Molecular Biology and Cell Membrane Concepts
1/284
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
285 Terms
Molecular biology
Group of processes to manipulate, analyze, expand, and express nucleotide sequences
Gene transfection
Inserting intact functioning genes
regulated GFP reporter
two types transient and stable
Genomics
Studying an organism's genome
Gene editing
Adding or removing a few bases or full genes
ex. CRISPR or organ xenotransplantation
CRISPR
A method used in gene editing. CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to edit genes in cells and tissues, potentially correcting the genetic basis of inherited diseases like sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and hemophilia.
Organ xenotransplantation
Transplanting organs from one species to another.
Controlling gene expression
Manipulating the expression of genes.
Gene knock in/knock out
Techniques used to add or remove genes from an organism.
embryonic cells are injected to mice
siRNA (small interferring)
DSRNA (double stranded) that will silence genes complementary to its sequencing via RNAi (RNA interference).
used for transient trasnfection
used to treat huntingtons disease (break down nerve endings) (less likely to have cancer)
shRNA
Same idea as siRNA but is in a hairpin shape.
used for both transfections
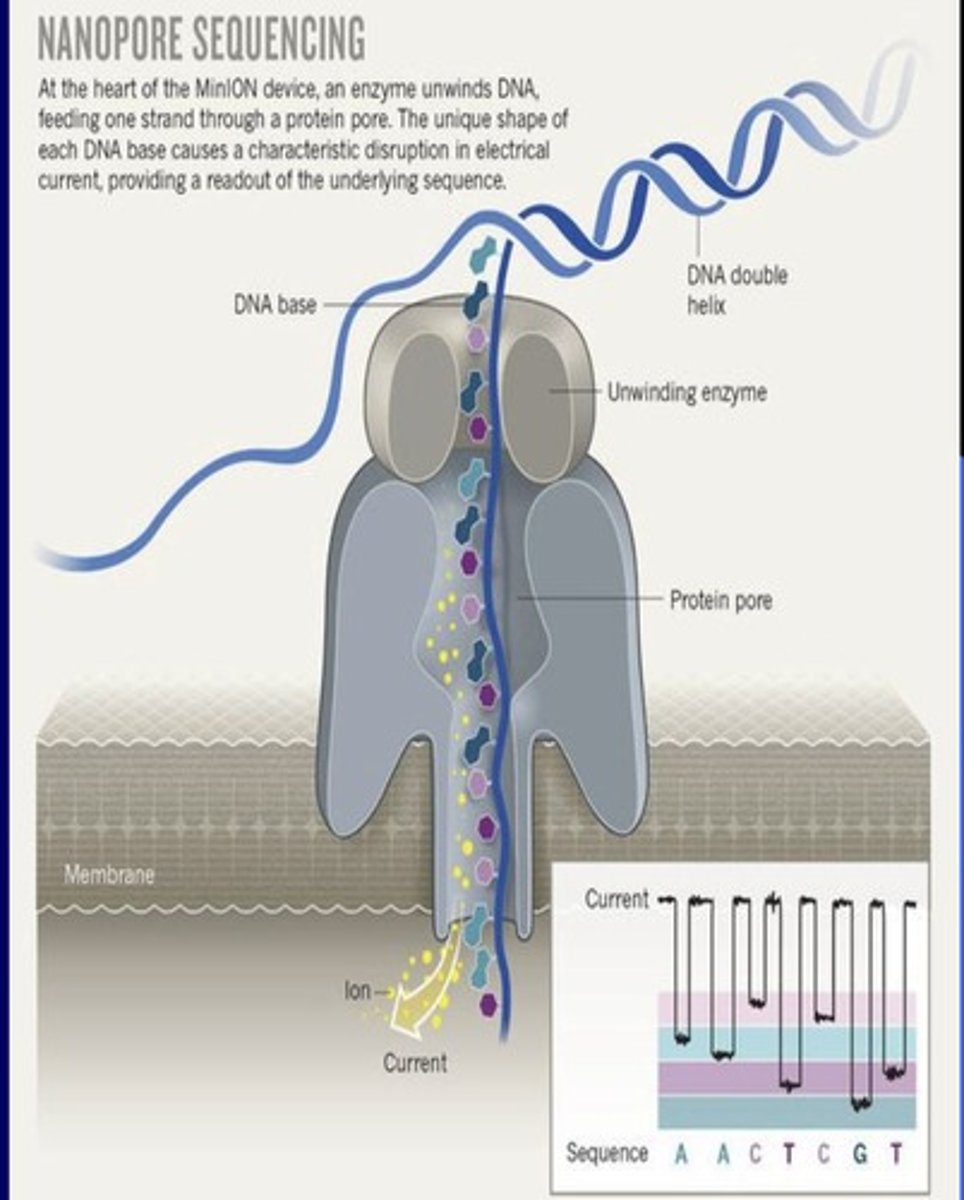
Oxford nanopore technology
1.Enzyme will pull DNA through a pore in a naturally occurring membrane protein.
