Chapter 33: Protostomes
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are the two clades of protostomes?
Lophotrochozoa and Ecdysozoa
How do Lophotrochozoa embryos develop?
Using a Spiral Clevage
Where do most Lophotrochozoa live?
In water
How do Lophotrochozoa move?
Using Cilia or contractions of the body musculature
What are two characteristics that describe members of Lophotrochozoa?
Trochophore and Lophophore
What is a Trocophore?
A free-living larva
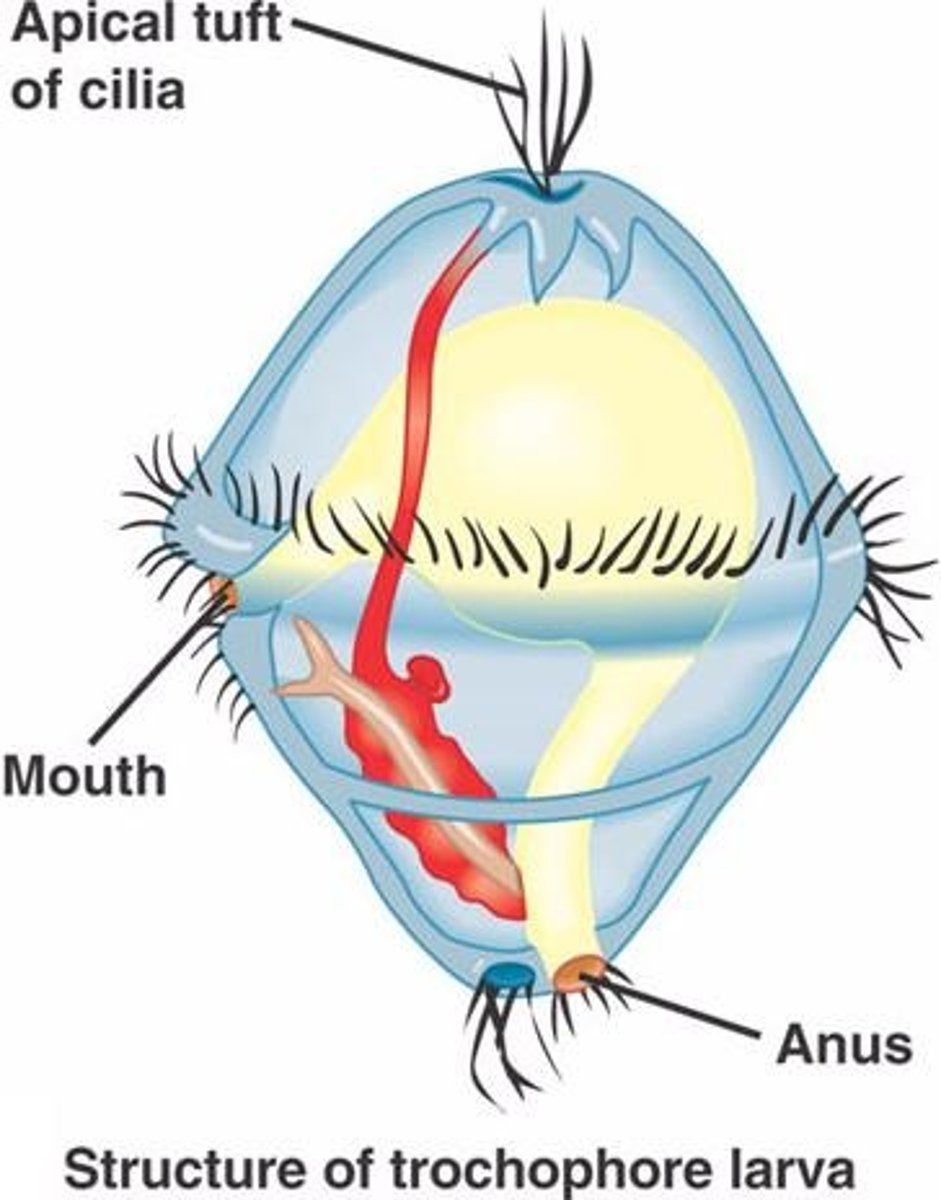
