Understanding Business Tools and Technology in Hospitality
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Business Tool
Any asset that helps or assists the organization to achieve its stated aims or objectives.
Business Technology
Describes all technology that helps an organization run its business and operational processes.
Communication Software
Allows businesses to discuss projects and plans with employees, even remotely.
Security Software
Helps keep electronic content safe, preventing unauthorized users and inputs.
Information Technology
The technology that employees use, including computers, internet systems, printers, mobile devices and software applications that help them organize and prioritize work.
Common Business Tools
Includes mobile and landline telephones, scanners, brochures, facsimile, manuals, software, email, business website, etc.
Benefits of Business Tool and IT
Includes increased productivity, lower business costs, increased work efficiency, larger business reach, increased business security, decreases staff workload, boosts revenue, improves access and sharing of information, enables better planning and management.
Challenges of Implementing New Technology
Includes lack of knowledge among top management, high initial investment costs, and resistance to change from personnel.
Types of Business Technology
Broad spectrum of hardware and software solutions that enables organizations to gather, organize, and analyze data.
Payroll
To transfer payment to employees and contractors during each pay period, some processes are entirely automatic.
Hiring
Businesses can access job forums to gain talent from around the world.
Task Allocation
Both offline and online processes for distributing tasks among employees.
Importance of Training
Crucial consideration when selecting and implementing business tools, ensuring employees are equipped with necessary knowledge and skills.
Process Tools
Tools that help streamline and manage business processes.
Employee Related Tools
Tools that assist in managing employee-related tasks and functions.
Decision Making Tools
Tools that aid in making informed business decisions.
Control Tools
Tools that help monitor and control business operations.
Inventory Control Systems
Systems that help manage inventory levels and stock.
Accounting Systems
Systems used for managing financial transactions and records.
Telephone Communication
Use of telephones for communication within a business.
Networking
Connecting computers and devices to share resources and information.
Technological business tools
Tools that help employees better cooperate, collaborate, and communicate.
Employee-Related Tools
Resources for managing, training, and evaluating staff.
Decision-making Tools
Tools that support informed business choices.
Control tools
Systems used to monitor performance and ensure quality.
Information Technology (IT)
A broader term that includes both hardware and software systems used to collect, organize, and analyze data to meet business goals.
Software
Programs or applications that run on computers or devices to perform specific tasks.
Hardware
Physical tech equipment like computers, printers, mobile phones, etc.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
Systems that help manage a company's interactions with current and potential customers.
Business tools
Any assets—physical or digital—that help an organization achieve its goals.
Common examples of business tools
Phones, scanners, manuals, brochures, software, emails, and websites.
Benefits of using business tools and IT
Boost efficiency, lower costs, improve work accuracy, expand a business's reach, enhance data sharing, and help in better planning and decision-making.
Challenges of implementing new technology
Lack of tech knowledge among top management, high startup costs, and resistance from staff.
Importance of training
Ensures employees know how to use tools effectively, reducing mistakes and improving output.
Technology for business operations
Technology used specifically to run and support business operations and processes.
Customer service software
Software that helps manage customer interactions and support.
Accounting systems
Systems that manage financial transactions and reporting.
Logistics platforms
Systems that manage the flow of goods and services.
Back-end systems
Systems that support the internal operations of a business, such as payroll.
Inventory management tools
Tools that help track inventory levels, orders, sales, and deliveries.
Networking systems
Technologies that connect computers and devices for communication and resource sharing.
Telephone communication tools
Devices and systems used for voice communication in business.
Business Tool
Any asset or resource used to help an organization meet its goals
Planning Tools
Tools used for setting goals and developing strategies.
Process Tools
Tools that help improve business operations and workflow efficiency.
Record Tools
Tools for storing and organizing business data and documents
Security Software
Tools that protect business data from cyber threats or unauthorized access
Payroll system
Tech used to automate salary and contractor payments
Inventory Control System
Software that tracks stock levels, orders, and deliveries
E-Tourism
Umbrella term that incorporates the entire range of ICT applications in the hospitality area.
