L5 - Tissue Types Histology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Epithelial Tissue
Covers body surfaces and lines cavities.
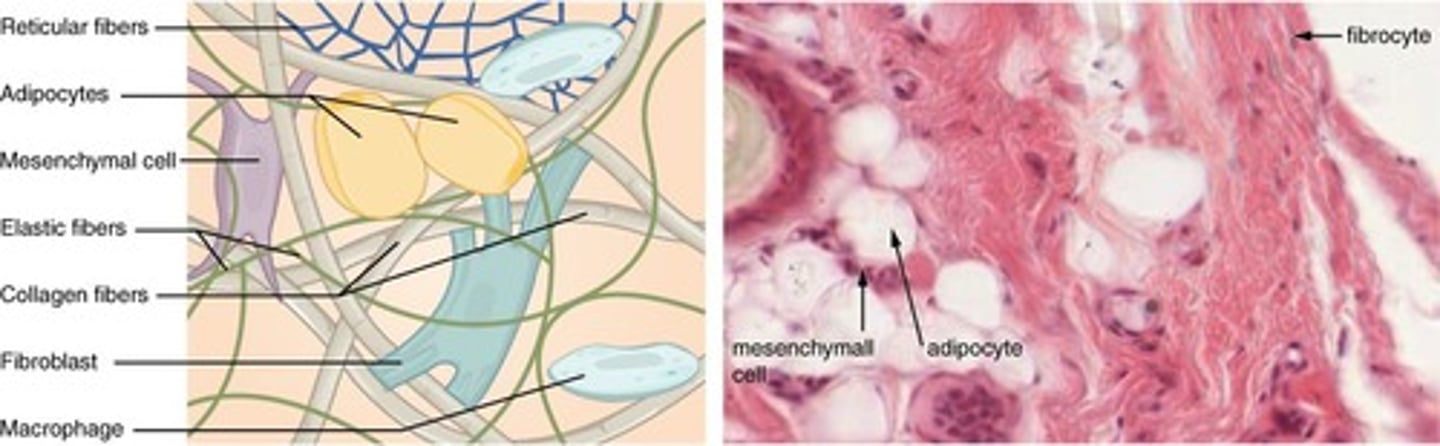
Connective Tissue
