Lab 1 - Bacterial Isolation
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
slide fixing, gram staining and identification, colony description and different medias, catalase test, oxidase test, motility test, oxidation/fermentation test, API tests, common issues
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is the process of identifying a bacteria (6 different steps)?
specimen taken
bacteria cultured
preliminary identification
further identification
antibiotic susceptibility
final report
What tests are carried out for preliminary identification of a bacteria (3)?
colony morphology / growth
gram stain
oxidase and catalase tests
What tests are carried out during further identification of a bacteria (after plate growth and colony morphology / gram stain) (2)?
motility test
oxidation / fermentation tests
What type of media is blood agar?
general purpose media
What type of media is MacConkey?
selective / differential media
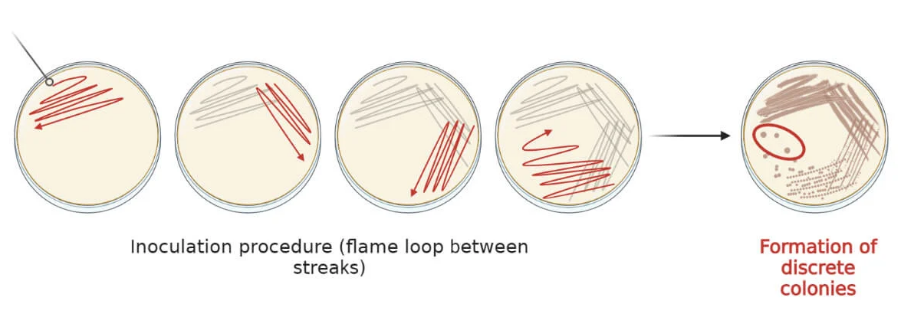
What is shown in this image?
plate streaking method for microbiology
How can blood agar be a differential media?
detects haemolytic activity
How is MacConkey agar a differential media (2)?
lactose fermenters - red colonies
non-lactose fermenters - colourless colonies
How is MacConkey agar a selective media (3)?
bile salts and crystal violet dye
gram positive growth inhibited
non-enteric gram negative growth inhibited
What should you look for when looking at a bacterial culture grown on agar (4)?
is there growth ?
is the culture pure ?
type of colony - shape, elevation, margin
type of haemolysis (blood agar)
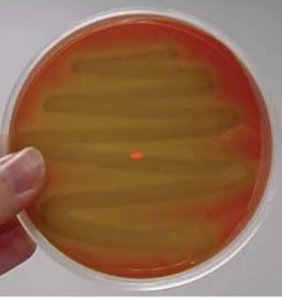
What type of blood agar haemolysis is shown in this image?
alpha haemolysis
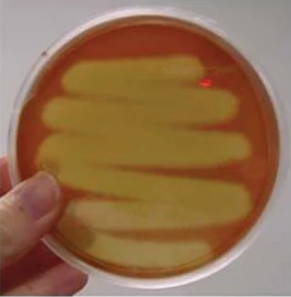
What type of blood agar haemolysis is shown in this image?
beta haemolysis
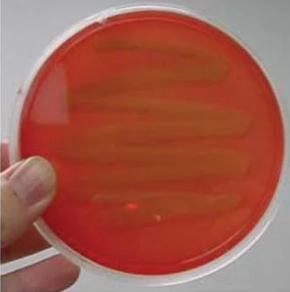
What type of blood agar haemolysis is shown in this image?
gamma haemolysis
What is alpha haemolysis and how is it identified (2)?
incomplete lysis of red blood cells
green area around colony growth
What is beta haemolysis and how is it identified (2)?
complete lysis of red blood cells
clear area around colony growth
What is gamma haemolysis and how is it identified?
growth with no blood cell lysis
What are the steps to perform a gram stain (8)?
fix slide
crystal violet
wash with water
iodine
decolourise with acetone
wash with water
counter stain with basic fuchsine
wash with water and blot dry
What different chemicals are used in a gram stain (4)?
methyl violet
iodine
acetone
basic fuchsine
What type of bacteria are purple after a gram stain?
gram positive
What type of bacteria are pink after a gram stain?
