9. small animal med- exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what is exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI)?
malabsorptive syndrome caused by insufficient secretion of digestive enzymes from pancreatic acinar cells
what is the typical signalment of animals with EPI?
dogs and cats (GSDs are predisposed)
any age, depends on etiology
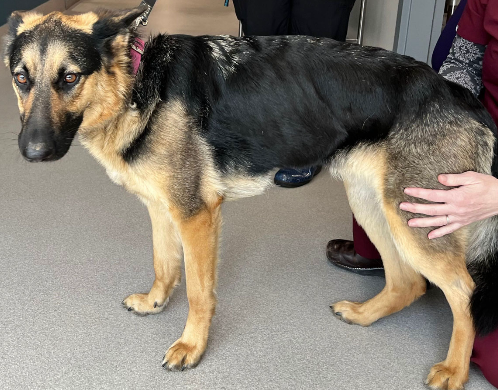
what are causes of EPI?
1. primary acinar atrophy
2. chronic pancreatitis
3. pancreatic duct obstruction
4. pancreatic neoplasia
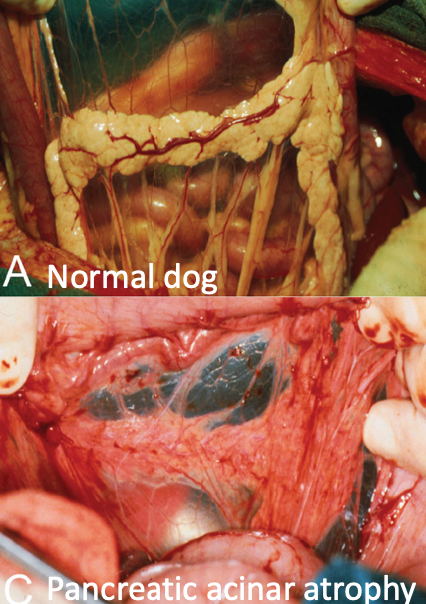
what is the most common cause of EPI in dogs?
pancreatic acinar atrophy
tends to develop at a younger age
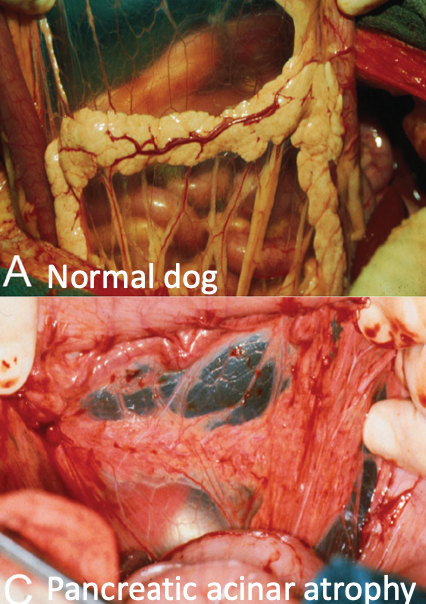
what occurs with pancreatic acinar atrophy?
pancreatic tissue replaced with adipose with adipose and connective tissue in absence of inflammation or fibrosis
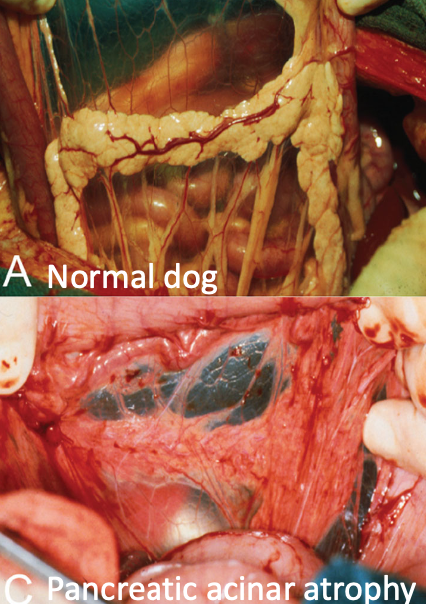
what is the most common cause of EPI in cats?
chronic pancreatitis
tend to be middle-aged to older
when do clinical signs of EPI develop?
emerge only when >90% of pancreatic acinar mass is lost
what are the general causes of clinical signs seen with EPI?
1. defective digestion and absorption of macronutrients (protein, fat, carbohydrates)
2. undigested and unabsorbed macronutrients in intestinal lumen often cause osmotic diarrhea
what are clinical signs of EPI in dogs?
