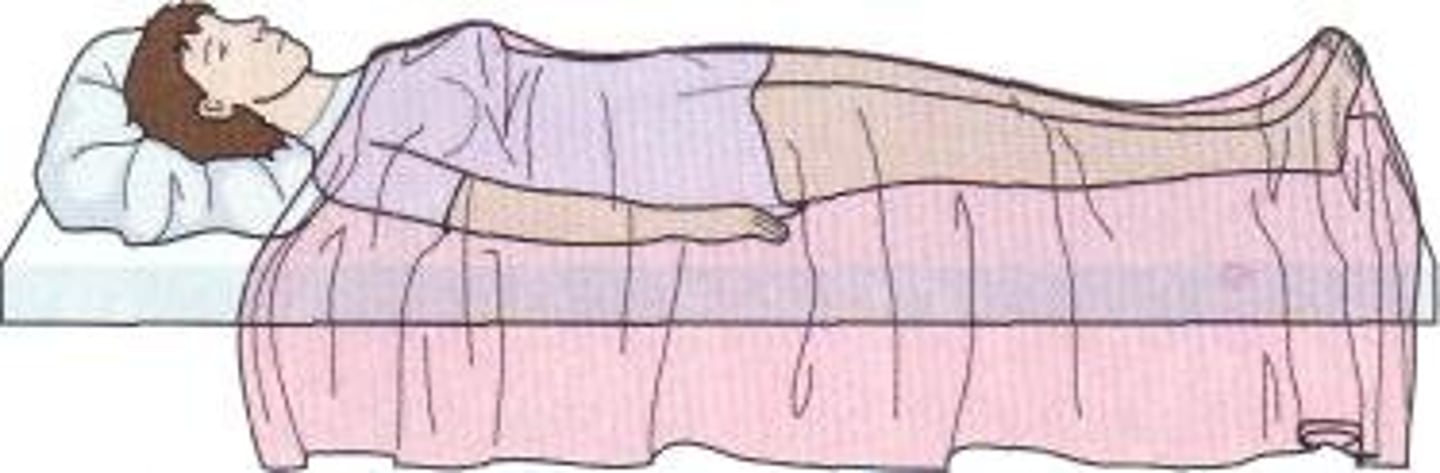
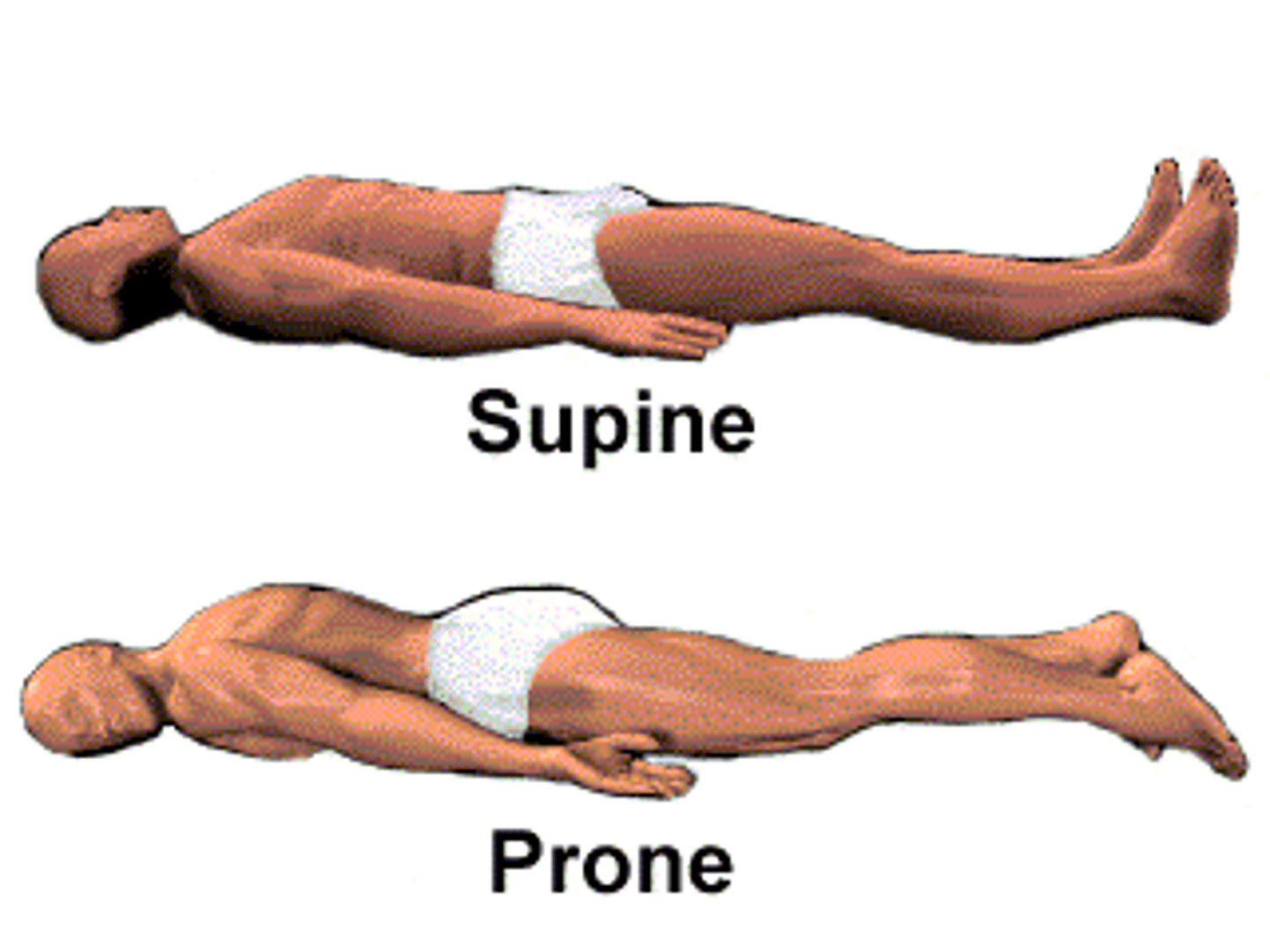
Supine position
lying horizontally with the face and torso facing up (on your back)
Prone position
lying horizontally with the face and torso facing down (on your stomach)
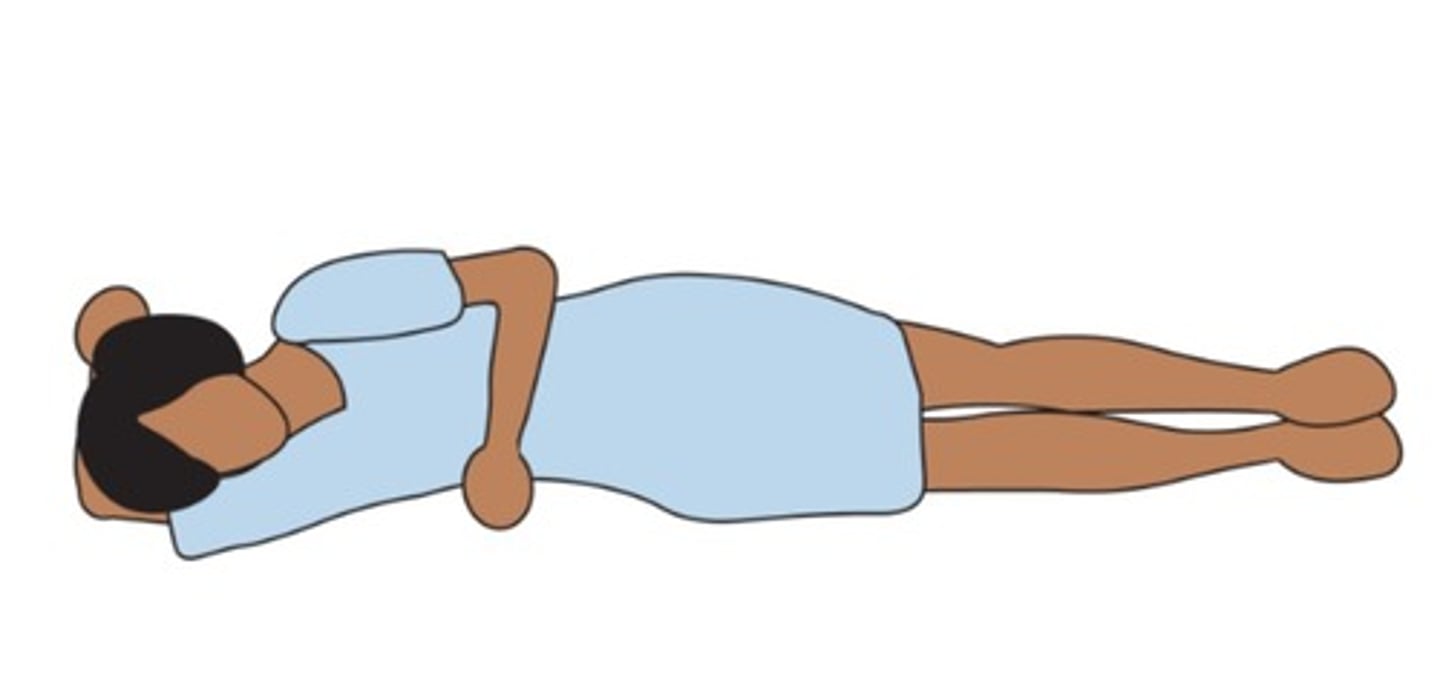
Right lateral recumbent
lying on your right side with the left arm over
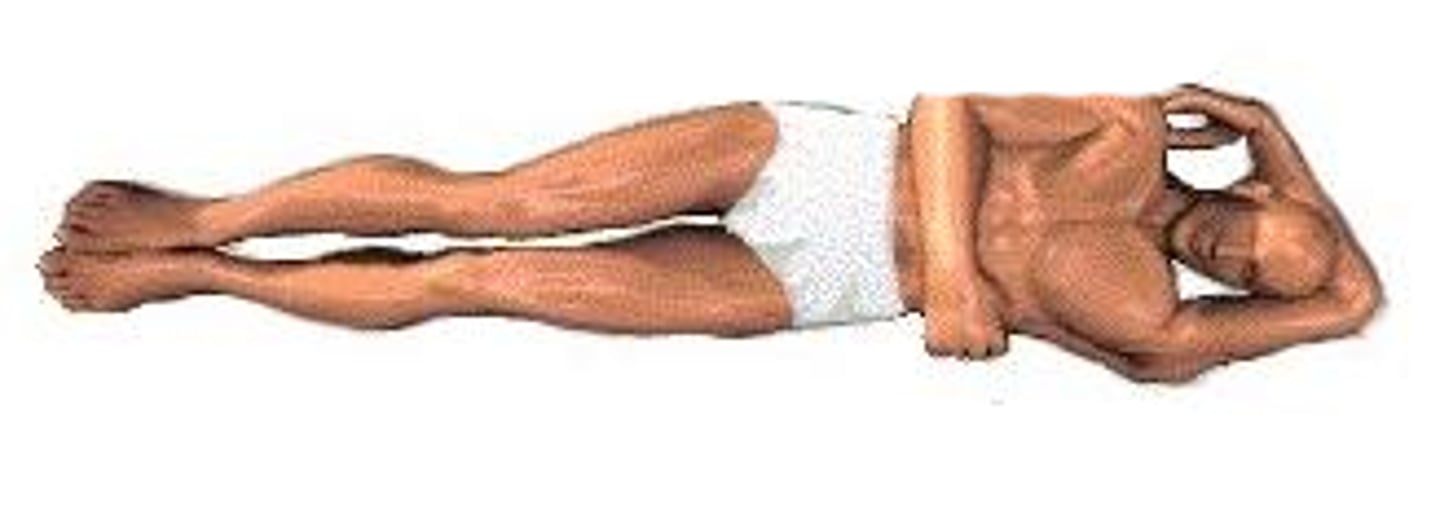
Left lateral recumbent
lying on your left side with the right arm over
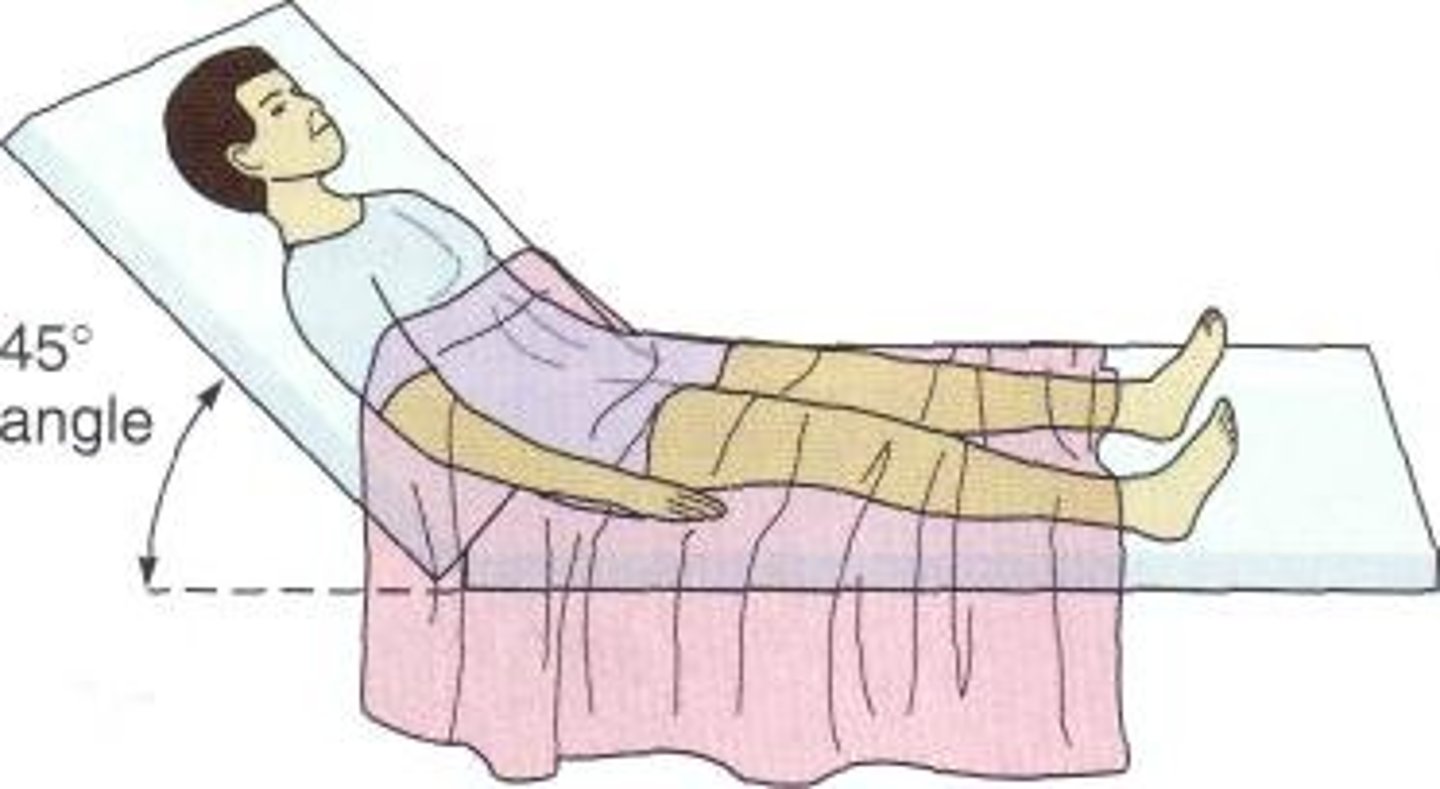
Trendelenburg
feet elevated higher than the head
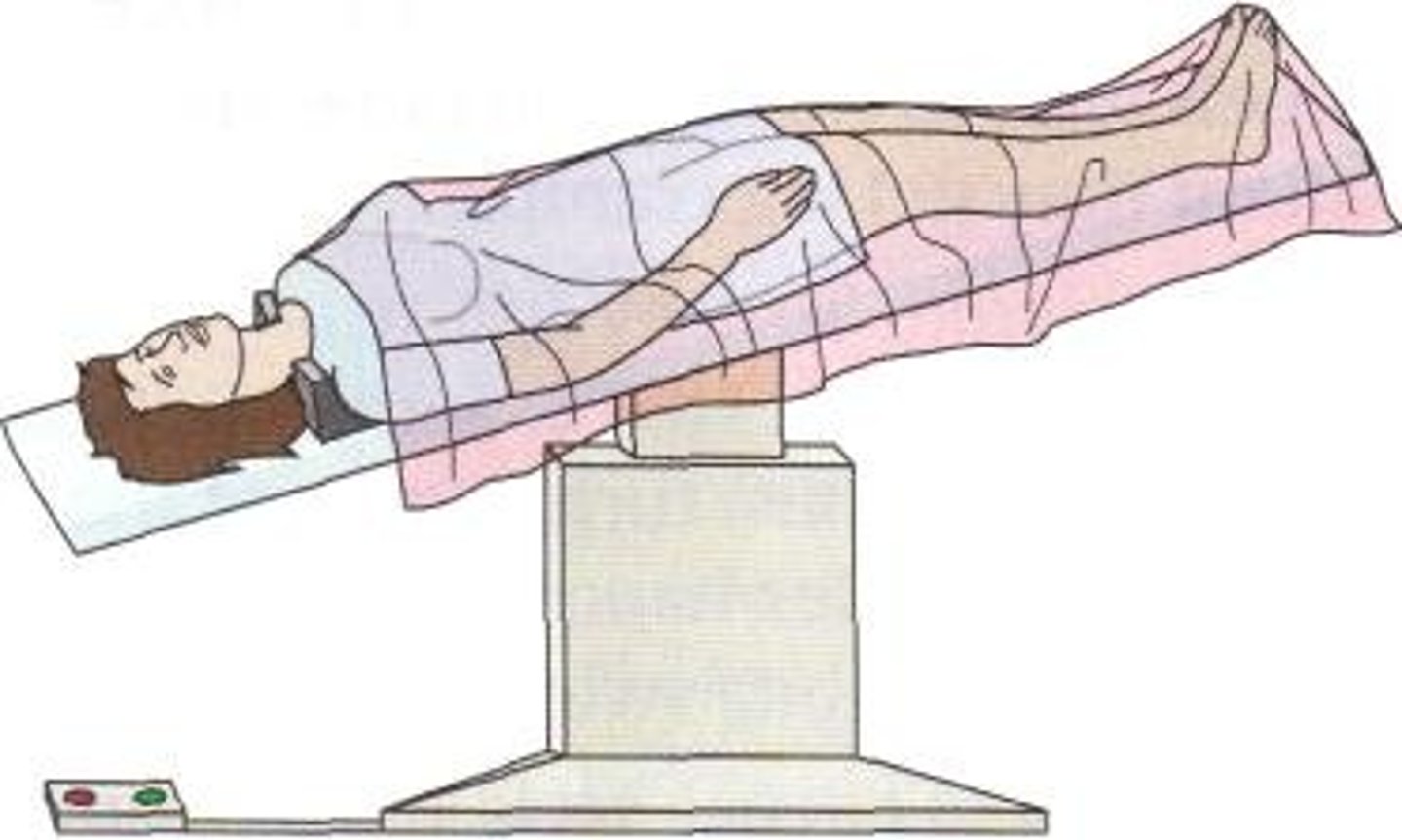
Fowler's position
sitting up
7 regions of the body
