B-cell activation and antibody production 13 & 14
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
**How do NK/CTL recognize antigen?
antigen bound to MHC class I (typically intracellular pathogens)
**What cells can present antigens to NK/CTL?
all nucleated cells infected with pathogen - they all express MHC class I
CTLs differentiate from pre-CTLs. Pre-CTLs possess functional _______ and ______ surface molecule, but do not possess cytolytic properties. Further differentiation is required for the attainment of these properties.
CD3
CD8
What are the five major steps of CTL mediated lysis of target cells?
1) Recognition of antigen and conjugate formation
2) Activation of CTL
3) Delivery of "lethal hit" by the CTL to the target
4) Release of the CTL from teh target
5) PCD of the target as a result of the lethal hit by the CTL
What two signals are required for a pre-CTL to differentiate into a function (activated CTL)?
a) The specific recognition of antigen on a target cell
b) Co-stimulator expression on APCs and/or cytokine
production by CD4 (Th1) T-cells
What cytokine promotes CTL proliferation and differentiation following recognition of antigen?
IL-2
1. CTL killing/lysis of target cells is ___________ specific.
2. CTL killing requires _________ contact.
3. CTLs themselves are not injured during cytolysis of targets
antigen
cell : cell
CD40L on _______ T cells bind to CD40 on APCs, which upregulates expression of ____ on APCs
CD4+ helper
B7
**What is the concept of T cell exhaustion?
In situations of persistent or chronic antigen exposure, the response of CD8+ T cells is suppressed by the expression and engagement of PD-1
(programmed cell death protein-1) and other inhibitory receptors. - These T cells are thought of as exhausted
**Why might inducing death via apoptosis be preferred over lysis of target cells?
apoptosis, shouldn't result in freeing virus for further infection (at least this is good early in infection) vs. lysis, which will release virus for further infection and will induce inflammation
**CTL can induce apoptosis of target cells when what interaction occurs on their cell surfaces?
FasL on CD8+ binds to Fas receptor on target cell
_______ produced by the CD8+ T cells themselves or by CD4+ helper cells promotes proliferation of the CD8+ T
cells and their differentiation into CTLs and memory cells
Interleukin-2 (IL-2)
_______ and ________ (cytokines) have both been shown to stimulate the differentiation of naive CD8+ T cells into effector CTLs.
IL-12
type I IFNs
CD8+ cells express the β and γ chains of the IL-2 receptor and may express high levels of the ____ chain transiently after activation
α chain
_______ is important for the survival of memory CD8+ T cells. It may be produced by many cell types, including DCs. Mice lacking _______ show a significant loss of memory CD8+ T cells.
IL-15
**The following describes the action on target cells of what protein in cytotoxic T cells?
aids in delivering contents of granules into the cytoplasm of target cell
perforin
**The following describes the action on target cells of what protein in cytotoxic T cells?
serine proteases, which activate apoptosis once in the cytoplasm of the target cell
granzymes
The following describes the action on target cells of what protein in cytotoxic T cells?
has anitmicrobial actions and can induce apoptosis
granulysin
Delayed Type Hypersensitivity is a form of CMI in which the ultimate effector cell is the _______________ ______________ - _______________
mononuclear phagocyte - macrophage
Delayed type hypersensitivity is a very important defense mechanism against
___________ bacteria, including Listeria
monocytogenes and Mycobacterium tuberculosis
intracellular
The following describes what step of delayed type hypersensitivity reactions?
T-cells (CD4 / Th1 cells) recognize peptide antigens on the surface of APCs and begin producing cytokines.
recognition/acitvation phase
What are the three steps of delayed type hypersensitivity reactions?
1. Recognition/Activation Phase
2. Inflammation
3. Resolution
The following describes what step of delayed type hypersensitivity reactions?
vascular endothelial cells, activated
by cytokines from activated T-cells, recruit circulating leukocytes into tissues at the local site of antigen challenge or location.
inflammation
The following describes what step of delayed type hypersensitivity reactions?
Activated macrophages eliminate
foreign antigen. This process may be
accompanied by tissue injury.
resolution
What are the three major phases of delayed type hypersensitivity? What are the effector cells of each phase?