2. The enzyme will unwind the DNA and the nucleotide
sequencing can be read as the DNA is brought through the
pore
3. Ion current can be used to read the nucleotide sequence
Transcriptomes
Umbrella term for RNA.
a). mRNA
b). tRNA
Proteomics
Study of all proteins.
Epigenetics
Change in DNA expression that can be reversed.
methylation
histone phorphorylation
Methylation
A process that can affect gene expression without changing the DNA sequence.
Histone phosphorylation
Modification of histone proteins that can influence gene expression.
Mutation
Damage to DNA bases.
many causes:
uv light
photo will hit the bases and destroy them
when bases are repaired they might not be correctly fixed
-chemicals
Metabolome
Small molecules found in a biological sample.
Secretome
Anything secreted by a biological sample.
ex. protein, cfDNA, exosomes
Cytokine storms
Overactivation of inflammatory immune cells.
can cause ARDS and MOF
STEM cell exosomes decrease cytokin storms
***Downgrades CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, regulatory T cells
***Upregulates hyperactivated T cells
Temperature sensitive mutants
Used to study in vivo (living) and in vitro (laboratory) protein function at higher temperatures.
genes that exhibit permissive (normal function) temp at 23 degrees celsius and non permissive temp (non functional) at 36 degrees celsius
cant grow at non permissive anymore because growth related proteins are denatured
ex. yeast
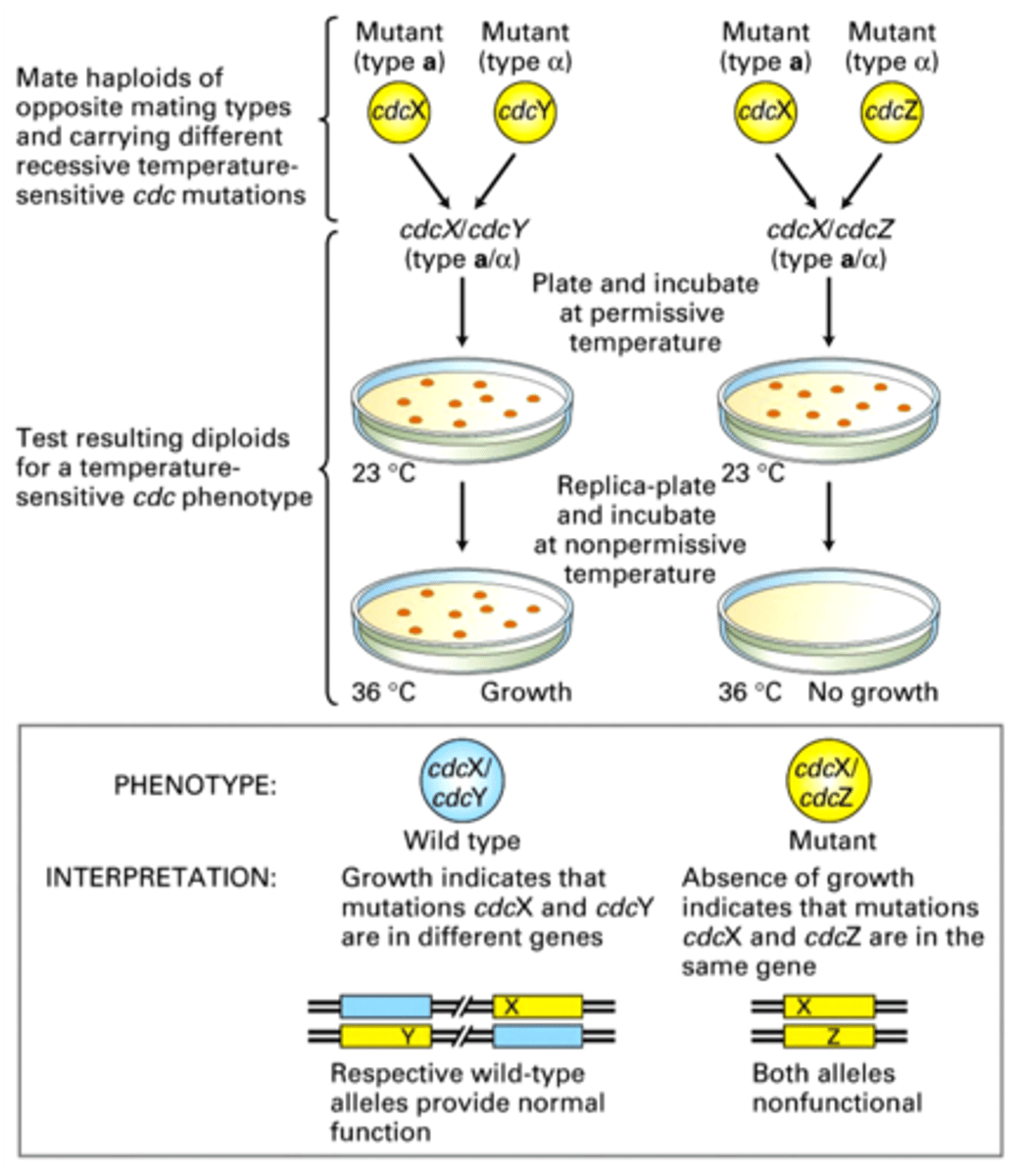
Complementation analysis
Used to see if two mutations are on the same gene.
