E.3 Summative
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What did gold foil experiment prove/find?
It found that most of the atom is in a small dense region with all the atom’s positive charge, the atom is made up of mostly empty space.
Milikan Photoelectic experiment
Radioactive decay
The random and spontaneous decay of a substance.
Alpha decay
A helium nucleus is emitted by the decaying nucleus.
Beta minus decay
Neutron rich. Neutron is converted into a proton, releasing an electron and an anti electron neutrino.
Beta plus decay
Proton rich. Proton gets converted into a neutron and releases a positron and an electron neutrino.
Electron capture
Proton rich. Parent neuclide captures an electron and results in a daughter electron neutron and an electron neutrino (X + e- → Y + υe).
Gamma decay
A type of radioactive decay where an excited nucleus releases energy in the form of gamma radiation without changing its number of protons or neutrons.
ionization
When decay particles (alpha, gamma, beta-plus, beta minus) pass through materials, they…
Alpha particles characteristics
Very highly ionizing, penetrate matter very poorly, are absorbed by a few cm of air and/or a thin sheet of paper.
Beta-minus particles characteristics
Moderate ionizing power compared to alpha particles of the same energy, a moderate ability to penetrate matter, are absorbed by around 25 cm of air, are absorbed by a few cm of plant or animal tissue, and/or are absorbed by a few mm of aluminum.
Gamma photons characteristics
Weakly ionizing, eject electrons from metals via the photoelectric effect that cause secondary ionization, are highly penetrating, are absorbed a few cm of lead, a few m of concrete, and are only weakly abrorbed by tissue.
The strong nuclear force
short-range and attractive, relative strength to gravity is 1038. Affects nuclear particles (p, n), not electrons nor neutrinos.
Lighter nuclides
3L, 2H
Most stable nuclides
Fe, Ni
Most stable nuclide range
8-9 MeV
Heavier Nuclides
U, Pu
Heavier nuclides range
7-8 MeV
Fusion
Left side
Fission
Right side
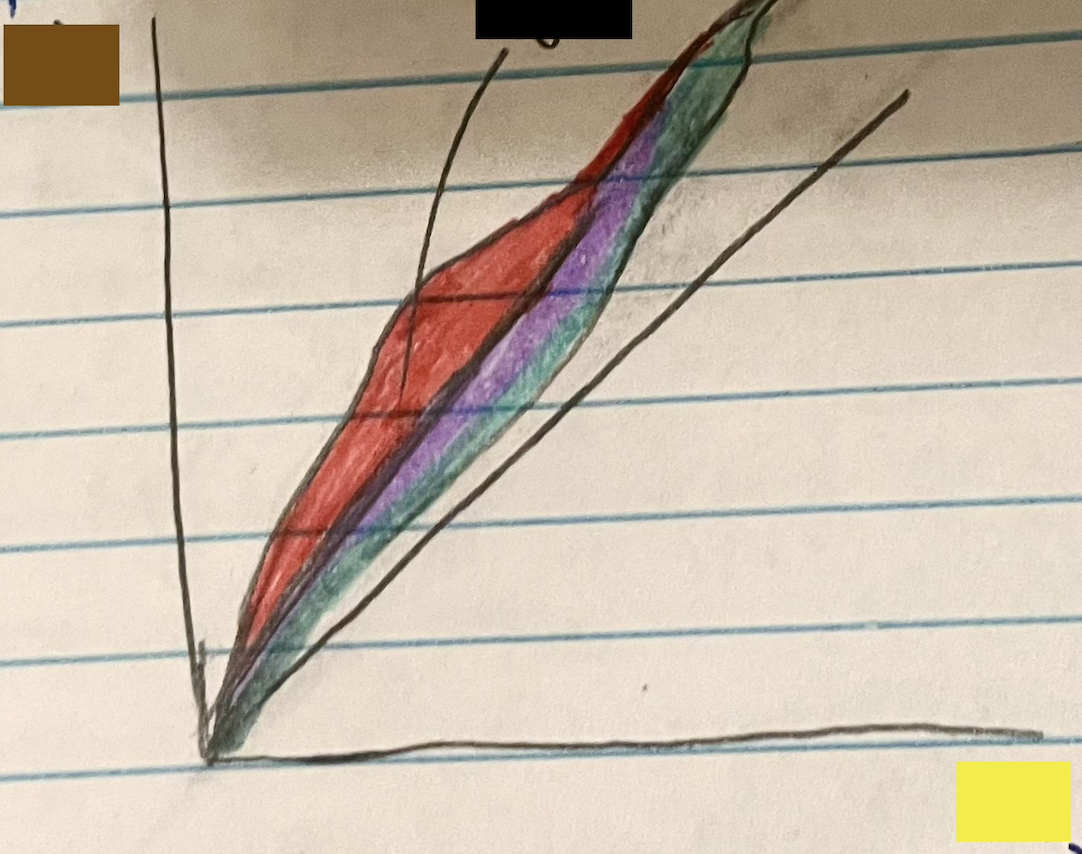

Brown: N
Yellow: P
Black: Zone of stability
Red: Beta minus
Purple: Beta plus
Green: alpha
Line: A=Z or P=N
Half-life
The amount of time taken for half of the sample to decay or to halve the activity.
Decay constant
The probability of decay of an individual nucleus in a given time interval represented by the time interval over the initial number of nuclei in the sample at the beginning of the time interval.
Binding energy
Energy required to break the nucleus apart into its constituent nucleons (protons and neutrons), overcoming stong nuclear force.
Mass-defect
The total mass of separate nucleons (protons and neutrons) in any nucleus is greater than the a mass of the nucleus since energy must be provided to separate the nucleons from the bound system. This can be described by the mass-energy equivalence.
Geiger-Muller tube
Sources of background radiation
Radon gas from the ground, food and drink, cosmic rays, artificial sources, building and the ground.
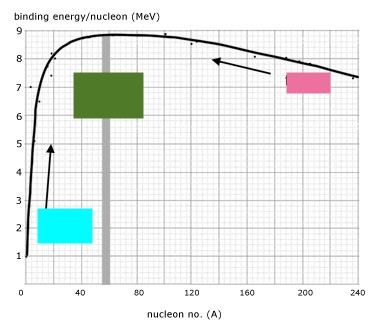
Blue: Fusion
Pink: Fission
Green: Stable