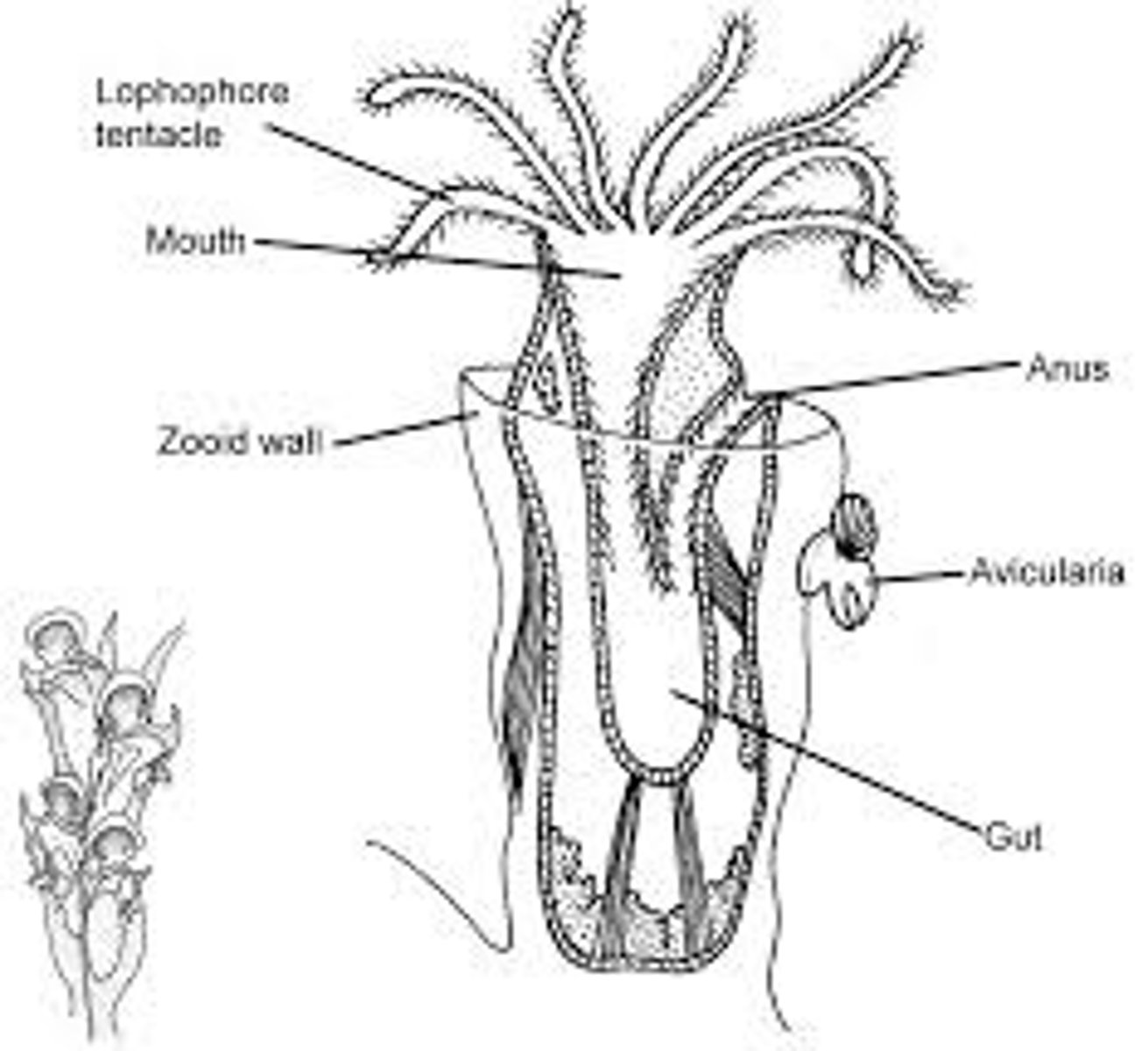
What is a Lophophore?
A horseshoe-shaped crown of ciliated tentacles surrounds the mouth used in filter-feeding.
What is a characteristic of Ecdysozoa?
Contains animals that molt

What are two large groups of Ecdysozoa?
Arthopods and Nematodes
Describe Platyhelminthes.
Simple bodies with no circulatory systems or respiratory systems, but complex reproductive systems.
Includes marine and freshwater planarians and parasitic flukes and tapeworms.
