Aggreage Demand, Aggregate Supply and Inflation
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
The Aggregate Demand Curve
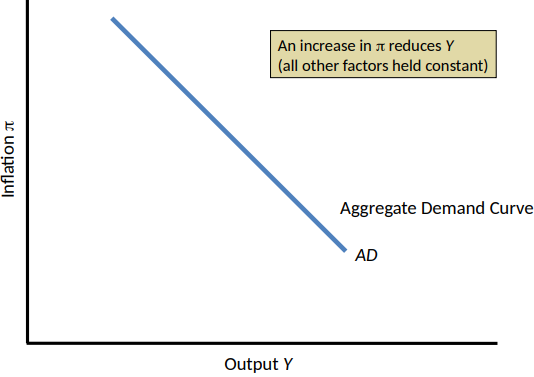
Shows the relationship between short-run equilibrium output Y and the rate of inflation, π
The name of the curve reflects the fact that short-run equilibrium output is determined by, and equals, total planned spending in the economy
Increases in inflation reduce planned spending and short-run equilibrium output, so the curve is downward-sloping
Movements along the AD Curve
π and Y are inversely related
Changes in π cause a change in Y or a movement along the curve
π increases → r increases → planned spending decreases → Y decreases
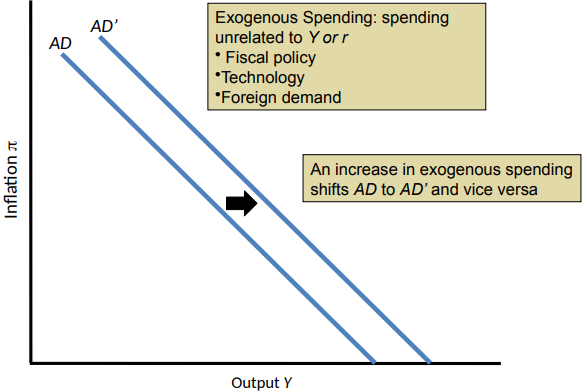
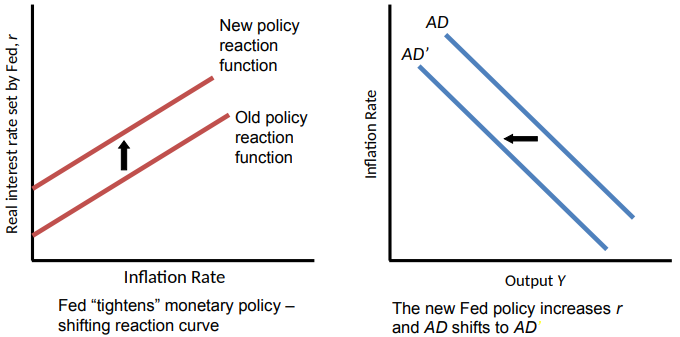
Shifts of the AD Curve
Any factor that changes Y at a given π shifts the AD curve
Can be caused by:
Changes in exogenous spending
Changes in the Fed’s policy reaction function
Keynesian Model
assumes output adjusts to demand at pre-set prices in the short run
prices don’t remain fixed indefinitely
doesn’t explain the behaviour of inflation
Why does the AD Curve Slope Downward?
Response of real interest rate to inflation through the Fed’s Reaction Function (Taylor Rule)
Distributional effects: Inflation hurts people with lower incomes more. These people also spend more of their income, so Y drops when their income does
Uncertainty: Inflation → uncertainty about future prices, so people may be more cautious in spending
Exports: Inflation → Prices of exported goods rises, lowering exports
The Aggregate Demand Curve
Effect of an Increase in Exogenous Spending
A Shift in the Fed’s Policy Reaction Function
When will Inflation remain Roughly Constant, or have Inertia?
if operating at Y* and there are no external shocks to the price level
Why does Inflation Inertia occur?
inflation expectations
long-term wage and price contracts
What are 3 Factors that Increase the Inflation Rate?
output gap
inflation shock
shock to potential output
What happens if you think there will be High Inflation?