if they were on the same gene then there would be no growth because the mutation makes them temperature sensitive so the dominant gene couldnt grow even at 36 degrees Celsius
Restriction nucleases/enzymes
Used to manage DNA and enable gene transcription (RNA copy)
discovered in 1963 in bacteria so they can ward off viruses
600+ commercially available
cleaves DNA or RNA at restriction sits
Hybridization
Used for techniques such as FISH, antisense DNA/RNA, Northern and southern blots, cDNA microarrays, and molecular beacons.
DNA gel electrophoresis
A technique that separates DNA fragments based on size.
evolved from SDS gel electrophoresis
-uses restriction enzymes
-uses polycrimaline sieve for smaller dNA fragments
-uses agarose sieve for larger DNA fragments
Band/gel shift experiment
An experiment to determine if a protein of interest (POI) binds to a gene of interest (GOI) by comparing gel bands.
if ban is higher up, poi has bound to GOI and hold it up from falling
apopotosis necrosis
apoptosis will show up as a ladder
necrosis= a continuous streak
electrophoresis
SDS gel electrophoresis
A method that DNA gel electrophoresis evolved from.
Restriction enzymes
Enzymes used to cut DNA at specific sequences.
Polyacrylamide sieve
A medium used for separating smaller DNA fragments.
Agarose sieve
