Anemias
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Acute Blood Loss anemia
Cause: trauma
-replaced w/ interstitial fluid
-decreased hematocrit
-Normocytic, normochromic
Chronic Blood Loss anemia
Cause: repetitive loss, GI bleed, heavy period
-only chronic if loss exceeds bone marrow reproduction
-iron reserve in liver keeps up #
-develops slowly, insidious until hemoglobin levels are realllllly low
-Microcytic Hypochromic
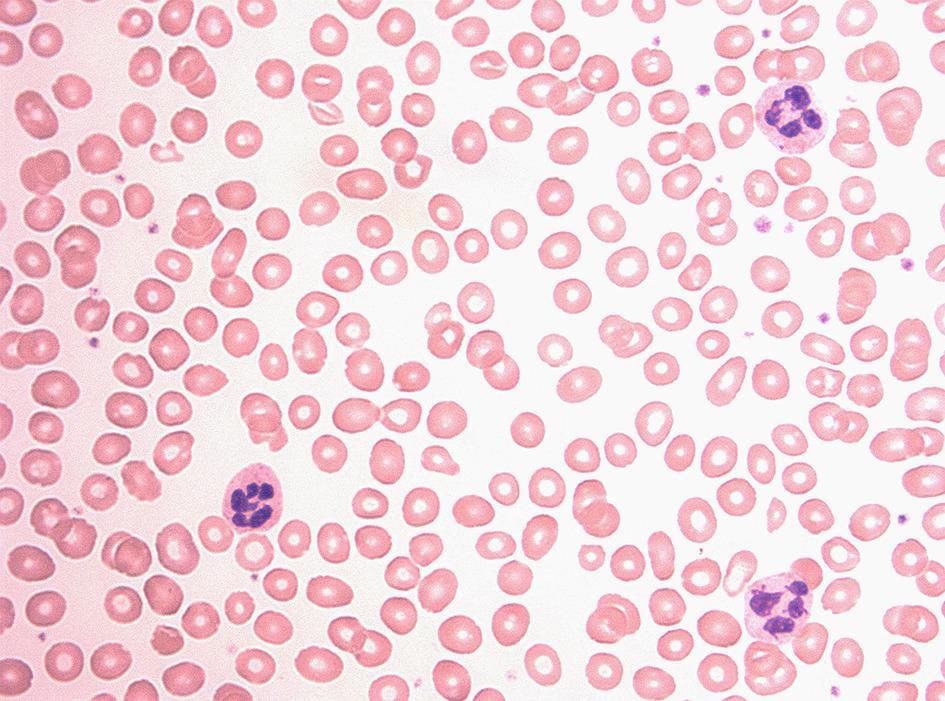
Hemolytic anemia
Cause: premature destruction of RBCs
-increase in reticulocytes
-inherited defects of membrane (SPEROCYTOSIS)
-inherited defects of hemoglobin (SICKLE CELL)
-antibody mediated destruction (HEMOLYTIC NEWBORN DISEASE & SLE)
-mechanical trauma (Defective valves, marathon)
-infections of RBCs (MALARIA)
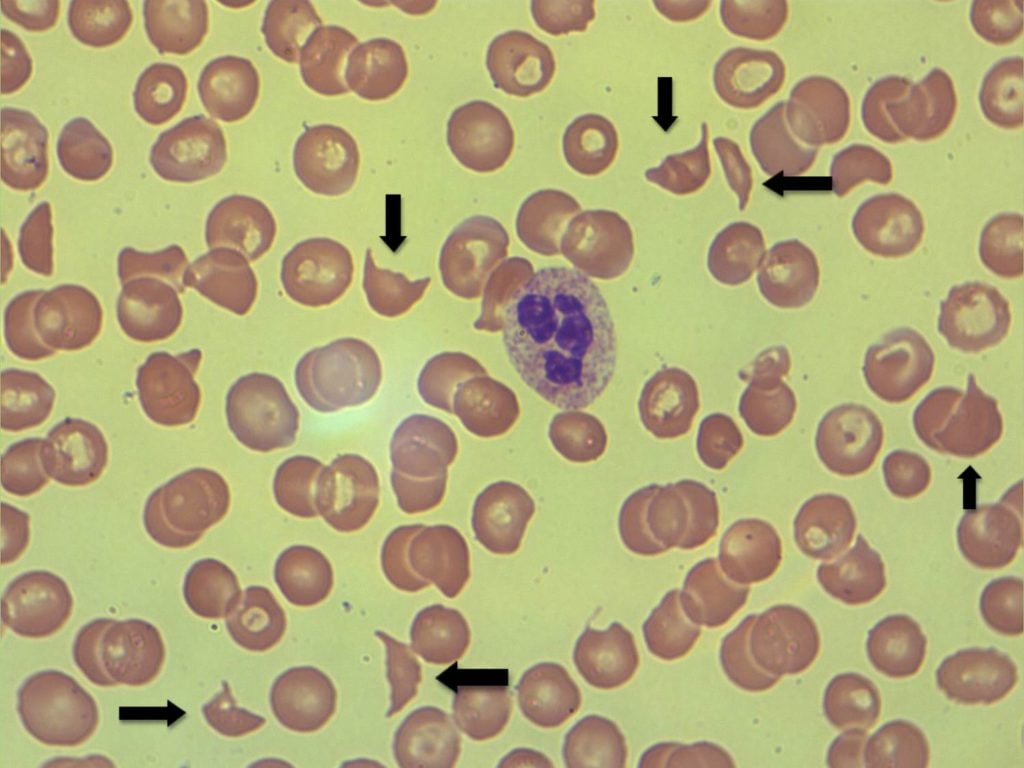
Sickle Cell anemia
Cause: inherited disorder mutated B hemoglobin chain
clumping NOT clotting of abnormally shaped RBCs from mutated hemoglobin chains
-damaged membranes increase hemolysis
-blood vessel blockage, ischemia, chronic
-sickle shape
Aplastic anemia
Cause: decrease RBC production
-radiation, chemotherapy, & toxins
-decrease in hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow
-decreased in number
-stem cell deficiency
-normocytic, normochromic OR megaloblastic
Iron Deficiency anemia
*most common type worldwide
Cause: diet, bleeding, increase in bodily demand (kids, pregnant)
-found when Hb levels are 7-8g/dL
-pale ear lobes, palms, and conjuctiva
-spoon shaped nails, sore tongue, dry corners of mouth
-microcytic, hypochromic
Inflammation Disease anemia
Cause: chronic infections
-Infections: HIV
-Inflammatory conditions: rheumatoid arthritis, SLE
-Diseases: renal failure, congestive heart failure, COPD
-Malignancies: leukemia, lymphoma
-microcytic, hypochromic
Pernicious anemia
Cause: decrease RBC production due to lack of Vit B12
- intrinsic factor binds to Vit B12 in parietal cells in stomach lining, protecting it from acid destruction in liver, and speeding up DNA erythropoiesis in bone marrow
-No Vit B12=unbound=takes much longer in DNA erythropoiesis
-clump not clot
-megaloblastic