back region, thorax, abdomen, pelvis and perineum region, lower extremities, upper extremities, head and neck region
Back region includes
the vertebral column (cervical, theoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccyx), extrinsic and intrinsic back muscles
Cervical
neck
Thoracic
middle back
Lumbar
lower back
Sacrum
lowest part of the back sometimes infused
Extrinsic back muscles
trapezius, latissimus dorsi, levator scapulae, rhomboids, serratus posterior (superior and inferior)
Intrinsic back muscles
16 of them
Thorax region
Axillary, costal, deltoid, mammary, pectoral, scapular, sternal, and vertebral
Axillary
armpit
Costal
ribs
Deltoid
shoulder
Mammary
breasts
Pectoral
chest
Scapular
shoulder blade
Sternal
breastbone
Vertebral
backbone
Abdomen region
Abdominal, gluteal, inguinal, lumbar, pelvic, perineal, pubic, sacral
Abdominal
abdomen
Gluteal
buttocks
Inguinal
bend of hips
Pelvic
area between the hipbones
Perineal
area between the anus and the genitals
Pubic
genitals
Sacral
end of the vertebral column
Pelvis and Perineum region
Superior pelvic region, inferior pelvic region, perineum
Superior Pelvic region
lower part of the lumbar vertebrae, upper pelvic bones
Inferior Pelvic region
inferior pelvic bones, sacrum, coccyx
Perineum
area between the anus and genitals
