Lecture 19 - Histamine and Histamine Receptors
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
structural evaluation of histamine
molecule consists of an imidazole ring and ethylamino side chain
CH2 groups near amino group are designated alpha and beta (alpha closest to NH2)
pKas are 5.8 (imidazole) and 9.40 (amine)
exists primarily in ionized form at physiological pH
biosynthesis of histamine
L-histidine (substrate) —> histamine via histidine decarboxylase (enzyme) and pyridoxal phosphate (co-factor)
how is histamine stored
as an inert, ionic complex
primary site of histamine storage
granules of mast cells
secondary sites of histamine storage
o Skin and Lungs (bronchial tissue) – highest concentration of mast cells/histamine
o Mucosal layer of GI tract
o Heart (cardiomyocytes)
o CNS – histamine biosynthesized locall
why is histamine released from cell
antibodies —> PLC activation —> IP3 + DAG —> intracellular calcium increase
pathway I of metabolism of histamine
1. Oxidative deamination to the aldehyde (oxidative deamination by diamine oxidase)
2. Oxidation of the aldehyde to the carboxylic acid (oxidation)
3. Ribosylation (similar to glucuronidation) of imidazole ring (non-basic nitrogen)
pathway II of metabolism of histamine
1. Methylation of imidazole non-basic nitrogen
2. Oxidative deamination to the aldehyde by MAO-B or diamine oxidase
3. Oxidation of the aldehyde to the carboxylic acid
ways histamine action can be terminated
cellular uptake (major)
receptor desensitization (secondary)
metabolism (minor)
minor mechanism for drugs that reduce histamine’s effects
Inhibit release of histamine from storage sites (few drugs belong to this class) - preventive
major mechanism for drugs that reduce histamine’s effects
Block the histamine receptors with antagonists (bulk of the drugs are in this category)
first generation H1 antagonist purpose
treatment of allergic responses such as hay fever, rhinitis, urticaria, and food allergies
issue with gen 1 antihistamines and receptors
gen 1 antihistamines can act on numerous receptor types, not just H1. this can cause many unintended side effects
adverse central effects of gen 1 antihistamines
sedation
drowsiness
decreased cognition
somnolence
adverse peripheral effects of gen 1 antihistamines
blurred vision
dry mouth
urinary retention
constipation
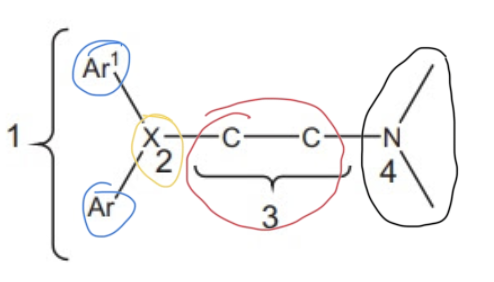
1st gen H1 antagonist SAR
two aromatic rings —> steric bulk required for antagonist
X group —> defines class
spacer linking bulk to basic amine
basic, tertiary aliphatic amine —> ionized so molecule can bind
advantages of 2nd gen over 1st gen antihistamines
2nd gen has higher affinity for H1 receptor, prolonging duration of action
2nd gen has high H1 selectivity due to polar group → decreased binding to other receptor types
2nd gen has low potential to cause CNS effects due to polar group AND lower affinity for central H1 receptors
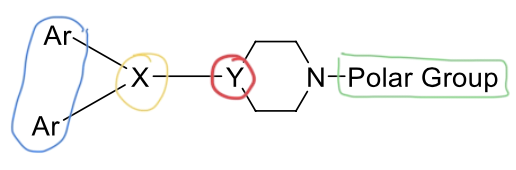
2nd gen H1 antagonist SAR
two aromatic rings —> steric bulk required for antagonist
X group —> defines class
Y group in ring —> defines ring structure
basic amine —> ionized so molecule can bind
polar group —> increases H1 receptor selectivity
(X and Y directly connected)
gen 1 vs gen 2 antihistamine SAR
polar group after nitrogen, and sometimes 2 nitrogens in 2nd gen
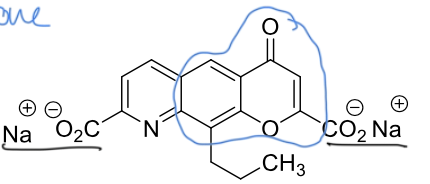
inhibitors of histamine release SAR
1. Chromone (benzopyrone) —> blue
2. Carboxylate anions (2) —> black
chemical classes of gen 1 antihistamines
ethylenediamine
phenothiazine
aminoalkyl ether / ethanolamine
propylamine
piperazine
Dibenzocycloheptanes/heptenes
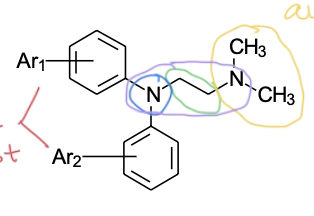
Ethylenediamine class SAR
two aromatic rings —> steric bulk required for antagonist
X group —> nitrogen
spacer linking bulk to basic amine
basic, tertiary aliphatic amine —> ionized so molecule can bind
(“ethyl” spacer, “di-amine” 2 nitrogens)
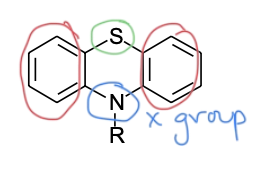
Phenothiazine Class SAR
two aromatic rings LINKED with sulfur—> steric bulk required for antagonist
X group —> nitrogen
spacer linking bulk to basic amine
basic, tertiary aliphatic amine —> ionized so molecule can bind
(pheno = phenyls, thi = sulfur, az = nitrogen, ine = 6 membered ring)
Aminoalkyl Ether Class (or Ethanolamine Class) SAR
two aromatic rings —> steric bulk required for antagonist
X group —> ether (C-O)
spacer linking bulk to basic amine
basic, tertiary aliphatic amine —> ionized so molecule can bind
(ethanol = ethanol spacer, amine = amine)
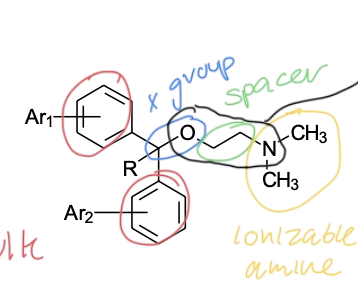
Propylamine Class SAR
two aromatic rings —> steric bulk required for antagonist
X group —> sp3 carbon (1 or 0 hydrogens OK)
spacer linking bulk to basic amine
basic, tertiary aliphatic amine —> ionized so molecule can bind
Piperazine Class SAR
two aromatic rings —> steric bulk required for antagonist
X group —> piperazine ring system (seems like 2nd gen, but no polar group attached)
spacer linking bulk to basic amine
basic, tertiary aliphatic amine —> ionized so molecule can bind
additional bulk attached to piperazine —> increase antagonist action
Dibenzocycloheptanes/heptenes SAR
two aromatic rings LINKED with 7 membered ring—> steric bulk required for antagonist
X group —> sp3 carbon (no hydrogens)
spacer linking bulk to basic amine
basic, tertiary aliphatic amine —> ionized so molecule can bind