BIOL 1306 Test 3 Study Guide
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
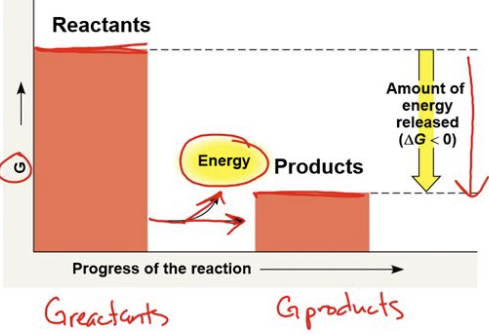
free energy
represents the energy available to do work in a system at constant temperature and pressure
determines the spontaneity and direction of reactions
drives an endergonic reaction when released from an exergonic reaction
exergonic
have a negative charge
energy of products is LOWER than energy of reactants
spontaneous but may still require an initial input of energy to overcome the activation energy barrier
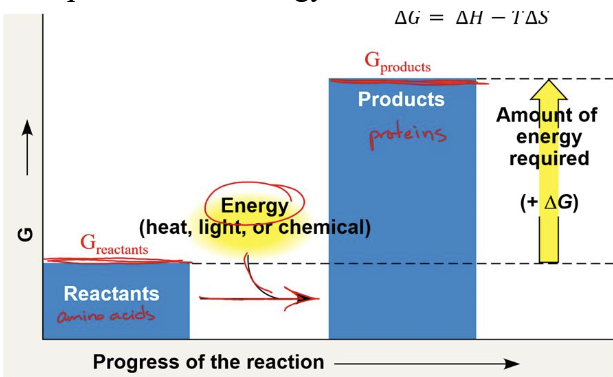
endergonic
have a positive charge
energy of products is GREATER than energy of reactants
not spontaneous & needs energy to start the reaction
catabolism
reactions that break down molecules and release energy
occurs in digestion, glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, etc.
eg. hydrolysis reactions
anabolism
synthesizing complex molecules and polymer by forming covalent bonds
requires energy input (often times from catabolism)
eg. dehydration reactions
activation energy
the minimum energy required to initiate a chem. reaction
energy required to change reactants from a stable to unstable state where electrons can be arranged
active site
the region of the enzyme that interacts with the substrate
has a unique structure and chemical properties with high selectivity that will bind to specific substrates
can be reused
substrate
reactant specific for a particular enzyme
can be simple molecules, complex molecules, and nucleic acids
catalyst
accelerates a chemical ration by decreasing activation energy
is not consumed during the reaction
enzyme activity
the rate at which the enzyme converts substrates to product(s)
depends on temp and pH
3D shape of protein can change, which alters its function
competitive inhibtor
attaches to the active site and blocks substrates from entering
reduces the activity of an enzyme
allosteric inhibitor
attaches to another region or enzyme
changes enzyme’s shape so the active site no longer grabs the substrate and altering the enzyme’s function
Interphase
where the cell spends most of its life
between one M phase and the next
includes G1, S phase, and G2
S phase
stands for synthesis of DNA
where chromosomes are copied to prepare for cell division
2nd phase in interphase
G1
where the cell grows, goes through cellular respiration, protein synthesis, and membrane transport
1st phase in interphase
In where does G1 causes cells to divide frequently?
epithelial cells and blood stem cells
In where does G1 may last for years and division can occur to repair injury?
liver cells
In where do certain cells remain in G0 after puberty and do not divide?