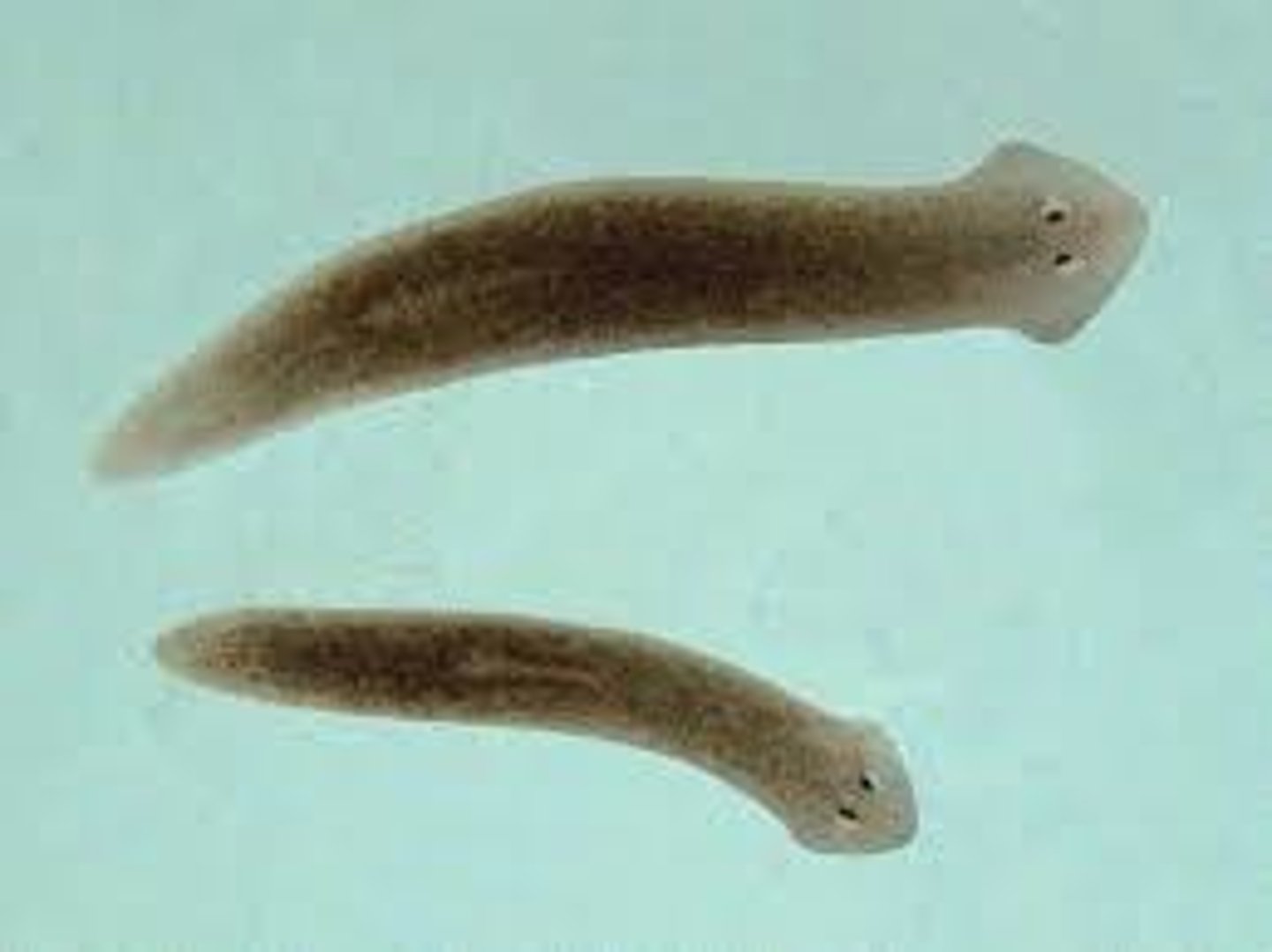

Flatworms have one opening to the digestive cavity. True or False.
True
How does the digestive activity in flatworms work?
Muscular contractions in the pharynx allows food to be ingested and torn into small bits.
How do Tapeworms absorb food since they lack a digestive system?
