Exam 2
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Functions of Skeletal System
Support/ Protections
Movement
Hematopoiesis (produce blood)
Storage of minerals
Calcium
Phosphate Lipds
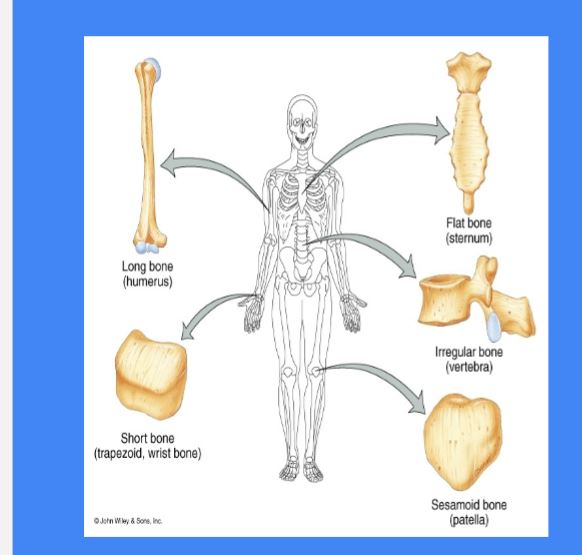
Types of Bones
Long Bones : longer than wide, spongy bone on the ends ex: Humerus, Ulna, Phalanges
Short Bones: Cube shape
equal length with wideness ex: carpals and tarsals
Flat Bones: Cranial bone, ribs, scapula
Irregular Bones: Complex bones ex: Coxae & Ethmoid
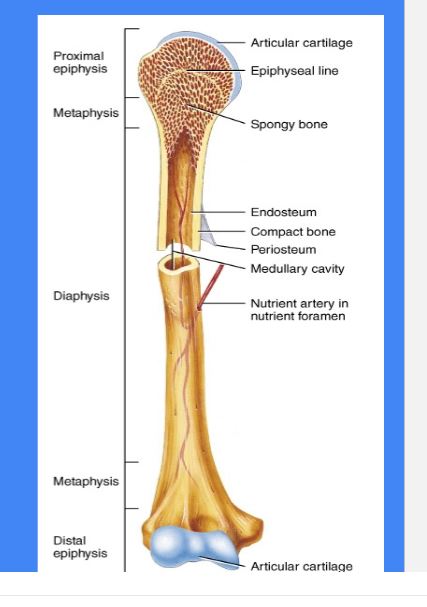
Diaphysis
Shaft of a long bone
yellow bone marrow can be found
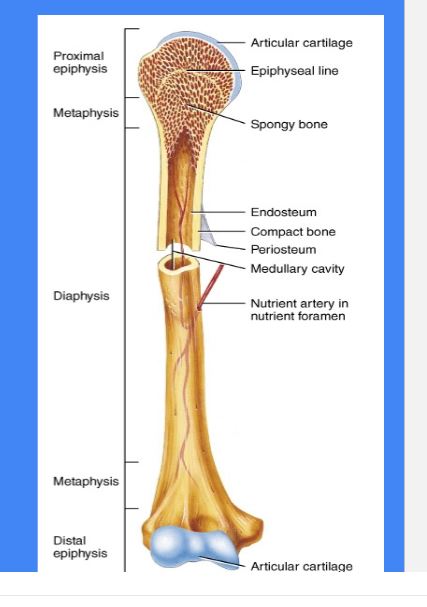
Epiphysis
Ends of the long bone
red bone marrow can be found
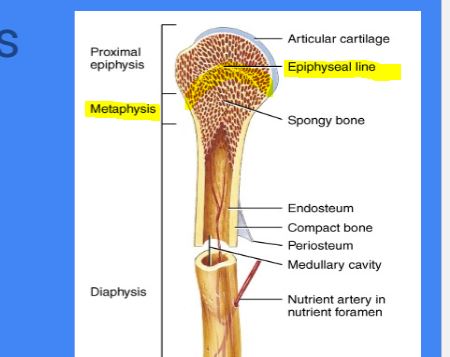
Epiphyseal Plate/line
Found in : Metaphysis ( middle)
where the final fuse of bone grown