muscle cells and some nerve cells
G2
where the cell prepares for mitosis and ensures all DNA is replicated and any damage is repaired
final phase of interphase
mitosis
the process of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells, which have chromosomes and genes identical to the parent
involves prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Mitotic normal function
Reproduction of single-celled organisms (eg. amoeba)
Development from zygote to embryo and growth to adult
Renewal of tissues, especially epithelium
Centrosome: point of origin for microtubules
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two daughter cells, each with its own nucleus
occurs immediately after cell division by mitosis/meiosis
facilitated by the formation of a cleavage furrow
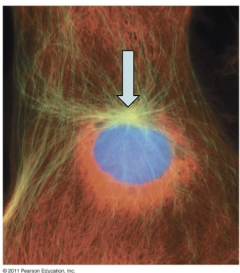
centrosome
point of origin for microtubules
crucial to organizing microtubules during cell division and maintaining the overall structure of the cell
help form the spindle fibers that separate chromosomes
duplicated during the cell cycle
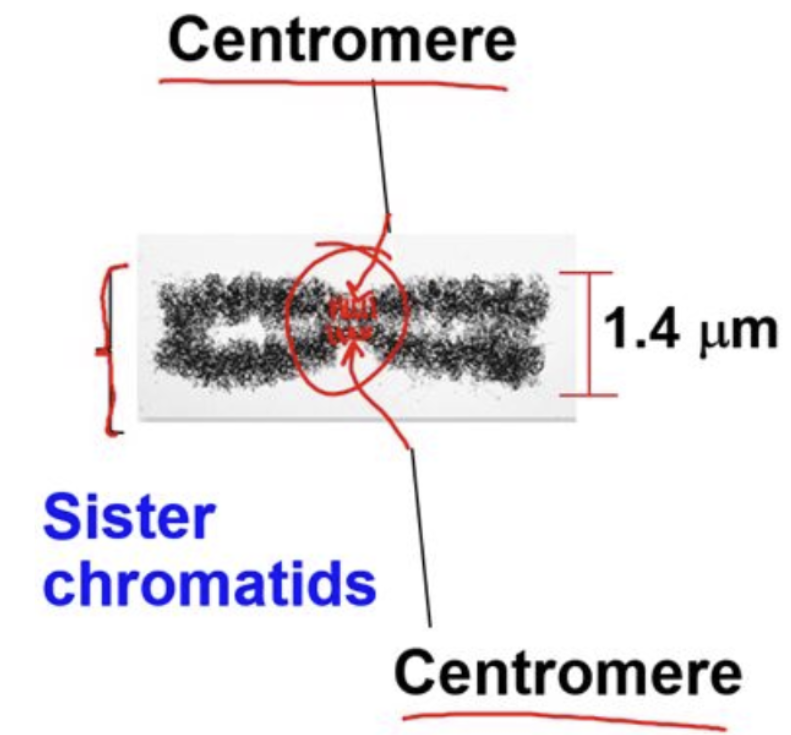
centromere
the point on a chromosome at which sister chromatids are closely attached
contains DNA sequences
where the spindle fibers attach to the chromosome to ensure proper segregation
where the kinetochore forms
chromosome
one double-stranded molecule of DNA wound around histone proteins
2 sets of 23 (one from mother, one from father)
chromatid
one of the two identical double-stranded DNAs that are connected at the centromere and compose a replicated chromosome (sister)
each has a kinetochore associated with its centromere
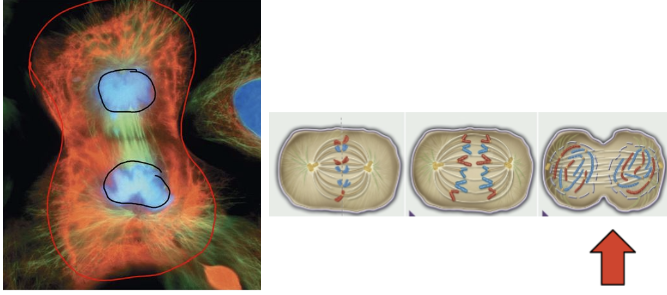
prophase
chromosomes condense
spindle apparatus forms
2nd centrosome forms
nuclear envelope begins to breakdown
nucleolus disappears
cytoskeleton of interphase is dismantled
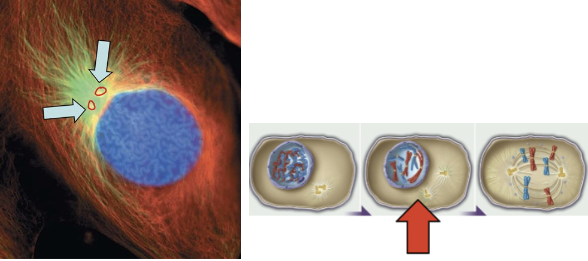
1st phase of mitosis
prophase
spindle apparatus
array of microtubules responsible for organizing and moving chromosomes during cell division
centriole
one of two small cylindrical structures contained within the centrosome near the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell
plays a role in the organization of the mitotic spindle
prometaphase
nuclear envelope breaks down and disappears
centrosomes are at opposite poles
spindle fibers attach to kinetochores or interact with microtubules from opposite pole