Supports, binds, and protects other tissues.
Muscle Tissue
Facilitates movement through contraction.

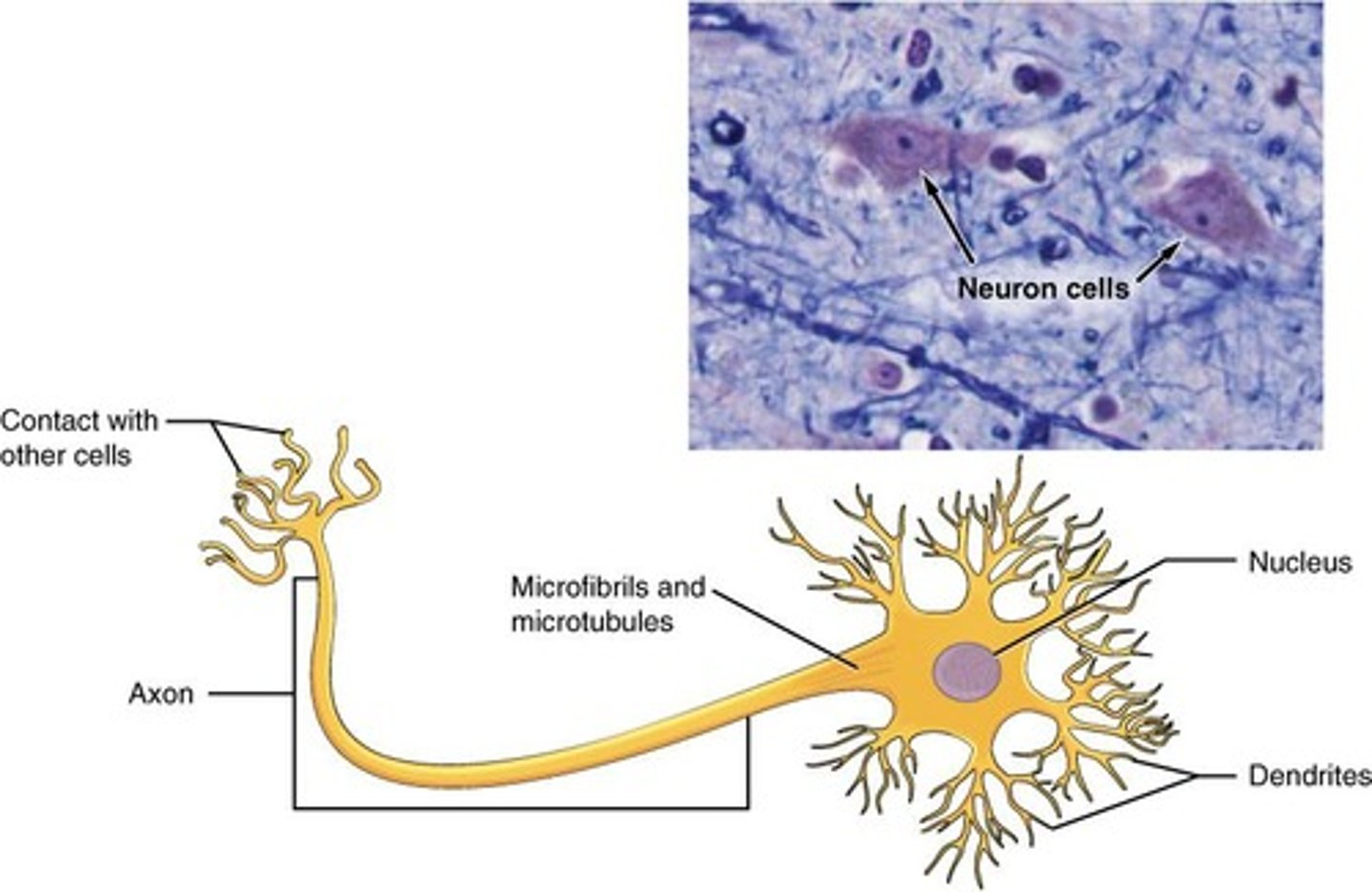
Neuronal Tissue
Transmits electrical signals in the body.
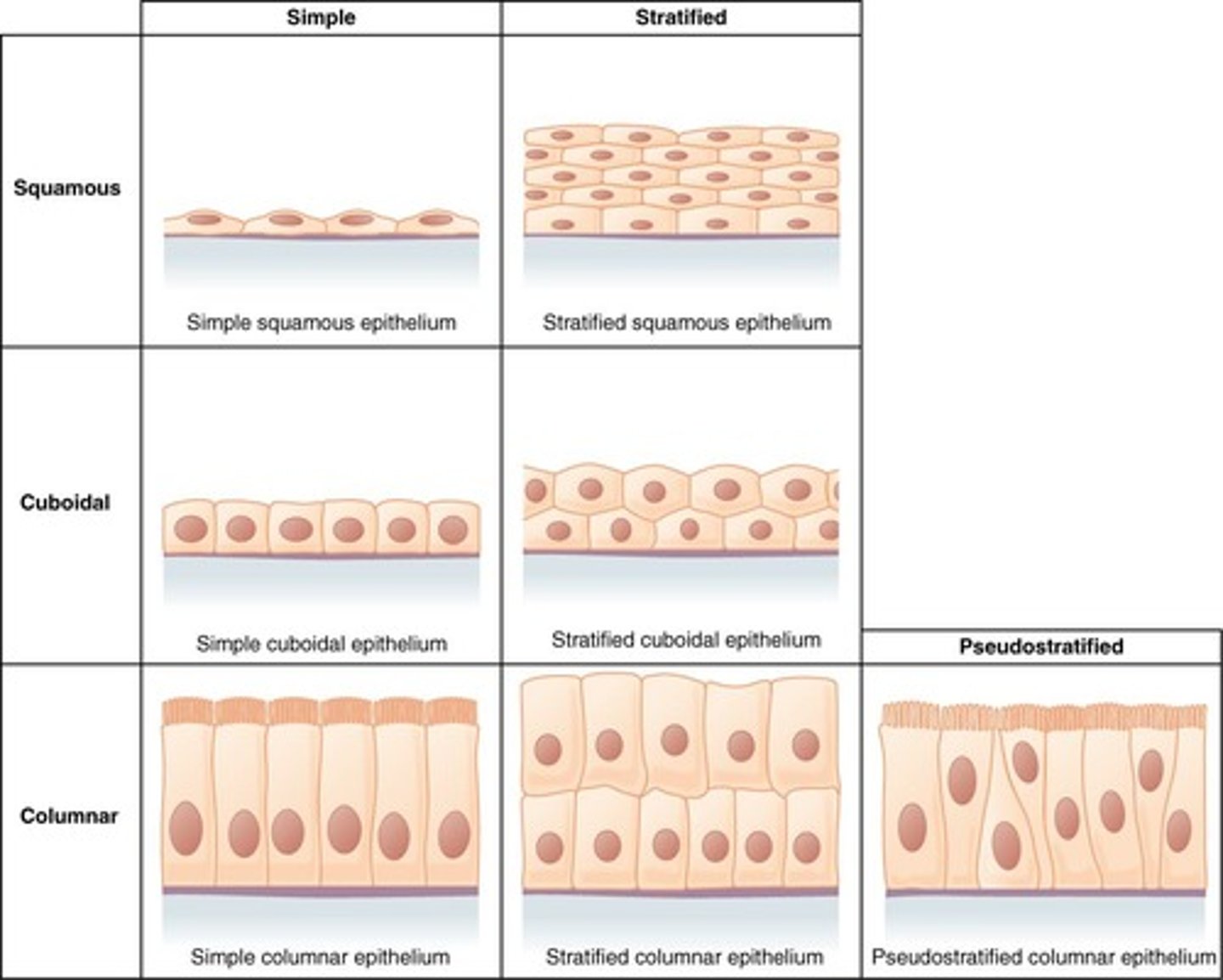
