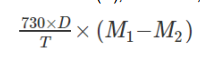Inhalation product designs and testing
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is the ultimate goal of inhaler design?
Deliver the right dose
To the right place (lungs)
At the right time
What are the key design aims for an effective inhaler?
Consistent drug delivery: From the first dose to the last
High lung deposition: Maximise fine particle fraction (1–5 µm)
Patient-centric design: Easy to use, portable, acceptable by patients
Robust and cost-effective: Suitable for large-scale manufacturing
What are the industrial and regulatory challenges in inhalation device design?
High R&D and manufacturing costs (£££)
Lack of licensed excipients for lung delivery
Regulatory hurdles (demonstrating bioequivalence is complex)
Patient acceptability
What are the scientific challenges in inhalation device design?
Site-specific targeting and delivery (getting drugs to the cells)
Toxicology & immunogenicity (ensuring long-term safety)
In vitro–in vivo correlation (lab tests must predict in vivo performance)
Formulation stability (maintaining drug integrity)
What is the purpose of in vitro studies in inhalation device development?
Determine performance in a controlled environment outside a living organism
Predict in vivo performance, estimating lung deposition and efficacy before human studies
Simpler, more controlled, and often cheaper than in vivo studies
How do in vitro studies support ethical and precise testing?
Follow the 3Rs: Replacement, Reduction, Refinement of animal testing (NC3Rs)
Allow detailed analysis with precise, reproducible data on dose and particle size
What are the key BP tests for inhalation devices?
Uniformity of delivered dose
Fine particle dose
Aerodynamic particle size distribution
Number of deliveries per inhaler
Effectiveness of antimicrobial preservative (for multi-dose products)
Leak rate (for pMDIs)
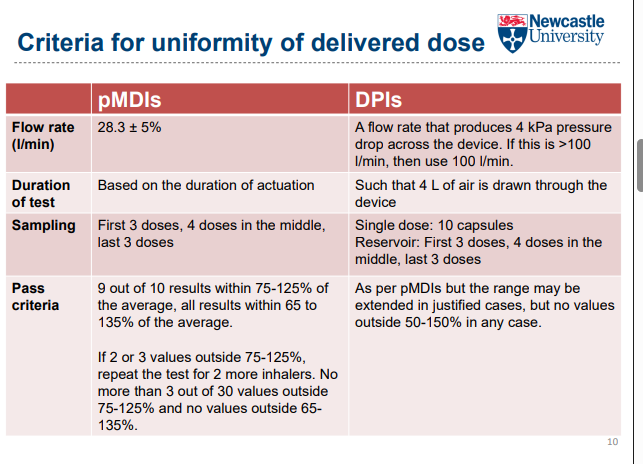
What is the purpose of the uniformity of delivered dose test in inhalers?
Ensures the dose emitted is consistent throughout the life of the device
Covers from the first dose to the last labelled dose
How is the uniformity of delivered dose test performed?
Dose is fired into a dose collection apparatus (e.g., tube with a filter)
Typically >10 doses tested from beginning, middle, and end of device
3 devices tested from two different batches
Drug collected on the filter is quantified
How is a pMDI tested for dose delivery?
Use a vacuum pump drawing air at a constant flow rate (e.g., 28.3 L/min)
Prevents loss of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) into the air
How is a DPI tested for dose delivery?
Use a critical flow controller
Simulates a patient’s inspiratory flow rate
How is a nebuliser tested for dose delivery?
Use a breathing simulator
Mimics human tidal breathing
What is the Fine Particle Dose (FPD) in inhalation devices?
Mass of drug in particles <5 µm
Represents the “therapeutically useful” dose likely to reach the lower airway
What is the Fine Particle Fraction (FPF) in inhalation devices?
Percentage of the delivered dose that is <5 µm
Indicates the efficiency of drug delivery to the lower airways
What is aerodynamic diameter and why is it important in inhalation therapy?
Diameter of a unit-density sphere with the same settling velocity as the particle
Accounts for particle size, density, and shape
Determines how a particle behaves in an air stream
What is Aerodynamic Particle Size Distribution (APSD) in inhalation therapy?
Full profile of particle sizes in an inhaled dose
Determines where in the respiratory tract the drug will deposit
What particle size is optimal for peripheral airway deposition?
Upper limit: 5 µm
Particles <1 µm are likely to be exhaled
No strict lower limit defined
How are fine particle dose, fine particle fraction, and APSD measured?
Determined using a cascade impactor as described in the British Pharmacopoeia (BP)
How do cascade impactors work in inhalation testing?
Comprise a series of progressively finer jets and collection plates
Fractionate aerosols according to their aerodynamic size
Aerosol is drawn through the device at a known flow rate
How does a cascade impactor separate particles by size?
Aerosol is drawn through the impactor at a controlled flow rate.
It passes through a series of stages with progressively finer jets.
Particles with too much inertia to follow the air stream impact on collection plates.
Large, denser particles deposit in the upper stages of the impactor.
what happens to smaller particles second aprt
Smaller, less dense particles remain in the air stream longer.
They reach stages with finer jets, giving them enough momentum to impact on collection plates.
Each stage corresponds to a cut-off diameter, separating particles by size.
How are residual materials and drug collected in a cascade impactor? step 2
Residual materials are captured in the final stage of the impactor
Drug contents from each stage, including the throat and rubber adapter, are collected
Analysis is typically performed using HPLC
How do glass (two-stage/twin) impingers work and what are their limitations?
Limited use today, mainly for simple and rapid checks
Provide limited information on particle size distribution
Stage 1 (throat & upper impinger): Collects non-respirable particles
Stage 2 (lower impinger): Collects respirable particles
What is a Multi-Stage Liquid Impinger (MSLI) and how does it work?
Most commonly used: 4-stage MSLI with a terminal filter
Collection stages are kept moist to prevent particle bouncing off the plates
Used to fractionate aerosols for particle size and respirable dose analysis
What is the Andersen Cascade Impactor (ACI) and its advantages?
Structure: 8 stages plus a final filter
Advantages:
Easy to handle stack-up design
Damaged stages can be replaced individually
What is the Next Generation Impactor (NGI) and its key features?
Structure: 7 collection cups + micro-orifice collector (MOC)
Each stage has a cut-off diameter determined by the flow rate
Operates over a wide flow range (15–100 L/min)
Particularly useful for nebuliser testing
How is the number of deliveries per inhaler tested?
Discharge the inhaler contents to waste until empty
Actuate the valve at intervals of not less than 5 seconds
Must meet the labelled requirement: total deliveries ≥ number stated on the product label
How is the efficacy of antimicrobial preservatives tested in multi-dose inhalers?
Samples are taken from the inhaler and inoculated with microbes
Stored at a specified temperature and duration
Preservative is considered effective if there is a significant fall or no increase in microbial count
Why is leak rate testing important for pMDIs and how is it measured?
Ensures the propellant does not leak during product shelf life
Weigh the inhaler (M1), store upright at 25 °C for ≥3 days, then weigh again (M2)
Total loss of mass over time is used to assess leakage
What is the acceptance criteria for pMDI leak rate testing?
Calculate total mass loss over the shelf life (D, in months)
Passes test if total loss ≤ 10% of total fill mass of the container