gram negative
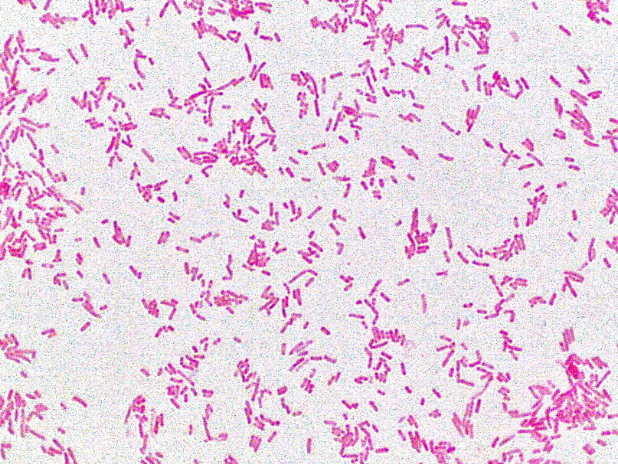
What type of bacteria is shown in this image (basic description - not actual name) ?
gram negative rods (image of E.coli)
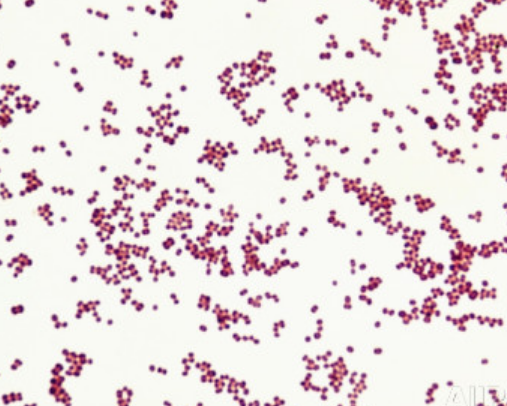

What type of bacteria is shown in this image (basic description - not actual name) ?
gram negative cocci
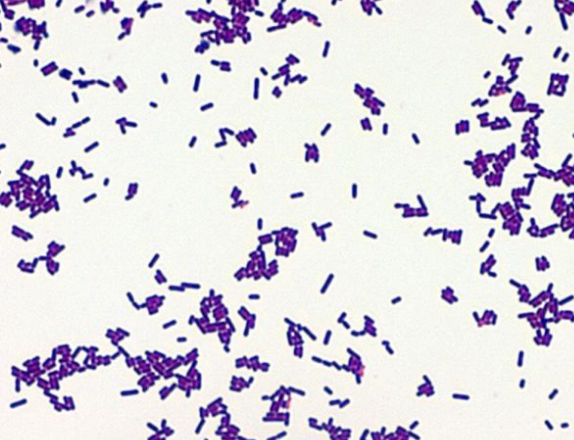
What type of bacteria is shown in this image (basic description - not actual name) ?
gram positive rods (image of Listeria)
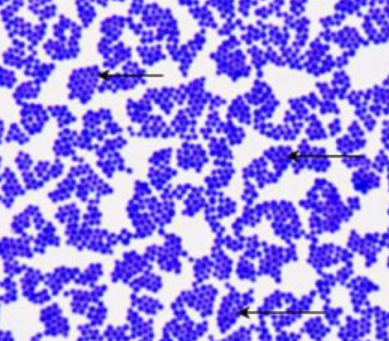
What type of bacteria is shown in this image (basic description - not actual name) ?
gram positive cocci (image of Staphylococcus)
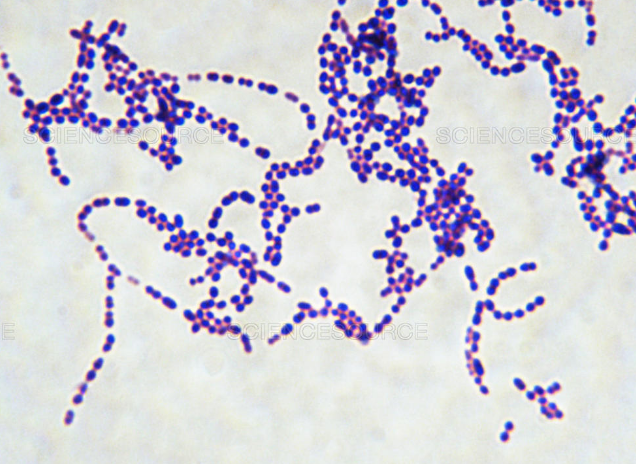
What type of bacteria is shown in this image (basic description - not actual name) ?
