(6.8-6.14) Current carrying wires + forces
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What forms around a current carrying wire?
A magnetic field
How is an electromagnet made?
A current is passed through a coil of wire
Describe the magnetic field around a straight wire.
Concentric circles
that get further apart
as distance from the wire increase
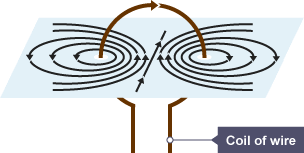
Describe the magnetic field around a flat circular coil.
N→S in the centre of the coil
Field lines curve outward and loop around,
forming concentric circles around the wire
The circles get further apart further away from the wire
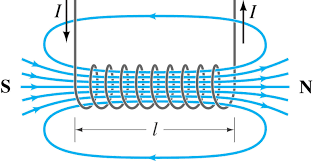
Describe the magnetic field around a solenoid.
Same as that of a bar magnet:
flowing N→S
uniform through it
N→S loops around it
How is a solenoid’s strength increased?
Increasing current
Increasing turns for a given length
Decreasing length and keeping the no. of turns
Adding an iron core through the centre
What is the right-hand rule used for?
To work out the direction of the magnetic field
How is the right hand rule used?
Thumb along direction of the current
Fingers loop to show direction of the field
What factors affect the strength of the field around a straight wire?
Higher current = larger field
Closer to wire = larger field
There is a force on a charged particle…
when it moves in a magnetic field
as long as the motion is not parallel to the field
When does the motor effect occur?
A current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field (normally between 2 magnets)
and experiences a force
What causes the motor effect?
The interaction between
the field of the wire
the field of the magnets
which results in a force on the wire
Describe the make-up of a simple D.C motor.
A coil of wire attached to a split ring commutator
which is connected to in a circuit with contacts to carbon brushes
all placed within a uniform magnetic field
When horizontal, the wire forms a complete circuit.
Describe the motion of a D.C. motor.
Force is exerted on the wire due to the interacting fields
they act in opposite directions on each side of the coil
causing the coil to rotate
At 90 degrees, the split ring isn’t in contact with the brushes
no forces and no current is flowing through the coil
Momentum of turn causes the coil to rotate slightly
ring connects to brushes
current remains in the same direction
the forces act on different sides now
coil spins in one direction continuously
What factors affect a D.C. motor?
Increase current/strength of field = increased speed
Reverse current/polarity = reverse direction
Increase current/strength of field/no. of turns = increased force supplied
How does a loudspeaker work?
A coil is wrapped around one pole of a permanent magnet
A/C current is passed through the coil
creating an alternating field around the coil
The coil’s A/C field interacts with the magnet’s field
exerting a force on the coil
that is an alternating force
causing oscillations
The vibrating coil = vibrating speaker cone
causing the air to oscillate, creating sound waves
What are the finger/value pairs for Fleming’s Left Hand Rule?
F- field
M- magnetic field
C- current
What factors affect the force on the wire?
Stronger fields = stronger forces
Higher current/stronger magnets/perpendicular wire = stronger forces