You’ll agree to much higher prices
This can lead to actual inflation as prices rise
Price Contracts
Union wage contracts set wages for several years
Contracts setting the price of raw materials and parts for manufacturing firms also cover several years
These long-term contracts reflect the inflation expectations at the time they are signed
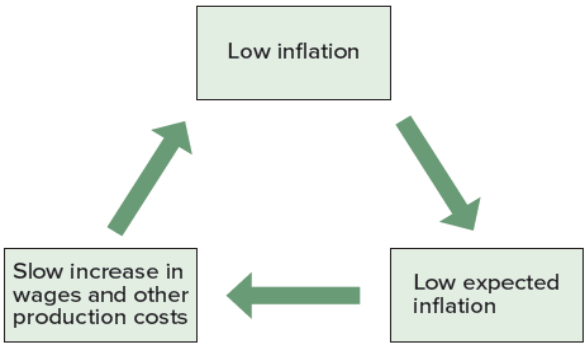
Virtuous Cycle of Low Inflation and Low Expected Inflation
The Output Gap and Inflation
Relationship of output to potential output | Behaviour of inflation |
No output gap | Inflation remains unchanged |
Expansionary gap | Inflation rises |
Recessionary gap | Inflation falls |
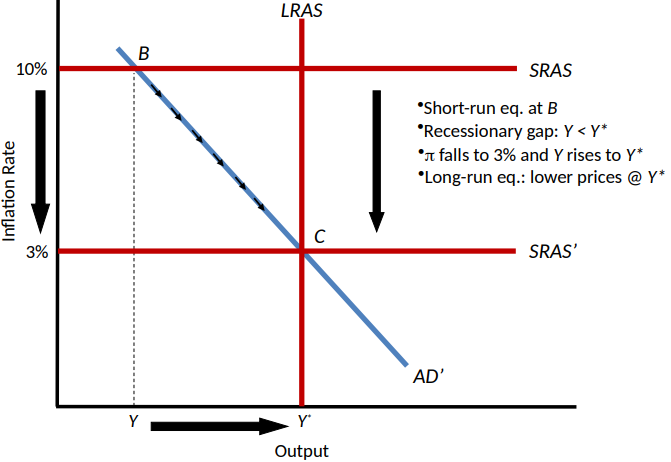
The Aggregate Demand-Aggregate Supply Diagram
Long-run aggregate supply (LRAS)
A vertical line showing the economy’s potential output Y*
Short-run Aggregate Supply (SRAS)
A horizontal line showing the current rate of inflation, as determined by past expectations and pricing decisions
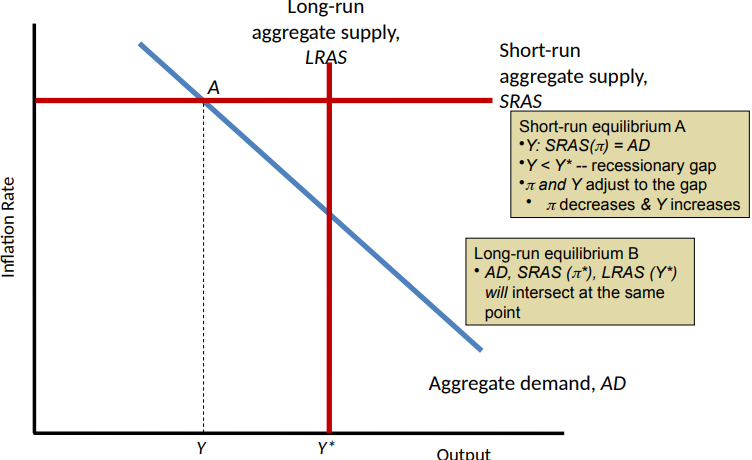
Short-Run Equilibrium
A situation in which inflation equals the value determined by past expectations and pricing decisions and output equals the level of short-run equilibrium output that is consistent with that inflation rate
Graphically, short-run equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the AD curve and the SRAS line
Long-Run Equilibrium
A situation in which actual output equals potential output and the inflation rate is stable
Graphically, long-run equilibrium occurs when the AD curve, the SRAS line, and the LRAS line all intersect at a single point
What does the Self-Correcting Economy concept state?
in the long-run, the economy tends to self-correct
What factors influence the speed of Economic Self-Correction?
