oral mucosa pt1 and 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
The basement membrane of the oral mucosa connect the epithelium and the inferior connective tissue. The membrane is made up of the superior ________ and inferior ___________.
basal lamina, reticular lamina
The basal lamina is made up of two layers. The superior ________ which attaches to the epithelial cells and the __________ which attaches to the reticular lamina of the basement membrane.
lamina lucida, lamina densa
Lining mucosa is ____________, Masticatory mucosa is ___________.
Nonkeratinized, keratinized
_________ is found in the buccal mucosa, labial mucosa, alveolar mucosa, the ventral surface of the tongue, the floor of the mouth, and the soft palate.
Histologically, it is __________ epithelium with a smooth interface and few rete ridges, and it contains __________ in the lamina propria and submucosa.
Lining mucosa, nonkeratinized, elastic fibers
____________ is located on the attached gingiva, hard palate, and dorsal surface of the tongue. It has a rubbery texture and provides firm support during chewing. Histologically, it is __________ epithelium with a highly interdigitated interface containing many rete ridges and connective tissue papillae, and it has little to no __________.
Masticatory mucosa, keratinized, submucosa
______________ is found on the dorsal and lateral surfaces of the tongue.
It is associated with lingual papillae, many of which contain __________.
Histologically, it has distinct epithelial and lamina propria structures that allow for taste sensation.
Specialized mucosa, taste buds
The _____________ is the deepest epithelial layer, made of a single row of cuboidal cells resting on the basement membrane, and it is responsible for producing the basal lamina that attaches the epithelium to the underlying lamina propria.
basal layer (stratum basale)
The ____________ lies above the basal layer in nonkeratinized epithelium and is made of larger, stacked, polyhedral cells that appear plumper due to increased fluid in their cytoplasm.
intermediate layer (stratum intermedium)
The _____________ is the top layer of nonkeratinized epithelium, made of large stacked polyhedral cells whose outermost cells flatten into _______ that are eventually shed as the tissue renews.
superficial layer (stratum superficiale), squames
A variable number of __________ are scattered throughout the tissue. These are a variant usually present in the oral cavity, which are visible as small, yellowish bumps on the surface of the oral mucosa.
Fordyce spots (or granules)
Nonkeratinized epithelium may, however, readily transform into a keratinizing type in response to frictional or chemical trauma, in which case it undergoes ____________. An example of this is linea alba.
hyperkeratinization
Changes such as hyperkeratinization are reversible if the _____________, but it takes time for the keratin to be shed by the tissue. Thus it is important to rule out malignant changes, and a _________ of any whitened tissue may be indicated.
source of the injury is removed, biopsy and study
Indication for biopsy is especially true if the patient is within a __________ category, such as those with a history of chronic tobacco or alcohol use or those who are human papillomavirus (HPV) positive.
high-risk cancer
A change to hyperkeratinization commonly occurs on the usually nonkeratinized buccal mucosa when _______ forms, a white ridge of calloused tissue that extends horizontally at the level where the maxillary and mandibular teeth come together and occlude.
linea alba
The tissue of the soft palate is compressible and _________ to allow for speech and swallowing.
extremely elastic
Unlike lining mucosa, the interface between the epithelium and lamina propria with masticatory mucosa is _____________ with numerous and more-pronounced rete ridges and connective tissue papillae, giving it a firm base.
highly interdigitated
In contrast to nonkeratinized tissue, the _________________ demonstrates a keratinization of the epithelial cells throughout its most superficial layers. It is associated with the masticatory mucosa of the hard palate and the attached gingiva and the specialized mucosa of the _________ on the dorsal of the tongue.
orthokeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, lingual papillae (parakeratinzed)
The most superficial layer in orthokeratinized epithelium is the ___________, which shows a variable thickness depending on the oral cavity region.
keratin layer or stratum corneum
Within orthokeratinized, like nonkeratinized epithelium, the basal layer has a single __________ undergoing mitosis. Superficial to the basal layer is the __________ where cells migrate and lose the ability to undergo mitosis.