2nd phase of mitosis
prometaphase
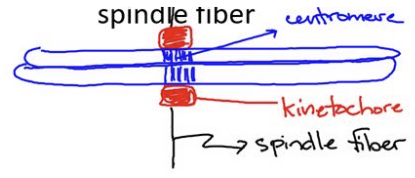
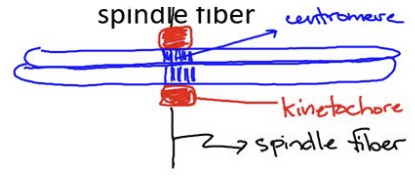
kinetochore
protein structure that links the centromere to the spindle fiber
facilitates the attachment of chromosomes to the mitotic spindle
involved in chromosome segregation during cell division
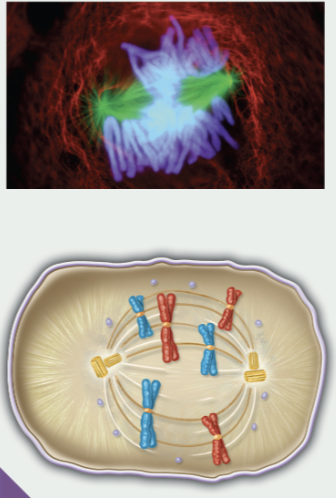
metaphase
chromosomes are in the middle of the spindle
kinetochore of each chromatid is attached to the microtubule from the opposite pole
centrosomes at opposite poles
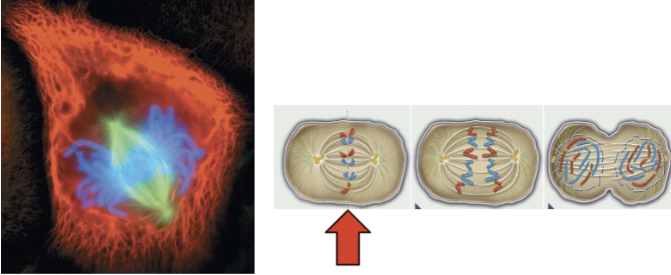
3rd phase of mitosis
metaphase
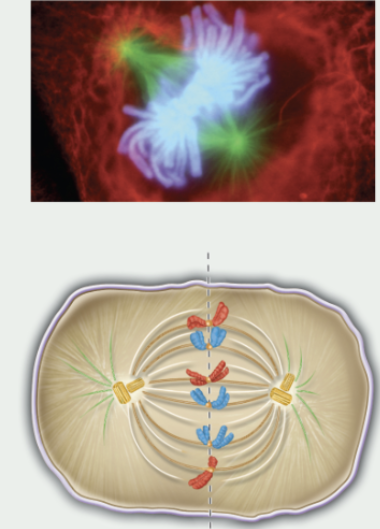
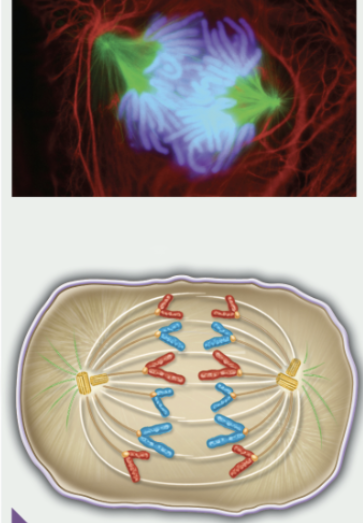
anaphase
sister chromatids separate
kinetochore microtubules shorten
chromosomes move to opposite poles of the spindle apparatus
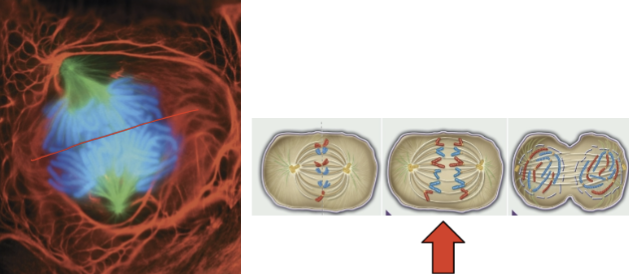
4th phase of mitosis
anaphase
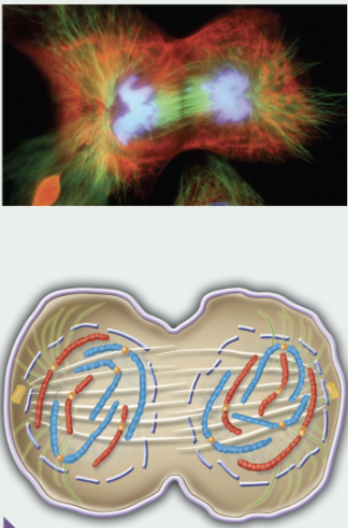
telophase
chromosomes de-condense back into chromatin
nuclear envelope re-forms, making 2 nuclei
spindle microtubules break down/depolymerize
nucleoli re-appear, making ribosomes
rebuilding of interphase cytoskeleton
5th & final phase of mitosis
telophase
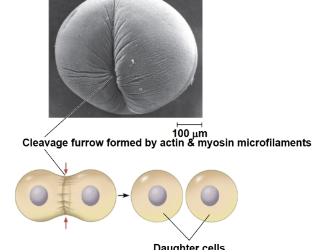
cleavage furrow
an indentation in the cell surface that occurs as the plasma membrane is pulled inward during cytokinesis
deepens until the membrane fuses, dividing the cytoplasm into two daughter cells
adaptation
heritable characteristics that enhances survival and reproduction
good enough but not perfect
frequency can change between generations
acclimatization
short-term change in an individual’s physiology in response to a change in the environment
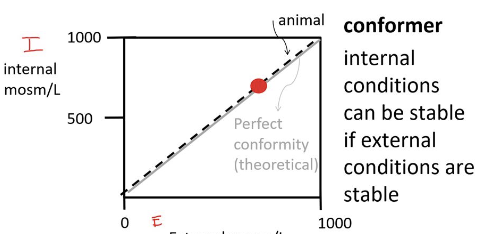
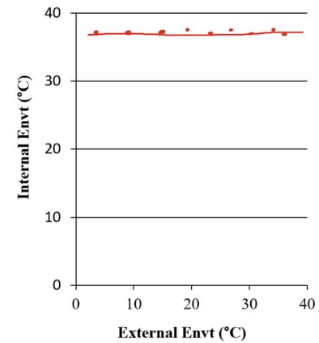
conformer
an organism that adjusts to its environment, allowing its internal conditions to change with external factors
ectotherms, such as fish, amphibians, and reptiles
limited range of environments to survive in
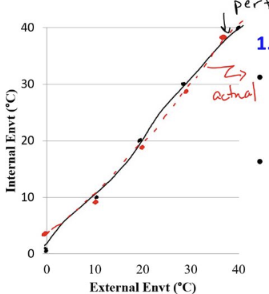
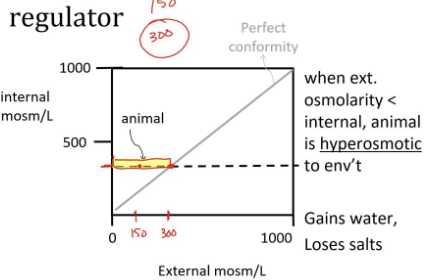
regulator
an organism that maintains homeostasis and regulate internal conditions despite changes in the external environment
uses energy to counteract environmental changes
endotherms, such as birds and mammals
homeostasis
maintaining a predictable and stable internal environment