A medium used for separating larger DNA fragments.
Apoptosis
A form of programmed cell death that induces non-random DNA cleavage.
Necrosis
A form of cell death that induces random DNA cleavage.
Southern blots
(1) DNA gel electrophoresis bands placed onto blotting paper (nitrocellulose membrane) (a) Nitrocellulose membrane placed on top of gel inside alkaline solution (b) Bands transfer from the gel to the membrane
Nitrocellulose membrane
A type of blotting paper used in Southern blots.
Complementary DNA/RNA probe
A probe used to detect specific DNA/RNA sequences, often radioactive.
Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs)
Regions of the genome where short strands of nucleotides are repeated adjacent to each other
used in forensic medicine
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
Genetic variations that looks at sigle nucleotide differences primarily in noncoding genes
98-99% of genes are non coding so 1 base can make a big difference in the coding region
used for personalized medicine
Northern blots
A technique similar to Southern blots but used for tracking RNA instead of DNA.
-used to measure gene expression (mRNA)
-can only analyze 1 mRNA transcript at a time
-if we look at multiple mRNA transcripts we will get mixed up on what is used to code what
Snow=drop
Southern= DNA
Northern=RNA
Western= proteins
Gene expression
The process by which information from a gene is used to synthesize functional gene products, typically proteins.
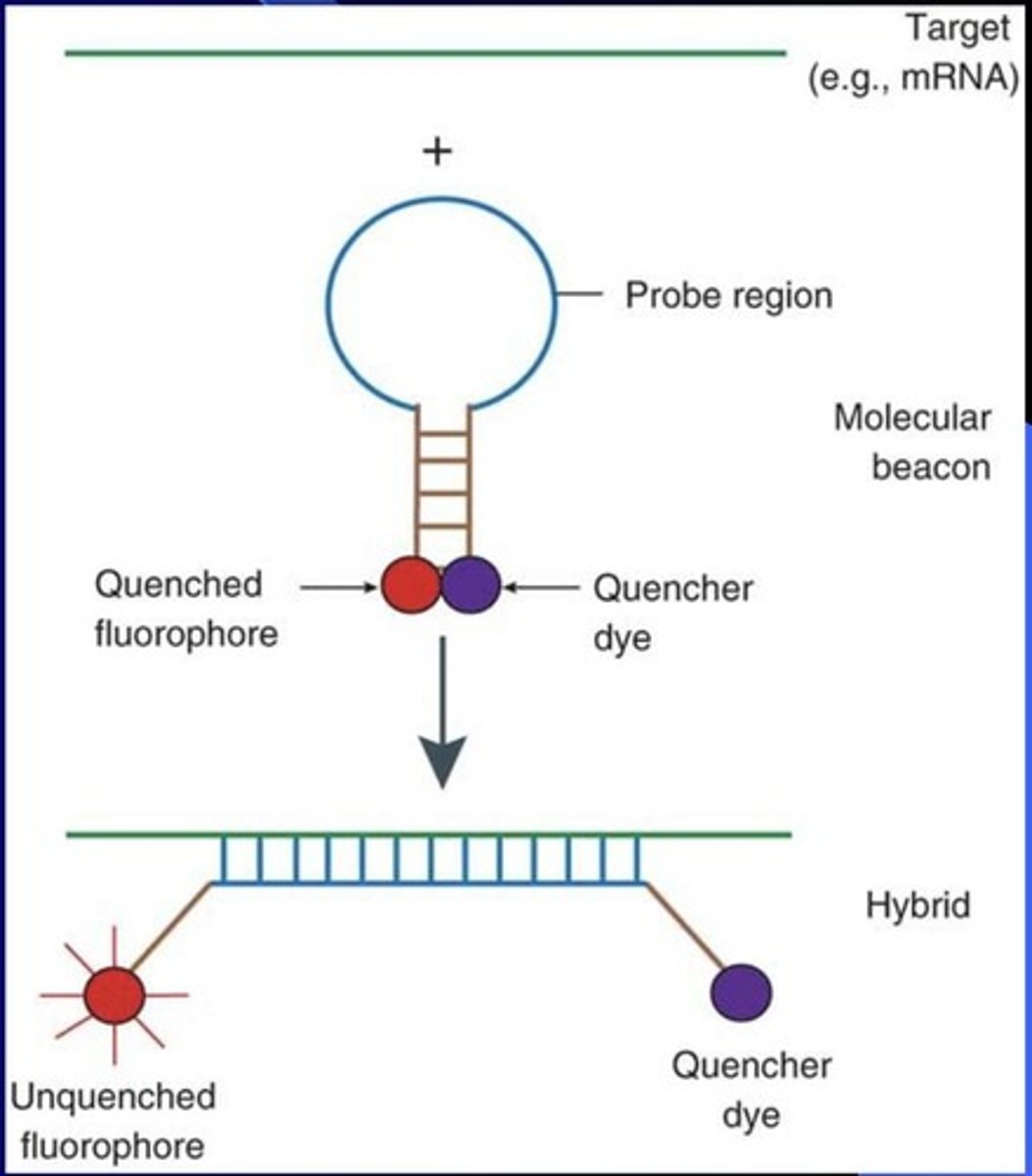
Molecular beacons
(1) Takes RNA or ssDNA complementary probe that has fluorophore and quencher dye on either end (2) The probe region is circular so the fluorophore and quencher dye are next to each other (3) Complementary probe bound to the target (a) Fluorophore and quencher dye are farther away and the fluorophore will fluoresce (b) Tells us the same thing as FISH but is more efficient
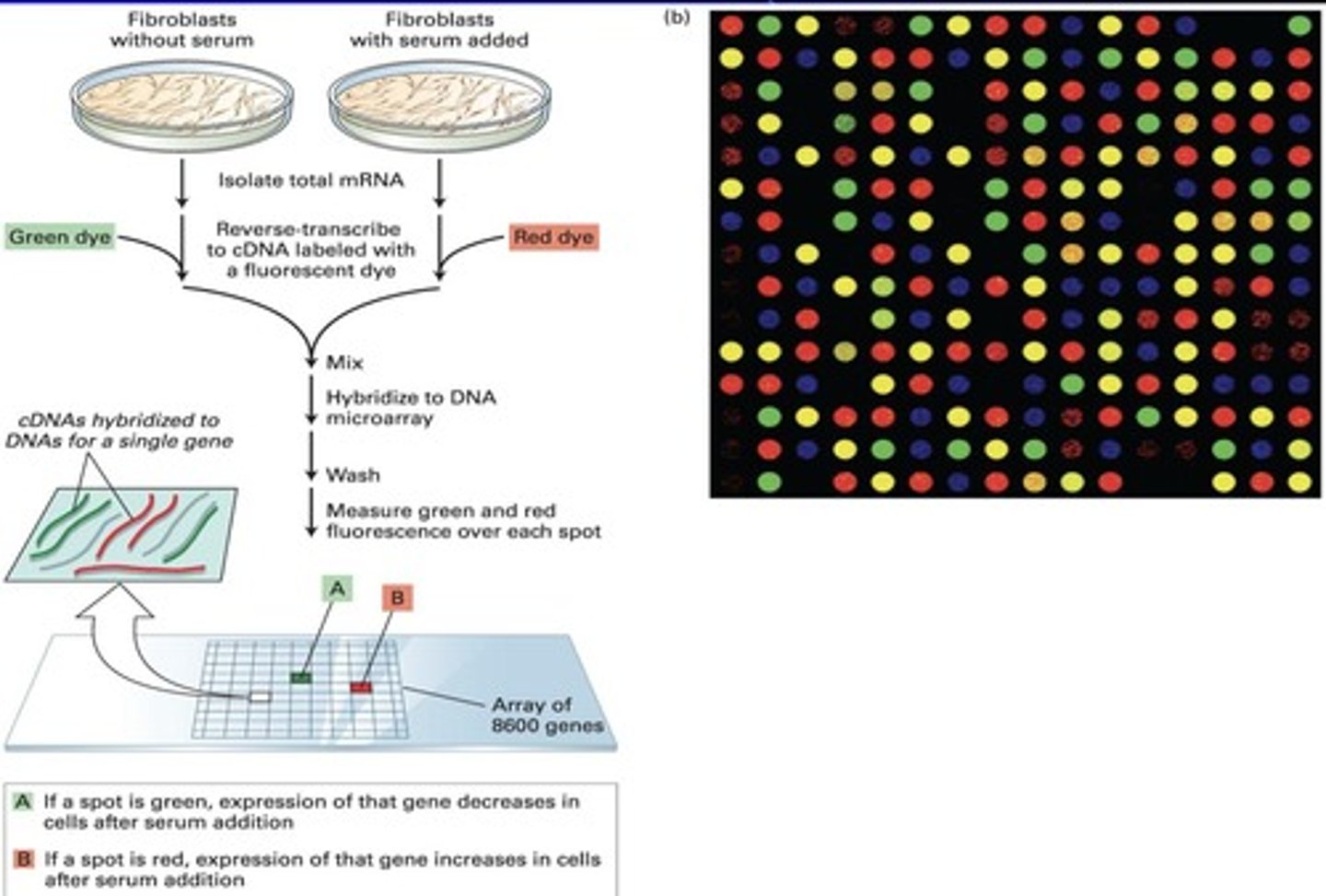
cDNA (complementary DNA) microarrays
used to examine up to 8600 genes expressed
harvest mRNA cells and reverse transciptast them to form sscDNA
transfection delivery methods
Transient transfection (i) cDNA placed onto a vector (ii) (iii) Electroporation used to allow vector into cells Used for short term protein synthesis (b) Stable transfection (i) Same as transient transfection except this introduces the GOI permanently in the cell (ii) Will cause permanent protein synthesis c) Both types of cloning require cutting out pieces of bacterial plasmid vectors to place the DNA or cDNA i
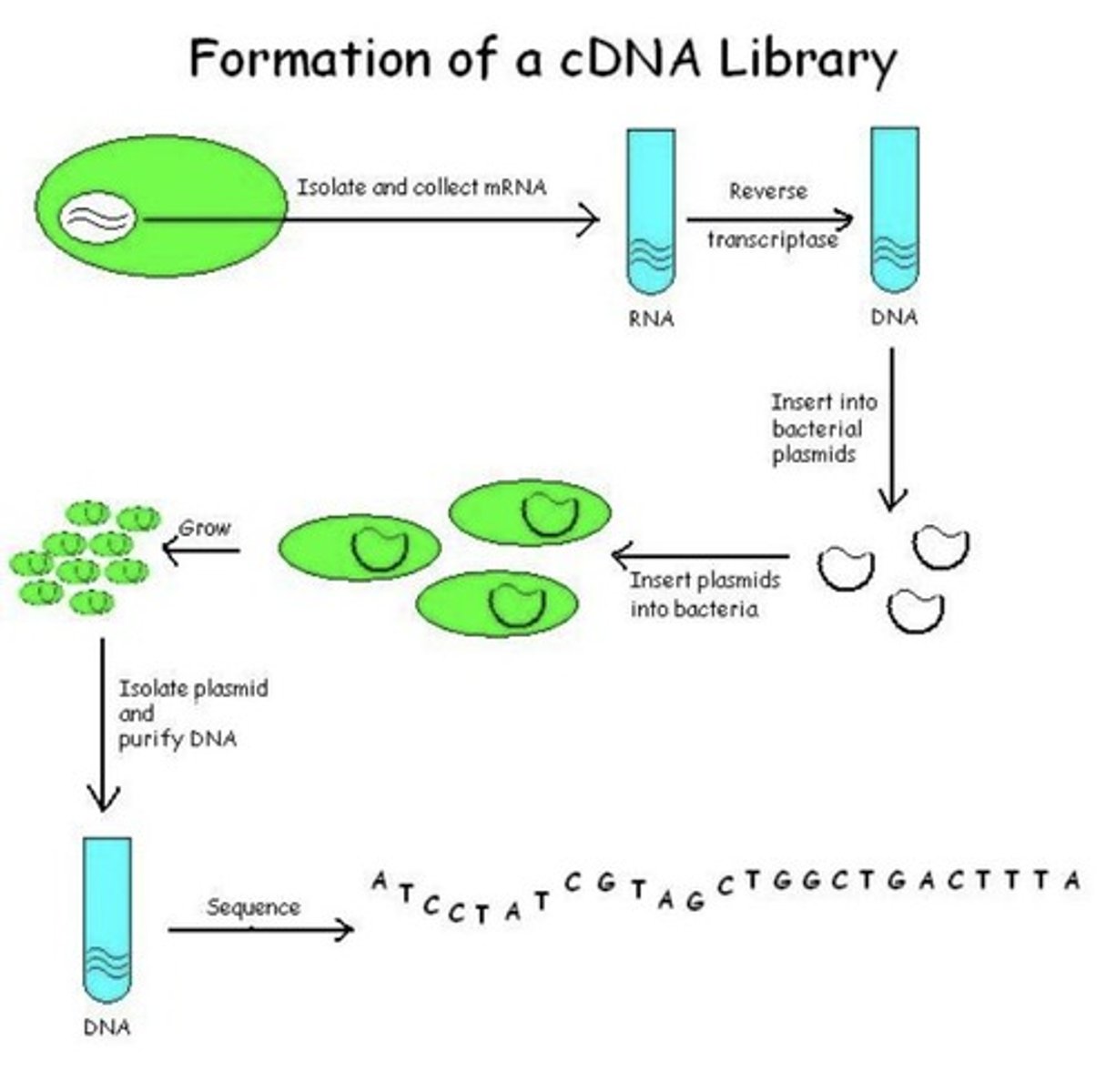
Reverse transcriptase
An enzyme used to convert mRNA into complementary DNA (cDNA).
