AP Psychology - Unit 2: Biological Bases
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Heredity
The genetic transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring.
Ex: Height and eye color
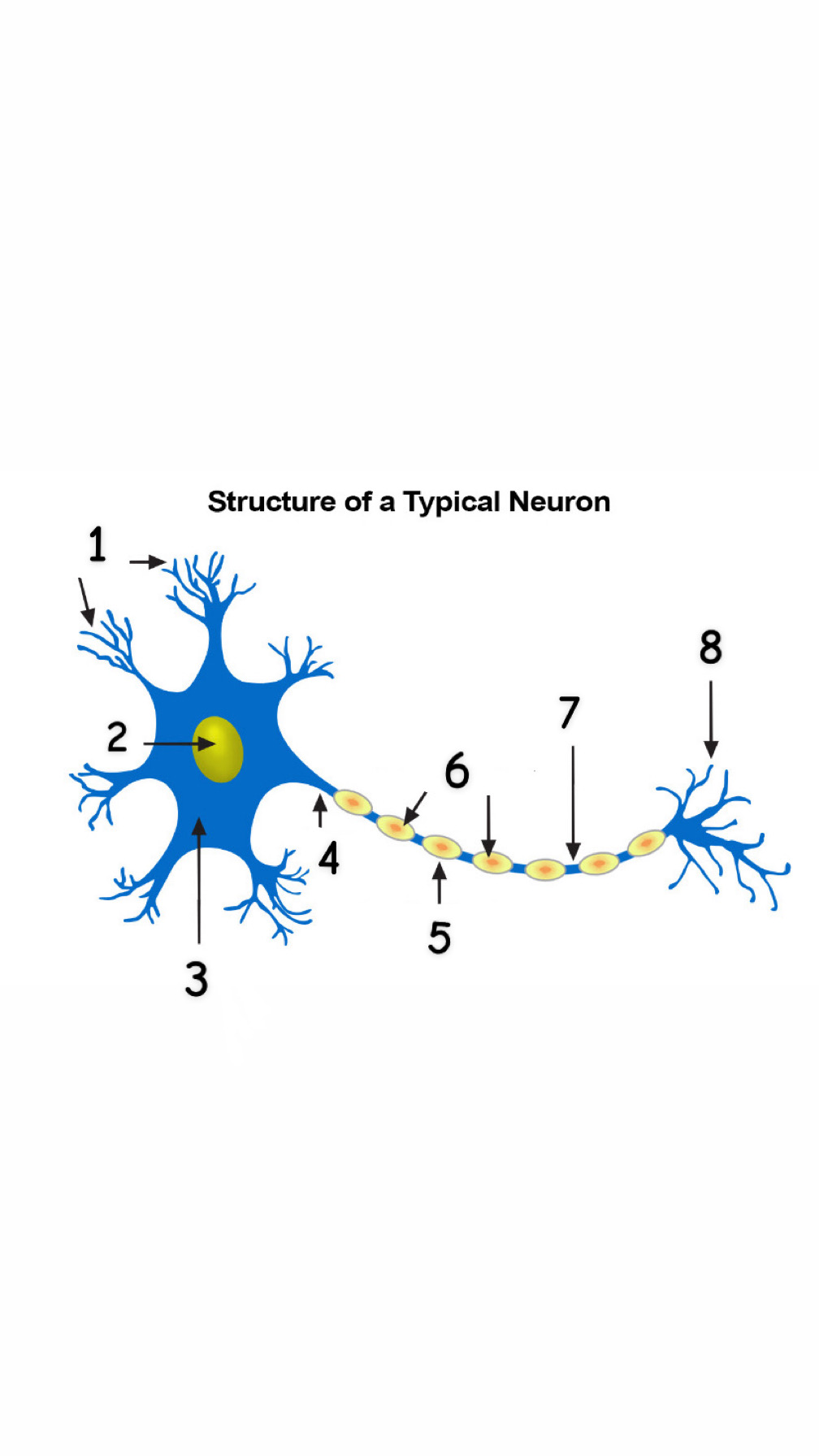
Dendrites
Nucleus
Cell Body (Soma)
Axon
Myelin Sheath
Schwann Cells
Nodes of Ranvier
Axon Terminals
Nature
The genetic and hereditary influences on an individual’s development and behavior, which are inherited from their biological parents.
