Endocrine Exam
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
alike
they both release ligands (chemical messengers) that bind to receptors on target cells
different
the endocrine system:
transmits hormones through the blood
can target any cell in the body that has the right receptors
exhibits longer reaction times and has longer-lasting effects
How are the endocrine system and nervous system alike and different?
regulating growth, development, and metabolism
maintaining homeostasis of blood composition and volume
(hormones regulate blood solute concentration and volume)
controlling digestive processes
(by influencing secretory processes and movement)
controlling reproductive function and activities
What are the 4 general functions of the endocrine system?
pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenal
What glands are true endocrine glands?
hormonal stimulation
gland cells release hormone when some other hormone binds to it
humoral stimulation
gland cells release hormone when there’s a certain change in levels of a nutrient or ion in the blood
nervous system stimulation
gland cells release hormone when a neuron stimulates it
What are the 3 methods of stimulation that release hormones into the blood?
lipid-soluble hormones created by cholesterol
functions: growth, development, and reproduction
examples: testosterone, estrogen, cortisol
What are steroid hormones?
water-soluble, modified amino acids
examples: epinephrine, norepinephrine, thyroid hormone, and melatonin
What are biogenic amine hormones?
water-soluble chains of amino acids
consists of most hormones (antidiuretic hormone, insulin, glucagon, etc.)
What are protein hormones?
signaling molecules that DO NOT circulate in the blood
autocrine stimulation
local hormone binds to the cells that release them
paracrine stimulation
local hormone binds to neighboring cells
What are local hormones and the 2 types of local signaling they perform?
eicosanoids are local hormones formed from fatty acids
prostaglandins are eicosanoids that stimulate pain and inflammatory processes
What are eicosanoids and prostaglandins?
the time it takes to reduce a hormone’s concentration in the blood to half of its original value
hormones that have a short half life must be secreted frequently into the blood
steroid hormones have longer half lives
What is the half life of a hormone?
up-regulation is when the number of receptors on a target cell is increased (this creates increased sensitivity to hormones that bind)
down-regulation is when the number of receptors on a target cell is decreased (this creates decreased sensitivity to hormones that bind)
What is up-regulation and down-regulation?
target cells do this in response to hormone levels in the blood
low amount of hormone = up-regulate
high amount of hormone = down-regulate
Why might target cells up-regulate and down-regulate?
synergistic interaction
one hormone reinforces the activity of another
ex: estrogen & progesterone are more powerful together
permissive interaction
one hormone requires the activity of another hormone to work
ex: oxytocin (milk ejection) cannot work without prolactin (milk production)
antagonistic interaction
one hormone opposes the activity of another
ex: insulin lowers blood glucose and glucagon
What are the three types of interactions hormones can have on a target cell?
anatomy
inferior to hypothalamus and is connected to hypothalamus by the infundibulum
divided into anterior and posterior parts
functions
master gland that produces, stores, and releases hormones
Describe the anatomy and functions of the pituitary gland
maintaining homeostasis by producing and releasing hormones for:
regulating body temperature
maintaining blood pressure
reproduction
appetite
Describe the function of the hypothalamus
IGF works synergistically with growth hormone to stimulate cell growth and division in bone and other tissue
it manages the effects of growth hormone
What are the effects of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)?
follicular cells
they also create thyroglobulin (the precursor for thyroid hormone)
What cells of the thyroid gland synthesize T3 and T4 hormones?
parafollicular cells
What cells in the thyroid gland synthesize calcitonin?
medulla
inner part that releases epinephrine and norepinephrine
cortex
synthesizes lots of corticosteroids
What are the two sections of the adrenal gland?
melatonin
it causes drowsiness and regulates the body’s circadian rhythm
What hormone is released by the pineal gland, and what is its function?
clusters of endocrine cells on the pancreas
alpha cells
secretes glucagon
beta cells
secretes insulin
What are pancreatic islets?
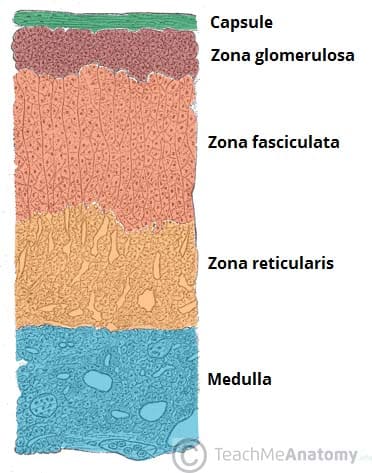
zona glomerulosa
zona fasciculata
zona reticularis
What are the three layers of the adrenal cortex, from superficial to deep?
the efficiency of the endocrine system decreases
additionally, some hormones decrease (ex: GH and sex hormones)
How does endocrine activity change as you age?
leptin
controls appetite and regulates energy expenditure
(low body fat = less leptin, which stimulates appetite)
What hormone does adipose CT produce?
