AP Euro Unit 2 | Ch 3 Protestant Reformation
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Causes of the Reformation
Simony (selling offices), Nepotism (family favors), Pluralism (holding multiple offices), Absenteeism, indulgences, priestly ignorance.
Printing Press
Fragmented Germany (HRE)/princes revolting
"New Piety" (lay movements) sought direct relationship with God.
Ren antiquity & Christian Huamanism.
Lutheranism (Germany)
Sola Fide: Salvation by Faith Alone (not good works).
Sola Scriptura: Authority lies only in the Bible (not Pope/Tradition).
Priesthood of All Believers: All Christians are spiritually equal.
2 Sacraments: Baptism & Eucharist (Consubstantiation/Real Prescence).
Marburg Colloquy (1529)
Meeting (Luther vs. Zwingli) that failed to unite Protestants over the Eucharist doctrine (Real Prescence vs. Symbolic).
Anabaptists
Key belief: Adult baptism
Advocated separation of Church/State and pacifism (Schleitheim Confession)
John Calvin
Geneva Theocrat.
Key doctrine: Predestination ("Elect").
Wrote Institutes of Christian Religion (Calvinist manuel) & Geneva Catechism (Book for help children understand faith)
Influenced Protestant work ethic
Calvin’s Geneva
Theocracy (Church/State merged)
Governed by the Consistory (regulatory moral court) w/ strict moral codes
Refuge for Protestants.
Edward VI
Embraced full Protestantism (Calvinist influence) via Book of Common Prayer.
Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra
Spanish author who wrote Don Quixote
Satirized the romanticized ideals of medieval chivalry and tradition of the time
William Shakespeare
English dramatist
Works showed universal human themes, often rooted in contemporary religious traditions
95 Theses (1517)
Luther's arguments against Indulgences (sold by Tetzel for St. Peter's Basilica) posted on Church door
Marked the start of the Reform, spread via printing press.
Augsburg Confession
Articles of Lutheran beliefs (Church abuses)
Presented at Diet of Augsburg, but rejected
Led to formation of Schmalkaldic League
Tragedy at Münster
Radical Anabaptist attempt at theocracy by expelling dissenters; crushed by both Catholic and Protestant forces.
Thomas More
Henry VIII’s advisor; executed for refusing to recognize Acts of Succession & Supremacy
Act of Supremacy (1534)
Made the King (Henry VIII) the Supreme Head of the Church of England (broke from Rome).
Mary I/Tudor (“Bloody Mary”)
Attempted to restore Catholicism by reverting changes; persecuted Protestants; failed (led to Marian Exiles).
Elizabeth I
Politique (unity > doctrine)
Established Anglicanism (Protestant doctrine, Catholic ritual) via the Elizabethan Settlement.
Allowed private worship & forced Book of Common Prayer
Politique
Politicians who prioritized political unity over other parts of society (religious unity)
Teresa de Avila
Spanish mystic who reformed the Carmelite order, stressing deep personal prayer and self-discipline.
Catholic (Counter) Reformation
Response to Protestantism.
Key elements: Council of Trent, Jesuits, and the Roman Inquisition (persecution of heretics).
Council of Trent
Reaffirmed Catholic Dogma (7 Sacraments, Faith + Works, Scripture + Tradition), cementing division
Reformed abuses (simony, priest training, indulgences)
Approved Index of Forbidden Books
Established public/parental consent for valid marriage.
Jesuits (Ignatius of Loyola)
Founded to fight Protestantism through education and missionary work
Vowed chastity & obedience to Pope
Impact on Women
Domestic role glorified (housewife/mother); shift away from Catholic nunnery
Literacy increased; girls gained vernacular edu
Lost status/career path (convents closed).
Laws for equality (divorce) & protection
Increased edu due to Reform + printing press
Baroque Art
Style of the Counter-Reformation
Used dramatic light/emotion to convey the power and glory of the Catholic Church & regain spirituality of common ppl
Example: Paul Rubens (The Elevation of the Cross; intense action around Christ)

Christian Humanism (Northern)
Goal: Reform Church from within using education and simple early-Christian piety (ad fontes).
Erasmus: Wrote In Praise of Folly (satire of clergy); "Laid the egg that Luther hatched."
Thomas More: Wrote Utopia; executed for refusing Henry VIII's break from Rome.
Indulgences
Definition: Paper grants lessening time in Purgatory for sins.
Trigger: Pope Leo X sold them to fund St. Peter’s Basilica; marketed aggressively by Tetzel.
Result: Sparked Luther's 95 Theses.
Diet of Worms (1521)
Meeting where Charles V declared Luther an outlaw after he refused to recant his writings.
German Peasants' Revolt (1525)
Peasants used "Christian Freedom"/sola fide to rebel.
Luther condemned it as it threatened his sect & to secure Princely support, who crushed it
Schmalkaldic League
Lutheran Princes' defensive alliance against Charles V (distracted by Habsburg-Valois War).
Ended Cath unity
Peace of Augsburg (1555)
Ended religious civil war in HRE.
Principle: Cuius regio, eius religio (ruler's choice of religion Lutheranism/Catholicism).
Henry VIII’s Motive
Political/Dynastic: Wanted papal annulment (no male heir); Pope refused (due to Charles V).
Formed Anglican Church, Act of Supremacy, Act of Succession (forced to recognize heir)
Impact on Education
Protestants (Luther/Calvin) emphasized universal literacy (Bible) & personal understanding
Vernacular lit, humanist themes
Jesuits created elite humanist schools
Theological Consensus
Vernacular worship and fewer holidays (Puritan influence) became common across Protestant regions.
Witchcraft Craze
Surge in persecutions (c. 1580–1650)
Blamed social/religious upheaval; victims were often single/widowed women
Imperial Distractions
Charles V was preoccupied by wars vs. France (Habsburg-Valois War) and Ottoman Turks, allowing the Reform to solidify.
Family Impact (Reformation)
Nuclear Family model favored
Children sent out (8-13) for apprenticeships/work
Remarriage common/quick for utility (especially widows/widowers)
German Pietism
17th-18th cent. movement within Lutheranism
Emphasized deep personal faith and spiritual experience over dogmatic rigidity
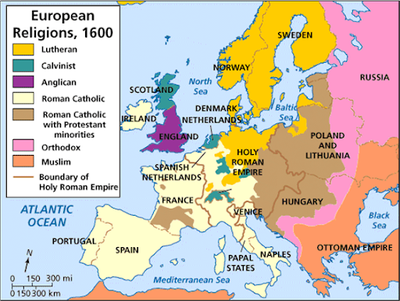
Religious Map (Post-1555)
Catholic: Spain, Italy, Austria, S. Germany, France
Lutheran: N. Germany, Scandinavia (SWE, DEN, NOR)
Calvinist: Netherlands, Scotland, Switzerland
Anticlericalism (Early 16th C.)
Focused on piests who preached messages contrary to church doctrine
Massacre at Vassy
Guise massacred many Huguenots @ Vassy, starting French rel wars