insulin
peptide hormone
secreted by the pancreas in response to high levels of glucose in the blood
enables cells to absorb glucose
glucagon
peptide hormone
secreted by the pancreas in response to low blood glucose levels
ectotherm
cold-blooded
source of heat from the external environment
eg. fish, amphibians, and reptiles
endotherm
warm-blooded
source of heat from the internal metabolism
eg. birds and mammals
convection
heat transfer by a moving fluid
conduction
heat transfer between objects in direct contact
radiation
electromagnetic radiation
any object warmer than 0 K radiates infrared
evaporation
liquid molecules with the highest kinetic energy escape into the gas phase
removes heat from the animal
osmolarity
The concentration of dissolved solutes in a solution, measured in osmoles per liter
moles solute particles/L
units: mosm/L
(# of ions)(concentration)
eg. 50 mM NaCl sol’n - ionic, dissociates into (2) ions -> (Na+ and Cl-)
2 x 50 mM = 100 mOsm
eg. 50 mM glucose sol’n - covalently bonded, doesn't dissociate
1 x 50 mM = 50 mOsm
hyposmotic
a solution that has a LOWER solute concentration & HIGHER water concentration than another solution
swelling and cell lysis
hyperosmotic
a solution that has a HIGHER solute concentration & LOWER water concentration than another solution
dehydration
cell shrinkage
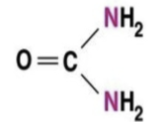
ammonia
NH3
is the byproduct of the breakdown of proteins and nucleic acids in cells
is a metabolic waste that is excreted
toxic to cells
major nitrogenous waste of bony fishes and aquatic invertebrates
urea
synthesized from NH3 by vertebrate liver
less toxic than NH3
requires less H2O to excrete than NH3
require energy to synthesize
is a metabolic waste excreted by mammals, adult amphibians, sharks, and some marine fish
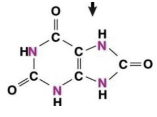
uric acid
low toxicity
generates H2O
requires energy to synthesize from NH3
is a metabolic waste excreted as a paste by birds, reptiles, insects, and snails
hemolymph
the circulatory fluid of animals with open circulatory systems (eg. insects), in which the fluid is not confined to blood vessels
interstitial fluid
fluid in extracellular space surrounding body cells
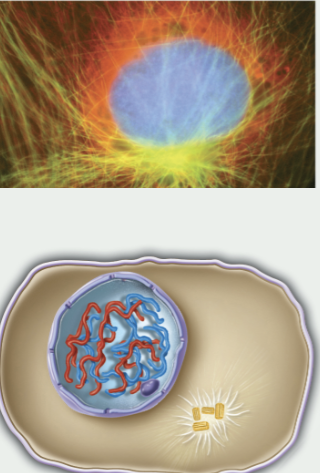
interphase
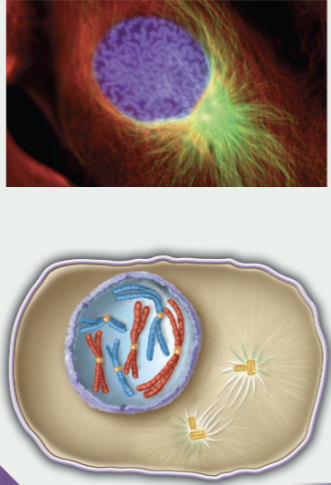
prophase
prometaphase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