Lower extremities
Crural, femoral, patellar, plantar, popliteal, sural, tarsal
Crural
skin, front or lower leg
Femoral
thigh
Patellar
front of knee
Plantar
arch of the foot
Popliteal
back of the knee
Sural
calf, back of the lower leg
Tarsal
ankle
Upper extremities
Antebrachial, antcubital, brachial, carpel, cubital, digital, manual, palmer
Antebrachial
forearm
Antecubital
inner elbow
Brachial
upper arm
Caprel
wrist
Cubital
elbow
Digital
fingers/toes
Manual
hand
Palmer
palm
Head and neck region
Cephalic, cervical, cranial, frontal, nasal, occipital, oral, orbital/ocular, auricular
Cephalic
head
Frontal
forehead
Nasal
nose
Occipital
base of the skull
Oral
mouth
Oribital/ocular
eyes
Auricular
ears
Diagnostic Imaging Interpretation
ways to help study the human body and how the systems of the body work together.
ex. MRI, Substance ingestion
MRI (magnetic imagery)
revolutionized the abiltity to evaluate the cranium (brain causing) and the human brain inside
Substance ingestion (ingestion of radioactive isotopes)
allows the evaluation of the process of digestion and the movement of blood through circulatory system
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
plain radiography, contrast imaging, subtraction angiography, magnetic imagery, ultrasound, nuclear medicine imaging, and computer topography
Plain radiography
X-rays from an x-ray tube (radiopaque vs. radiolucent)
Contrast imaging
filling a structure with a substance like barium sulfate or iodine to see how it moves through the structure
Subtraction angiography
using a radioactive isotope or gamma rays for visualization or detection
Ultrasound
using electromagnetic rays to bounce off structures for visualization - used during pregnancy to check fetus status
Nuclear medicine imaging
using radioactive isotopes or gamma rays
Computer Topography
CT scan
Mnemonic for Cranial Nerves (12 of them)
On Old Olympus Towering Top, A Finn And German Viewed A Hop
"On" - 1
Olfactory
"Old" - 2
Optic