Simple Epithelium
Single layer of cells for absorption.
Stratified Epithelium
Multiple cell layers for protection.
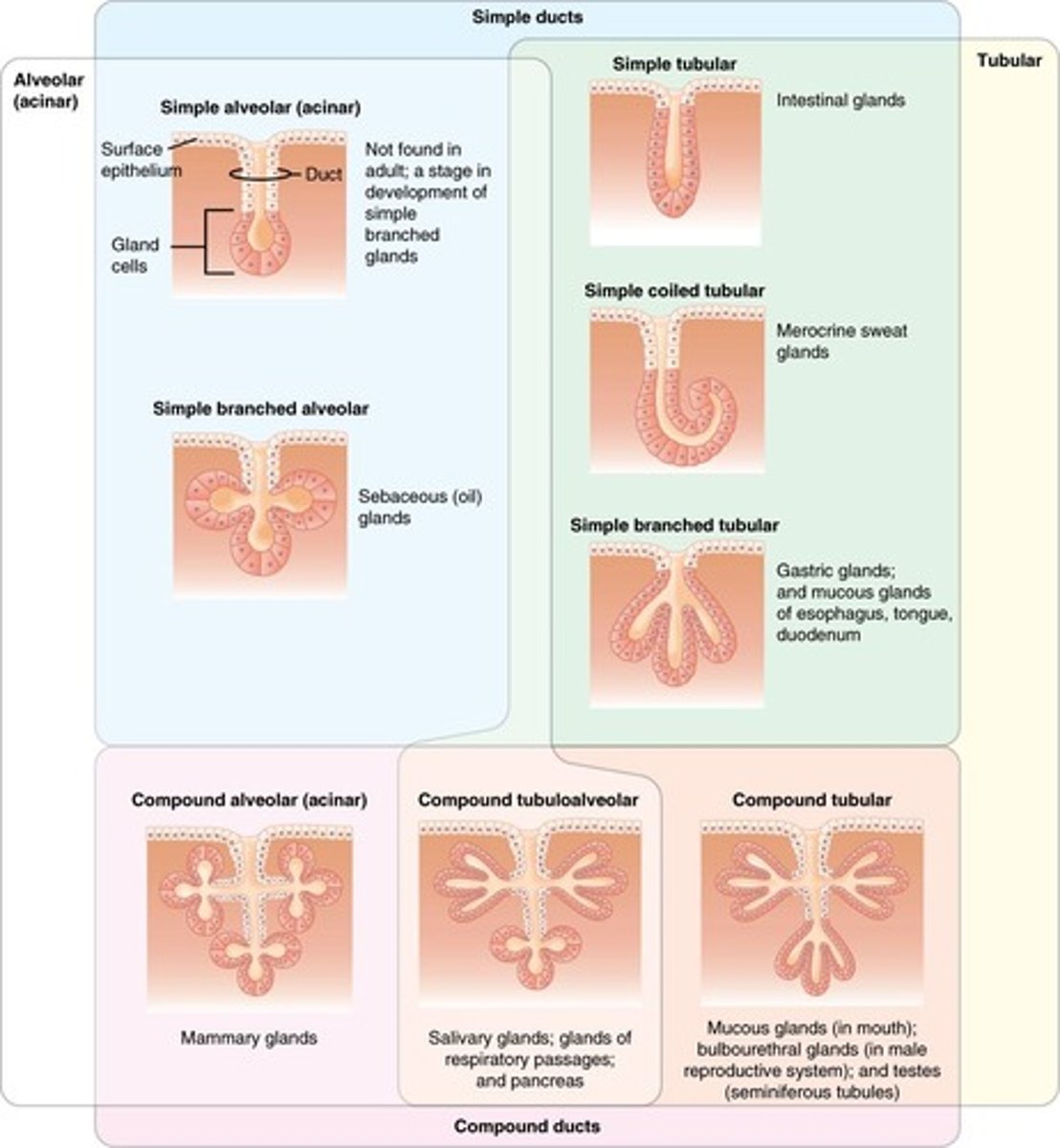
Glandular Epithelium
Specialized for secretion of substances.