Directly through their body walls
Metabolic wastes are excreted into the gut and eliminated through the __________ .
Mouth
Flatworm Excretory system.
Flagella move water and excretory substance into the tubules and then to pores located between the epidermal cells through which the liquid is expelled.
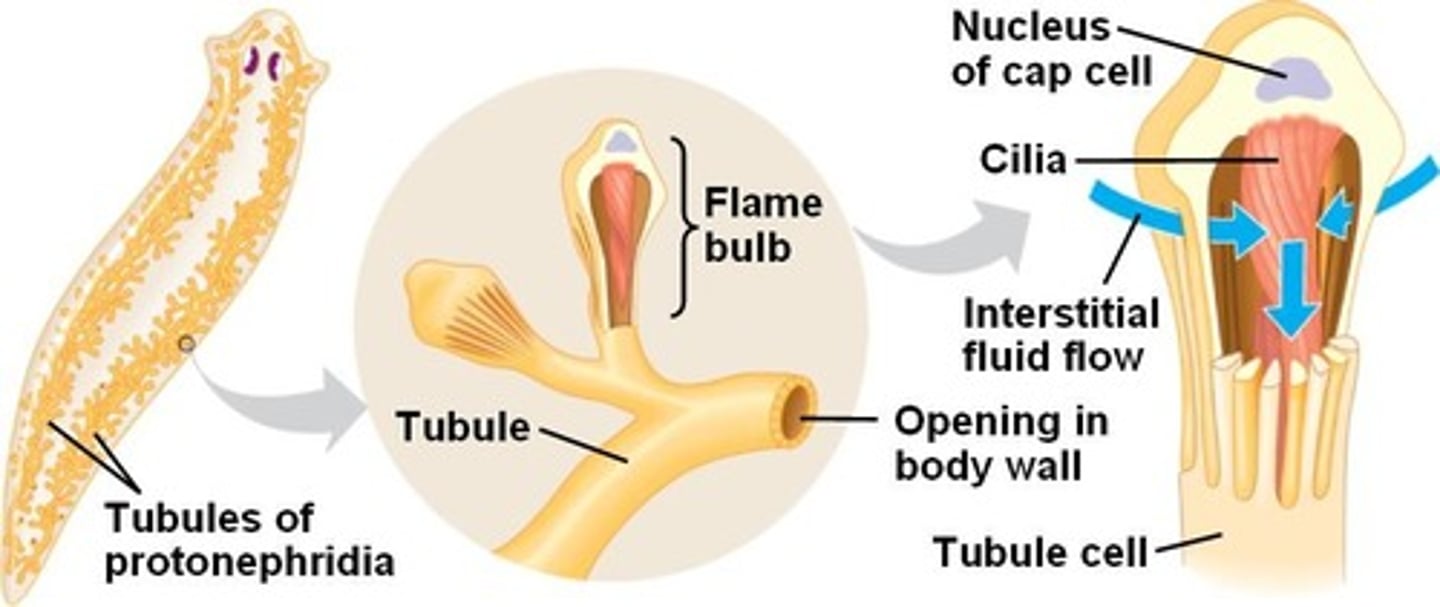
What type of nervous system does a flatworm have?
A simple nervous system
What can the eyespots of flatworms detect?