growth plate
Medullary Cavity
yellow bone marrow can be found
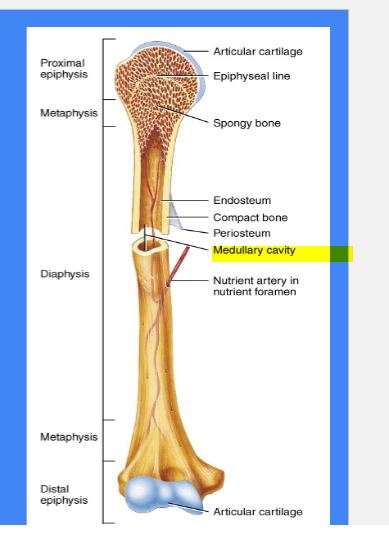
Endosteum
Inside membrane *
Periosteum
Outside membrane
Osteoprogenitor Cells
Bone Stem Cells derived from mesenchyme; divide to produce another stem cell and an osteoblast;
located in periosteum and endosteum ( Membranes)
Osteoblasts
Deposit osteoid (Bone Matrix) differentiate into osteocytes; bone builders
“Builders”
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells; maintain bone matrix reside within Lacunae ( place where they live)
Osteoclasts
Break down bone tissue ( Bone resorption) using hydrochloric acid and enzymes
Damaged bone tissue
Compact Bone
Named: Cortical or Dense
Solid & Dense
Forms at the external walls
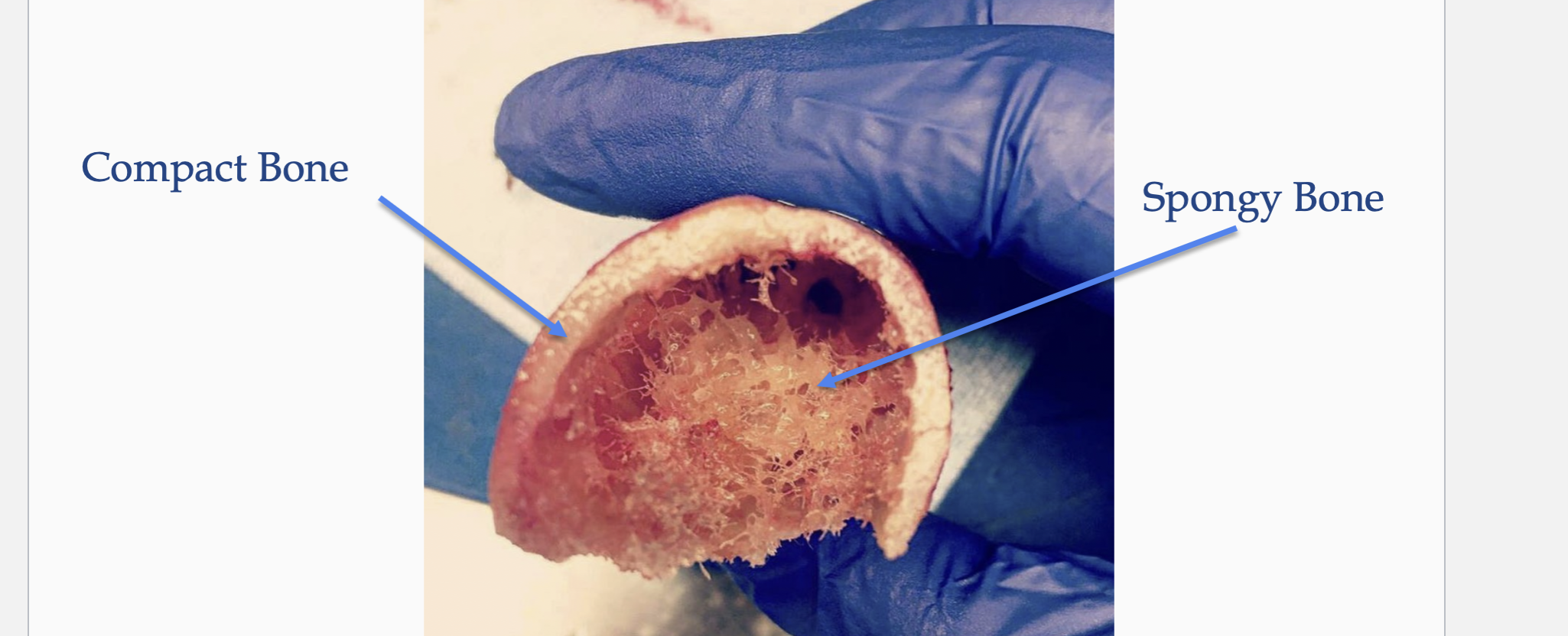
Spongy Bone
Names: Tabeculae