Mucous Membrane
Lines tracts, secretes mucus for lubrication.
Serous Membrane
Lines cavities, reduces friction between organs.
Synovial Membrane
Lines joint cavities, secretes synovial fluid.
Renal Capsule
Protective layer surrounding the kidney.
Hepatic Capsule
Protective layer around the liver.
Meninges
Protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
Loose Connective Tissue
Provides support and flexibility in organs.
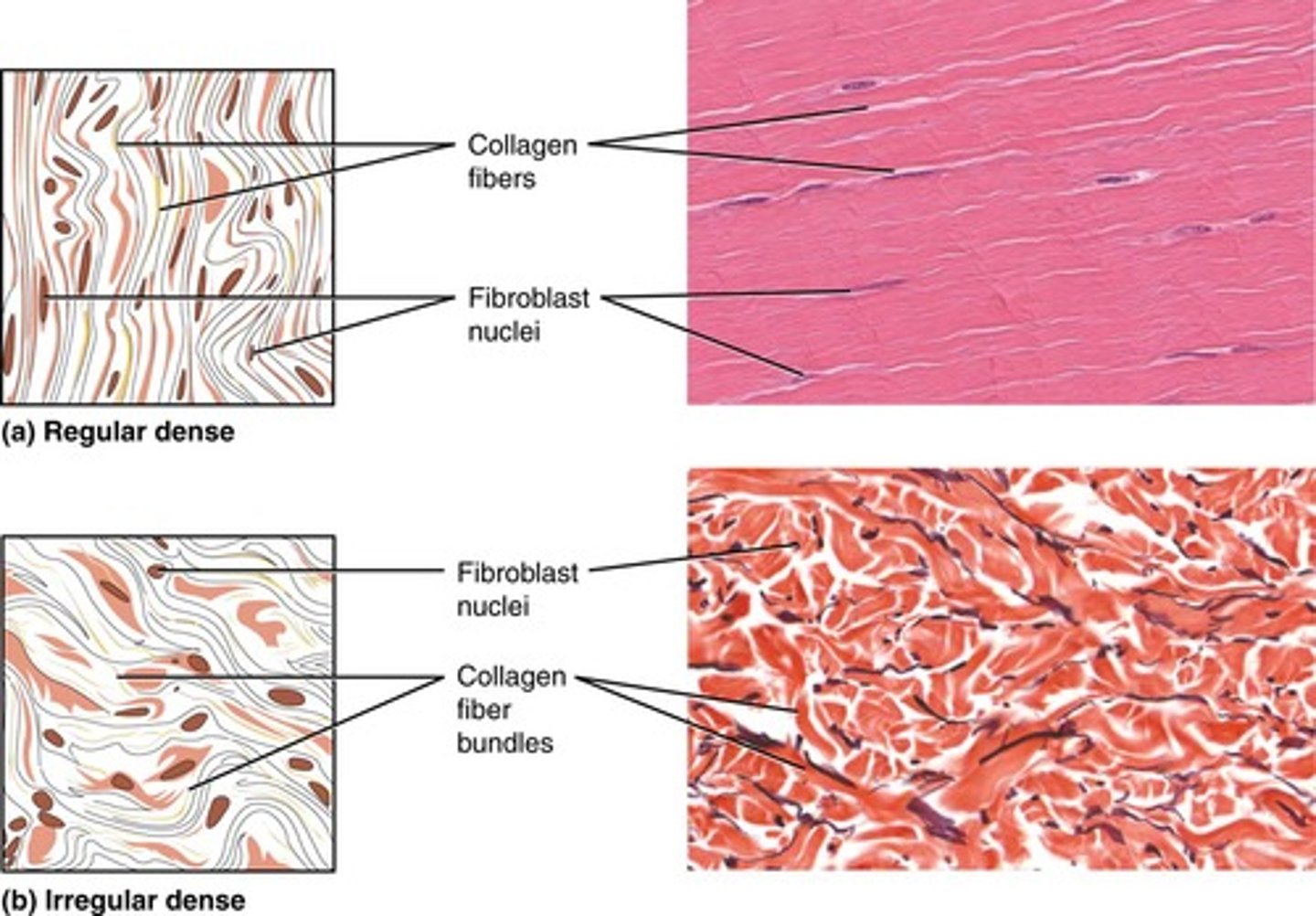
Dense Connective Tissue
Provides strength and resistance to stretching.