use of long-term contracts
efficiency and flexibility of labour markets
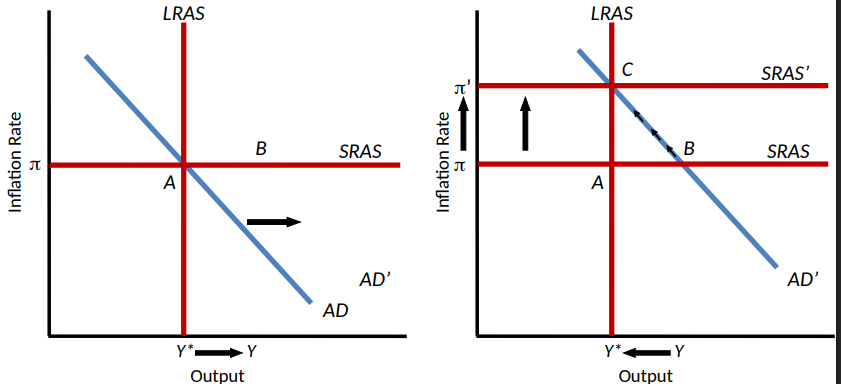
War and Military Build-up as a Source of Inflation
Military spending increase → AD increase → Expansionary gap (Y > Y*) → π increases → SRAS shifts to SRAS’ → Long-run equilibrium Y* and π*
Inflation Shock
a sudden change in the normal behaviour of inflation, unrelated to the nation’s output gap
The Effects of an Adverse Inflation Shock
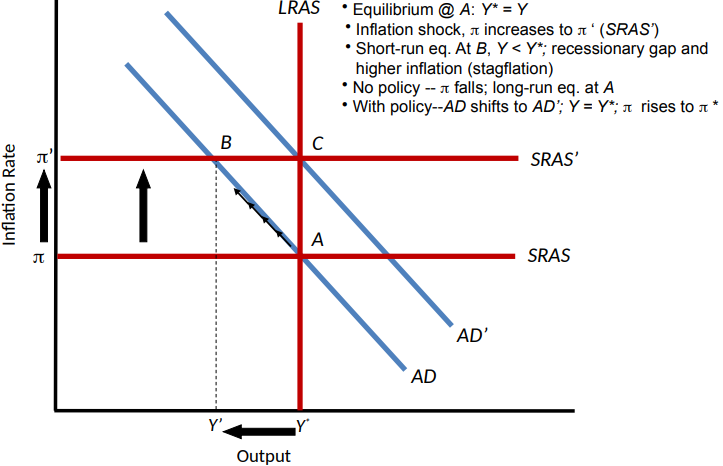
Aggregate Supply Shock
Either an inflation shock or a shock to potential output
Adverse aggregate supply shocks of both types reduce output and increase inflation
Effects of Aggregate Supply Shock
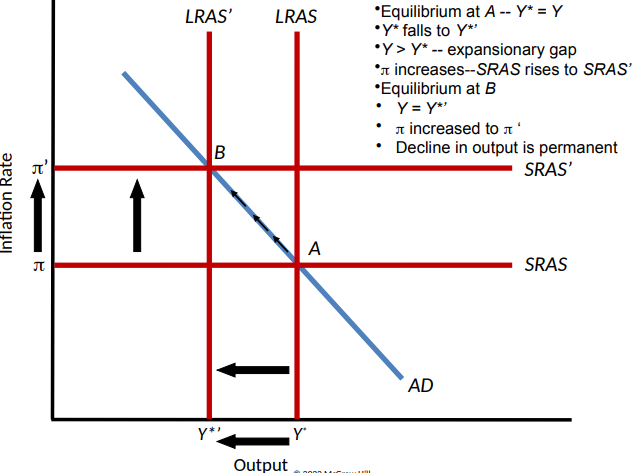
Short-Run Effects of an Anti-Inflationary Monetary Policy
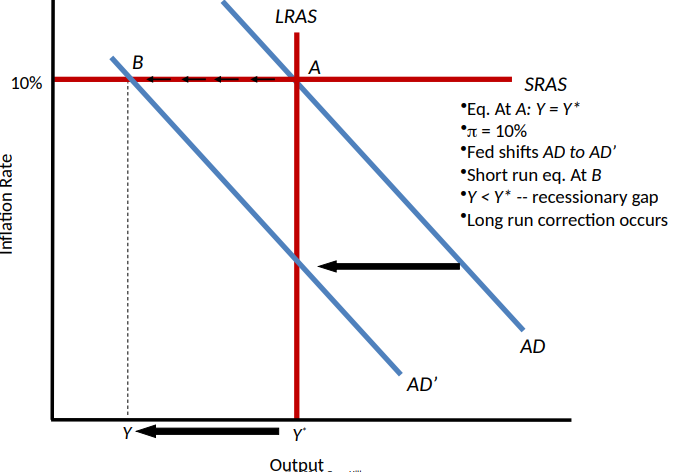
Long-Run Effects of an Anti-Inflationary Monetary Policy