Sensitization phase: APCs & Naive T cells
Elicitation phase: memory T cells (CD4/Th1 cells), vascular endothelial cells
Resolution phase: macrophages
__________- Plays a primary role in boosting the capacities (i.e. activates) of APCs, including macrophages and
VECs by increasing expression of MHC II and co-stimulatory molecules. This action enhances antigen presentation to T-cells.
IFN-gamma
**What are four major characteristics of activated macrophages?
1. Killing mechanisms upregulated
2. Fc receptors upregulated
3. Cytokine (pro-inflammatory + IL-12)
secretion upregulated
4. MHC II expression upregulated
What is the outcome of chronic DTH when antigen removal has been unsuccessful?
fibrosis
What are epithelioid macrophages?
macrophages around the site of antigen deposition that have undergone
morphologic changes and appear more like
epithelial cells in nature
What are giant cells?
fusion of epithelioid macrophages
What is required for B-cell activation by either TI or TD antigens?
A second signal
What must happen for B cells and helper T cells to interact?
They must recognize the same molecular complex

What are the steps of the B cell and helper T cell interaction?
1. B cell binds virus through viral coat protein
2. Virus particle is internalized and degraded
3. Peptides from internal proteins of the virus are presented to the T cell, which activates the B cell
4. Activated B cell produces antibody against viral coat protein
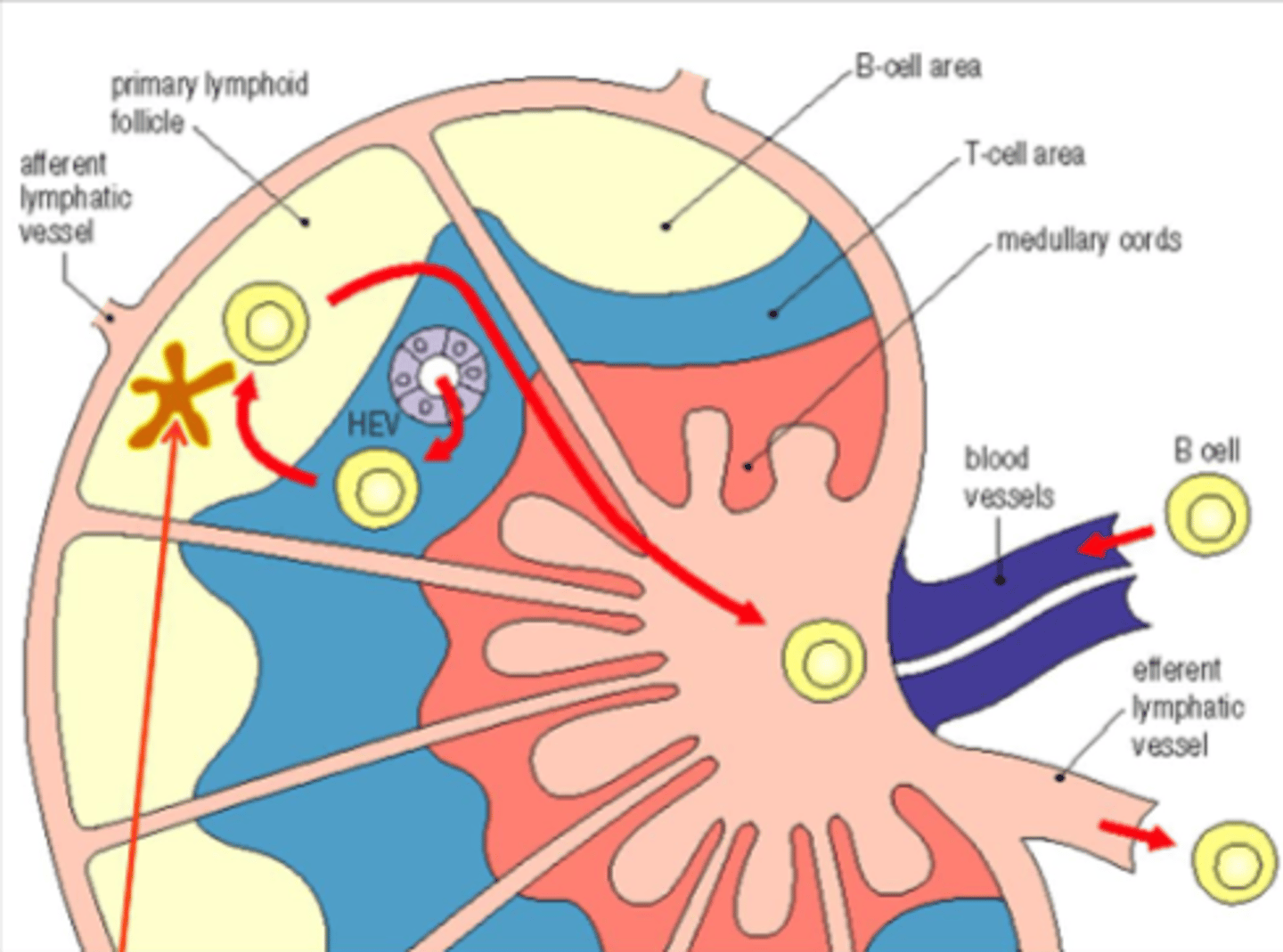
Circulation of naive B cells
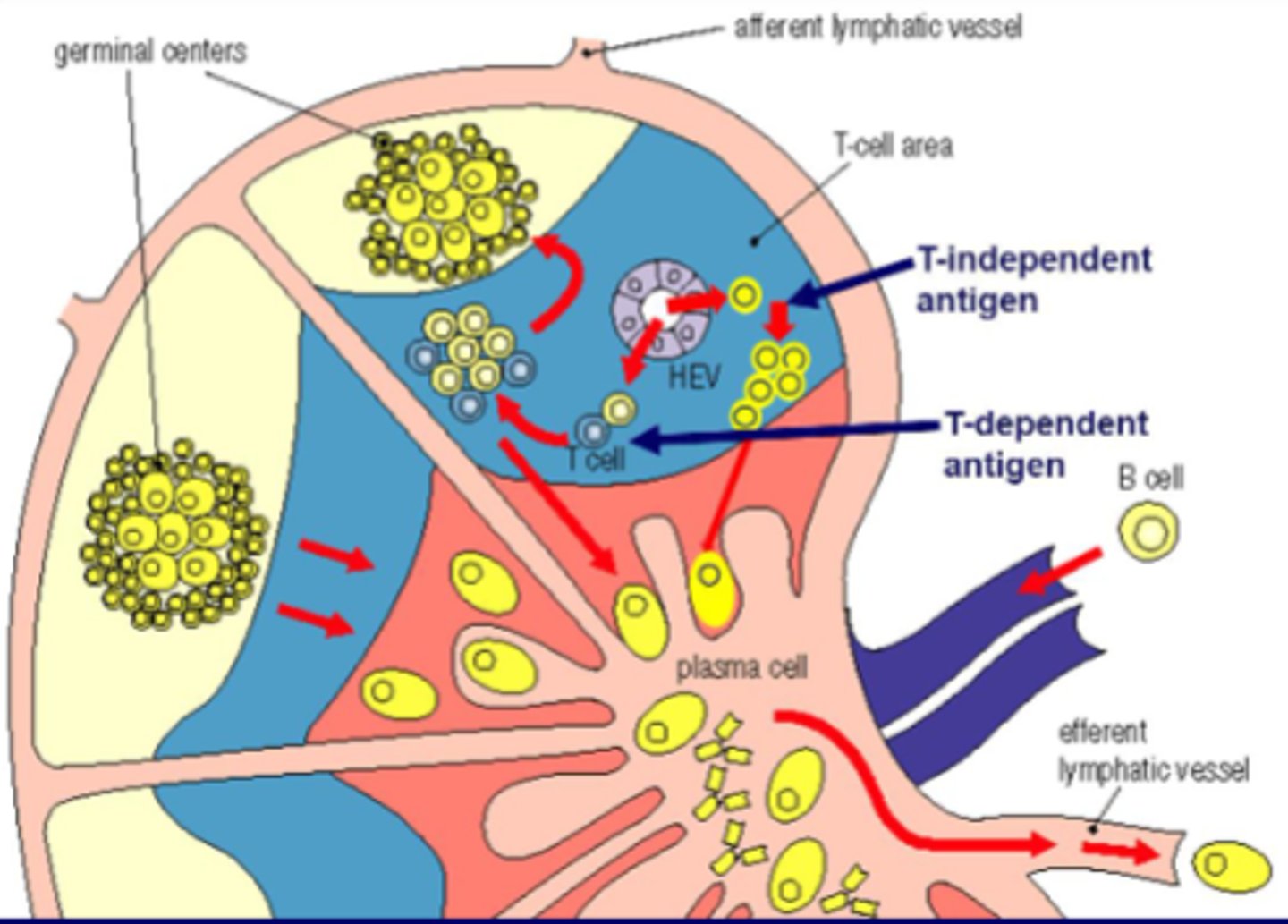
What occurs in the germinal center?