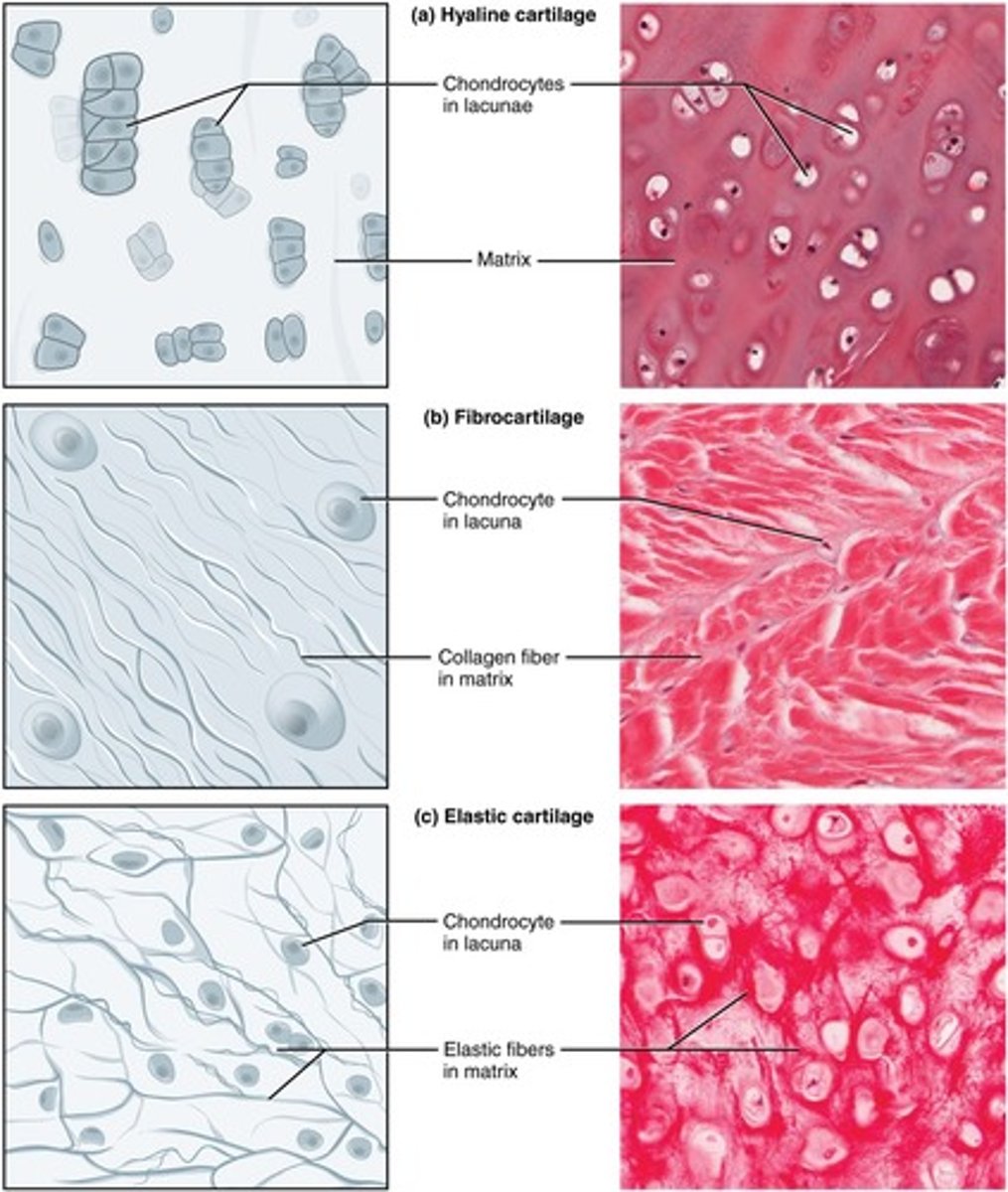
Cartilage
Flexible connective tissue, supports structures.