-chronic small bowel diarrhea (95% of cases) and often weight loss despite good appetite
-increased stool volume
-steatorrhea (light brown, greasy stool)
-flatulence
-intermittent hyporexia/vomiting if secondary to chronic pancreatitis

what are clinical signs of EPI in cats?
-more subtle and less specific than dogs
-weight loss (90% of cases) w/ or w/o diarrhea (60%)
-poor haircoat (50%)
-polyphagia (42%)
-anorexia (42%)
-vomiting (19%)

what CBC/chem/UA abnormalities are seen with EPI?
these are often normal
what diagnostic imaging abnormalities are seen with EPI?
imaging often normal, mean pancreatic thickness may be reduced
which tests are used to diagnose EPI?
serum trypsin-like immunoreactivity (TLI)
-measures serum trypsinogen concentrations
-species-specific
-collect blood in fasted state
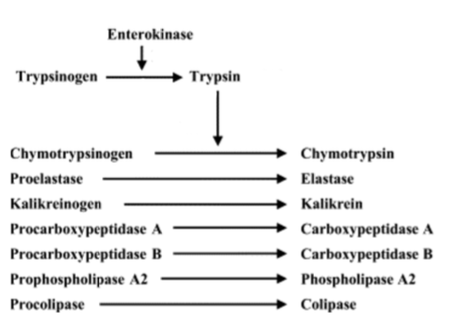
what serum TLI values are consistent with EPI?
low serum TLI concentrations
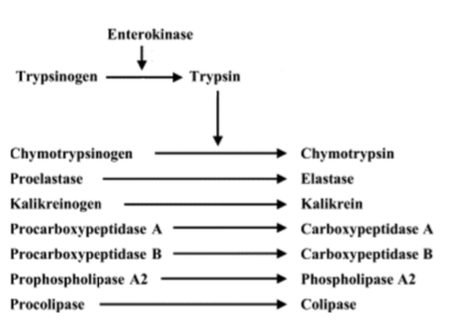
what should you do with a gray-zone result of serum TLI tests?
-retest weeks to months later
-isolated pancreatic enzyme deficiency (lipase) may cause low-normal TLI (respond favorably to tx)
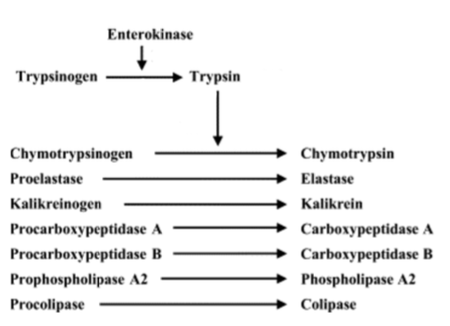
what does the general treatment for EPI consist of?
1. pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy
2. dietary modification
3. cobalamin (Vit B12) supplementation
what products are available for pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy?
commercial formulations (dried extracts of porcine/bovine pancreas)
-uncoated enzymes in powder or capsule (most common)
-enteric coated preparations for refractory cases
-increase dose to effect then taper to LED, start with dogs 1tsp/10kgBW/meal, cats 0.5-1tsp/meal
raw pancreas (porcine or bovine)
-last resort, cheaper, often contaminated with bacterial pathogens
does supplementation with pancreatic enzyme replacement products interfere with TLI assays?
no
what dietary modifications should be made for patients with EPI?
-highly digestible, low residue “GI” diets
-avoid high fiber diets (reduces digestibility of food, low energy density)
-some may respond to hypoallergenic diet (concurrent CIE?)
Why do pets with EPI often have cobalamin deficiency?
Pancreas produces intrinsic factor which is needed to bind to cobalamin to be absorbed by ileum
when should animals with EPI receive cobalamin supplementation?
