BCS 111 Lecture 10
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Research of reasoning and its application
Philosophy
Psychology
Computer Science
Deductive vs. Inductive reasoning
-
Deductive
Premises → conclusion
From broader scope to one (conclusion)
Inductive
Inference from available information →
possible outcomesFrom one condition to many (possibilities)
categorical syllogism
Drawing conclusion from more than one premise
Each premise is a description of a category.
example
Some professors are tall. Some tall people are skinny.
Is it always true that “Some professors are skinny”?
(judging from the premises given above, not by your real-world knowledge)
propositional reasoning
-
Proposition
the fact or assertion that you can infer from the sentence
Ex: How many kids do I have? Do you have enough information to make the conclusion?
Propositional reasoning: Four-card task
If a card has a consonant on one side, it must have an odd number on the other side. Which card(s) would you flip in order to test if the rules are true?

(cont)
What does flipping “1” tell us?
What does flipping “8” tell us?

Analogical reasoning
Inference based on an established relationship between two premises
Dog: German Shepherd = Bird:
Car: ground = __ : sky
Hypothesis testing
Why is hypothesis testing a type of inductive reasoning
Small set of conditions/premises → many possible outcomes
Null hypothesis
Higher IQ test scores is NOT correlated with better reasoning skills
Alternative hypothesis
Higher IQ test scores IS correlated with better reasoning
Type I error
Reject null hypothesis when it is true (i.e. falsely accept the alternative hypothesis)
An accidental finding of correlation between IQ and reasoning from a small (or biased) sample size when there is NO correlation
Type II error
Fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is NOT true
An accidental finding of no-correlation between IQ reasoning when there IS actually a correlation
(examples on slides)
Confirmation bias
Choose the evidence that supports our claims
Tendency to ignore counter-evidence
Tendency to remember supportive evidence better than counter-evidence
Tendency to ignore alternative hypothesis
What else is involved in hypothesis testing?
What’s the process involved in accepting or rejecting a hypothesis
Make a decision
Reasoning
Problem solving
Spatial reasoning - Raven’s Progressive Matrices
Which one should you choose to complete the series?
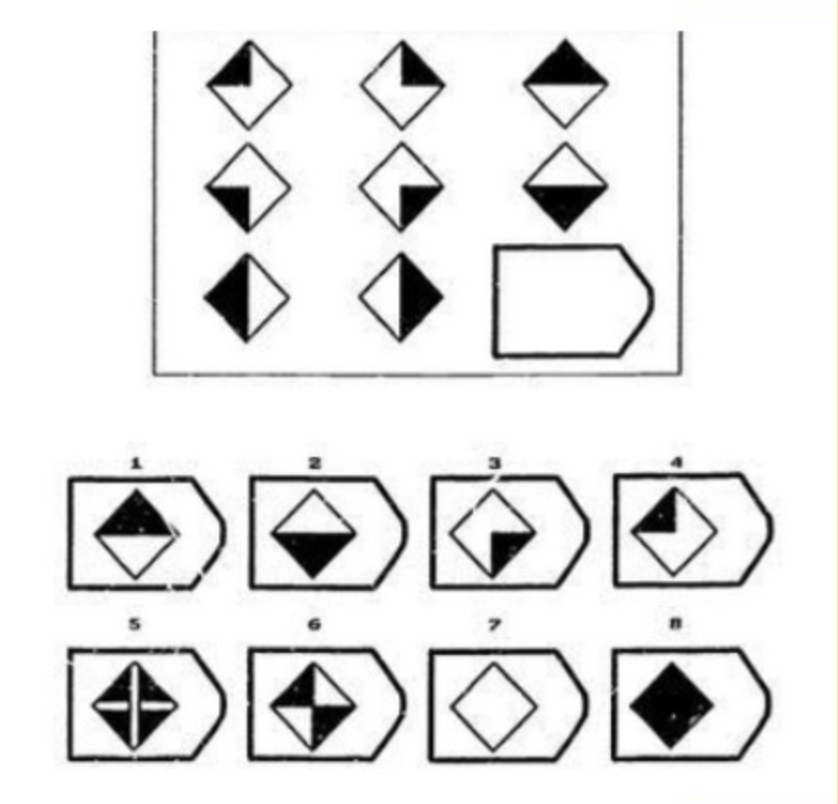
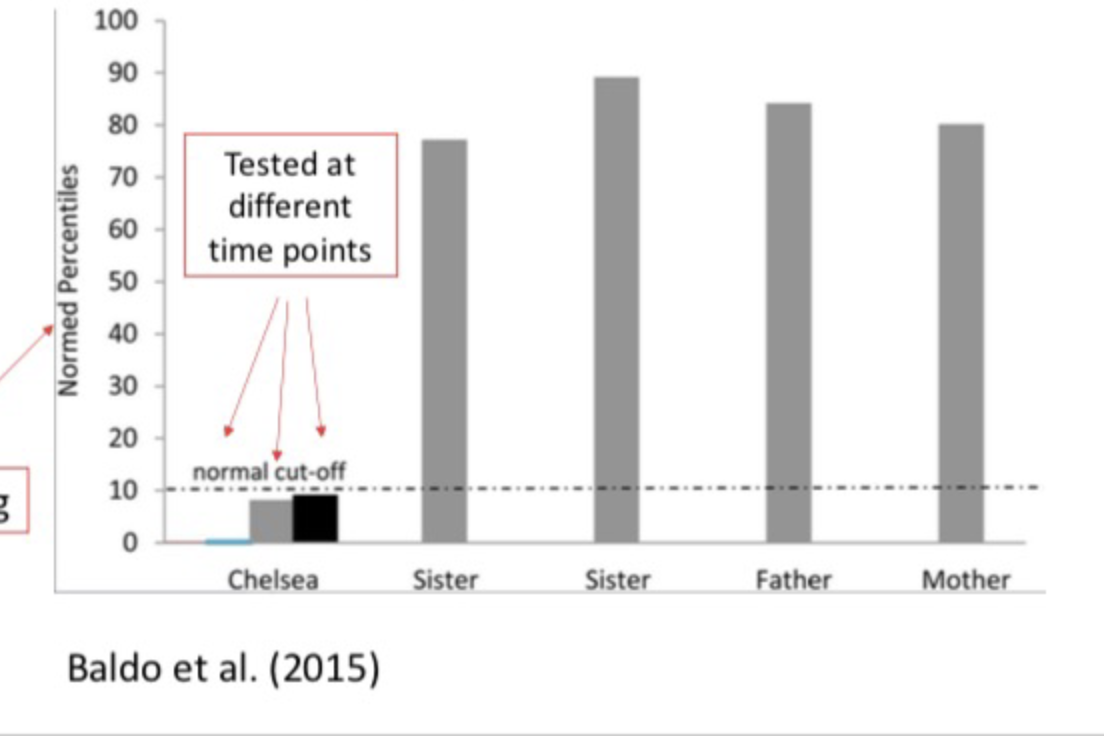
Language can also impact spatial reasoning: evidence from a case study of Raven’s progressive matrices
A case study: “Chelsea” a child with delayed language development
Summary: Problem solving and reasoning
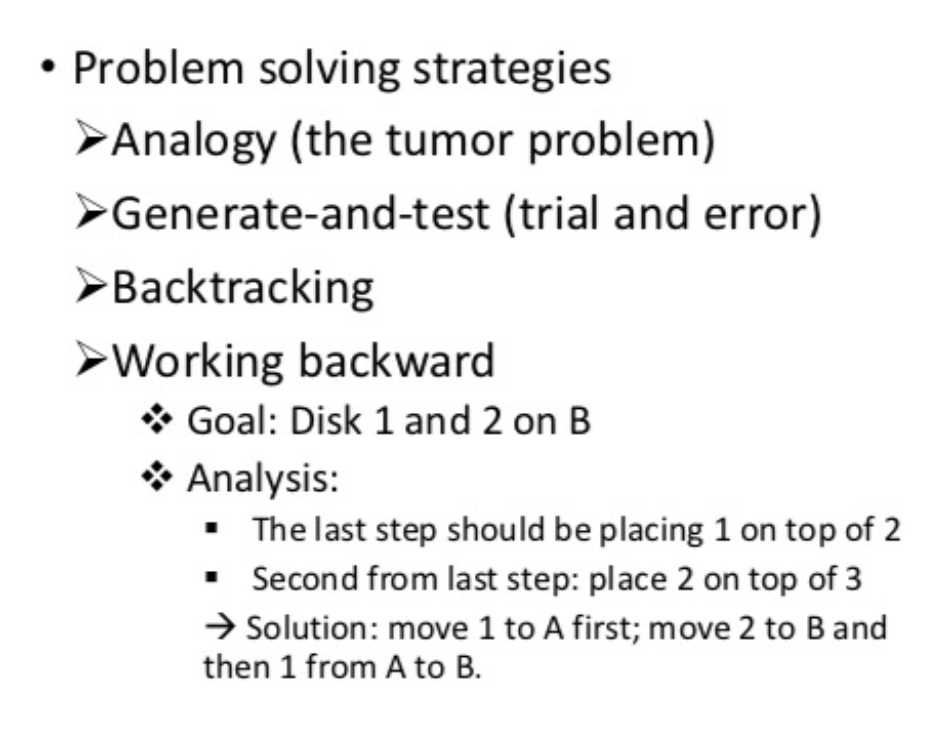
(cont)
