B13.1 Coordination and response
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is a stimuli, a receptor and an effector?
Stimuli: changes in organism’s environment
Receptors: specialised cells that detect stimuli
Effectors: muscles and glands that respond to stimuli
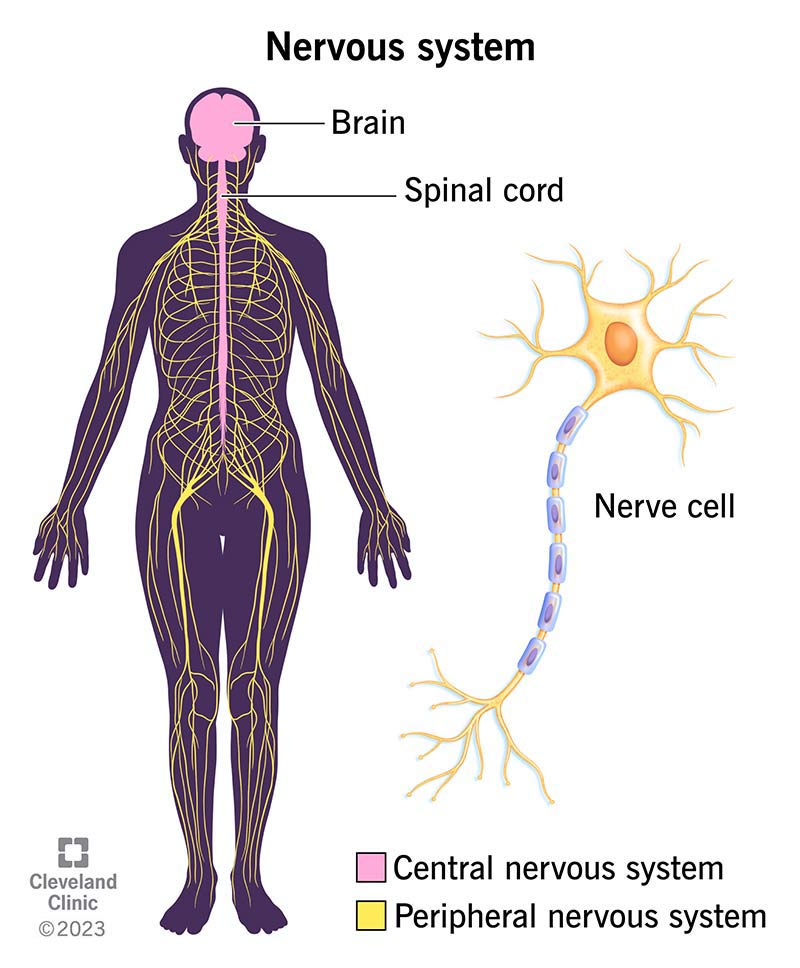
What are the 2 parts of the nervous system called?
Central Nervous System:
Brain and spinal chord
Responsible for coordinating all reactions and nervous communication around the body
Peripheral Nervous System:
Nerves in the rest of the body
Transmits impulses from CNS to the rest of the body
What are neurones and its 3 main types?
Specialised cells that carry impulses around the body
Types:
Sensory
Relay
Motor
What is the role of a sensory neurone? Identify in a diagram
Sensory neurones transfer nerve impulses away from receptor cells when a stimulus is detected
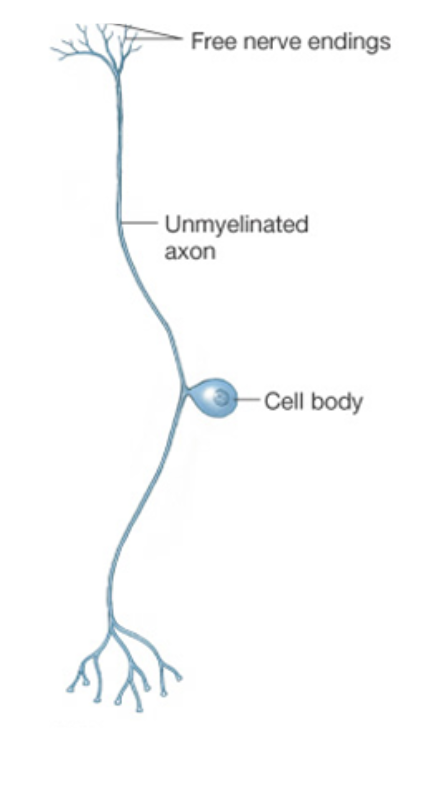
Adaptations of a sensory neurone
Can be long because they may need to transmit nerve impulses from receptors in distant parts of the body towards the spinal cord
Cell body outside so electrical impulses can move along faster
What is the role of a relay neurone? Identify in a diagram
Short to connect one neurone to the next (sensory to motor)
What is the role of a motor neurone? Identify in a diagram
Motor neurones transfer nerve impulses from the brain or the spinal cord to effectors
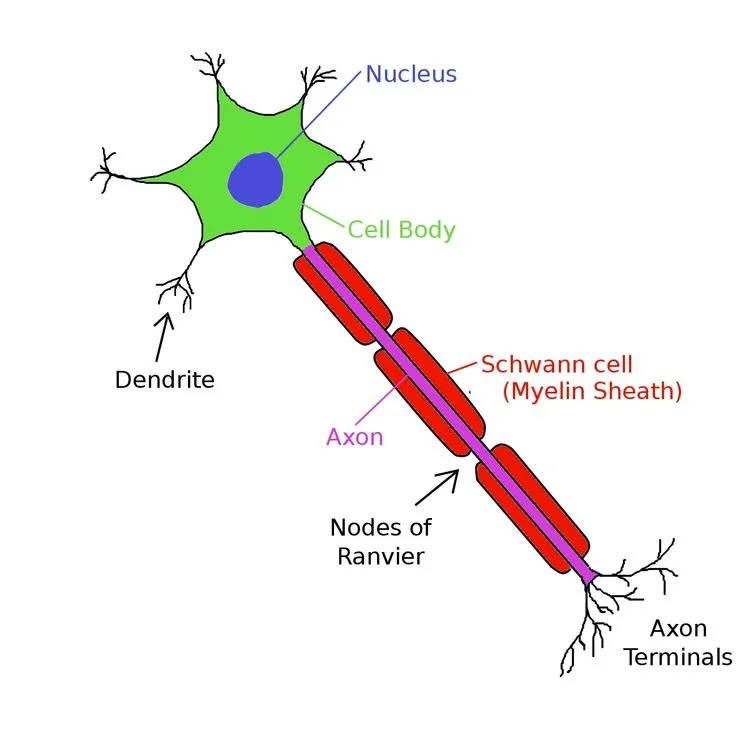
What are the adaptations of a motor neurone?
Long, thin fibres of cytoplasm to quickly carry electrical signals
Have dendrites which are shorter fibres that can pick up electrical signals from nearby neurones and pass them to the axons
Have axons which are long fibres to communicate neurone to neurone
Have myelins which insulate axons so the electrical impulses can travel faster
Describe a reflex arc
Reflex actions are fast, automatic and involuntary
1. Receptors: detect stimulus and converts it into nerve impulse, connects with sensory neurone
2. Sensory neurone: carries electrical impulse from receptor to spinal cord
3. Relay neurone: receives impulse from sensory neurone and passes it to motor neurone
4. Motor neurone: carries impulse away from CNS to the effector
5. Effector: receives impulse and carries out response
What is a synapse?
Ends of the two neurones and the gap in between is called a synapse