Ex: Susceptibility to physical or mental conditions, temperaments, or personality traits.
Nurture
The environmental influences and experiences that shape an individual’s traits, behaviors, and development.
Ex: Culture, social interactions, and education.
Evolutionary Perspective
The idea that all human behaviors reflect the influence of physical and psychological predispositions that helped human ancestors survive and reproduce.
Natural Selection
The principle that inherited traits that better enable an organism to survive and reproduce in a particular environment will (in competition with other trait variations) most likely be passed onto succeeding generations.
Charles Darwin
He established principles such as natural selection and “survival of the fittest”, and he encouraged the idea of eugenics.
Eugenics
The practice of selective breeding to create ideal specimens; it’s largely considered outdated and discriminatory.
Twin Studies
Twins are observed to study the presumption that all human behaviors reflect the influence of physical and psychological predispositions that helped human ancestors survive and reproduce.
Adoption Studies
Identical twins raised in the same household aren’t always the same. Similar to how identical twins separated at birth and raised in different environments can have many similarities.
Ex: The Jim Twins
Epigenetics
The study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without DNA change.
Ex: Although identical twins have the same DNA, their life experiences can cause their genes to be expressed differently.
Neuron
Building blocks of the nervous system; their jobs are to receive, carry, and send messages through neural impulses.
Cell Body (Soma)
The part of a neuron that contains the nucleus; the cell’s life-support center.
Axon
The segmented neuron extension that carries signals from one end to the other.
Myelin Sheath
A fatty substance encasing most neurons in the brain, which protects and insulates the axon. It speeds up the transmission of nerve impulses.
Terminal Buttons
Knobs at the end of each axon from which neurotransmitters are released into the synapse.
Synapse
The gap between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron.
Neurotransmitters cross this gap.
Nodes of Ranvier
The spaces between Schwann cells.
Schwann Cells
Cells that produce myelin for the myelin sheath.
Dendrites
They receive signals from other neurons.
Neurotransmitters
A chemical messenger that transmits signals across a synapse from one neuron to another.
Threshold
A signal enters, and if it’s strong enough to reach the threshold, the neuron will fire.
All or None Principle
Once at the threshold, the neuron will fire, and it’ll fire with the same intensity every time.
Resting Potential
The neuron is at rest, meaning it isn’t sending a message. The interior of the neuron is slightly negative compared to the outside.
Refractory Period
A brief period where the neuron can’t fire again.
Depolarization
When the neuron fires, positive ions rush into the cell. This causes the inside of the neuron to become more positive, and creates the action potential.
Action Potential
The electrical impulse that travels down the axon.
Direction of Impulse
The one-way, specific pathway that an action potential takes along a neuron.
Multiple Sclerosis
It attacks the myelin sheaths of axon bundles in the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves.
Ex: Selma Blair
Inhibitory
Neurotransmitters that make the next neuron less likely to fire; they slow neuro communication.
Ex: GABA
Excitatory
Neurotransmitters that make the next neuron more likely to fire.
Ex: Glutamate
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Involved in learning, voluntary muscle movement, and memory.
Alzheimer’s disease is associated with diminished ACh functioning.
Dopamine
Linked to the anticipation of pleasurable or rewarding activities, as well as movement, attention, and learning.
Lack of dopamine is associated with Parkinson’s disease.
Excess dopamine is associated with schizophrenia.
Endorphins
Involved in alleviating pain.
Those with low levels typically have chronic pain or fibromyalgia.