What is the ploidy level at the beginning of cell division?
diploid (2n); 46 chromosomes
What is the ploidy level at the end of cell division?
diploid in each identical daughter cell (2n); 46 chromosomes
Daughter cells are genetically
identical to the parent cell
counter-current exchange of heat between blood vessels entering and exiting an appendage
a physiological mechanism that helps conserve body heat in animals, especially in cold environments
occurs when two blood vessels—one carrying warm blood from the core of the body and the other carrying cooler blood from the appendage—pass in close proximity to each other and exchange heat in opposite directions
artery
carries warm blood from the body’s core toward the appendage
vein
returns cooler blood from the appendages back to the core of the body
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
a hormone that helps regulate ingestion, digestion, and absorption of nutrients
secreted by the small intestine
Gastrin
a hormone produced from the stomach lining in response to the arrival of food or to a neural signal from the brain
stimulates other stomach cells to release HCl
Secretin
peptide hormone secreted by cells in the small intestine in response to the arrival of food from the stomach
stimulates secretion of bicarbonate ions by the pancreas
Challenges to freshwater fish
water gain
salt loss
Solutions to challenges to freshwater fish
Import NA+ and Cl- by active transport
Excrete dilute urine
Net result: solute conservation
Challenges to marine animals
water loss
salt gain
Solutions to challenges to marine animals
Drink salt water
Excrete Na+ & Cl- by active transport
Net result: water conservation
Challenges to terrestrial animals
dehydration
Solutions to challenges to terrestrial animals
Nocturnal activity
Waxy coating on the exoskeleton
Keratinized skin
ammonia advantages
low energy cost
simple excretion
small molecular size
ammonia disadvantages
high toxicity
requires a large amount of water
limited to aquatic environments
urea advantages
lower toxicity
moderate water requirement
more adaptable
urea disadvantages
energy cost
requires some water
uric acid advantages
low toxicity
minimal water loss
ideal for water-conserving environments
uric acid disadvantages
high energy cost
waste accumulation
potential for solid waste
Why does excreting urea or uric acid requires energy?