gram positive cocci (image of Streptococcus)
What is detected by a catalase test?
presence of catalase enzyme
How is a catalase test carried out and what is a positive result (2)?
colony dipped into hydrogen peroxide
positive result - bubbles of oxygen given off
What is detected by an oxidase test?
presence of cytochrome oxidase
How is an oxidase test carried out and what is a positive result (2)?
drop oxidase reagent onto a swab and touch to colony
positive result - rapid appearance of purple colour on swab
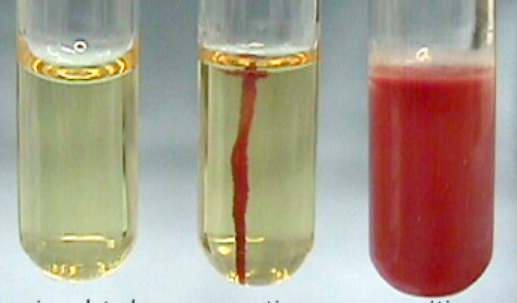
Which tube indicates a negative motility test result?
middle tube
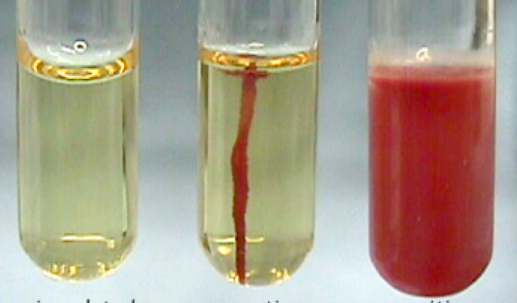
Which tube indicates a positive motility test result?
furthest right tube

Which set of tubes indicate the bacteria tested is fermentative?
furthest left tubes

Which set of tubes indicate the bacteria tested is oxidative?
middle tubes

Which set of tubes indicate the bacteria tested is neither fermentative nor oxidative?
furthest right tubes
What do API strips allow identification of?
bacterial genus and species
What API strip should be used for a gram negative bacteria?
API 20E
What API strip should be used for a gram positive bacteria?
API Coryne
What are some of the issues that can be encountered when gram staining (4)?
smear is too thick
mixed bacterial cultures (different shapes / colours)
not washed properly between steps
issues with decolourisation
What are some possible issues encountered when using API strips (4)?
correct strip used?
was the culture pure?
correctly examined / recorded?
were bubbles present?
What are some possible issues encountered when carrying out oxidation/fermentation and motility tests?
were tubes innoculated with enough bacteria?
What is a possible issue when carrying out oxidation/fermentation tests?
was a cm of oil placed on top of one tube (anaerobic conditions)?
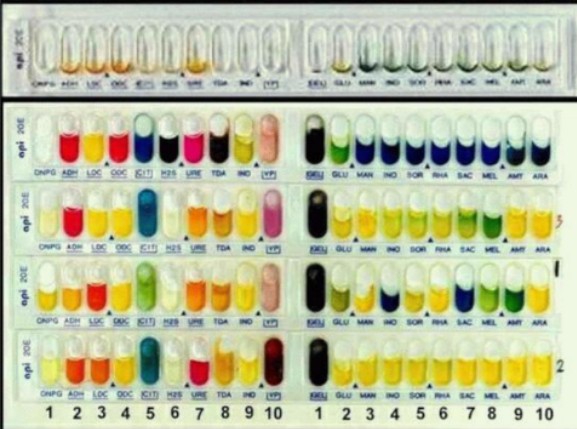
What are these images of?
API test strips
What are the steps to fix a bacteria sample onto a slide for gram staining / microscope examination (4)?
place loop of distilled water onto clean slide
using disposable loop pick up minute quantity of colony
make emulsion of bacteria into the water and spread thinly on slide
fix by placing onto a heating bench until dry