Chapter1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
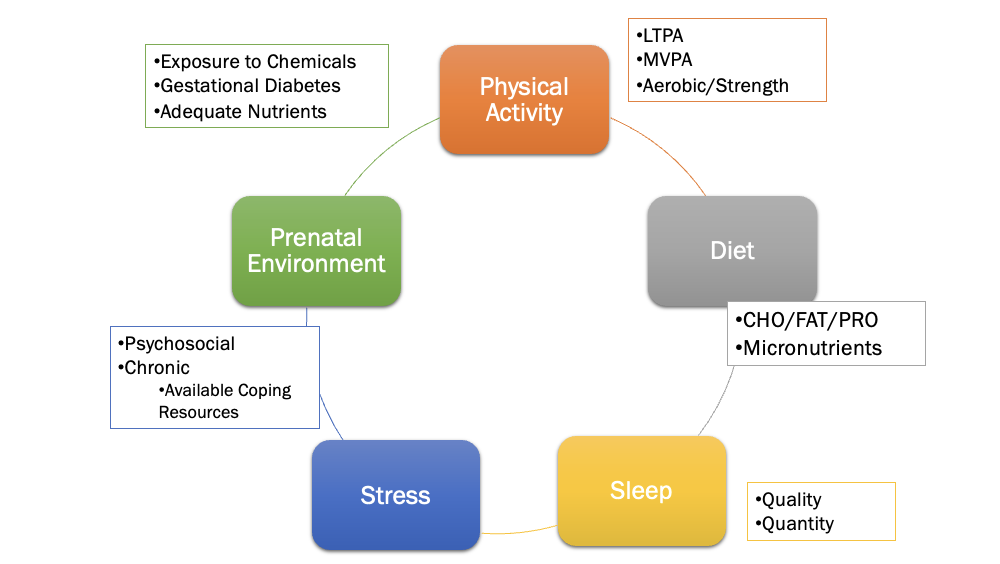
physical activity
any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles that result in an increase in energy expenditure above resting rate
how is physical activity different than exercise
exercise is subset of physical activity that is planned, structured and repetitive and has as a final or an intermediate objective the improvement or maintenance of physical fitness
physical fitness
a set of outcomes or traits that relate to the ability to perform physical activity
skill and sports related fitness
agility
balance
coordination
power
reaction time
speed
health related fitness
body composition
flexibility
muscular endurance
muscular strength
aerobic fitness
physical inactivity risk=
smoking +obesity combined
regular physical activity
guards against noncommunicable disease
protection against 25+ chronic medical conditions
numerous other health benefits
inactive children tend to become inactive adults
dose response relationship
dose= volume of activity
response=health benefits
some MVPA better than none
exceeding the recommended dose magnifies the response
exceeding the recommended dose by a factor of 10 is not harmful
active workstations
reduced sitting time
increased daily activity
CHD risk factors
age
family
hypercholesterolemia
hypertension
current cigarette smoking
prediabetes
obesity
physical inactivity
cardiovascular disease myth
its a man’s disease
its an older person’s disease
cardiovascular disease risk factors
worsened by physical inactivity
improved by physical activity
improvement is directly related to aerobic capacity
improvement also from regular resistance training
AHA’s key measure for improving and maintaining cardiovascular health
eat better
be more active
quit tobacco
get healy sleep
manage weight
control cholesterol
manage blood sugar
manage blood pressure
hypertension
leading preventable cause of premature death for age < 70
if unchecked, it is a primary risk factor for other conditions
stroke
heart attaack
heart failure
kidney failure
COPD
dementia
blindness
categorizing BP values for risk factor analysis
use highest SBP or DBP average of at least two measurements
measurements acquired in two separate visits
best of assess BP in both arms
optimal to record avaerage values from arm having higher values
Exercise prescription for individuals with hypertension
Typer: primarily endurance activities supplemented by resistance exercise
intensity: moderate intensity endurance (40%-59% VO2R) rate of perceived exertion 12 to 13 and resistance training (40-80% 1rm)
Duration: 30 min or more of continuous or accumulate aerobic physical activity per day, and a minimum of two sets (8-12 reps) of resistance training exercise for each major group
frequency: most days of the week for aerobic exercise 2 to 3 days/ wk for resistance training
hypercholesterolemia
elevation of total cholesterol
dyslipidemia
abnormal blood lipid profile
lipoprotein categories
chylomicron
vldl
ldl
hdl
benefits of aerobic exercise and resistance exericse
hypercholesterolemia
strong predictor of CHD
tobacco
cigar, cigarette usage
decreasing in many not all countries
preventable risk factor for many chronic diseases and premature death
second hand smoke hazard
electronic cigarette risk not yet known
quitting has health benefits within weeks
risk declines 50% in the first years
relative risk of stroke and CHD death is similar to that of a nonsmoker in 15 years
diabetes mellitus
pandemic level
among top 10 causes of death in U.S.
