C21 - Kinetic Theory of Gases
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Kinetic theory of gases
Describes microscopic movements of gas molecules in a container
cubic container, side length d
identical molecules, large N
Vgas « Vcontainer
Elastic collisions only, no IMFs
Elastic collisions occur with walls & other molecules
isotropic motion (any speed, any direction)
pressure-KEmicro theorem
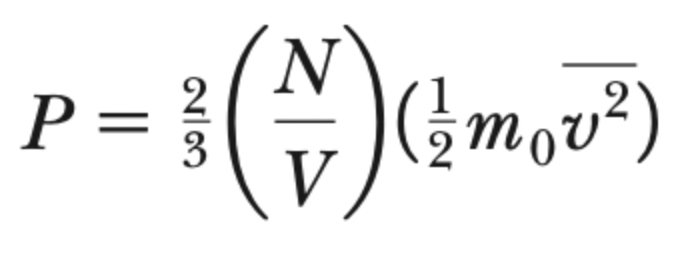
temperature-KEmicro theorem
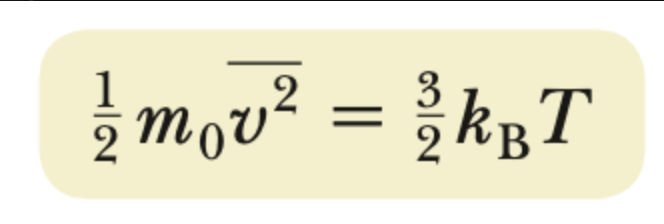
Ktotal translational
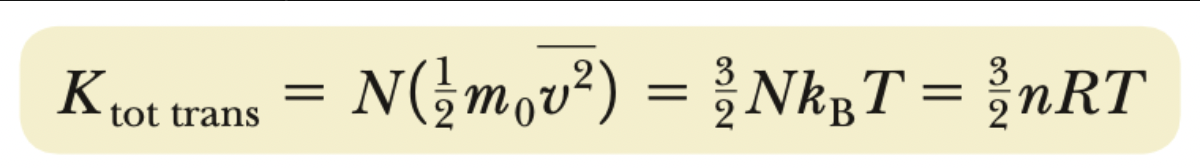
vrms
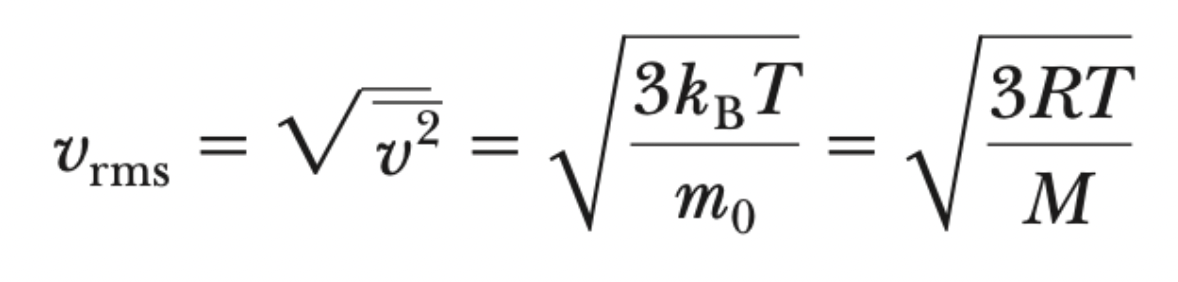
vmp
vmp = sqrt(2RT/M)
vavg
vavg = sqrt(8RT/πM)
theorem of equipartition of energy
each degree of freedom contributes an equal amount of energy to the system, E = kbT/2
degrees of freedom
individual means of storing energy
translation, x, y, z (3)
rotation, x-axis, y-axis (2)
Iz-axis negligible for linear molecules
vibration: Uelastic, KE (2)
Molar specific heat
amount of energy required to increase 1 mol of a substance by 1K (based on process)
Qisovolumetric = nCv∆T
Qisobaric = nCP∆T
CP > Cv
CV (general eqn)
CV = (1/n)(dEint/dT)
CP (general eqn)
CP = R + CV
γ (general eqn)
γ = CP/CV
molar specific heat constants
translation:
CV = 3R/2 = 12.5 J/(mol • K)
rotation:
CV = 5R/2 = 20.8 J/(mol • K)
vibration:
CV = 7R/2 = 29.1 J/(mol • K)
adiabatic processes
PVγ = constant
TVγ-1 = constant
distribution of molecular speeds
vrms > vavg > vmp
vrms: assume all particles have vrms, calculate accurate values for pressure or energy
vmp: speed that most particles have at any given point in time
vavg: averaged speed
kb (again)
1.38 × 10-23 J/K