FAR Excel Problems
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
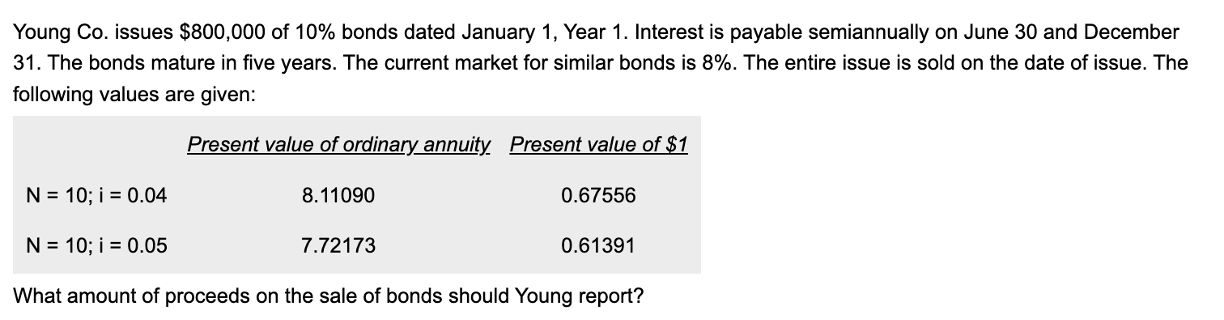
Thomas & Co issued $1,000,000 in bonds and receives proceeds of $1,085,302. The stated rate on the bond is 8%. The effective rate is 6%. The bond was issued on January 1st year 1 and have a 5 year maturity. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31.
Create a table straight method
JE for Bond Issuance, Interest payment and maturity
Bond Issued @premium-Straight
Thomas & Co issued $1,000,000 in bonds and receives proceeds of $957,350. The stated rate on the bond is 5%. The effective rate is 6%. The bond was issued on January 1st year 1 and have a 5 year maturity. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31.
Create a table for the straight method
JE for Bond Issuance, Interest payment and maturity
Bond Issued @discount-Straight
Thomas & Co issued $1,000,000 in bonds and receives proceeds of $1,085,302. The stated rate on the bond is 8%. The effective rate is 6%. The bond was issued on January 1st year 1 and have a 5 year maturity. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31.
Create a table for effective method
JE for Bond Issuance, Interest payment and maturity
Bond Issued @premium- Effective
Bond @premium- Find Proceed
Thomas & Co issued $1,000,000 in bonds and receives proceeds of $957,350. The stated rate on the bond is 5%. The effective rate is 6%. The bond was issued on January 1st year 1 and have a 5 year maturity. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31.
Create a table for the straight method
JE for Bond Issuance, Interest payment and maturity
Bond Issued @discoun- Effective