treat when low or low-normal serum cobalamin concentrations
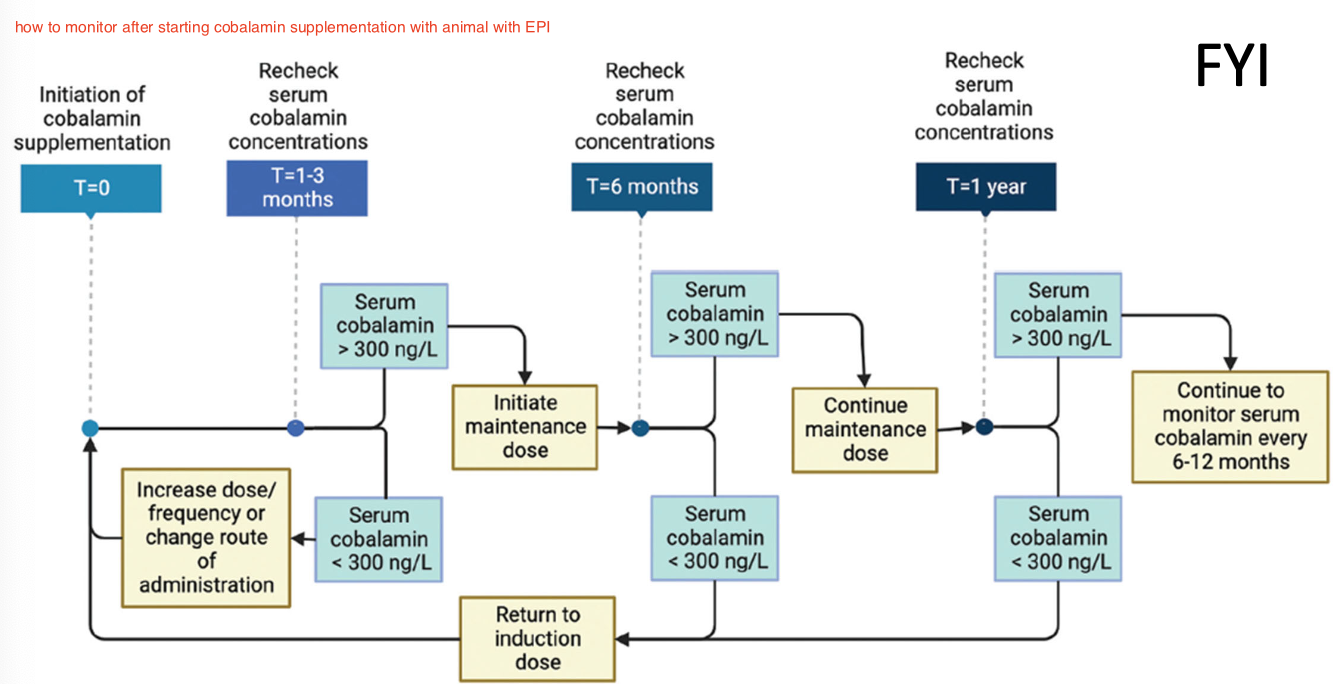
after starting cobalamin supplementation for animals with EPI, when should serum cobalamin concentrations be rechecked?
induction phase: recheck serum concentrations 1-3 months later to confirm supplementation was adequate
maintenance: once normal concentrations achieved- monitor cobalamin every 6-12 months
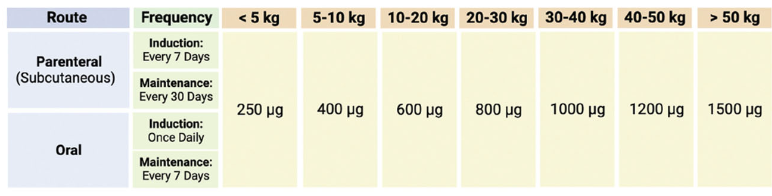
True or False? Treatment with cobalamin improves outcome of EPI - can be given orally or via SQ injections.
True. Improves outcomes and can give either orally or SQ. Oral route can take longer to respond.
what is the prognosis of EPI in dogs with treatment?
good:
-complete response 65%
-partial 17%
-poor 23%
what is the prognosis of EPI in cats with treatment?
good:
-complete response 50-60%
-27-60% partial response
what expectations should be communicated with owners regarding treatment for animals with EPI?
these animals require life-long treatment (a forever disease)
how long after starting treatment for EPI should normal stool consistency/weight gain be seen?
normal stool consistency within 2-4 weeks
weight gain and restoration of BCS may take several months
when may you need to troubleshoot a case of EPI not responding to treatment?
if the animal is receiving over 2tsp/cup of food of pancreatic enzyme replacement
what are reasons for lack or impartial response to treatment for EPI?
1. enzyme not mixing well with food after ingestion (may be an issue with tablets/capsules)
2. poor quality pancreatic enzyme formulation
3. concurent CIE
4. persistent dysbiosis
what is a solution for lack of/impartial response of EPI tx due to enzymes not mixing well with food after ingestion?
switch to powder, mix well into food with added water, let premixed food stand for at least 30 minutes (sometimes overnight helps)
what is a solution for lack of/impartial response of EPI tx due to poor-quality pancreatic enzyme formulation?
switch to another product
what is a solution for lack of/impartial response of EPI tx due to concurrent CIE?
start diet trial with hypoallergenic diet
what is a solution for lack of/impartial response of EPI tx due to persistent dysbiosis?
give prebiotics, probiotics, FMT