Lecture 2: Scientific Processes & Chemistry
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Themes of biology
Evolution
Emergent properties
Levels of biological organization
Unifying idea of biology
All living descendants are modified descendants of common ancestors
Emergent properties
Properties that result from arrangement and interaction of parts within a system
Emergence
The whole is more than the sum of its parts
Example of emergent properties
Organelles of a cell
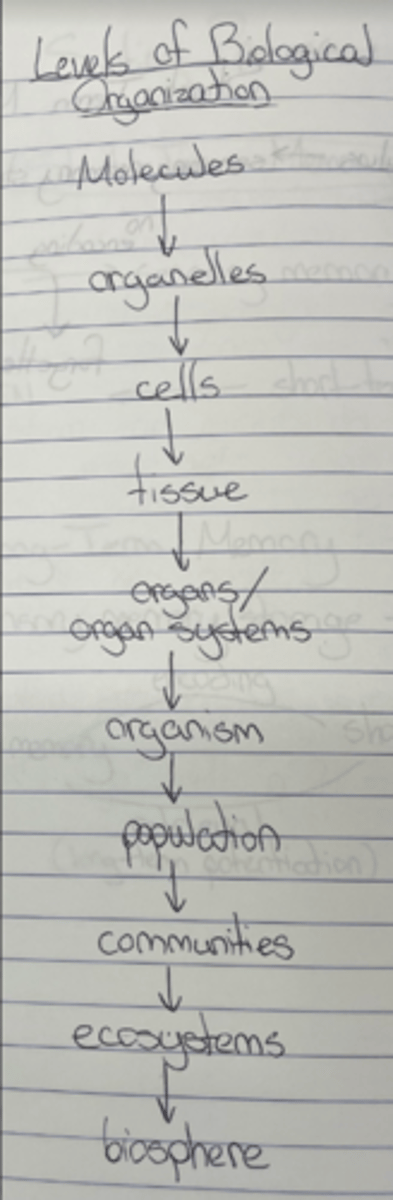
Levels of biological organization
Molecules → organelles → cells → tissues → organs/organ systems → organisms → populations → communities → ecosystems → biosphere
Scientific process
Observation & question
Background information
Hypothesis
Prediction
Experiments/observations
Evaluate
Science
From Latin word "to know"
Limited to observable and measurable structures
Systematic
Hypothesis
Testable proposed explanation for observations
Prediction
Expected outcome of a tested hypothesis
Theory
Broad explanation with significant support
Explains "what" and "why"
Law
Statements that always occur under certain circumstances
Explains "what" but not "why"
3 subatomic particles
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
Electrons (e-)
-1 charge
Surround atomic nucleus
Have potential energy
Involved in bonds and chemical reactions
Potential energy
Energy that a material possesses due to its location or structure
How are electrons involved in energy?
Have potential energy due to distance from nucleus
Absorb energy moving to higher shells
Release energy moving to lower shells
Valence shell
The outermost electron shell
Valence electrons
Electrons occupying the valence shell
Molecule
A compound of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
Chemical formula
Composes of types and amount of atoms making up the compound
Types of bonds
Nonpolar covalent bond
Polar covalent bond
Ionic bond
Hydrogen bond
Covalent bond
Strongest type of chemical bond
Sharing e- between atoms
Polar covalent bond
Unequal electronegativity
Unequal e- sharing
Causes partial + and - charges
Nonpolar covalent bond
Similar electronegativity
e- shared equally
How are chemical bonds formed?
Sharing e-
Donating e-
Accepting e-
Electronegativity
Measure of atom's affinity for e-
Higher electronegativity results in higher pull of e- towards nucleus
Ionic bonds
Highly unequal electronegativity
e- lost or gained
Bond formed by attraction between cation and anion
Dissolve in water
Ion
Charged atom
Cation
Positively charged ion
Anion
Negatively charged ion
Example of ionic bond
Salts
Van der Waals interactions
Relatively short-lived and weak interactions
Interaction of + and - charges
Strong in numbers
Hydrogen bonds
When hydrogen bonds to an electronegative atom
Emergent properties of water
Hydrogen bonds
Cohesive behavior
Moderates temperature
Expansion upon freezing
Versatility as a solvent
What kind of bond is H2O?
Polar covalent bond
Hydrogen bonds in water
Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other
Constantly broken and reformed
Cohesion
Water molecules stick to each other
Surface tension
Measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid
Result of cohesion
Adhesion
Water molecules stick to other things
Capillary action
The tendency of water to rise against gravity into small spaces of hydrophilic material
Specific heat
The amount of heat that must be absorbed to raise 1g of a substance by 1*C
Why does water have high specific heat?
Hydrogen bonds in water resist faster movement of molecules
Evaporative cooling
The process in which the surface of an object becomes cooler during evaporation
Molecules with higher energy/heat evaporate
Expansion upon freezing
All molecules have 4 hydrogen bonds
Less dense than liquid water
Prevents bodies of water from freezing solidly from the bottom
What causes hydrophilia?
Polar covalent bonds due to their partial positive or negative charge
What type of bond and substance does not dissolve in water?
Nonpolar covalent or nonionic bonds; hydrophobic