Gustation (taste)
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
What does gustation (sense of taste) provide?
Information about the foods and liquids we consume
Where can taste receptors be found?
Mainly on the superior surface of the tongue
Some located in pharynx and larynx
What is the sensory structure that consist of taste (gustatory) receptors?
Taste buds
Gustatory Receptors
The tongue consist of
Papillae consist of
Taste buds consist of
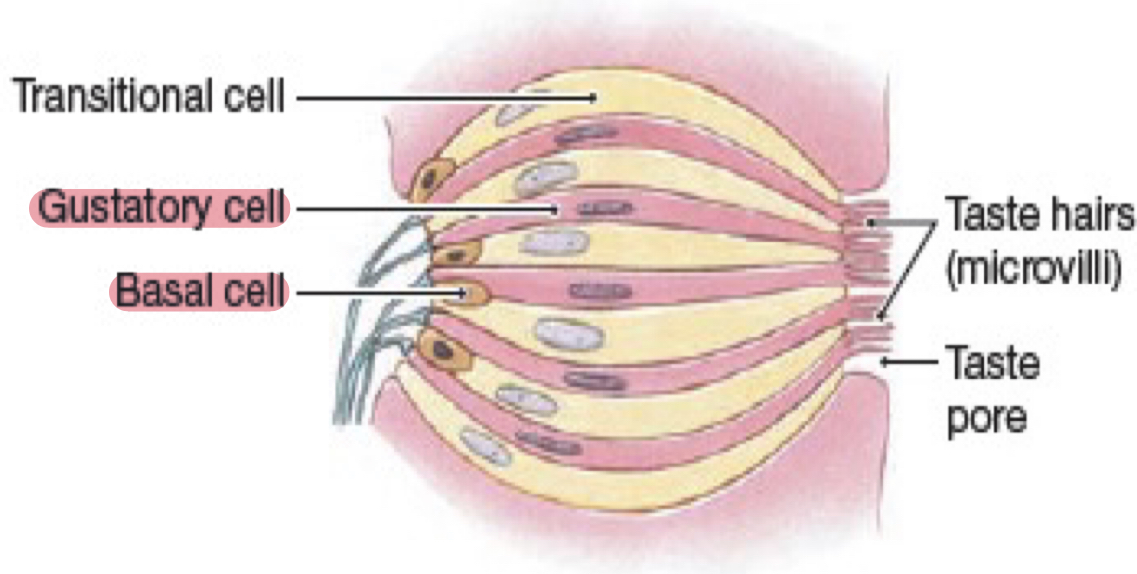
Structure of gustatory cell
Why short half life
What replaces it?
Tongue consist of: Papillae
Papillae consist of: Taste buds
Taste buds consist of: Gustatory cells
Structure of gustatory cell: Has slender microvilli that extends through taste pore into surrounding fluid
Why short have life: Because they are prone to damage
Replaced by: Basal cells
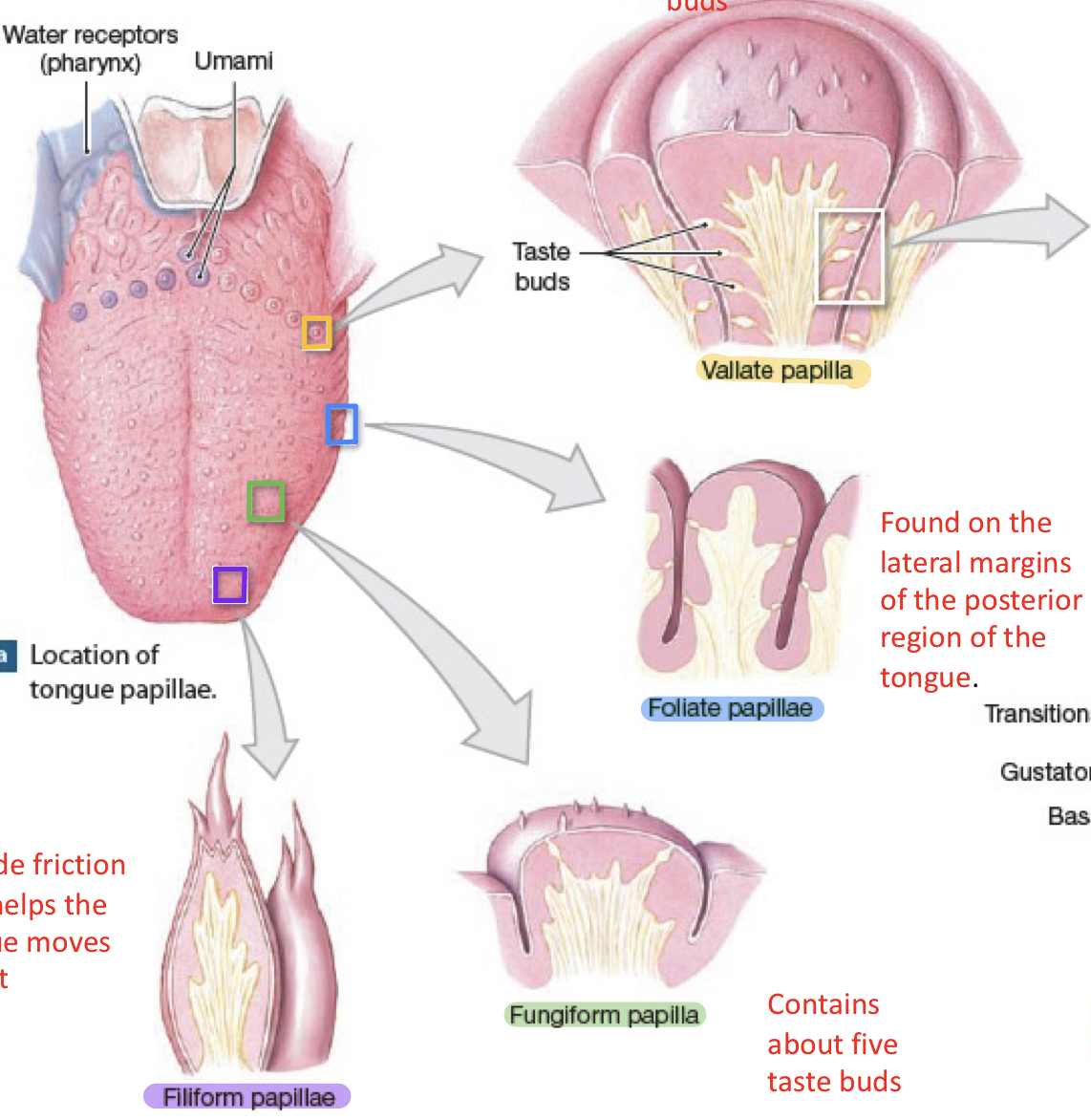
What are the 4 types of papillae
Filiform
Helps move object
Fungiform
Contains about 5 taste buds
Foliate
Vallate
Taste Sensations
What are the 4 primary sensations
What are the 2 other sensations
What is the location of these sensations
What type of sensation sensitivity can be inherited and why
Which foods taste bitter
4 primary sensations: Sweet, salty, sour and bitter
2 other sensations:
Umami
Savoury
Receptor binds to amino acids
Water receptors
Demonstrated in human pharynx
Information sent to hypothalamus to manage thirst
Inherited type of sensation: Extreme sensitivity to bitter taste such as alkaloid foods
Why: This includes poisons so spitting out is a protective mechanism