D3 enters the blood and is converted to calcidiol by liver enzymes
Calcidiol then arrives at the kidneys and becomes calcitriol (via kidney enzymes)
What happens to vitamin D3 in the body?
releasing hormones (increases secretion of anterior pituitary hormones)
thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
stimulates anterior pituitary to release TSH
prolacin-releasing hormone (PRH)
stimulates anterior pituitary to release prolactin
gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
stimulates anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH (gonadotropins)
corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
stimulates the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary
growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
stimulates anterior pituitary to release growth hormone (GH)
inhibiting hormones (decreases secretion of anterior pituitary hormones)
prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH)
stops the release of prolactin
growth-inhibiting hormone (GIH)
stops the release of GH
HAS A BIG ROLE IN INFLUENCING THE PITUITARY
What hormones are released by the hypothalamus, and what are their basic functions?
hormone diffuses across plasma membrane of cell
hormone binds to a receptor and creates a hormone-receptor complex
the complex binds to a specific segment of DNA called the hormone-response element
mRNA synthesis is stimulated
mRNA exits nucleus and binds to a ribosome and protein synthesis occurs
How do steroid hormones interact with target cells?
water soluble
diffuses into the blood
lipid soluble
requires a carrier protein to travel through the blood
What is the difference between how water soluble and lipid soluble hormones travel through the blood?
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
trigger: thyroid release hormone from the hypothalamus
function: causes the release of thyroid hormone from the thyroid
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
trigger: corticotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus
function: causes the release of corticosteroids from the adrenal cortex
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
trigger: GnRH release from the hypothalamus
function: in women: regulates ovarian development and secretion of estrogen; in men: sperm development and secretion of testosterone
List 4 hormones the anterior pituitary gland releases, their trigger for release, and their functions
the hypothalamus hormonally stimulates the anterior pituitary to release hormones
the hypothalamus releases releasing/inhibiting hormones, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release tropic hormones
How does the hypothalamus influence the anterior pituitary gland?
second messenger system
Protein hormones must use a ______ to interact with their target cells
enzymatic degradation (happens in liver cells)
removal via kidney excretion
target cell uptake
What are the 3 ways hormones can be eliminated from the blood?
the surgical removal of the pituitary gland due to tumors present
post-procedure: various hormones need to be replaced and their levels are consistently monitored
What is a hypophysectomy?
low growth hormone production
results in pituitary dwarfism (short stature and low blood sugar)
due to problems of the hypothalamus or pituitary gland
What is growth hormone deficiency?
the release of too much growth hormone
characterized by excessive growth, large internal organs, and increased blood sugar
What is pituitary gigantism?
disorder caused by excessive growth hormone production as an adult
effects: large bones of the face, hands, feet, and internal organs
also results in increased release of glucose
What is acromegaly?
excessive production of thyroid hormone
increased metabolic rate, weight loss, hyperactivity, and heat intolerance
can result from:
T4 ingestion
excessive stimulation by the pituitary gland
loss of feedback control in the thyroid
What is hyperthyroidism?
the result of decreased thyroid hormone (TH) production
low metabolic rate, lethargy, cold intolerance, and weight gain
caused by:
decreased iodine intake
loss of pituitary stimulation by the thyroid
postsurgical or immune system destruction of thyroid gland
What is hypothyroidism?
the enlargement of the thyroid
typically due to insufficient intake of iodine in the diet (this results in a lack of thyroid hormone production)
What is goiter?
the chronic exposure to excessive glucocorticoid hormones in people taking corticosteroids for therapy
can result in obesity, hypertension, hirsutism, kidney stones, and menstrual irregularities
What is cushing syndrome?
develops when the adrenal glands fail
chronic shortage of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids
weight loss, fatigue and weakness, hypotension, and skin darkening
What is Addison’s disease?
disorder that begins in the embryo or fetus
the inability to synthesize corticosteroids
leads to overproduction of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), high ACTH causes an increased size of the adrenal glands and production of hormones with testosterone-like effects
What is adrenogenital syndrome (congenital adrenal hyperplasia)?
general umbrella term for diabetes
it is the inadequate uptake of glucose from the blood
results in chronically elevated glucose in the blood
leads to blood vessel damage, blindness, kidney failure, and amputations
increased risk of heart disease and stroke
What is diabetes mellitus?
the diminished release of insulin by the pancreas
requires daily injections of insulin
What is type 1 diabetes?
condition caused by a decreased insulin release
obesity is a major cause
What is type 2 diabetes?
potential condition in pregnant women
if untreated, it can cause risk to the fetus and increases delivery complications
also increases the chances of developing type 2 diabetes later on
What is gestational diabetes?
when blood glucose levels are below 60 mg/dL
can be caused by:
insulin overdose
prolonged exercise
alcohol use
liver or kidney disfunction
hormone deficiency
symptoms include hunger, dizziness, confusion, sweating, and sleepiness
What is hypoglycemia?
a chemical made by follicular cells in the thyroid gland
contains the amino acid tyrosine (important in TH synthesis)
What is thyroglobulin?
iodide (I-) enters a follicular cell (via active transport) from the blood
iodide diffuses into the colloid
iodide converts to iodine and binds to thyroglobulin
thyroglobulin binds its tyrosine to the iodine, then the thyroglobulin detaches
tyrosine and iodine together are T3 and T4 (depending on the number of iodine atoms they have) and are released into the blood (via simple diffusion)
What are the 5 steps of thyroid hormone production?
ADH
fluid retention and maintaining blood volume and pressure
Oxytocin
stimulates contraction of uterus and breasts, emotional bonding
What two hormones are released from the posterior pituitary, and what are their functions?