Bond with issuance cost
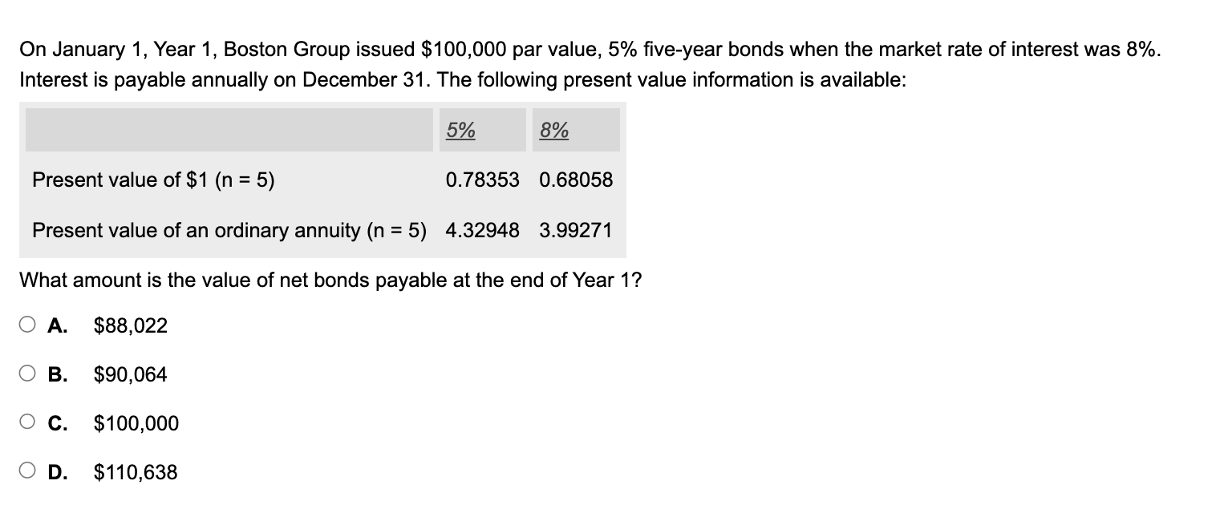
Without CV Bond

Create a table and JE for all 3 years
Finance Lease

Create a table and JE for all 3 years
Operating Lease
Adam Company issued three-year, $100,000, zero-interest-bearing note to Ryan. The implicit rate is 5%. PV is 0.86384 Create Table
Interest Bearing Notes
Leaf Co. purchased from Oak Co. a $20,000, 8%, 5-year note that required five equal annual year-end payments of $5,009. The note was discounted to yield a 9% rate to Leaf. At the date of purchase, Leaf recorded the note at its present value of $19,485. What should be the total interest revenue earned by Leaf over the life of this note?
Interest Bearing Notes
On July 31, Year 1, Dome Co. issued $1,000,000 of 10 percent, 15-year bonds at par and (as a typical risk-management strategy to Dome Co.) used a portion of the proceeds to call its 600 outstanding 11 percent, $1,000 face value bonds, due on July 31, Year 11, at 102. On that date, unamortized bond premium relating to the 11 percent bonds was $65,000. In its Year 1 income statement, what amount should Dome report as gain or loss from retirement of bonds?
Bond Retirement
During Year 2, Colt Co. experienced financial difficulties and is likely to default on a $1,000,000, 15%, 3-year note dated January 1, Year 1, payable to Cain National Bank. On December 31, Year 2, the bank agreed to settle the note and unpaid Year 2 interest of $150,000 for $820,000 cash payable on January 31, Year 3. What is the amount of gain, before income taxes, from the debt restructuring?
Debt Restructuring Gain/Loss
Embrin Inc. issued a 10-year, $1,000,000 bond at a discount price of $945,000. The company incurred bond issuance costs of $25,000, which are amortized straight-line over 10 years. Three years after issuance, the company redeemed the issue at 102. At the time the issue was redeemed, $12,500 of the discount had been amortized. Under U.S. GAAP, which of the following components of the loss booked by the company when the issue is redeemed is correct?
Bond Redemption
A company issues $1,500,000 of par bonds at 98 on January 1, Year 1, with a maturity date of December 31, Year 30. Bond issuance costs are $90,000, and the stated interest rate of the bonds is 6 percent. Interest is paid semiannually on January 1 and July 1. Ten years after the issue date, the entire issue was called at 102 and canceled. The company uses the straight-line method of amortization for bond discounts and issuance costs, and the result of this method is not materially different from the effective interest method. The company should classify what amount as the loss on extinguishment of debt at the time the bonds are called?
Bond Extinguishment
At the beginning of Year 2, Kennedy enters into a four-year operating lease with payments due at the end of the year beginning on December 31, Year 2. The rate implicit in the lease is 4.50 percent and Kennedy will owe annual payments of $5,200. The present value factor of an ordinary annuity for four years at 4.50 percent is equal to 3.5875. The carrying value of the lease liability at the end of Year 2 will be closest to:
Leases Operating Lease
Oak Co. leased equipment for its entire nine-year useful life, agreeing to pay $50,000 at the start of the lease term on December 31, Year 1, and $50,000 annually on each December 31 for the next eight years. The present value on December 31, Year 1, of the nine lease payments over the lease term, using the rate implicit in the lease which Oak knows to be 10%, was $316,500. The December 31, Year 1, present value of the lease payments using Oak's incremental borrowing rate of 12% was $298,500. Oak made a timely second lease payment. What amount should Oak report as a lease liability in its December 31, Year 2, balance sheet?
Leases Operating Lease
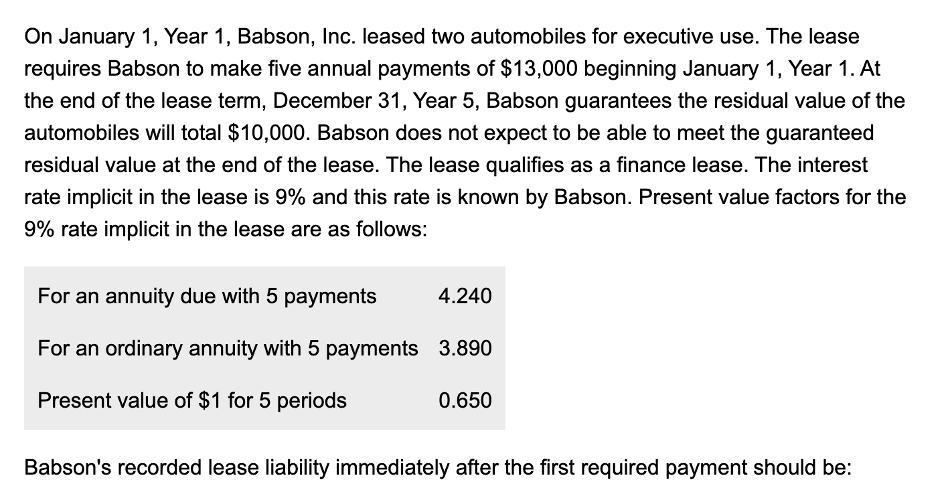
Lease Finance Lease