basal layer or stratum basale, prickle layer or stratum spinosum
Superficial to the prickle layer is the ______________. The epithelial cells in this layer are flat and are stacked in a layer three to five cells thick.
granular layer or stratum granulosum
A ___________ is a structure consisting of a mucous membrane combined with the periosteum of the adjacent bone
mucoperiosteum
Palatal tori are developmental growths of bone with a ______________.
hereditary etiology
The ____________ is associated with the masticatory mucosa of the attached gingiva in higher levels than the presence of orthokeratinization. may have all the same layers of epithelium as orthokeratinized epithelium, although the granular layer may be indistinct or absent altogether. Also contains nuclei.
parakeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
__________ is observed clinically as small pinpoint depressions, which give the surface of the attached gingiva an orange-peel appearance; this is analogous to the button tufting on upholstery
Stippling
__________ has tall, narrow connective tissue papillae in the lamina propria, creating strong epithelial attachment that results in the clinical appearance of stippling. The oral mucosa when combined with the periosteum of the underlying alveolar process forms a _________ where there is no intervening submucosa present.
Attached gingiva, mucoperiosteum
The ____________ can be seen as a dividing zone between the keratinized attached gingiva and the nonkeratinized alveolar mucosa and thus between a masticatory mucosa and a lining mucosa.
mucogingival junction
A ________________ is from lamina propria that is taken from the surrounding keratinized attached gingiva and then grafted directly to the root.
subepithelial connective tissue graft
_____________ is the overgrowth of the interproximal gingiva caused by the intake of certain drugs for seizure control (phenytoin sodium), certain antibiotics, and specific heart medications (calcium channel blockers).
Gingival hyperplasia
The most common cell in the lamina propria of all types of oral mucosa, similar to differing locations of connective tissue proper, is the ________.
fibroblast
A submucosa may or may not be present deep to the dense layer of the lamina propria, depending on the region of the oral cavity. If present, it usually contains ____________ and may contain __________ tissue or salivary glands.
loose connective tissue, adipose (fat) connective
Melanocytes have small cytoplasmic granules or inclusions called ___________, which store the melanin pigment.
melanosomes
The junctional epithelium, has the fastest turnover time of all the oral tissue at ________. One of the lowest turnover times is for the hard palate at _____. The turnover times of all other oral mucosa regions fall between these two end points—between 4 and 24 days.
4 to 6 days, 24 days
During repair of the oral mucosa fibroblasts migrate to produce an immature connective tissue considered __________ that has fewer fibers and an increased number of blood vessels.
granulation tissue
_______ of the oral mucosa is seen clinically as a reduction of ________ on the attached gingiva, an increase of Fordyce spots in the labial and buccal mucosa, and an enlargement of the lingual veins to form lingual varicosities on the ventral surface of the tongue.
Aging, stippling
During aging the number of lingual papillae and associated taste buds, especially the foliate lingual papillae, is also reduced and may be related to changes noted in _____________ as a person ages. Turnover times _____ for all regions of the oral cavity, and ________ in the epithelium diminish.
taste perception , slow down, rete ridges
Biopsy followed with microscopic study is the only way to effectively _____________.
diagnose any lesion
The _________ surface of the tongue has both a masticatory mucosa and specialized mucosa present.
dorsal
Three types of lingual papillae are associated with taste buds: ________, ______, and _________.
fungiform, foliate, circumvallate
The _________ of the lingual papillae receive messages of taste sensation through the taste receptors. The message generated is then sent to the central nervous system by the connecting nerves where it is identified as a __________.
sensory neurons, certain type of taste
Properties of the lingual papilla that can affect ___________ is aging, color/vision impairments, hormonal influences, genetic variations, oral temperature, drugs and chemicals, CNS tumors, and plugged noses.