Appears Spongy & Porous
Located: internally epiphyses
Irregular network of parallel lamellae
Provides resistance to stress by distributing it throughout the framework Thin plates of bone with lots of
intercellular space
• Spaces filled with Red Bone Marrow
- Hematopoiesis
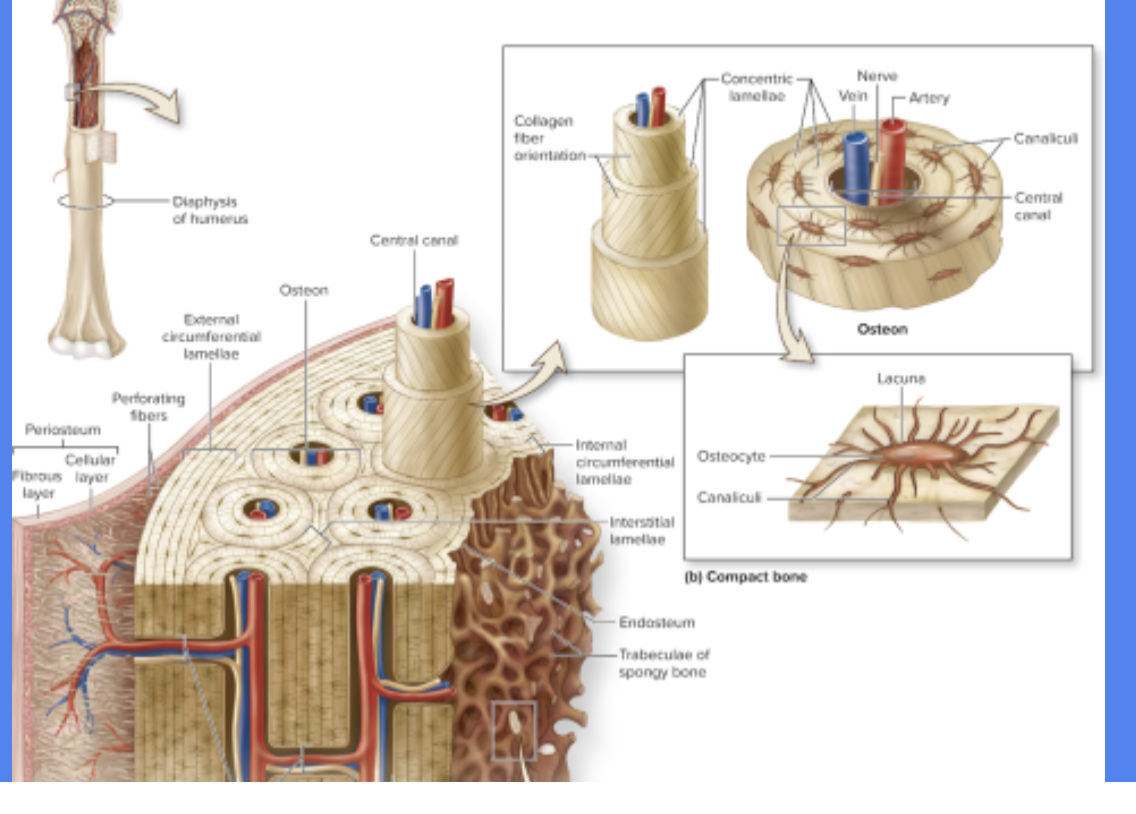
Osteons
Basic
Functional and structural unit of compact bone
Runs Parallel to diaphysis
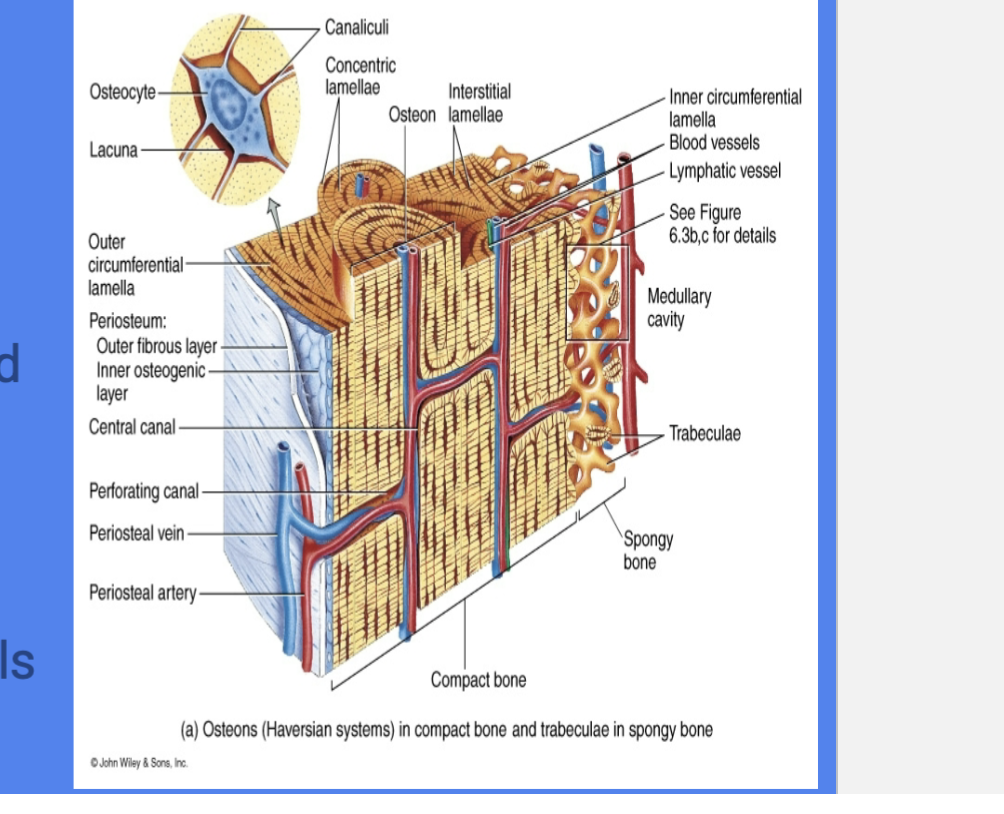
Central Canal
Cylindrical channel in the center
that contains blood vessels and nerves
* in the middle
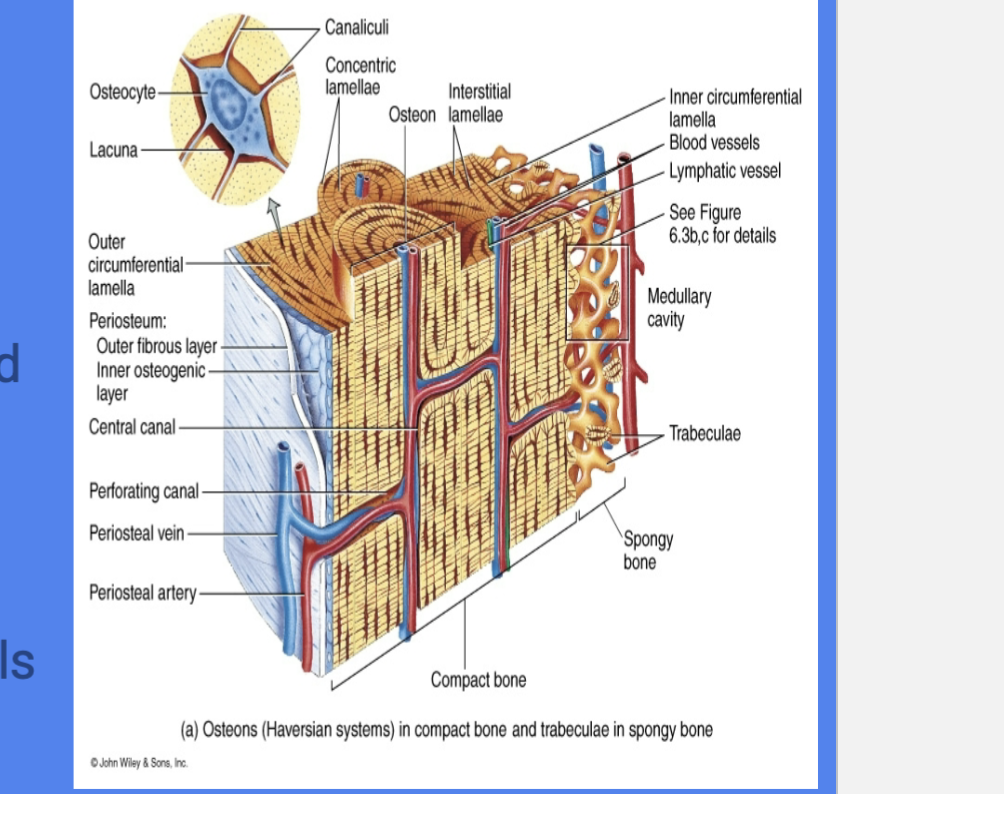
Concentric Lamellae
Rings of bone surrounding central canal
* each ring
Lacunae
Spaces in matrix where osteocytes reside
each little space where osteocytes live in
Canaliculi
Tiny, interconnecting channels w/ in bone connects lacunae and central canal