Fluorescent dyes
Dyes used to tag cDNA in microarray experiments for visualization.
Oligonucleotides
Short DNA or RNA sequences used in microarrays to capture cDNA.
Single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq)
Sequences RNA to determine gene expression of a cell.
-used in tissue engineering
-RNA signature
(1) Part of mRNA that is reflective based off the state of the cell (a) Healthy
(b) Diseased
(c) Old
(d) Etc
RNA signature
Part of mRNA that is reflective based off the state of the cell.
Single cell genome sequencing
Taking a cells genome and comparing it to sequencing library for analysis.
-can tell you cell type
-cells from a tissue sample MUST be sorted before sequenced
Genetic cloning
The process of creating copies of DNA fragments.
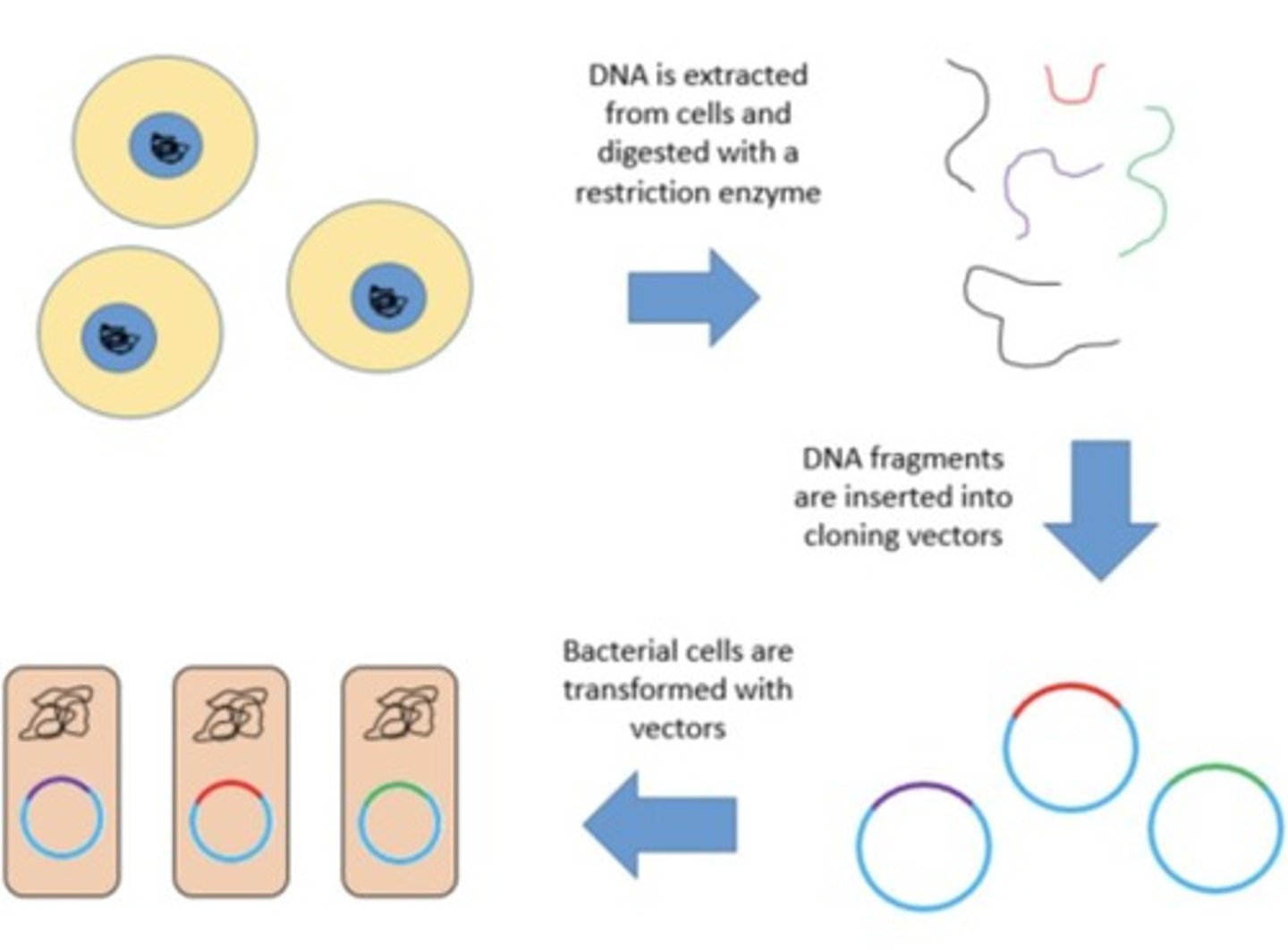
Genomic cloning
Take all the DNA of one organism, place it into vector, place vector into bacteria (E.coli).