1. Proliferation of B cells
2. Affinity maturation
3. Isotype switching
4. Memory cell induction
What does antigen recognition induce in regard to B cells?
Expression of CD40 and cytokines by Th2, which activates
What occurs after B cell activation?
B cell proliferation and differentiation to antibody-secreting plasma cells
What do cytokines and CD40 induce?
Isotype switching
What are intrinsic properties of Naive B cells?
Surface Ig and surface MHC class II
What are inducible properties of naive B cells?
Growth, somatic hypermutation, and isotype switching
What are the inducible properties of plasma cells?
None
What are intrinsic properties of plasma cells?
High-rate Ig secretion
Induce B cell activation and proliferation
Mitogenic T-independent antigens
What is an example of a mitogenic T-independent antigens?
Lipopolysaccharide
What is an example of a multivalent antigen with identical epitopes?
Certain polysaccharides
What are characteristics of the immune response to T-independent antigens?
Weaker response - lower levels of antibodies, no isotype switching - only IgM, and no memory B cell development
What are the effector functions of antibodies?
Neutralization, blocking, phagocytosis, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, mast cell/basophil degranulation, and complement activation
What effector functions of antibodies require binding of the Fc region with Fc receptors?
Phagocytosis of opsonized bacteria, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, and mast cell/basophil degranulation
What effector function of antibodies requires binding of the Fc region with complement component?
Complement activation
What does phagocytosis, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, and mast cell/basophil degranulation require?
Binding of the Fc region with Fc receptors
What does complement activation require?
Binding of the Fc region with complement component
What is the pathway of B cell development in primary lymphoid organs?
Stem cell, Pre-B cell, Immature B cell (IgM+), and Mature B cell (IgM+ , IgD+)
What are the outcomes of B cell development in secondary lymphoid organs?
IgM, IgG, Memory B cell, IgA, and IgE
What occurs to allow mature B cells to develop into IgG, Memory B cells, IgA, and IgE?
Isotype switching and somatic mutations
B cell development in primary lymphoid organs is?
Antigen independent
B cell development in secondary lymphoid organs is?
Antigen-dependent
Immature B cells undergo selection process to become [blank]
self-tolerant
Multivalent self-antigen undergo apoptosis after what?
Clonal deletion
Soluble self-antigen IgM migrate to periphery to become?
Anergic B cells
No self-reaction with IgM migrate to the periphery to become?
Self-tolerant mature B cells
Describe the circulation of naive B cells in lymph nodes
Blood vessels, HEV, T-cell area, B-cell area, primary lymphoid follicle, T cell area, medullary cords, efferent lymphatic vessel
What are the two types of antigens for B-cell stimulation?
Thymus-dependent (TD) antigens and Thymus-independent (TI) antigens
-Need T-cell help for activation of B cells and production of antibodies
-Usually are protein or glycoprotein antigens
Thymus-dependent (TD) antigens
-Can induce antibody production in the absence of T-cell help
-Usually these are bacterial capsular polysaccharides with highly repetitive structures or B-cell mitogens such as LPS
Thymus-independent (TI) antigens
Effect of specific antigen on B cell migration and differentiation