E-Hospitality
Supports companies in transforming digitalization into a competitive factor.
Training
The process of educating staff on how to effectively use new tools and equipment.
Technologies in E-Tourism
It accelerates digitalization, develops products and services, and supports the development of sustainable and smooth service solutions.
E-Travel Agencies
Covers all technical means used to handle information and aid communication.
E-Tour Operators
The internet, electronic payment system, mobile phones, C.R.S., G.D.S, virtual reality, online word of mouth.
Benefits of E-Tourism
Ease in booking, better destination planning decision, easy payment, lowering of cost, well-organized distribution, employee empowerment, enhanced market penetration.
Resistance to change
A common challenge when introducing new tech, often from employees.
Communication software
Applications or platforms that allow remote communication.
Task allocation
The process of assigning specific duties to team members using digital or manual systems.
Networking
The linking of devices to share data and resources.
Real time details
Information available instantly as events occur.
More communication channels
Increased methods for exchanging information.
See before you go mode
A feature allowing users to preview destinations before visiting.
Easy reservation
Simplified process for booking services or accommodations.
Sharing of travel experiences online
Users posting their travel stories and tips on the internet.
Digitization
The digitization of all the processes and value chains in the tourism, travel, hospitality, and catering industries that enable organizations to maximize their efficiency and effectiveness. (Buhalis, 2003)
E-Tourism
The term "e-tourism" refers to the use of e-business systems in the tourism industry.
Electronic Tourism
Also known as electronic tourism or digital tourism.
Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs)
It is the use of Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) in the tourism industry.
Online Presence
Buying/selling monetary transactions online.
E-Business
E-Business transforms the tourism industry.
E-Management
Connects critical business systems directly to its customers, employees, partners, and suppliers using Internet technologies.
Reservation Systems
Travel agencies operate various reservation systems, which mainly enable them to check availability and make reservations for tourism products.
Smart Destinations
Smart destinations are tourist areas that can be defined as innovative, accessible and consolidated spaces in a given area.
Technological Infrastructure
State-of-the-art technological infrastructure that guarantees the sustainable development of the territory.
E-Commerce
Is the transaction of goods and services between businesses or between consumers themselves over the Internet.
E-Commerce Transactions
Transactions are not limited and involve use of only one website.
E-Business Strategy
Is a subset of an overall e-business strategy.
Multiple Websites and CRMs
ERPs that connect different business processes are used.
Intelligent Tourist Destinations
These intelligent tourist destinations facilitate the interaction of the visitor with the environment.
E-Business Models
E-business models include E-business, C-Customer/Consumer/Citizen, G-Government, E-employee.
Difference Between E-Commerce and E-Business
E-business involves conducting business processes through the web, internet, or extranet.
Key Activities in E-Business
Key activities include online buying/selling, customer service, payment processing, and supply chain management.
Partner Collaboration
It also supports partner collaboration, information sharing, employee services, and recruitment.
E-Commerce
Conducting key business functions over electronic systems.
E-business
Carrying out commercial transactions online.