“Little Canals” that connect lacunae to reach center canal for nutrients and osteocytes
Perforating Canals
run perpendicular to central canal
create vascular and innervation network among osteons
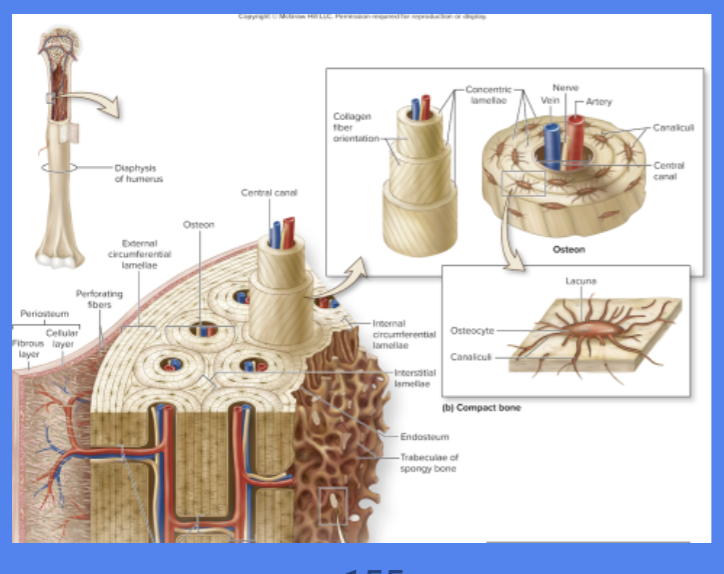
Circumferential lamellae
Rings of the bond
internal to the periosteum or endosteum
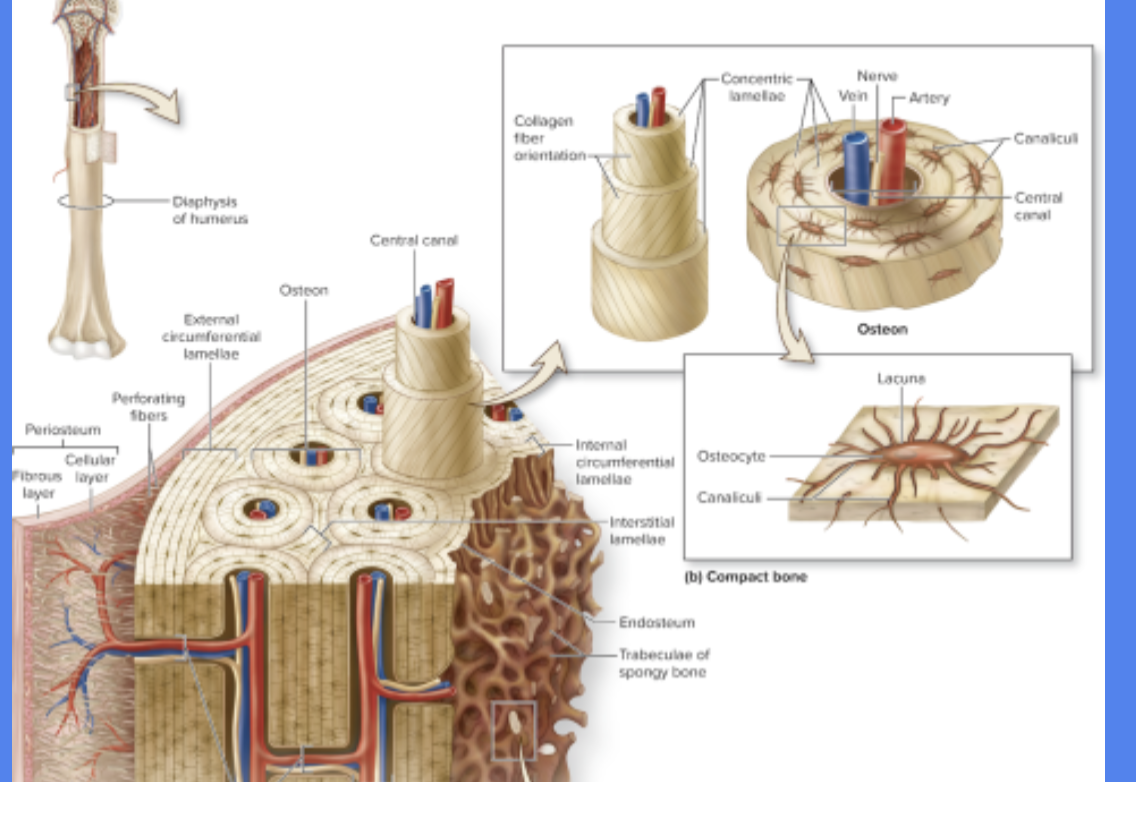
Interstitial Lamellae
Leftover parts of osteons that been partially resorbed
Hyaline Cartilage
Becomes Bone
Epiphyseal Growth plate
Length wise growth *
Interstitial bone growth
Is the ossification of cartilage which occurs within the epiphyseal plate
with ( 5 Zones )
Bone Remodeling
Deposition and resorption of bone
Helps maintain calcium and phosphate levels in body fluids and be stimulated by stress on a bone (fractures)