(a) When bacteria undergo mitosis, the gene will be cloned along with the entire genome that we inserted into the vector (2) GOI will always be in the DNA but it is harder to search for it specifically
cDNA cloning
Reverse transcript mRNA to form cDNA of GOI that we place into vector that we place into bacteria (E.coli).
GOI will only be clones if it is used by the E.coli
takes longer than genomic cloning
can make humulin from E.coli by taking out lac operon, place G-SCF cDNA instead
GOI
Gene of Interest.
Humulin
Insulin produced from E.coli, commercially available since 1982.
it works with e.coli bc or pur luck
Transient transfection
cDNA placed onto a vector and electroporation used to allow vector into cells for short term protein synthesis.
Stable transfection
Introduces the GOI permanently in the cell, causing permanent protein synthesis.
PCR
Polymerase chain reaction, used to expand a DNA sample.
c) Uses taq polymerase (1) Heat resistant DNA polymerase
Taq polymerase
Heat resistant DNA polymerase used in PCR.
Transgenic mice
a) Take foreign DNA that you want to study
b) Inject it into fertilized egg cell nucleus
c) Place egg into mother rat
(1) 10-30% chance offspring will have foreign DNA
d) Mice expressing foreign dna are rebred so we can have 100% if
them having foreign DNA
Antisense DNA/RNA
Used to knock in or knock out genes by blocking mRNA coding for a specific protein.
-less effective than si/shRNA
siRNA
Simpler to make than shRNA, used for transient transfection.
short term protein synthesis
-hard to transfect
-used to treat huntingtins disease
Huntington's disease (HD)
Causes breakdown of nerve cells, associated with high levels of huntingtin mRNA.
shRNA
Harder to make than siRNA, used for transient and stable transfection.
gene stays in the genome
Schleiden and Schwann
Suggested there is a 'barrier' between cells in 1830s.
Overton
Used lipid soluble dyes to penetrate cells and determined 'barrier' was made of lipids in the 1890s.
Langmuir trough experiment
Used water surface and placed phospholipids on the water to measure lateral pressure.
when too much pressure the phospholipids formed a double layer
membrane was either mono or bi layered
Phospholipids
Molecules that form the bilayer structure of cell membranes.
Electroporation
A technique used to introduce DNA into cells by applying an electrical field.
Bacterial plasmid vectors
Circular DNA molecules used to transfer genetic material into bacteria.
Gorter and Grended
Extracted phospholipids from RBC to see if membrane is mono or bi layered.
membrane was bi layered
Mudd's Experiment
Placed RBC and WBC in water and mixed them; RBC stayed on top and WBC on bottom.
Membrane Composition
Determined that membrane is made up of phospholipids AND proteins.
Davson-Danielli Model
Depicted membrane as phospholipid bilayer sandwiched between 2 protein layers.
Robertson's TEM Observation
Used TEM to observe cell membrane and used OsO4 for staining.
proved the davson-danielli model
Freeze Fracture Technique
Originally developed for quick fixation like cryosectioning; did not work for this.
E Face Freeze Fracture
Shows inner membrane of cell.
P Face Freeze Fracture
Shows cytoplasm; more bumps than E face.