taste sensation or perception
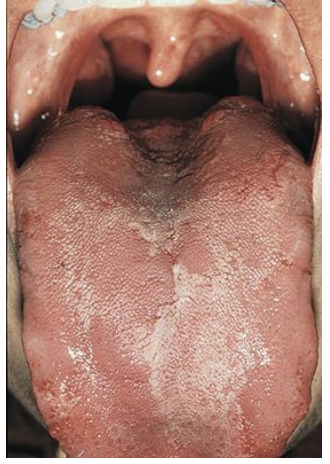
___________ appears as red (parakeratinized) and then paler pink to white patches (orthokeratinized) on the body of the tongue. These patches change shape with time, resembling a geographic map. These patches correspond to groups of _________ undergoing changes from epithelium,
Geographic tongue, filiform papillae
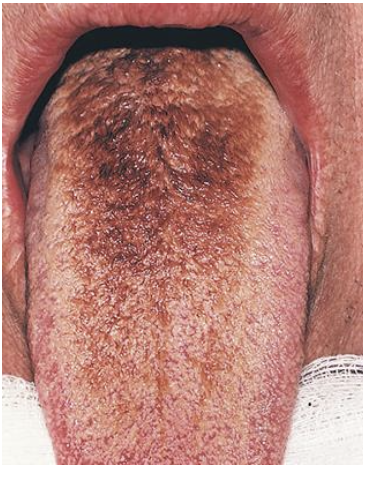
_____________ occurs when the usual level of shedding of epithelium of the filiform lingual papillae does not occur. As a result, a thick layer of dead cells and keratin builds up on the tongue surface, which becomes ___________ by tobacco, medicines, or chromogenic (colored) oral bacteria.
black hairy tongue, extrinsically stained
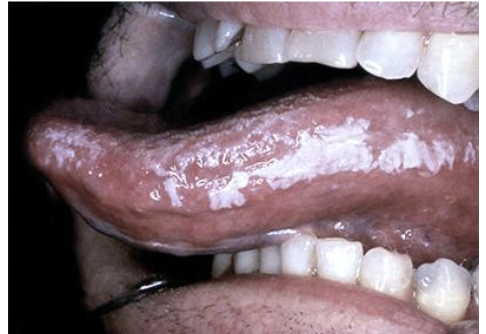
___________ is an irregular and corrugated white lesion most commonly occurring on the lateral border of the tongue. Occurs most often by EBV or in patients with HIV.
Hairy leukoplakia
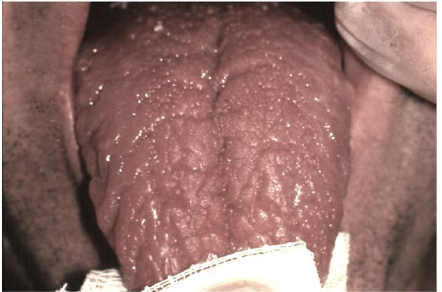
___________, a condition seen frequently in the general population, is characterized by grooves that vary in depth and are noted along the dorsal and lateral aspects of the tongue.
Fissured tongue
Although oral cancer may arise at any site in the oral cavity, one of the most common sites includes the ____________.
lateral border of the tongue
The ____________ is measured by the distance between the mucogingival junction that remains stationary after the permanent dentition eruption and the projection on the external surface of the apex of the gingival sulcus.
width of the attached gingiva
The ____________ is the junction between the tooth surface and the gingival tissue. The sulcular epithelium and junctional epithelium together form this tissue.
dentogingival junction
The suprabasal cells, which make up the most superficial layer of the JE, serve as part of the EA of the gingiva to the tooth surface. These more suprabasal epithelial cells of the JE provide the ____________ and an internal basal lamina that create the EA because this is a cell-to-noncellular type of intercellular junction.
hemidesmosomes
The internal basal lamina of the EA is also continuous with the _____________ between the JE and the lamina propria at the apical extent of the JE.
external basal lamina
The marginal gingiva can become extremely rolled. The lifesaver-shaped edema of the marginal gingiva is called _________.
McCall festoon
A cleft-like area of gingival recession is called __________ and is related to occlusal trauma.
Stillman cleft
A __________ is a generic name for any of a number of surgical periodontal procedures whose combined aim is to cover an area of exposed tooth root surface with grafted oral tissue.
gingival graft
Thus the ____________ uses a thickness of both keratinized epithelium and lamina propria harvested from the hard palate and grafted to the root to form a new band of keratinized attached gingiva.
free gingival graft (FGG)