Older Adults: Bone resorption tends to exceed bone formation
Projections
Tendon/Ligament attachment
Smooth Areas
Articulations between bones
Depression/grooves/tunnels
Blood and nerves
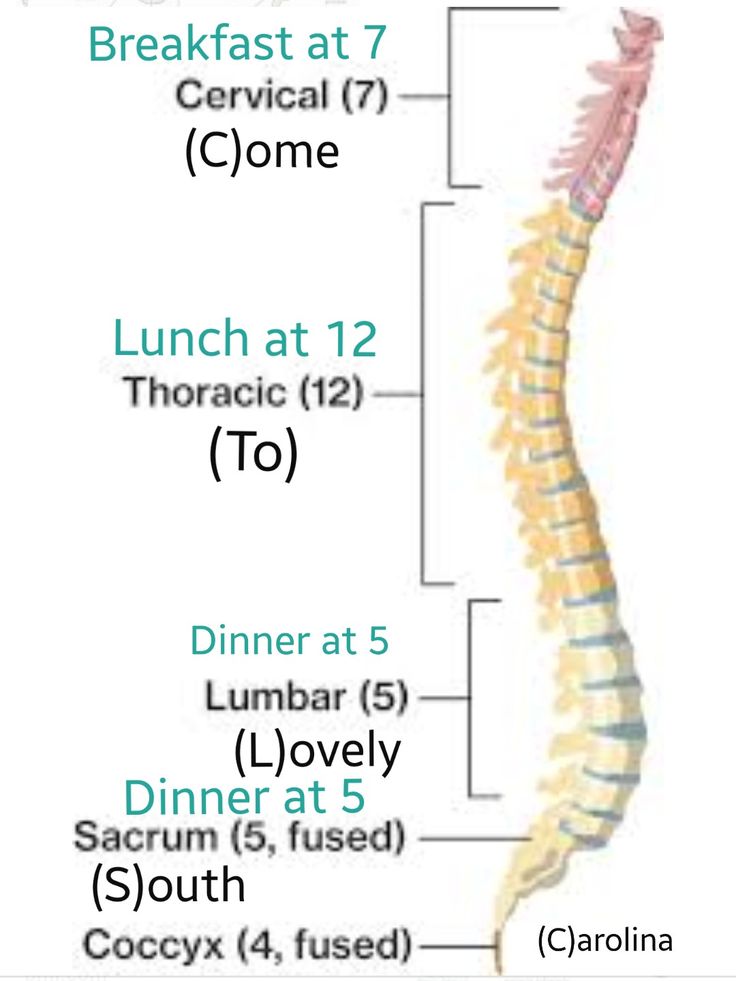
Vertebral Column
Cervical - 7
Thoracic - 12
Lumbar - 5
Function of Vertebral Column
Provide support for body
support weight of head
Maintain upright body position
Protect spinal cord
Vertebra Structure
Vertebral Body
Vertebral Spinous
transverse a
articular facets
pedicle and laminae
Appendicular Skeleton
-Attached to axial skeleton
Pectoral Girdle
Pelvic Girdle
Upper and Lower extremities
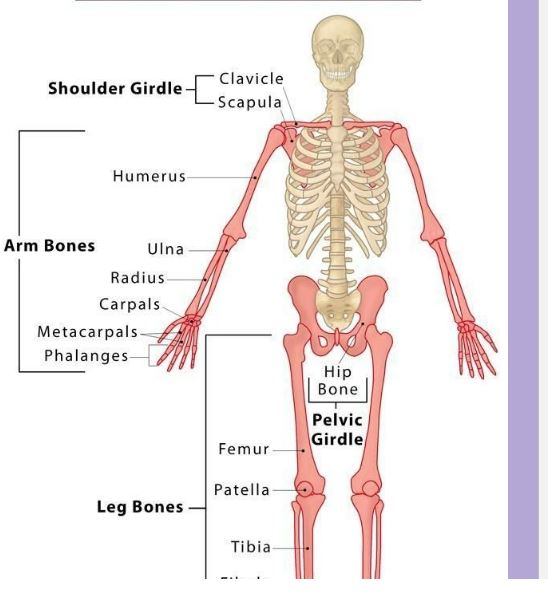
Pectoral Gridle
attaches the bones of the upper extremities to the axial skeleton
Articulates with trunk and supports upper limbs
Consist of: Clavicle and scapula
Attach to many muscles