mosaic freeze fracture
shows most bumps
Cell Fusion Experiment
Fused human and mice cells; integral membranes can be fluid
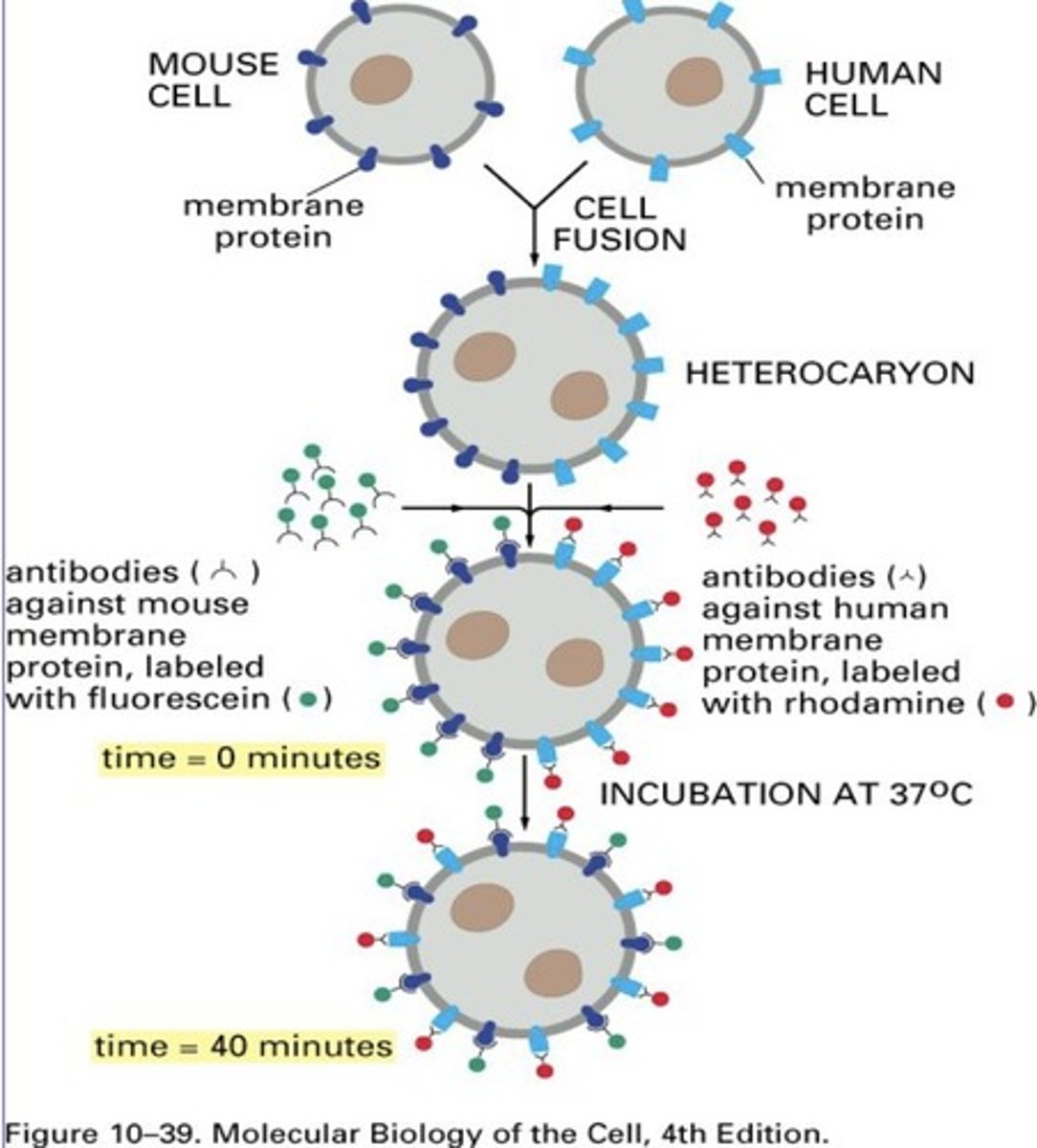
Cell Patching
We add anti-X Abs; protein X will start to patch up in certain parts.
Capping
Visualizing the concentration of the protein in the part of the cell it clusters in.
Con A FRAP
Uses concanavalin A. binds to carbohydrates and glycosylated proteins.
-most proteins on membrane are glycosylated
used for FRAP
Fluidity of Membrane Proteins
Showed that half of proteins are fluid but not all; stationary proteins stay in place due to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix.
Mosaic Model
Accurate description of how the cell membrane actually looks.
Advantages of Using RBCs
-Easily purified
-simple centrifugation can separate RBC from WBC.
-RBC has no toher membranes or organelles
-has few cell proteins
-RBC ghosts
RBC Ghosts
RBC undergoes hypotonic lysis; disturbed and resealed to see inner and outer membrane proteins.
RBC Half Life
RBC has half life of ~ 120 days; when RBC gets old, it undergoes shape changes and the body will replace the old ones.
Sickle Cell Anemia
RBC has shorter half life because it is oddly shaped when first produced.
Phosphoglycerides
part of inner membrane that moves to outer membrane in apoptosis.
Sphingolipids
Sphingomyelin is important for nerves and myelin; associated with demyelinating diseases like multiple sclerosis and dementia.
Cholesterol (steroids)
50% of all cholesterol is found in cell membrane; precursor to hormones, Vit D, steroids.
Statins
Gets rid of LDL by interfering with pathway we don't need; LDL causes several health problems.
Flippase
Also known as ABCB4; is an ATPase; can take phospholipids from inner membrane and flip them to outer membrane.
Phospholipid synthesis
Phospholipids are synthesized in the smooth ER inside the cell.
Transport of phospholipids and cholesterol
Not really known; 3 possibilities: vesicles transport them, proteins pinch membrane inwards, or proteins in cytosol transport them.
Integral cell membrane proteins
Typically transmembrane proteins; protein is sticking out of membrane inside and outside the cell.
shows up one only one layer
Peripheral membrane proteins
Lipid anchored proteins; can be single pass or triple pass transmembrane proteins.
Glycophorin
Single pass dimer in RBC; is glycosylated;
is why RBC has a hydrophilic coat
all hydrophobic AAs
Porin
Barrel shaped membrane protein; serves as a passive diffusion channel for small molecules, water, and ions.