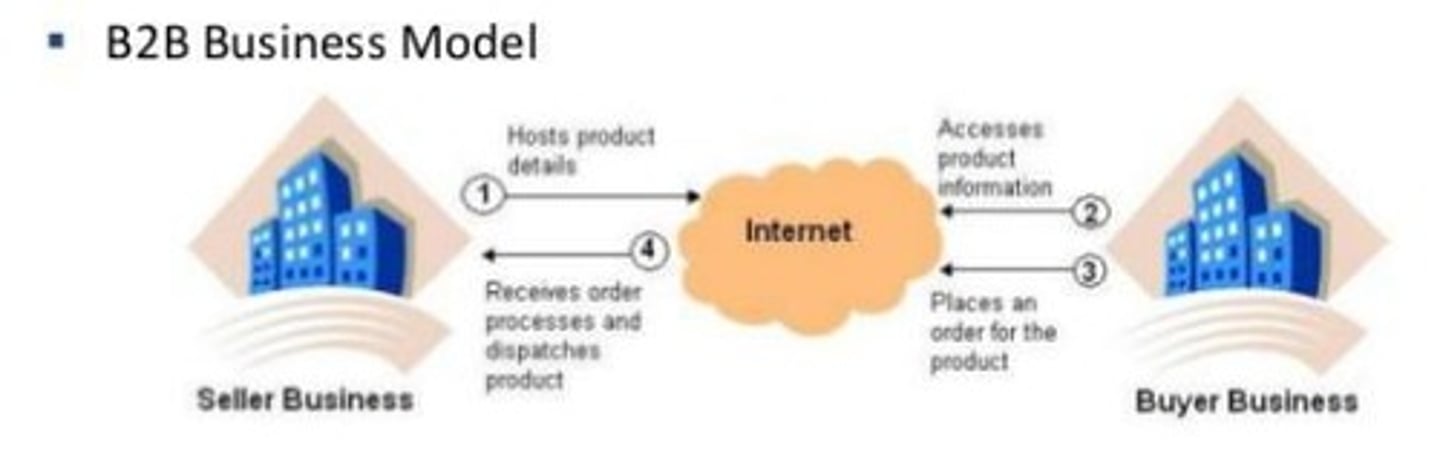
B2B
Transactions between firms.
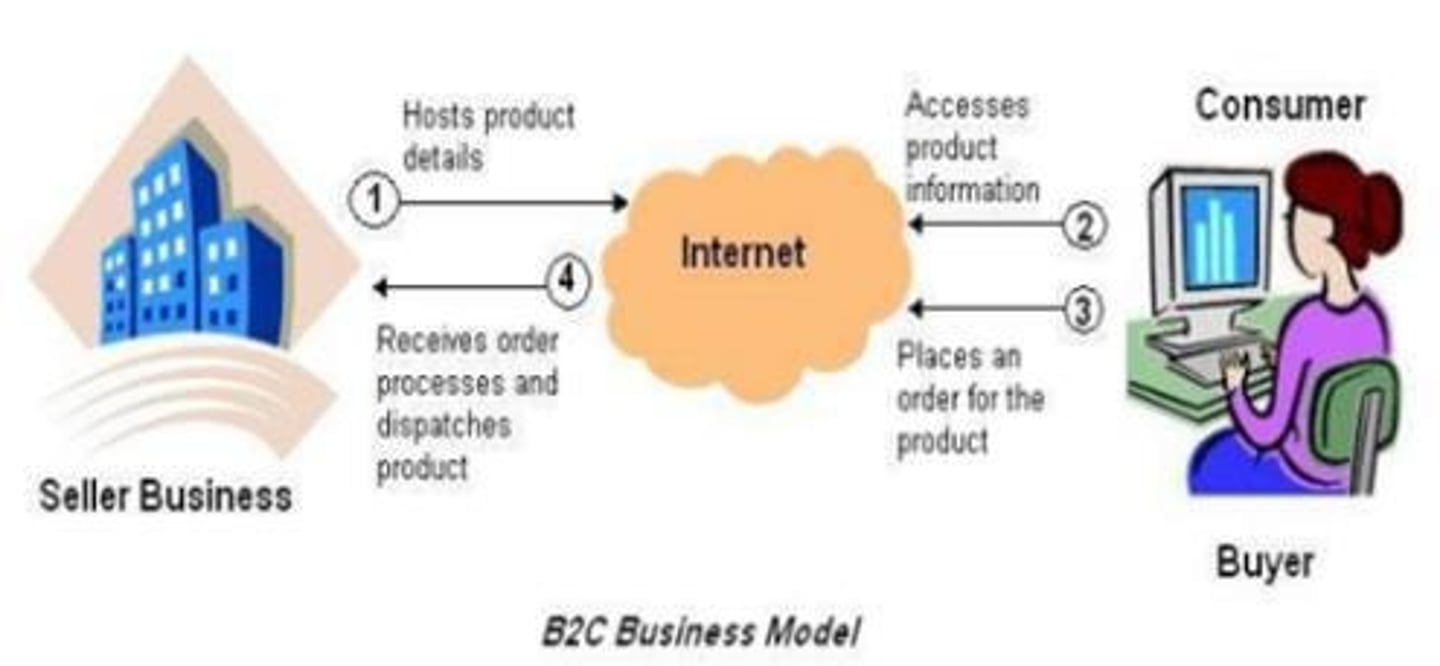
B2C
Describes firms that sell goods or services to a final consumer.