Upper limb mobility
Upper Extremity
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
Carpals
The Pelvis
Sacrum
Coccyx
Right and left Ossa Coxae
Lower Extremity
Os coxa- pelvis
• Ilium
• Ischium
• Pubis
• Femur – thigh
• Patella – kneecap
• Tibia – shin
• Fibula – outer lower leg
• Tarsals - ankle
Articulation (Joint)
Place of contact between bones
bones to cartilage
Bones to teeth
Structure of Joint
Structure determines it’s mobility and stability
Joints Structures
Joints are classified structurally on basis of
connective tissue that binds to the joint
Ex:
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
Synovial
Joints Functionally
Basis of movement at joint
Examples:
Synarthrosis (Don’t move)
Amphiarthrosis (Slightly movable)
Diarthrosis (Move freely)
Fibrous Joints
Immovable or slightly movable
thin layer of CT
Ex:
Gomphoses - roots of teeth
Synarthroses ( Skull)
the small ct in between the bones like in the tibia and fibula
Cartilaginous Joints
Connected by Hyaline or Fibrocartilage (Cartilage)
Slightly movable
Synarthoroses - found at ribs to manubrium
Ampiarthroses- Found to Pubic symphysis
Synovial Joints
Found in joint cavity, synovial fluid and ligaments
Free movable
Accessory structures like: Bursa, fat pads and tendons
Types of Synovial Joints
Saddle Joint
Ball and Socket Joints
Pivot
Planar Joint
Condyloid Joint
Hinge Joint
Movement of Synovial Joints
Flexion/Extension/Hyperextension
Lateral flexion
Abduction/adduction
Circumduction
Rotation
Lateral/medial rotation
Pronation/supination
Depression/elevation
Dorsiflexion/plantarflexion
Inversion/eversion
Protraction/retraction
Opposition