Physiology skeletal system + directional terms
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Bone Marrow
Found in the hollow sections of bone, and in spongy bone
Red – Primarily responsible for new blood cells of all varieties
Yellow – Primarily responsible for producing/storing fat, producing bone tissue/cartilage, and producing red blood cells during emergencies
Both – house stem cells
Osteoblasts
Cells that produce new bone tissue, these cells are responsible for ossification. They secrete enzymes that dissolve the bone matrix, releasing calcium and phosphate into the bloodstream.
Osteocytes
They are matured osteoblasts that have become entrapped within the bone matrix. They form when an Osteoblast finishes its job. While trapped, they monitor the health of the bone.
Osteoclasts
cells that break down and reabsorb bone tissue when needed. They make space for osteoblasts to create new bone tissue in areas that are growing or need repair. If osteoblasts are builders, osteoclasts are your bones' demolition crew. (think “remodeling” a house)
Osteogenic cells
Stem cells that can develop into osteoblasts. Osteogenic cells differentiate and develop into osteoblasts which, in turn, are responsible for forming new bones.
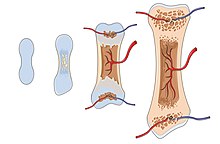
Ossification
The process of bone formation. Our bones actually start as cartilage
1.Starting around the center, Osteoblasts produce bone tissue while the cartilage is digested simultaneously. This process progresses outwardly
Blood vessels (among other things) form in the new canals, and allow various bone cells to transfer in/out
Mineralization occurs afterwards
Calcium Regulation
Your body must maintain the correct balance of calcium between bones and blood
Osteoblasts need Ca to make new bone tissue
Bone tissue needs Ca to remain strong
Blood needs Ca to deliver to nerves/muscles so that they function properly
Osteoclasts provide an increase of Ca when they break bone tissue down
Hormone and Calcium regulation
Hormones PTH and calcitonin work to maintain a balance between those needs
When blood Ca levels fall, PTH works to bring it back up by
Having osteoclasts break down bone tissue for Ca ⇒ send to blood
Telling the body to ingest/retain more Ca
When blood Ca levels rise, calcitonin works to bring it back down by
Preventing osteoclasts from breaking down bone ⇒ keeps Ca in bones
Telling the body to excrete more Ca
Stimulating the transference of blood Ca to bones*
superior
above; or more towards the head
inferior
below; or way from the head
anterior
towards the front; towards the belly
posterior
towards the back
medial
closer to the midline of body or structure
lateral
further from the midline of body structure
proximal
nearer to the point of attachment
distal
further from point of attachment
superficial
towards, or on the surface
deep
away from the surface of the body