Lease Finance Lease

Revenue over time
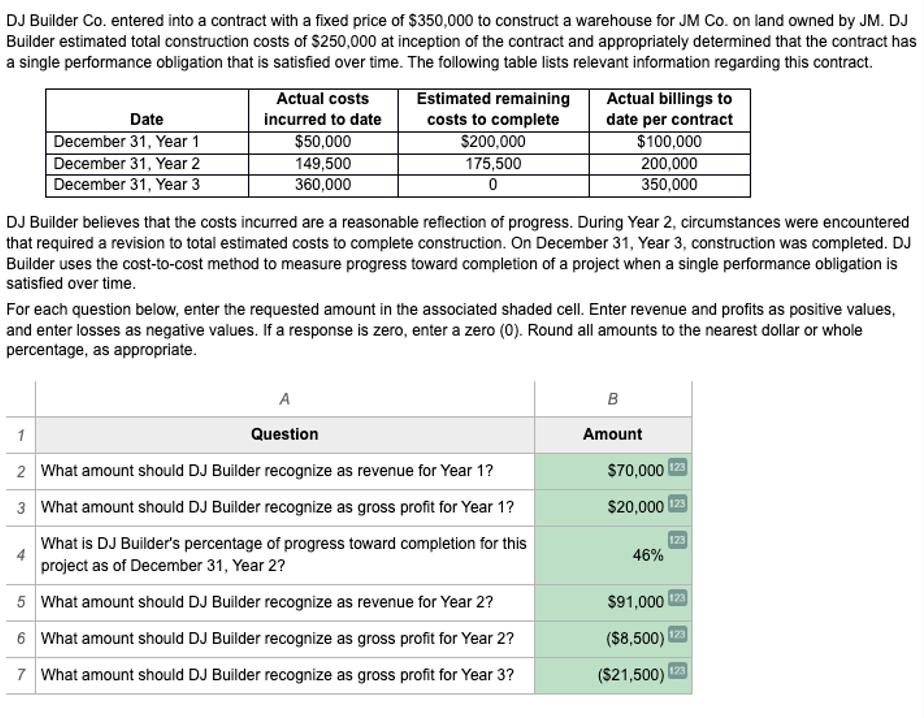
Revenue over time

Dollar Value Basis

Dollar Value Basis