both processes involve detoxifying ammonia (a byproduct of protein and nucleic acid breakdown) and converting it into less toxic forms, which requires energy
solute movement across transport epithelia in marine vertebrates
focus heavily on salt excretion and water conservation to maintain osmotic balance in a hyperosmotic environment (salt water), with specialized gill cells and salt glands
solute movement across transport epithelia in mammalian kidney
adapted for a broader set of functions, including waste excretion, regulation of electrolyte balance, and water conservation in a hypoosmotic environment (terrestrial life)
step 1 of reabsorbing water across the kidney epithelium
Na⁺-K⁺-ATPase in basolateral membrane creates a Na+ gradient
step 2 of reabsorbing water across the kidney epithelium
Na+ gradient drives the co-transport of glucose, Cl- & vitamins into cells through co-transporters in the apical membrane
step 3 of reabsorbing water across the kidney epithelium
high solute concentration makes epithelial cell hyperosmotic to blood
step 4 of reabsorbing water across the kidney epithelium
each solute diffuses across the basolateral membrane and reenters blood
step 5 of reabsorbing water across the kidney epithelium
H2O diffuses through aquaporins in apical membrane and in basolateral membrane
step 6 of reabsorbing water across the kidney epithelium
H2O reenters blood
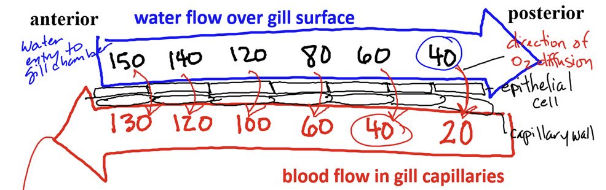
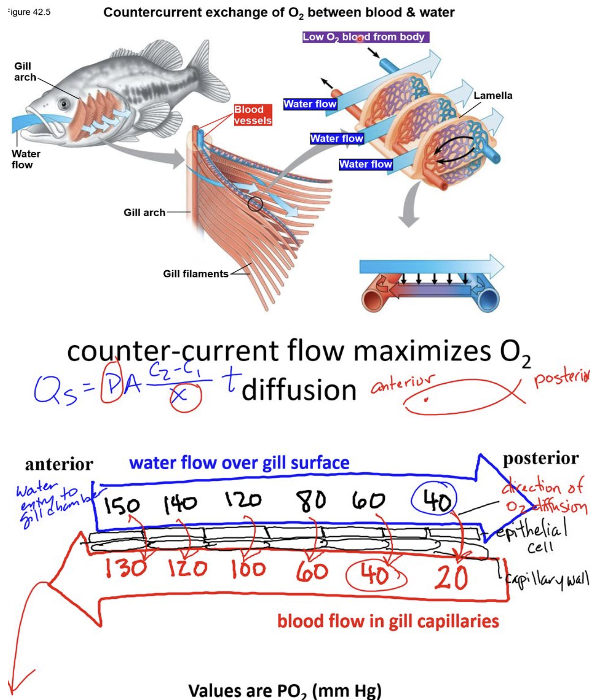
Describe solute movement across transport epithelia in fish gills
there is a countercurrent exchange of O2 between blood and water (where water flows over the gill filament in the opposite direction from the blood flowing inside the gill filament), which maximizes O2 diffusion into the blood and prevents equilibrium PO2 from developing between water and blood
What would happen to the blood osmolarity if Na⁺-K⁺-ATPase is inhibited in the nephron epithelial cells of a terrestrial vertebrate?
disruption of sodium and water reabsorption in the kidneys
reduced generation of the osmotic gradient necessary for eater reabsorption
increased urine volume with more dilute urine
increased blood osmolarity
potential dehydration and electrolyte imbalances
What would happen to the blood osmolarity if the number of aquaporins increases in a terrestrial vertebrate's epithelial cell membrane?
more water reabsorbed from the filtrate into the blood
less urine produced, and urine is more concentrated
blood osmolarity decreases (more water in the blood)