light dependent reactions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
where do protons accumulate in chloroplast
thylakoid interior
electron carriers in photophosphorylation
platiquinone
platocyanin
ferredoxin
what is the reduced form of plastoquinone
platoquinol
proton gradient of chloroplast
lower conc in stroma
higher conc in thylakoid lumen
passes through chloroiplast atp synthase
what pigments are found in the photosystems
chlorpphyll a and b
carotenoids (reflect red and yellow - orange )
what connects psii and psi
cytochrome bf complex
where is the special pair of chlorpohyll molecules found
reaction centre
active site of photosystem
what happens after excitation of P680*
electrons transferred to pheophytin
then plastoquinone at site Qa (fixed)
to plastoquinone at site Qb (mobile)
how is plastoquinone reduced to plastoquniol
second electron reduces mobile plastoquinone
oxygen evolving center
water oxidising enzyme
water molecule bind to calcium ion and manganese ion
4 manganese ions for every calcium
tyrosine residue
facilitates oxygen transfer from P680 to reach chlorophyll residues
photophosphorylation
electron tranfer from psii to plastoquinone
then cytochrome bf
then plastocyanin
then psi
then phyloquinone
then iron clusters
then ferrodoxin
then nadp reductase
resonance energy transfer
energy released excites electron from neighbouring pigment
energy passes from one pigment to the next
photoinduced charge separation
electron transfer from one chlorophyll molecule to another
only happens in special pair
what can happen when electrons are excited from ground state to excited state
returns to ground - heat or fluorescence released
resonance energy transfer
photoinduced charge separation
chlorophyll a and b structure
contains cyclic tetrapyrrole
planar structure (delocalisation of electrons)
mg2+ bound to centre
one pyrrole ring is reduced
highly hydrophobic chain
a has methyl where b has aldehyde
plastoquinone
lipid soluble electron carrier
similar structure to ubiquinone
chain is hydrophobic so can travel through lipid membrane
reduction of plastoquinone for oxygen generation
two electrons needed one by one
transfer of two electrons and two protons from stroma by cytochrome bf complex
this happens twice to generate one oxygen, so requires 2 molecules of water
4 protons are released
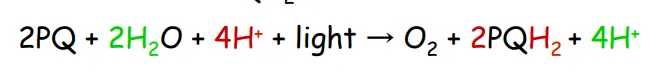
plastocyanin
blue copper proetin
soluble in thylakoid lumen
reduced at copper atom
how many molecules of plastocyanin needed to oxidise plastoquinol
2
what agent is plastocyanin
oxidising
what happens after excitation of P700 in PSI
electron transferrred to chlorophyll a0
then to phyloquinone
then to 3-iron sulphur clusters
then ferredoxin
where are electrons finally transferred from photosystem i p700*?
ferredoxin
how does ionised p700* recover?
electrons from plastocyanin
iron sulphur clusters
contain cysteine residues
each atom of iron is surrounded by 4 atoms of sulphur
creates cubic structure
ferredoxin NADP+ reductase
catalyses transfer of electrons from ferredoxin to nadp+
creates nadph
semiquinone formed as intermediate
z-scheme
electron transfer to cofactors is energetically favorable
electron flow from water to nadph is endergonic process - requires free energy
free energy from photons of light at psii (p680) and psi (p700)
are p680* and p700* good oxidising agents or reducing agents?
reducing agents
chlorplast ATP synthase
structure with knob (CF1) and stalk (CF0)
CF0 - spans the membrane, forms a proton channel for H+ travel from the thylakoid lumen to the stroma
CF1 - protrudes into stroma, contains catalytic subunits for ATP synthesis from ADP and Pi
CF0
- spans the membrane, forms a proton channel for H+ travel from the thylakoid lumen to the stroma
CF1
protrudes into stroma, contains catalytic subunits for ATP synthesis from ADP and Pi
how many photons per atp
2.7
cyclic phosphorylation
when no co2 is available or no NADP+, no electrons accepted from ferredoxin
cytochrome bf complex used instead
protons are pumped but no oxygen or nadph produced
2 photons per atp