Major contributor to other conditions
heart disease
amputations of leg or foot
stroke
kidney failure
blindness
cognitive disability
some cancer
diabetics have risk of postexericse hypoglycemia and transiet hyperglycermia
diabetes mellitus
prediabetes condition identified by fasting blood glucose and HbA1c levels
type 1 diabetes associated with sedentary time
etiology differs
response to exercise differs
risk of type 2 diabetes associated with sedentary time
those with diabetes have risk of post-exercise hypoglycemia and transient hyperglycemia
obesity and overweight
classified in terms of BMI cut points
Pros: BMI has utility as a simple index of obesity
cons: cannot identify relative fatness or site of fat storage; traditional cut point do not work for all races/ ethnicities
fifth leading cause of death globally is obesity
high prevalence for adults and children
threatens longevity and quality of life
obesity and overweight
obesity is associated with CHD risk factors
obesity paradox: prognosis for survival from CVD is better for those who are overweight or mildly obese (BMI=25-27ish)
prevalence of obesity varies by race/ethnicity
metabolic syndrome
adult prevalence
highest in the united states
underestimated globally
underlying factors
age
physical inactivity
genetics
increases risk of other conditions
stroke
CVD
type 2 diabetes
metabolic syndrome
cluster of CVD risk factots
must have three of the following risk factors
HTN
dyslipidermia
insulin resistance
Abdominal obesity
waist circumference helps not abdominal obesity
cancer
leading cause of death globally
primary risk factors
tobacco and alcohol use
unhealthy food choices
physical inactivity
high bmi
chronic or systemic inflammation
inverse relationship between many cancers and LTP
Physically active patients have better survival rates
musculoskeletal diseases and disorder
osteoporosis
preceded by osteopenia (low bone mineral mass)
osteoarthritis
fragility fractures
primary sites: hip, spine, wrist, shoulder
connective tissue tears
low back syndrome
Musculoskeletal Diseases and Disorders
•Related to physically inactive lifestyle
•Osteoporosis (primary and secondary)
•More prevalent in women
•Fracture may be first clue and indicator of future fractures
•Prevalence varies by race, age, sex
•Diagnostic criteria for osteoporosis
•Low BMD of hip or lumbar spine
•History of site-specific low trauma fracture
•FRAX score ≥ cut-point values for intervention for low BMD
Musculoskeletal Diseases and Disorders
Weight-bearing exercise modalities = preventative
Targeted effect varies by exercise intensity
Adequate vitamin D and calcium sources
Bone-strengthening for children is the key to adult prevention
Aging
Life expectancy directly related to physically active life
May delay onset or development of many chronic diseases
May reverse or limit effects of existing chronic diseases
Regular LTPA and exercise may increase telomere length
Short telomeres associated with numerous chronic diseases
Target 40- to 60-year-olds for increasing LTPA
Cognitive Performance
Can be improved with exercise interventions
Inverse relationship between PA and cognitive function
MVPA = higher cognitive function scores
Lots of sedentary time = lower cognitive function scores
Prepubertal and mid-to-late life are influential periods
Exercise for cardiovascular system protects the brain
Not one best exercise modality
Exercise as Medicine
Dose-response relationship in terms of health benefits
Delays onset of chronic NCDs
Inactivity is a better predictor of mortality than are hypertension, diabetes, blood lipid levels, and smoking
Exercise Is Medicine initiative
Targets primary care physicians and other health care providers
Focus on including physical activity in treatment plans
Global initiative
Documented Benefits of Exercise
Inflammation
Cognitive function
Vitality
Social function
Blood lipids
Blood glucose
Insulin sensitivity
Body composition