Distinguish light from dark
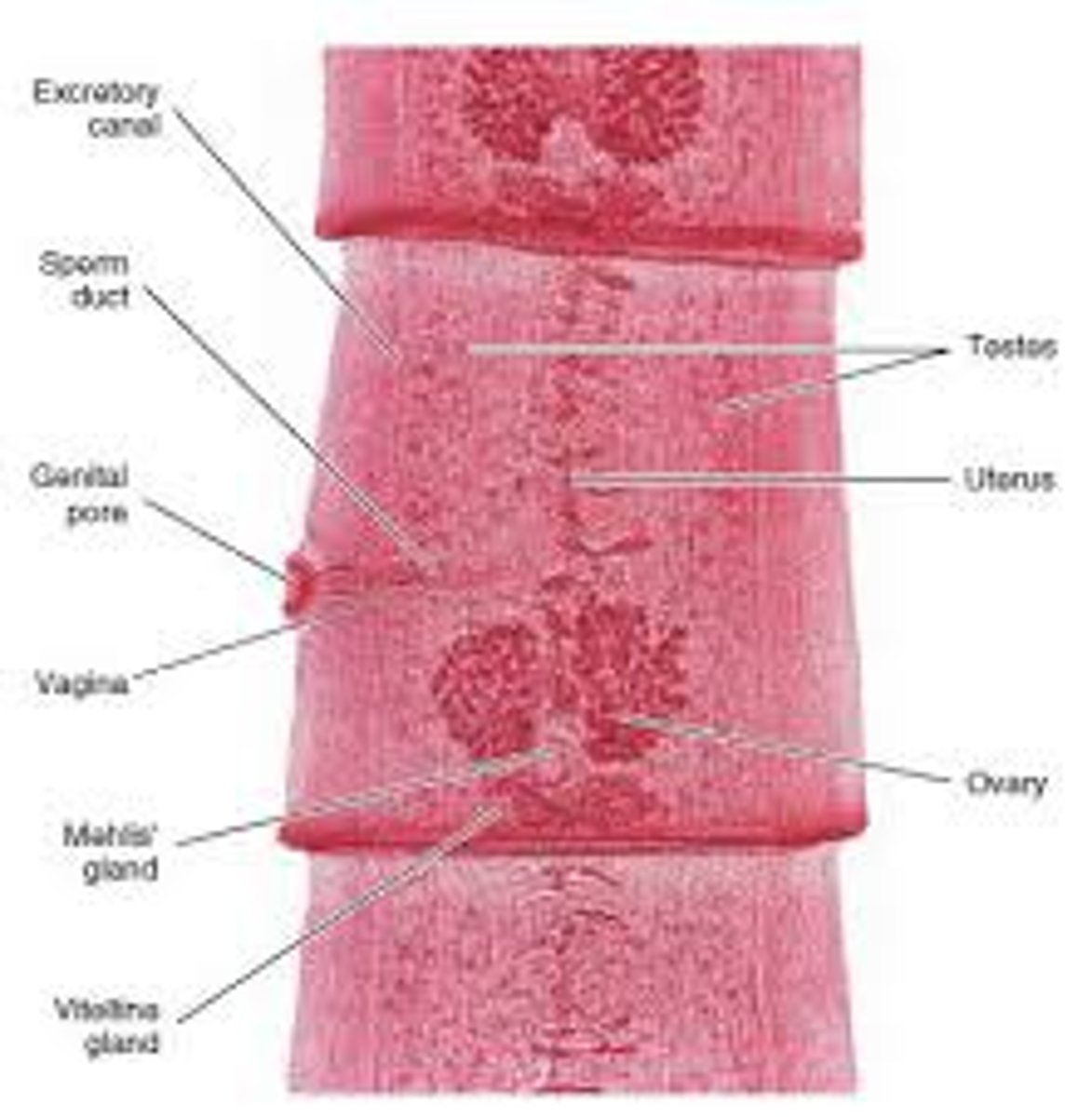
Describe the Reproduction of a flatworm.
- Most are hermaphroditic
- Undergo Sexual reproduction
- Have capacity for asexual regeneration
Define Hermaphoroditic.
Possessing both male and female reproductive organs, structures, or tissue.
What are the two major groups of flatworms?
Free-living Turbellaria and
Parasitic Neodermata
What do Parasitic Neodermata do?
Attach within host body by suckers, anchors, or hooks.
What is one of the most important trematodes to human health?
Blood flukes, Schistosoma
About how many people die each year from schistosomiasis?
200,000 people each year
Most of a tapeworm body is __________ .
Proglottids
What is a proglottid?
A segment of a tapeworm containing both male and female reproductive organs
What is a frequent human parasite?
Beef tapeworm (Taenia saginata)
How may a human get a beef tapeworm?
From eating uninspected rare beef.