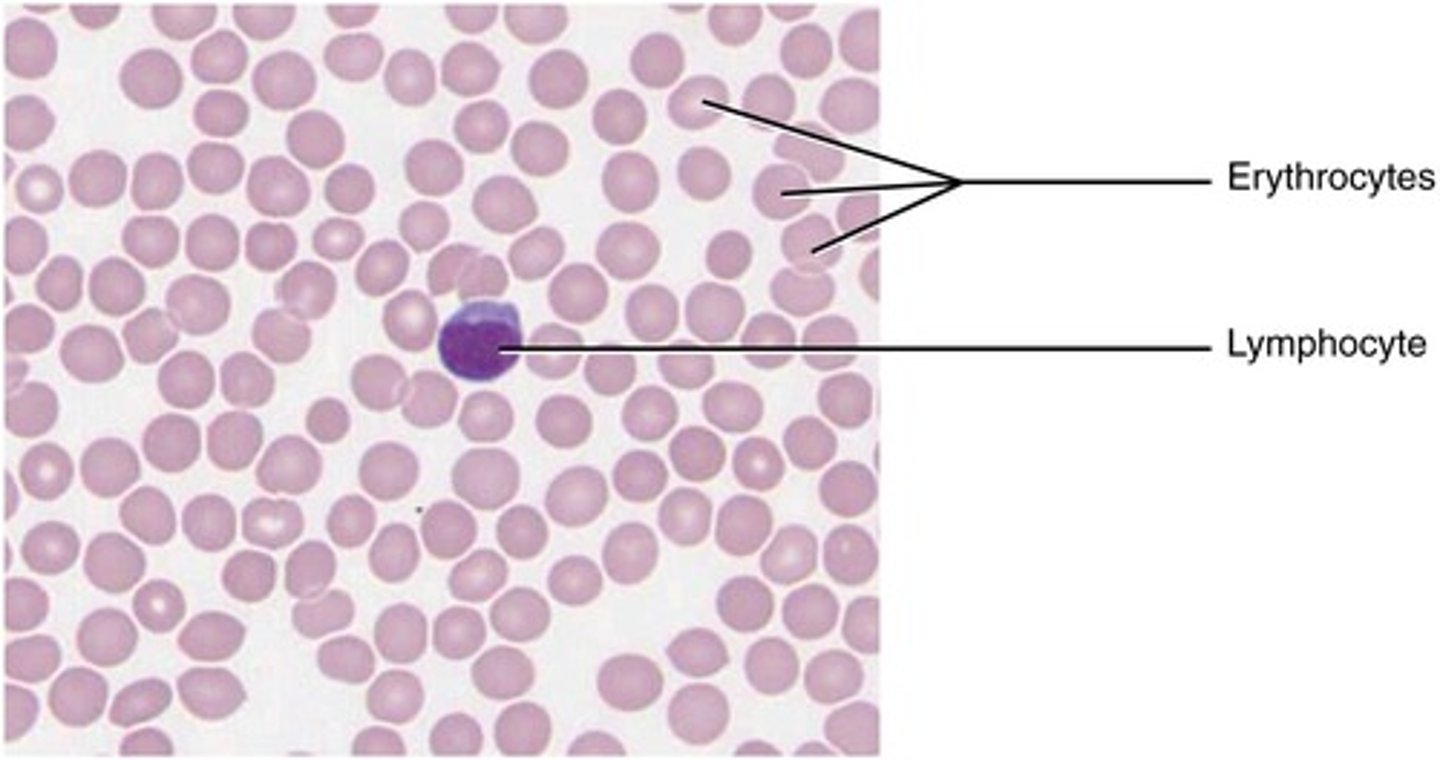
Fluid Connective Tissue
Includes blood and lymph for transport.
Stroma
Supporting tissue framework of an organ.
Parenchyma
Functional tissue of an organ.
Histological Hallmarks
Microscopic features distinguishing tissue types.
Embryonic Lineage
Origin of tissues during development.