C2B
Involves customers offering products or services to businesses.
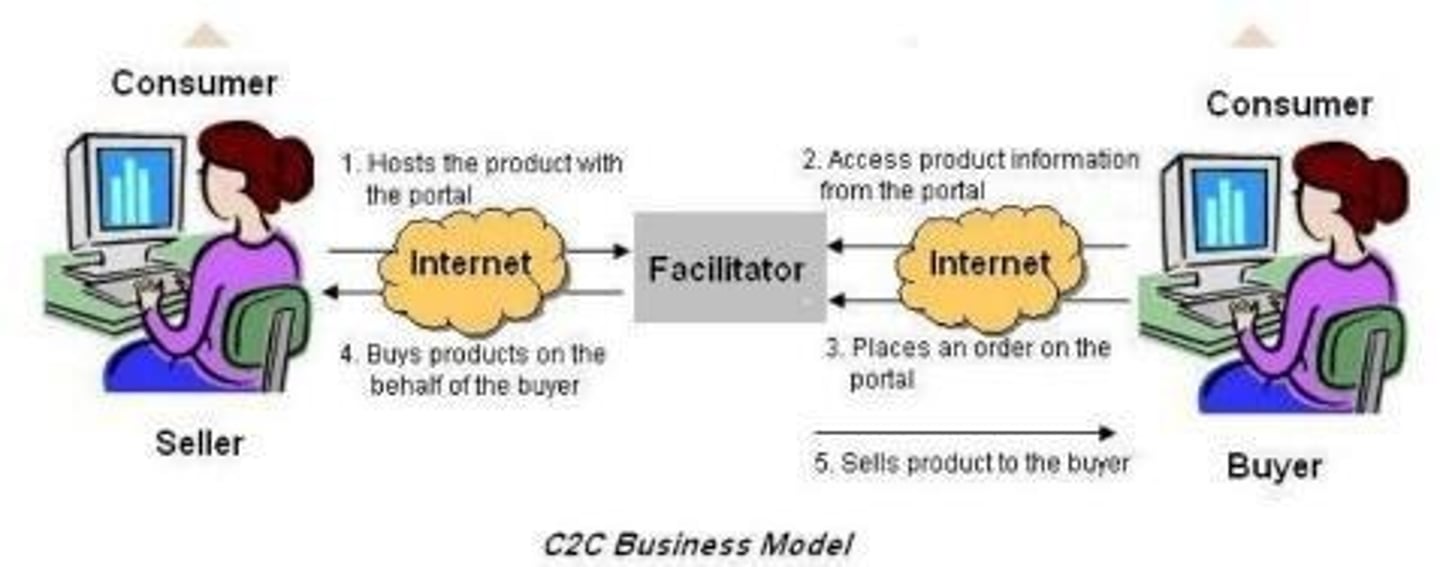
C2C
Applies to transactions between consumers.
G2B
Government to business transactions.
G2C
Government to consumer transactions.
B2B2C2C
Describes the all-in-one platform for interactive transaction of selling goods or services among firms and consumers.
B2B Business Model
Facilitating online sales and improving relationships with employees, businesses, citizens, and other government agencies.
B2C Business Model
Describes the business model where businesses sell directly to consumers.
C2C Business Model
Facilitates transactions between consumers.
C2B Business Model
Streamlining procurement processes and improving supply chain efficiency.
E-Government Models
Provides and improves online services and transactions with various stakeholders.
Mobile Commerce
Delivery of e-commerce capabilities via wireless technology.
E-Payment
Electronic transfer of money from one account to another.