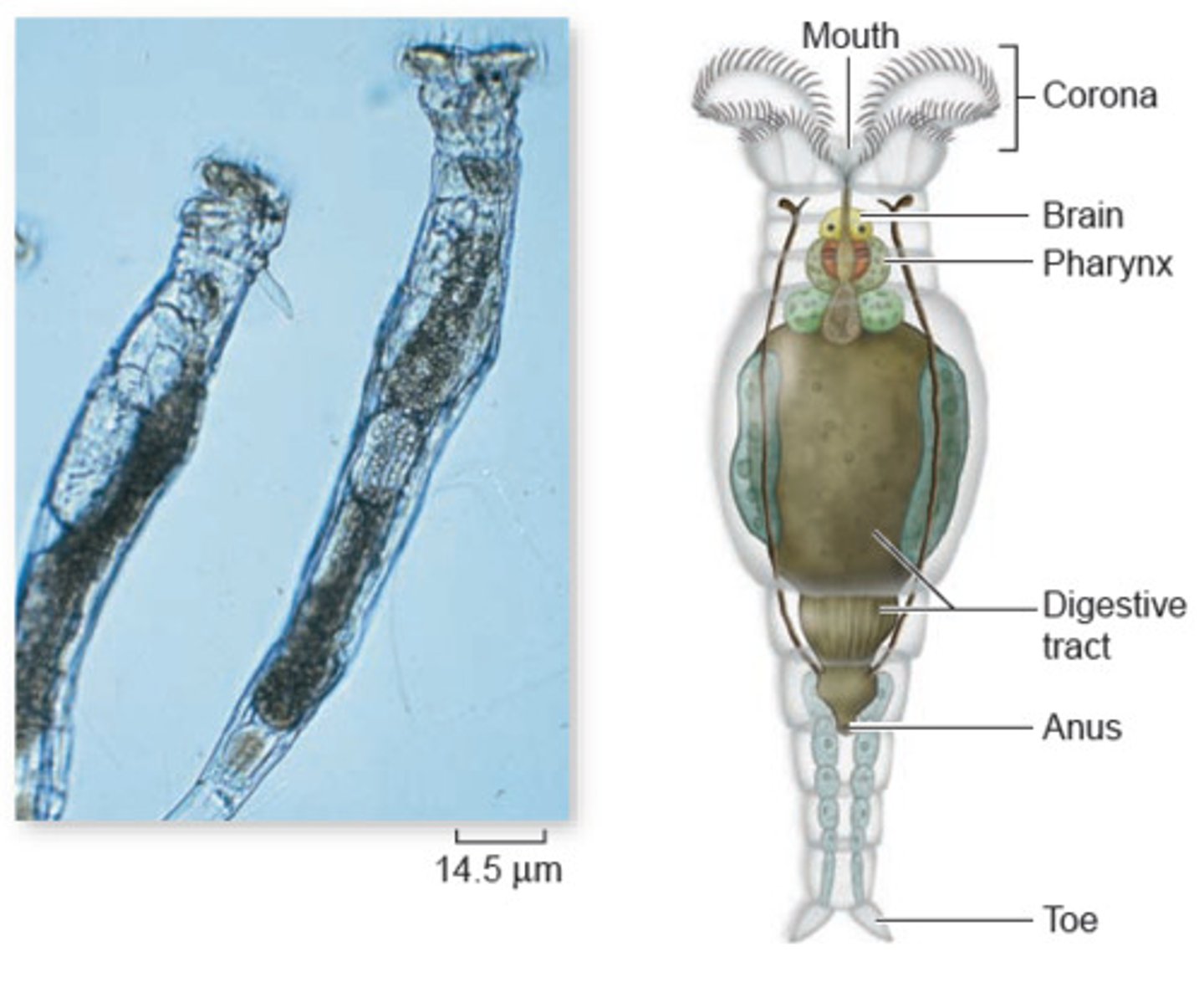
Describe the Phylum Rotifera.
- Bilaterally symmertrical, unsegmented pseudocoelomates
- Highly developed internal organs
- Corona - "Wheel animals"
What is the Corona used for in Rotifera?
Used for locomotion and sweeping food into the mouth.
What does the Phylum Mollusca include?
Snails, slugs, oysters, clams, octopuses, and squids.
Do all Mollusca have a shell?
No, some have no shell
Where did the Phylum Mollusca evolve?
In the oceans, and most groups have remained there.
Why are Mollusca important for humans?
They are a source of human food.
Describe the Mantle in a Mollusk.
- Thick epidermal sheet
- Bounds mantle cavity
- Secrete shell (if there is one)
Describe the Foot in a Mollusk.
- Primary means of locomotion for many
- Divided into arms or tentacles in cephalopds