Serotonin
Plays a significant role in mood, appetite, and sleep.
Low levels have been associated with depression, and may also be a factor in anxiety disorders.
Norepinephrine
Involved in arousal, alertness, and your sleep cycle.
Low levels are associated with depression.
GABA
The primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain.
Low levels are involved in anxiety and seizure disorders.
Substance P
Involved in the transmission of pain signals.
Undersupply linked with pain insensitivity.
Oversupply linked to chronic pain and fibromyalgia.
Glutamate
The primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain.
Oversupply can be associated with seizure disorders, and may play a role in degenerative disorders of the CNS, as well as bipolar disorder.
Antagonists
Drugs that block receptor sites.
Curare poisoning, which paralyzes victims by blocking ACh receptors.
Agonists
Drugs that increase, or mimic, a neurotransmitter’s action.
Morphine, which mimics endorphins by stimulating receptors involved in mood and pain sensations.
Withdrawal
The physical and psychological symptoms that occur when a person who is dependent on a substance abruptly stops or significantly reduces their intake.
Anxiety, insomnia, depression, hallucinations, etc.
Psychoactive Drug
They stimulate, inhibit, or mimic neurotransmitter activity.
Caffeine
Physical Dependence
A state where the body has adapted to a substance, requiring it to function normally.
Without it, the body then begins to experience physical withdrawal symptoms.
Psychological Dependence
The emotional craving to use a substance, driven by the desire for the pleasure, escape, or mood change it provides.
It can stem from using a substance to manage stress or emotions.
Depressants
They reduce neural activity by:
increasing relaxation
decreasing mood and arousal
slowing down bodily processes
Ex: Alcohol
Stimulants
They excite neural activity by:
increasing energy
decreasing appetite
creating brief feelings of euphoria
speeding up bodily processes
Ex: caffeine, nicotine, cocaine
Hallucinogens
They distort perception by:
causing false sensory hallucinations
impairing memory
causing feelings of relaxation and/or euphoria
Ex: marijuana, mushrooms, LSD
Barbiturates
Depressant drugs that slow down CNS activity by:
reducing anxiety
inducing sedation
potentially causing sleep
impairing memory and judgement
Ex: methohexital
Opiates
They decrease feelings of pain.
Ex: Heroin, morphine
Amphetamines
CNS stimulants that increase alertness, attention, and energy.
Medically used to treat conditions like ADHD and narcolepsy.
Ecstasy
A synthetic psychoactive drug that functions both as a stimulant and a mild hallucinogen, causing:
a short-term euphoric high
distorted perception
It can cause long-term damage to serotonin-producing neurons.
LSD
A powerful hallucinogen that primarily affects serotonin receptors.
It causes altered perceptions, thoughts, and emotions.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The information highway that connects the peripheral NS to the brain.
Made up of the brain and the spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System
The entire network of nerves located outside of the CNS, connecting it to the body’s limbs and organs.
Divided into the autonomic and somatic nervous systems.
Afferent Neurons (Sensory)
Nerves that bring information TO your spinal cord or brain.
They’re involved in your senses of vision, hearing, smell, taste, touch, pain, and temperature.
Efferent Neurons (Motor)
Nerves that receive signals FROM the brain, and carry them towards your muscles and glands so your body can take action.
They control voluntary movements of the skeletal muscles, such as in your arms or legs.
Interneurons
Once information reaches the brain or spinal cord, they take the messages and send them elsewhere in the brain or onto efferent neurons.
Spinal Cord
The long, cylindrical bundle of nervous tissue that extends from the brainstem down the back, serving as the main communication pathway for the CNS.
It carries both sensory and motor signals.
Somatic Nervous System
Contains the nerves you use to voluntarily activate muscles in your body.
Ex: Controlling the movement of your legs when you walk.
Autonomic Nervous System
Automatically controls gland activity and the muscles of internal organs.
Ex: Heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, and digestive processes.